mirror of
https://github.com/zebrajr/pytorch.git
synced 2025-12-06 12:20:52 +01:00
Summary: Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/61903 ### Remaining Tasks - [ ] Collate results of benchmarks on two Intel Xeon machines (with & without CUDA, to check if CPU throttling causes issues with GPUs) - make graphs, including Roofline model plots (Intel Advisor can't make them with libgomp, though, but with Intel OpenMP). ### Summary 1. This draft PR produces binaries with with 3 types of ATen kernels - default, AVX2, AVX512 . Using the environment variable `ATEN_AVX512_256=TRUE` also results in 3 types of kernels, but the compiler can use 32 ymm registers for AVX2, instead of the default 16. ATen kernels for `CPU_CAPABILITY_AVX` have been removed. 2. `nansum` is not using AVX512 kernel right now, as it has poorer accuracy for Float16, than does AVX2 or DEFAULT, whose respective accuracies aren't very good either (#59415). It was more convenient to disable AVX512 dispatch for all dtypes of `nansum` for now. 3. On Windows , ATen Quantized AVX512 kernels are not being used, as quantization tests are flaky. If `--continue-through-failure` is used, then `test_compare_model_outputs_functional_static` fails. But if this test is skipped, `test_compare_model_outputs_conv_static` fails. If both these tests are skipped, then a third one fails. These are hard to debug right now due to not having access to a Windows machine with AVX512 support, so it was more convenient to disable AVX512 dispatch of all ATen Quantized kernels on Windows for now. 4. One test is currently being skipped - [test_lstm` in `quantization.bc](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/59098) - It fails only on Cascade Lake machines, irrespective of the `ATEN_CPU_CAPABILITY` used, because FBGEMM uses `AVX512_VNNI` on machines that support it. The value of `reduce_range` should be used as `False` on such machines. The list of the changes is at https://gist.github.com/imaginary-person/4b4fda660534f0493bf9573d511a878d. Credits to ezyang for proposing `AVX512_256` - these use AVX2 intrinsics but benefit from 32 registers, instead of the 16 ymm registers that AVX2 uses. Credits to limo1996 for the initial proposal, and for optimizing `hsub_pd` & `hadd_pd`, which didn't have direct AVX512 equivalents, and are being used in some kernels. He also refactored `vec/functional.h` to remove duplicated code. Credits to quickwritereader for helping fix 4 failing complex multiplication & division tests. ### Testing 1. `vec_test_all_types` was modified to test basic AVX512 support, as tests already existed for AVX2. Only one test had to be modified, as it was hardcoded for AVX2. 2. `pytorch_linux_bionic_py3_8_gcc9_coverage_test1` & `pytorch_linux_bionic_py3_8_gcc9_coverage_test2` are now using `linux.2xlarge` instances, as they support AVX512. They were used for testing AVX512 kernels, as AVX512 kernels are being used by default in both of the CI checks. Windows CI checks had already been using machines with AVX512 support. ### Would the downclocking caused by AVX512 pose an issue? I think it's important to note that AVX2 causes downclocking as well, and the additional downclocking caused by AVX512 may not hamper performance on some Skylake machines & beyond, because of the double vector-size. I think that [this post with verifiable references is a must-read](https://community.intel.com/t5/Software-Tuning-Performance/Unexpected-power-vs-cores-profile-for-MKL-kernels-on-modern-Xeon/m-p/1133869/highlight/true#M6450). Also, AVX512 would _probably not_ hurt performance on a high-end machine, [but measurements are recommended](https://lemire.me/blog/2018/09/07/avx-512-when-and-how-to-use-these-new-instructions/). In case it does, `ATEN_AVX512_256=TRUE` can be used for building PyTorch, as AVX2 can then use 32 ymm registers instead of the default 16. [FBGEMM uses `AVX512_256` only on Xeon D processors](https://github.com/pytorch/FBGEMM/pull/209), which are said to have poor AVX512 performance. This [official data](https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/specification-updates/xeon-scalable-spec-update.pdf) is for the Intel Skylake family, and the first link helps understand its significance. Cascade Lake & Ice Lake SP Xeon processors are said to be even better when it comes to AVX512 performance. Here is the corresponding data for [Cascade Lake](https://cdrdv2.intel.com/v1/dl/getContent/338848) - 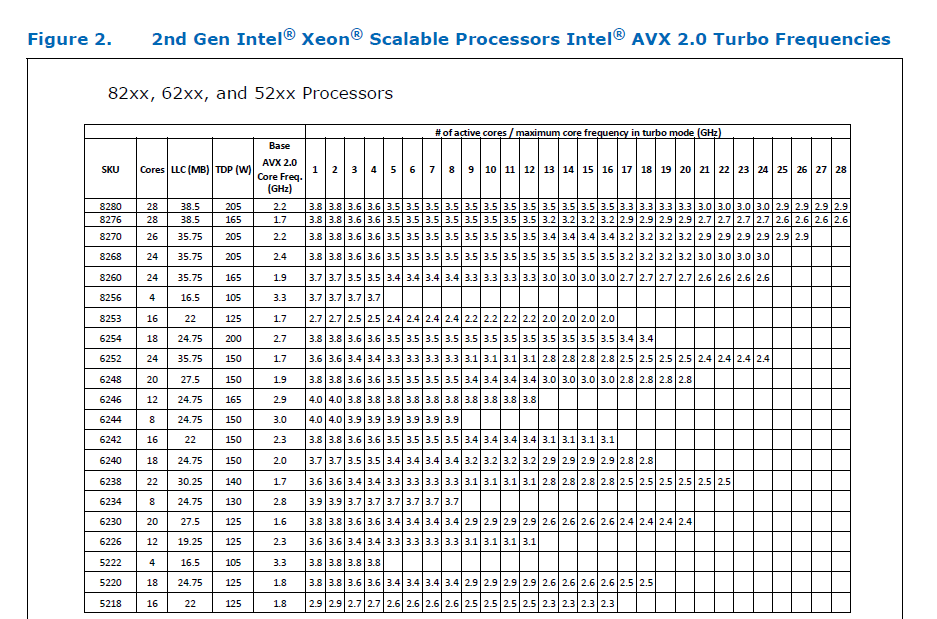 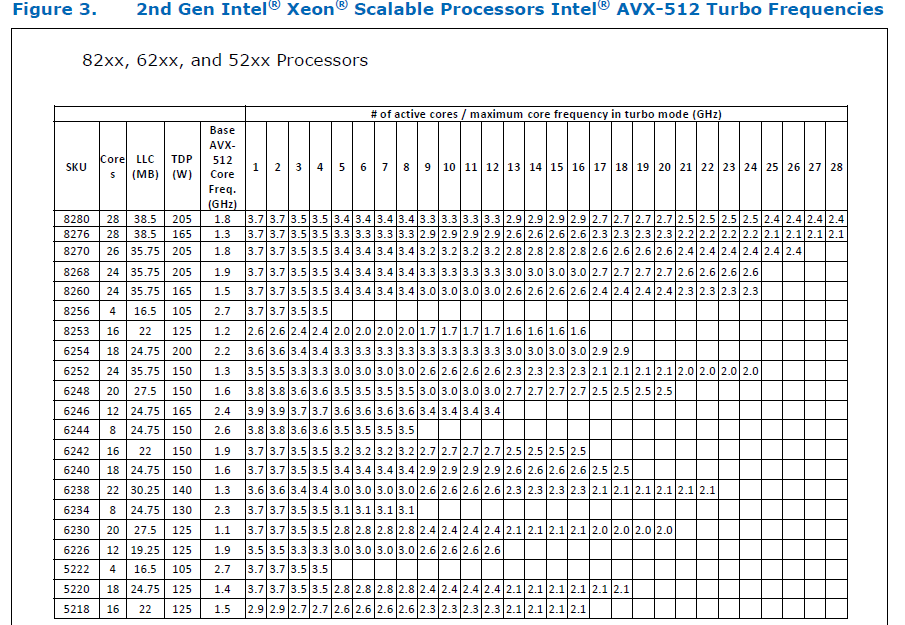 The corresponding data isn't publicly available for Intel Xeon SP 3rd gen (Ice Lake SP), but [Intel mentioned that the 3rd gen has frequency improvements pertaining to AVX512](https://newsroom.intel.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/11/2021/04/3rd-Gen-Intel-Xeon-Scalable-Platform-Press-Presentation-281884.pdf). Ice Lake SP machines also have 48 KB L1D caches, so that's another reason for AVX512 performance to be better on them. ### Is PyTorch always faster with AVX512? No, but then PyTorch is not always faster with AVX2 either. Please refer to #60202. The benefit from vectorization is apparent with with small tensors that fit in caches or in kernels that are more compute heavy. For instance, AVX512 or AVX2 would yield no benefit for adding two 64 MB tensors, but adding two 1 MB tensors would do well with AVX2, and even more so with AVX512. It seems that memory-bound computations, such as adding two 64 MB tensors can be slow with vectorization (depending upon the number of threads used), as the effects of downclocking can then be observed. Original pull request: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/56992 Reviewed By: soulitzer Differential Revision: D29266289 Pulled By: ezyang fbshipit-source-id: 2d5e8d1c2307252f22423bbc14f136c67c3e6184
2502 lines
102 KiB
Python
2502 lines
102 KiB
Python
r"""Importing this file must **not** initialize CUDA context. test_distributed
|
|
relies on this assumption to properly run. This means that when this is imported
|
|
no CUDA calls shall be made, including torch.cuda.device_count(), etc.
|
|
|
|
torch.testing._internal.common_cuda.py can freely initialize CUDA context when imported.
|
|
"""
|
|
|
|
import sys
|
|
import os
|
|
import platform
|
|
import re
|
|
import gc
|
|
import types
|
|
import math
|
|
from functools import partial
|
|
import inspect
|
|
import io
|
|
import copy
|
|
import operator
|
|
import argparse
|
|
import unittest
|
|
import warnings
|
|
import random
|
|
import contextlib
|
|
import shutil
|
|
import pathlib
|
|
import socket
|
|
import subprocess
|
|
import time
|
|
from collections import OrderedDict
|
|
from collections.abc import Sequence
|
|
from contextlib import contextmanager, closing
|
|
from functools import wraps
|
|
from itertools import product
|
|
from copy import deepcopy
|
|
from numbers import Number
|
|
import tempfile
|
|
import json
|
|
import __main__ # type: ignore[import]
|
|
import errno
|
|
from typing import cast, Any, Dict, Iterable, Iterator, Optional, Union
|
|
|
|
import numpy as np
|
|
|
|
from torch.testing import floating_types_and, integral_types, complex_types
|
|
import expecttest
|
|
from .._core import \
|
|
(_compare_tensors_internal, _compare_scalars_internal, _compare_return_type)
|
|
|
|
import torch
|
|
import torch.cuda
|
|
from torch._utils_internal import get_writable_path
|
|
from torch._six import string_classes
|
|
import torch.backends.cudnn
|
|
import torch.backends.mkl
|
|
from enum import Enum
|
|
|
|
torch.backends.disable_global_flags()
|
|
|
|
FILE_SCHEMA = "file://"
|
|
if sys.platform == 'win32':
|
|
FILE_SCHEMA = "file:///"
|
|
|
|
# Environment variable `IN_CI` is set in `.jenkins/common.sh`.
|
|
IS_IN_CI = os.getenv('IN_CI') == '1'
|
|
IS_SANDCASTLE = os.getenv('SANDCASTLE') == '1' or os.getenv('TW_JOB_USER') == 'sandcastle'
|
|
IS_FBCODE = os.getenv('PYTORCH_TEST_FBCODE') == '1'
|
|
IS_REMOTE_GPU = os.getenv('PYTORCH_TEST_REMOTE_GPU') == '1'
|
|
|
|
DISABLED_TESTS_FILE = '.pytorch-disabled-tests.json'
|
|
SLOW_TESTS_FILE = '.pytorch-slow-tests.json'
|
|
|
|
slow_tests_dict: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None
|
|
disabled_tests_dict: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None
|
|
|
|
class ProfilingMode(Enum):
|
|
LEGACY = 1
|
|
SIMPLE = 2
|
|
PROFILING = 3
|
|
|
|
def cppProfilingFlagsToProfilingMode():
|
|
old_prof_exec_state = torch._C._jit_set_profiling_executor(True)
|
|
old_prof_mode_state = torch._C._jit_set_profiling_mode(True)
|
|
torch._C._jit_set_profiling_executor(old_prof_exec_state)
|
|
torch._C._jit_set_profiling_mode(old_prof_mode_state)
|
|
|
|
if old_prof_exec_state:
|
|
if old_prof_mode_state:
|
|
return ProfilingMode.PROFILING
|
|
else:
|
|
return ProfilingMode.SIMPLE
|
|
else:
|
|
return ProfilingMode.LEGACY
|
|
|
|
@contextmanager
|
|
def enable_profiling_mode_for_profiling_tests():
|
|
if GRAPH_EXECUTOR == ProfilingMode.PROFILING:
|
|
old_prof_exec_state = torch._C._jit_set_profiling_executor(True)
|
|
old_prof_mode_state = torch._C._jit_set_profiling_mode(True)
|
|
try:
|
|
yield
|
|
finally:
|
|
if GRAPH_EXECUTOR == ProfilingMode.PROFILING:
|
|
torch._C._jit_set_profiling_executor(old_prof_exec_state)
|
|
torch._C._jit_set_profiling_mode(old_prof_mode_state)
|
|
|
|
@contextmanager
|
|
def enable_profiling_mode():
|
|
old_prof_exec_state = torch._C._jit_set_profiling_executor(True)
|
|
old_prof_mode_state = torch._C._jit_set_profiling_mode(True)
|
|
try:
|
|
yield
|
|
finally:
|
|
torch._C._jit_set_profiling_executor(old_prof_exec_state)
|
|
torch._C._jit_set_profiling_mode(old_prof_mode_state)
|
|
|
|
@contextmanager
|
|
def num_profiled_runs(num_runs):
|
|
old_num_runs = torch._C._jit_set_num_profiled_runs(num_runs)
|
|
try:
|
|
yield
|
|
finally:
|
|
torch._C._jit_set_num_profiled_runs(old_num_runs)
|
|
|
|
func_call = torch._C.ScriptFunction.__call__
|
|
meth_call = torch._C.ScriptMethod.__call__
|
|
|
|
def prof_callable(callable, *args, **kwargs):
|
|
if 'profile_and_replay' in kwargs:
|
|
del kwargs['profile_and_replay']
|
|
if GRAPH_EXECUTOR == ProfilingMode.PROFILING:
|
|
with enable_profiling_mode_for_profiling_tests():
|
|
callable(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
return callable(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
|
|
return callable(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
|
|
def prof_func_call(*args, **kwargs):
|
|
return prof_callable(func_call, *args, **kwargs)
|
|
|
|
def prof_meth_call(*args, **kwargs):
|
|
return prof_callable(meth_call, *args, **kwargs)
|
|
|
|
# TODO fix when https://github.com/python/mypy/issues/2427 is address
|
|
torch._C.ScriptFunction.__call__ = prof_func_call # type: ignore[assignment]
|
|
torch._C.ScriptMethod.__call__ = prof_meth_call # type: ignore[assignment]
|
|
|
|
def _get_test_report_path():
|
|
# allow users to override the test file location. We need this
|
|
# because the distributed tests run the same test file multiple
|
|
# times with different configurations.
|
|
override = os.environ.get('TEST_REPORT_SOURCE_OVERRIDE')
|
|
test_source = override if override is not None else 'python-unittest'
|
|
return os.path.join('test-reports', test_source)
|
|
|
|
|
|
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(add_help=False)
|
|
parser.add_argument('--subprocess', action='store_true',
|
|
help='whether to run each test in a subprocess')
|
|
parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=1234)
|
|
parser.add_argument('--accept', action='store_true')
|
|
parser.add_argument('--jit_executor', type=str)
|
|
parser.add_argument('--repeat', type=int, default=1)
|
|
parser.add_argument('--test_bailouts', action='store_true')
|
|
parser.add_argument('--save-xml', nargs='?', type=str,
|
|
const=_get_test_report_path(),
|
|
default=_get_test_report_path() if IS_IN_CI else None)
|
|
parser.add_argument('--discover-tests', action='store_true')
|
|
parser.add_argument('--log-suffix', type=str, default="")
|
|
parser.add_argument('--run-parallel', type=int, default=1)
|
|
parser.add_argument('--import-slow-tests', type=str, nargs='?', const=SLOW_TESTS_FILE)
|
|
parser.add_argument('--import-disabled-tests', type=str, nargs='?', const=DISABLED_TESTS_FILE)
|
|
|
|
args, remaining = parser.parse_known_args()
|
|
if args.jit_executor == 'legacy':
|
|
GRAPH_EXECUTOR = ProfilingMode.LEGACY
|
|
elif args.jit_executor == 'profiling':
|
|
GRAPH_EXECUTOR = ProfilingMode.PROFILING
|
|
elif args.jit_executor == 'simple':
|
|
GRAPH_EXECUTOR = ProfilingMode.SIMPLE
|
|
else:
|
|
# infer flags based on the default settings
|
|
GRAPH_EXECUTOR = cppProfilingFlagsToProfilingMode()
|
|
|
|
|
|
IMPORT_SLOW_TESTS = args.import_slow_tests
|
|
IMPORT_DISABLED_TESTS = args.import_disabled_tests
|
|
LOG_SUFFIX = args.log_suffix
|
|
RUN_PARALLEL = args.run_parallel
|
|
TEST_BAILOUTS = args.test_bailouts
|
|
TEST_DISCOVER = args.discover_tests
|
|
TEST_IN_SUBPROCESS = args.subprocess
|
|
TEST_SAVE_XML = args.save_xml
|
|
REPEAT_COUNT = args.repeat
|
|
SEED = args.seed
|
|
if not expecttest.ACCEPT:
|
|
expecttest.ACCEPT = args.accept
|
|
UNITTEST_ARGS = [sys.argv[0]] + remaining
|
|
torch.manual_seed(SEED)
|
|
|
|
# CI Prefix path used only on CI environment
|
|
CI_TEST_PREFIX = str(pathlib.Path(os.getcwd()))
|
|
|
|
def wait_for_process(p):
|
|
try:
|
|
return p.wait()
|
|
except KeyboardInterrupt:
|
|
# Give `p` a chance to handle KeyboardInterrupt. Without this,
|
|
# `pytest` can't print errors it collected so far upon KeyboardInterrupt.
|
|
exit_status = p.wait(timeout=5)
|
|
if exit_status is not None:
|
|
return exit_status
|
|
else:
|
|
p.kill()
|
|
raise
|
|
except: # noqa: B001,E722, copied from python core library
|
|
p.kill()
|
|
raise
|
|
finally:
|
|
# Always call p.wait() to ensure exit
|
|
p.wait()
|
|
|
|
def shell(command, cwd=None, env=None):
|
|
sys.stdout.flush()
|
|
sys.stderr.flush()
|
|
# The following cool snippet is copied from Py3 core library subprocess.call
|
|
# only the with
|
|
# 1. `except KeyboardInterrupt` block added for SIGINT handling.
|
|
# 2. In Py2, subprocess.Popen doesn't return a context manager, so we do
|
|
# `p.wait()` in a `final` block for the code to be portable.
|
|
#
|
|
# https://github.com/python/cpython/blob/71b6c1af727fbe13525fb734568057d78cea33f3/Lib/subprocess.py#L309-L323
|
|
assert not isinstance(command, torch._six.string_classes), "Command to shell should be a list or tuple of tokens"
|
|
p = subprocess.Popen(command, universal_newlines=True, cwd=cwd, env=env)
|
|
return wait_for_process(p)
|
|
|
|
|
|
# Used to run the same test with different tensor types
|
|
def repeat_test_for_types(dtypes):
|
|
def repeat_helper(f):
|
|
@wraps(f)
|
|
def call_helper(self, *args):
|
|
for dtype in dtypes:
|
|
with TestCase.subTest(self, dtype=dtype):
|
|
f(self, *args, dtype=dtype)
|
|
|
|
return call_helper
|
|
return repeat_helper
|
|
|
|
|
|
def discover_test_cases_recursively(suite_or_case):
|
|
if isinstance(suite_or_case, unittest.TestCase):
|
|
return [suite_or_case]
|
|
rc = []
|
|
for element in suite_or_case:
|
|
rc.extend(discover_test_cases_recursively(element))
|
|
return rc
|
|
|
|
def get_test_names(test_cases):
|
|
return ['.'.join(case.id().split('.')[-2:]) for case in test_cases]
|
|
|
|
def chunk_list(lst, nchunks):
|
|
return [lst[i::nchunks] for i in range(nchunks)]
|
|
|
|
# sanitize filename e.g., distributed/pipeline/sync/skip/test_api.py -> distributed.pipeline.sync.skip.test_api
|
|
def sanitize_test_filename(filename):
|
|
# inspect.getfile returns absolute path in some CI jobs, converting it to relative path if needed
|
|
if filename.startswith(CI_TEST_PREFIX):
|
|
filename = filename[len(CI_TEST_PREFIX) + 1:]
|
|
strip_py = re.sub(r'.py$', '', filename)
|
|
return re.sub('/', r'.', strip_py)
|
|
|
|
def run_tests(argv=UNITTEST_ARGS):
|
|
# import test files.
|
|
if IMPORT_SLOW_TESTS:
|
|
if os.path.exists(IMPORT_SLOW_TESTS):
|
|
global slow_tests_dict
|
|
with open(IMPORT_SLOW_TESTS, 'r') as fp:
|
|
slow_tests_dict = json.load(fp)
|
|
else:
|
|
print(f'[WARNING] slow test file provided but not found: {IMPORT_SLOW_TESTS}')
|
|
if IMPORT_DISABLED_TESTS:
|
|
if os.path.exists(IMPORT_DISABLED_TESTS):
|
|
global disabled_tests_dict
|
|
with open(IMPORT_DISABLED_TESTS, 'r') as fp:
|
|
disabled_tests_dict = json.load(fp)
|
|
else:
|
|
print(f'[WARNING] disabled test file provided but not found: {IMPORT_DISABLED_TESTS}')
|
|
# Determine the test launch mechanism
|
|
if TEST_DISCOVER:
|
|
suite = unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromModule(__main__)
|
|
test_cases = discover_test_cases_recursively(suite)
|
|
for name in get_test_names(test_cases):
|
|
print(name)
|
|
elif TEST_IN_SUBPROCESS:
|
|
suite = unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromModule(__main__)
|
|
test_cases = discover_test_cases_recursively(suite)
|
|
failed_tests = []
|
|
for case in test_cases:
|
|
test_case_full_name = case.id().split('.', 1)[1]
|
|
exitcode = shell([sys.executable] + argv + [test_case_full_name])
|
|
if exitcode != 0:
|
|
failed_tests.append(test_case_full_name)
|
|
|
|
assert len(failed_tests) == 0, "{} unit test(s) failed:\n\t{}".format(
|
|
len(failed_tests), '\n\t'.join(failed_tests))
|
|
elif RUN_PARALLEL > 1:
|
|
suite = unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromModule(__main__)
|
|
test_cases = discover_test_cases_recursively(suite)
|
|
test_batches = chunk_list(get_test_names(test_cases), RUN_PARALLEL)
|
|
processes = []
|
|
for i in range(RUN_PARALLEL):
|
|
command = [sys.executable] + argv + ['--log-suffix=-shard-{}'.format(i + 1)] + test_batches[i]
|
|
processes.append(subprocess.Popen(command, universal_newlines=True))
|
|
failed = False
|
|
for p in processes:
|
|
failed |= wait_for_process(p) != 0
|
|
assert not failed, "Some test shards have failed"
|
|
elif TEST_SAVE_XML is not None:
|
|
# import here so that non-CI doesn't need xmlrunner installed
|
|
import xmlrunner # type: ignore[import]
|
|
test_filename = sanitize_test_filename(inspect.getfile(sys._getframe(1)))
|
|
test_report_path = TEST_SAVE_XML + LOG_SUFFIX
|
|
test_report_path = os.path.join(test_report_path, test_filename)
|
|
os.makedirs(test_report_path, exist_ok=True)
|
|
verbose = '--verbose' in argv or '-v' in argv
|
|
if verbose:
|
|
print('Test results will be stored in {}'.format(test_report_path))
|
|
unittest.main(argv=argv, testRunner=xmlrunner.XMLTestRunner(output=test_report_path, verbosity=2 if verbose else 1))
|
|
elif REPEAT_COUNT > 1:
|
|
for _ in range(REPEAT_COUNT):
|
|
if not unittest.main(exit=False, argv=argv).result.wasSuccessful():
|
|
sys.exit(-1)
|
|
else:
|
|
unittest.main(argv=argv)
|
|
|
|
IS_LINUX = sys.platform == "linux"
|
|
IS_WINDOWS = sys.platform == "win32"
|
|
IS_MACOS = sys.platform == "darwin"
|
|
IS_PPC = platform.machine() == "ppc64le"
|
|
|
|
def is_avx512_vnni_supported():
|
|
if sys.platform != 'linux':
|
|
return False
|
|
with open("/proc/cpuinfo", encoding="ascii") as f:
|
|
lines = f.read()
|
|
return "avx512vnni" in lines
|
|
|
|
IS_AVX512_VNNI_SUPPORTED = is_avx512_vnni_supported()
|
|
|
|
if IS_WINDOWS:
|
|
@contextmanager
|
|
def TemporaryFileName(*args, **kwargs):
|
|
# Ideally we would like to not have to manually delete the file, but NamedTemporaryFile
|
|
# opens the file, and it cannot be opened multiple times in Windows. To support Windows,
|
|
# close the file after creation and try to remove it manually
|
|
if 'delete' in kwargs:
|
|
if kwargs['delete'] is not False:
|
|
raise UserWarning("only TemporaryFileName with delete=False is supported on Windows.")
|
|
else:
|
|
kwargs['delete'] = False
|
|
f = tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
try:
|
|
f.close()
|
|
yield f.name
|
|
finally:
|
|
os.unlink(f.name)
|
|
else:
|
|
@contextmanager # noqa: T484
|
|
def TemporaryFileName(*args, **kwargs):
|
|
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(*args, **kwargs) as f:
|
|
yield f.name
|
|
|
|
if IS_WINDOWS:
|
|
@contextmanager
|
|
def TemporaryDirectoryName(suffix=None):
|
|
# On Windows the directory created by TemporaryDirectory is likely to be removed prematurely,
|
|
# so we first create the directory using mkdtemp and then remove it manually
|
|
try:
|
|
dir_name = tempfile.mkdtemp(suffix=suffix)
|
|
yield dir_name
|
|
finally:
|
|
shutil.rmtree(dir_name)
|
|
else:
|
|
@contextmanager # noqa: T484
|
|
def TemporaryDirectoryName(suffix=None):
|
|
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory(suffix=suffix) as d:
|
|
yield d
|
|
|
|
IS_FILESYSTEM_UTF8_ENCODING = sys.getfilesystemencoding() == 'utf-8'
|
|
|
|
def _check_module_exists(name):
|
|
r"""Returns if a top-level module with :attr:`name` exists *without**
|
|
importing it. This is generally safer than try-catch block around a
|
|
`import X`. It avoids third party libraries breaking assumptions of some of
|
|
our tests, e.g., setting multiprocessing start method when imported
|
|
(see librosa/#747, torchvision/#544).
|
|
"""
|
|
import importlib.util
|
|
spec = importlib.util.find_spec(name)
|
|
return spec is not None
|
|
|
|
TEST_NUMPY = _check_module_exists('numpy')
|
|
TEST_SCIPY = _check_module_exists('scipy')
|
|
TEST_MKL = torch.backends.mkl.is_available()
|
|
TEST_NUMBA = _check_module_exists('numba')
|
|
|
|
TEST_DILL = _check_module_exists('dill')
|
|
|
|
TEST_LIBROSA = _check_module_exists('librosa')
|
|
|
|
# Python 2.7 doesn't have spawn
|
|
NO_MULTIPROCESSING_SPAWN = os.environ.get('NO_MULTIPROCESSING_SPAWN', '0') == '1'
|
|
TEST_WITH_ASAN = os.getenv('PYTORCH_TEST_WITH_ASAN', '0') == '1'
|
|
TEST_WITH_TSAN = os.getenv('PYTORCH_TEST_WITH_TSAN', '0') == '1'
|
|
TEST_WITH_UBSAN = os.getenv('PYTORCH_TEST_WITH_UBSAN', '0') == '1'
|
|
TEST_WITH_ROCM = os.getenv('PYTORCH_TEST_WITH_ROCM', '0') == '1'
|
|
# Enables tests that are slow to run (disabled by default)
|
|
TEST_WITH_SLOW = os.getenv('PYTORCH_TEST_WITH_SLOW', '0') == '1'
|
|
|
|
# Disables non-slow tests (these tests enabled by default)
|
|
# This is usually used in conjunction with TEST_WITH_SLOW to
|
|
# run *only* slow tests. (I could have done an enum, but
|
|
# it felt a little awkward.
|
|
TEST_SKIP_FAST = os.getenv('PYTORCH_TEST_SKIP_FAST', '0') == '1'
|
|
|
|
# Disables noarch tests; all but one CI configuration disables these. We don't
|
|
# disable them for local runs because you still want to run them
|
|
# (unlike slow tests!)
|
|
TEST_SKIP_NOARCH = os.getenv('PYTORCH_TEST_SKIP_NOARCH', '0') == '1'
|
|
|
|
# Determine whether to enable cuda memory leak check.
|
|
# CUDA mem leak check is expensive and thus we don't want to execute it on every
|
|
# test case / configuration.
|
|
# See: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/59402#issuecomment-858811135
|
|
TEST_SKIP_CUDA_MEM_LEAK_CHECK = os.getenv('PYTORCH_TEST_SKIP_CUDA_MEM_LEAK_CHECK', '0') == '1'
|
|
|
|
# Disables tests for when on Github Actions
|
|
ON_GHA = os.getenv('GITHUB_ACTIONS', '0') == '1'
|
|
|
|
# Dict of NumPy dtype -> torch dtype (when the correspondence exists)
|
|
numpy_to_torch_dtype_dict = {
|
|
np.bool_ : torch.bool,
|
|
np.uint8 : torch.uint8,
|
|
np.int8 : torch.int8,
|
|
np.int16 : torch.int16,
|
|
np.int32 : torch.int32,
|
|
np.int64 : torch.int64,
|
|
np.float16 : torch.float16,
|
|
np.float32 : torch.float32,
|
|
np.float64 : torch.float64,
|
|
np.complex64 : torch.complex64,
|
|
np.complex128 : torch.complex128
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
if IS_WINDOWS:
|
|
# Size of `np.intc` is platform defined.
|
|
# It is returned by functions like `bitwise_not`.
|
|
# On Windows `int` is 32-bit
|
|
# https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/cpp/data-type-ranges?view=msvc-160
|
|
numpy_to_torch_dtype_dict[np.intc] = torch.int
|
|
|
|
# Dict of torch dtype -> NumPy dtype
|
|
torch_to_numpy_dtype_dict = {value : key for (key, value) in numpy_to_torch_dtype_dict.items()}
|
|
|
|
ALL_TENSORTYPES = [torch.float,
|
|
torch.double,
|
|
torch.half]
|
|
|
|
# bfloat16 bringup is currently only available on ROCm
|
|
# ALL_TENSORTYPES2 will eventually be unified with ALL_TENSORTYPES
|
|
# when bfloat16 bringup is complete on all platforms
|
|
if TEST_WITH_ROCM:
|
|
ALL_TENSORTYPES2 = [torch.float,
|
|
torch.double,
|
|
torch.half,
|
|
torch.bfloat16]
|
|
else:
|
|
ALL_TENSORTYPES2 = ALL_TENSORTYPES
|
|
|
|
def skipIfRocm(fn):
|
|
@wraps(fn)
|
|
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
|
|
if TEST_WITH_ROCM:
|
|
raise unittest.SkipTest("test doesn't currently work on the ROCm stack")
|
|
else:
|
|
fn(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
return wrapper
|
|
|
|
# Context manager for setting deterministic flag and automatically
|
|
# resetting it to its original value
|
|
class DeterministicGuard:
|
|
def __init__(self, deterministic):
|
|
self.deterministic = deterministic
|
|
|
|
def __enter__(self):
|
|
self.deterministic_restore = torch.are_deterministic_algorithms_enabled()
|
|
torch.use_deterministic_algorithms(self.deterministic)
|
|
|
|
def __exit__(self, exception_type, exception_value, traceback):
|
|
torch.use_deterministic_algorithms(self.deterministic_restore)
|
|
|
|
# This decorator can be used for API tests that call
|
|
# torch.use_deterministic_algorithms(). When the test is finished, it will
|
|
# restore the previous deterministic flag setting.
|
|
#
|
|
# If CUDA >= 10.2, this will set the environment variable
|
|
# CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG=:4096:8 so that the error associated with that
|
|
# setting is not thrown during the test unless the test changes that variable
|
|
# on purpose. The previous CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG setting will also be
|
|
# restored once the test is finished.
|
|
#
|
|
# Note that if a test requires CUDA to actually register the changed
|
|
# CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG variable, a new subprocess must be created, because
|
|
# CUDA only checks the variable when the runtime initializes. Tests can be
|
|
# run inside a subprocess like so:
|
|
#
|
|
# import subprocess, sys, os
|
|
# script = '''
|
|
# # Test code should go here
|
|
# '''
|
|
# try:
|
|
# subprocess.check_output(
|
|
# [sys.executable, '-c', script],
|
|
# stderr=subprocess.STDOUT,
|
|
# cwd=os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__)),
|
|
# env=os.environ.copy())
|
|
# except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
|
|
# error_message = e.output.decode('utf-8')
|
|
# # Handle exceptions raised by the subprocess here
|
|
#
|
|
def wrapDeterministicFlagAPITest(fn):
|
|
@wraps(fn)
|
|
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
|
|
with DeterministicGuard(torch.are_deterministic_algorithms_enabled()):
|
|
class CuBLASConfigGuard:
|
|
cublas_var_name = 'CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG'
|
|
|
|
def __enter__(self):
|
|
self.is_cuda10_2_or_higher = (
|
|
(torch.version.cuda is not None)
|
|
and ([int(x) for x in torch.version.cuda.split(".")] >= [10, 2]))
|
|
if self.is_cuda10_2_or_higher:
|
|
self.cublas_config_restore = os.environ.get(self.cublas_var_name)
|
|
os.environ[self.cublas_var_name] = ':4096:8'
|
|
|
|
def __exit__(self, exception_type, exception_value, traceback):
|
|
if self.is_cuda10_2_or_higher:
|
|
cur_cublas_config = os.environ.get(self.cublas_var_name)
|
|
if self.cublas_config_restore is None:
|
|
if cur_cublas_config is not None:
|
|
del os.environ[self.cublas_var_name]
|
|
else:
|
|
os.environ[self.cublas_var_name] = self.cublas_config_restore
|
|
with CuBLASConfigGuard():
|
|
fn(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
return wrapper
|
|
|
|
def skipIfCompiledWithoutNumpy(fn):
|
|
# Even if the numpy module is present, if `USE_NUMPY=0` is used during the
|
|
# build, numpy tests will fail
|
|
numpy_support = TEST_NUMPY
|
|
if numpy_support:
|
|
try:
|
|
# The numpy module is present, verify that PyTorch is compiled with
|
|
# numpy support
|
|
torch.from_numpy(np.array([2, 2]))
|
|
except RuntimeError:
|
|
numpy_support = False
|
|
|
|
@wraps(fn)
|
|
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
|
|
if not numpy_support:
|
|
raise unittest.SkipTest("PyTorch was compiled without numpy support")
|
|
else:
|
|
fn(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
return wrapper
|
|
|
|
def _test_function(fn, device):
|
|
def run_test_function(self):
|
|
return fn(self, device)
|
|
return run_test_function
|
|
|
|
|
|
def skipIfNoLapack(fn):
|
|
@wraps(fn)
|
|
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
|
|
if not torch._C.has_lapack:
|
|
raise unittest.SkipTest('PyTorch compiled without Lapack')
|
|
else:
|
|
fn(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
return wrapper
|
|
|
|
|
|
def skipIfNotRegistered(op_name, message):
|
|
"""Wraps the decorator to hide the import of the `core`.
|
|
|
|
Args:
|
|
op_name: Check if this op is registered in `core._REGISTERED_OPERATORS`.
|
|
message: message to fail with.
|
|
|
|
Usage:
|
|
@skipIfNotRegistered('MyOp', 'MyOp is not linked!')
|
|
This will check if 'MyOp' is in the caffe2.python.core
|
|
"""
|
|
try:
|
|
from caffe2.python import core
|
|
skipper = unittest.skipIf(op_name not in core._REGISTERED_OPERATORS,
|
|
message)
|
|
except ImportError:
|
|
skipper = unittest.skip("Cannot import `caffe2.python.core`")
|
|
return skipper
|
|
|
|
|
|
def skipIfNoSciPy(fn):
|
|
@wraps(fn)
|
|
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
|
|
if not TEST_SCIPY:
|
|
raise unittest.SkipTest("test require SciPy, but SciPy not found")
|
|
else:
|
|
fn(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
return wrapper
|
|
|
|
|
|
def skipIfOnGHA(fn):
|
|
@wraps(fn)
|
|
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
|
|
if ON_GHA:
|
|
raise unittest.SkipTest("Test disabled for GHA")
|
|
else:
|
|
fn(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
return wrapper
|
|
|
|
|
|
def slowTest(fn):
|
|
@wraps(fn)
|
|
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
|
|
if not TEST_WITH_SLOW:
|
|
raise unittest.SkipTest("test is slow; run with PYTORCH_TEST_WITH_SLOW to enable test")
|
|
else:
|
|
fn(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
wrapper.__dict__['slow_test'] = True
|
|
return wrapper
|
|
|
|
|
|
# noarch tests are tests that should be only run on one CI configuration,
|
|
# because they don't exercise any interesting platform specific code
|
|
# and so if run once, indicate the test should pass everywhere.
|
|
# See https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/53743
|
|
def noarchTest(fn):
|
|
@wraps(fn)
|
|
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
|
|
if TEST_SKIP_NOARCH:
|
|
raise unittest.SkipTest("test is noarch: we are skipping noarch tests due to TEST_SKIP_NOARCH")
|
|
else:
|
|
fn(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
return wrapper
|
|
|
|
|
|
def slowAwareTest(fn):
|
|
fn.__dict__['slow_test'] = True
|
|
return fn
|
|
|
|
|
|
def skipCUDAMemoryLeakCheckIf(condition):
|
|
def dec(fn):
|
|
if getattr(fn, '_do_cuda_memory_leak_check', True): # if current True
|
|
fn._do_cuda_memory_leak_check = not condition
|
|
return fn
|
|
return dec
|
|
|
|
def skipCUDANonDefaultStreamIf(condition):
|
|
def dec(fn):
|
|
if getattr(fn, '_do_cuda_non_default_stream', True): # if current True
|
|
fn._do_cuda_non_default_stream = not condition
|
|
return fn
|
|
return dec
|
|
|
|
def suppress_warnings(fn):
|
|
@wraps(fn)
|
|
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
|
|
with warnings.catch_warnings():
|
|
warnings.simplefilter("ignore")
|
|
fn(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
return wrapper
|
|
|
|
|
|
def to_gpu(obj, type_map=None):
|
|
if type_map is None:
|
|
type_map = {}
|
|
if isinstance(obj, torch.Tensor):
|
|
assert obj.is_leaf
|
|
t = type_map.get(obj.dtype, obj.dtype)
|
|
with torch.no_grad():
|
|
res = obj.clone().to(dtype=t, device="cuda")
|
|
res.requires_grad = obj.requires_grad
|
|
return res
|
|
elif torch.is_storage(obj):
|
|
return obj.new().resize_(obj.size()).copy_(obj)
|
|
elif isinstance(obj, list):
|
|
return [to_gpu(o, type_map) for o in obj]
|
|
elif isinstance(obj, tuple):
|
|
return tuple(to_gpu(o, type_map) for o in obj)
|
|
else:
|
|
return deepcopy(obj)
|
|
|
|
|
|
def get_function_arglist(func):
|
|
return inspect.getfullargspec(func).args
|
|
|
|
|
|
def set_rng_seed(seed):
|
|
torch.manual_seed(seed)
|
|
random.seed(seed)
|
|
if TEST_NUMPY:
|
|
np.random.seed(seed)
|
|
|
|
|
|
@contextlib.contextmanager
|
|
def freeze_rng_state():
|
|
rng_state = torch.get_rng_state()
|
|
if torch.cuda.is_available():
|
|
cuda_rng_state = torch.cuda.get_rng_state()
|
|
yield
|
|
if torch.cuda.is_available():
|
|
torch.cuda.set_rng_state(cuda_rng_state)
|
|
torch.set_rng_state(rng_state)
|
|
|
|
@contextlib.contextmanager
|
|
def set_default_dtype(dtype):
|
|
saved_dtype = torch.get_default_dtype()
|
|
torch.set_default_dtype(dtype)
|
|
try:
|
|
yield
|
|
finally:
|
|
torch.set_default_dtype(saved_dtype)
|
|
|
|
def iter_indices(tensor):
|
|
if tensor.dim() == 0:
|
|
return range(0)
|
|
if tensor.dim() == 1:
|
|
return range(tensor.size(0))
|
|
return product(*(range(s) for s in tensor.size()))
|
|
|
|
|
|
def is_iterable(obj):
|
|
try:
|
|
iter(obj)
|
|
return True
|
|
except TypeError:
|
|
return False
|
|
|
|
|
|
def is_iterable_of_tensors(iterable, include_empty=False):
|
|
""" Returns True if iterable is an iterable of tensors and False o.w.
|
|
|
|
If the iterable is empty, the return value is :attr:`include_empty`
|
|
"""
|
|
# Tensor itself is iterable so we check this first
|
|
if isinstance(iterable, torch.Tensor):
|
|
return False
|
|
|
|
try:
|
|
if len(iterable) == 0:
|
|
return include_empty
|
|
|
|
for t in iter(iterable):
|
|
if not isinstance(t, torch.Tensor):
|
|
return False
|
|
|
|
except TypeError as te:
|
|
return False
|
|
|
|
return True
|
|
|
|
|
|
class CudaNonDefaultStream():
|
|
def __enter__(self):
|
|
# Before starting CUDA test save currently active streams on all
|
|
# CUDA devices and set new non default streams to all CUDA devices
|
|
# to ensure CUDA tests do not use default stream by mistake.
|
|
beforeDevice = torch.cuda.current_device()
|
|
self.beforeStreams = []
|
|
for d in range(torch.cuda.device_count()):
|
|
self.beforeStreams.append(torch.cuda.current_stream(d))
|
|
deviceStream = torch.cuda.Stream(device=d)
|
|
torch._C._cuda_setStream(deviceStream._cdata)
|
|
torch._C._cuda_setDevice(beforeDevice)
|
|
|
|
def __exit__(self, exec_type, exec_value, traceback):
|
|
# After completing CUDA test load previously active streams on all
|
|
# CUDA devices.
|
|
beforeDevice = torch.cuda.current_device()
|
|
for d in range(torch.cuda.device_count()):
|
|
torch._C._cuda_setStream(self.beforeStreams[d]._cdata)
|
|
torch._C._cuda_setDevice(beforeDevice)
|
|
|
|
class CudaMemoryLeakCheck():
|
|
def __init__(self, testcase, name=None):
|
|
self.name = testcase.id() if name is None else name
|
|
self.testcase = testcase
|
|
|
|
# initialize context & RNG to prevent false positive detections
|
|
# when the test is the first to initialize those
|
|
from torch.testing._internal.common_cuda import initialize_cuda_context_rng
|
|
initialize_cuda_context_rng()
|
|
|
|
@staticmethod
|
|
def get_cuda_memory_usage():
|
|
# we don't need CUDA synchronize because the statistics are not tracked at
|
|
# actual freeing, but at when marking the block as free.
|
|
num_devices = torch.cuda.device_count()
|
|
gc.collect()
|
|
return tuple(torch.cuda.memory_allocated(i) for i in range(num_devices))
|
|
|
|
def __enter__(self):
|
|
self.befores = self.get_cuda_memory_usage()
|
|
|
|
def __exit__(self, exec_type, exec_value, traceback):
|
|
# Don't check for leaks if an exception was thrown
|
|
if exec_type is not None:
|
|
return
|
|
|
|
afters = self.get_cuda_memory_usage()
|
|
|
|
for i, (before, after) in enumerate(zip(self.befores, afters)):
|
|
self.testcase.assertEqual(
|
|
before, after, msg='{} leaked {} bytes CUDA memory on device {}'.format(
|
|
self.name, after - before, i))
|
|
|
|
@contextmanager
|
|
def skip_exception_type(exc_type):
|
|
try:
|
|
yield
|
|
except exc_type as e:
|
|
raise unittest.SkipTest(f"not implemented: {e}") from e
|
|
|
|
# "min_satisfying_examples" setting has been deprecated in hypythesis
|
|
# 3.56.0 and removed in hypothesis 4.x
|
|
try:
|
|
import hypothesis
|
|
|
|
def settings(*args, **kwargs):
|
|
if 'min_satisfying_examples' in kwargs and hypothesis.version.__version_info__ >= (3, 56, 0):
|
|
kwargs.pop('min_satisfying_examples')
|
|
return hypothesis.settings(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
|
|
|
|
hypothesis.settings.register_profile(
|
|
"pytorch_ci",
|
|
settings(
|
|
derandomize=True,
|
|
suppress_health_check=[hypothesis.HealthCheck.too_slow],
|
|
database=None,
|
|
max_examples=50,
|
|
verbosity=hypothesis.Verbosity.normal))
|
|
hypothesis.settings.register_profile(
|
|
"dev",
|
|
settings(
|
|
suppress_health_check=[hypothesis.HealthCheck.too_slow],
|
|
database=None,
|
|
max_examples=10,
|
|
verbosity=hypothesis.Verbosity.normal))
|
|
hypothesis.settings.register_profile(
|
|
"debug",
|
|
settings(
|
|
suppress_health_check=[hypothesis.HealthCheck.too_slow],
|
|
database=None,
|
|
max_examples=1000,
|
|
verbosity=hypothesis.Verbosity.verbose))
|
|
|
|
hypothesis.settings.load_profile(
|
|
"pytorch_ci" if IS_IN_CI else os.getenv('PYTORCH_HYPOTHESIS_PROFILE', 'dev')
|
|
)
|
|
except ImportError:
|
|
print('Fail to import hypothesis in common_utils, tests are not derandomized')
|
|
|
|
def check_if_enable(test: unittest.TestCase):
|
|
test_suite = str(test.__class__).split('\'')[1]
|
|
test_name = f'{test._testMethodName} ({test_suite})'
|
|
if slow_tests_dict is not None and test_name in slow_tests_dict:
|
|
getattr(test, test._testMethodName).__dict__['slow_test'] = True
|
|
if not TEST_WITH_SLOW:
|
|
raise unittest.SkipTest("test is slow; run with PYTORCH_TEST_WITH_SLOW to enable test")
|
|
if not IS_SANDCASTLE and disabled_tests_dict is not None:
|
|
if test_name in disabled_tests_dict:
|
|
issue_url, platforms = disabled_tests_dict[test_name]
|
|
platform_to_conditional: Dict = {
|
|
"mac": IS_MACOS,
|
|
"macos": IS_MACOS,
|
|
"windows": IS_WINDOWS,
|
|
"linux": IS_LINUX
|
|
}
|
|
if platforms == [] or any([platform_to_conditional[platform] for platform in platforms]):
|
|
raise unittest.SkipTest(
|
|
f"Test is disabled because an issue exists disabling it: {issue_url}" +
|
|
f" for {'all' if platforms == [] else ''}platform(s) {', '.join(platforms)}." +
|
|
" To enable, set the environment variable PYTORCH_RUN_DISABLED_TESTS=1")
|
|
if TEST_SKIP_FAST:
|
|
if not getattr(test, test._testMethodName).__dict__.get('slow_test', False):
|
|
raise unittest.SkipTest("test is fast; we disabled it with PYTORCH_TEST_SKIP_FAST")
|
|
|
|
# Acquires the comparison dtype, required since isclose
|
|
# requires both inputs have the same dtype, and isclose is not supported
|
|
# for some device x dtype combinations.
|
|
# NOTE: Remaps bfloat16 to float32 since neither the CPU or CUDA device types
|
|
# support needed bfloat16 comparison methods.
|
|
# NOTE: Remaps float16 to float32 on CPU since the CPU device type doesn't
|
|
# support needed float16 comparison methods.
|
|
# TODO: Update this once bfloat16 and float16 are better supported.
|
|
def get_comparison_dtype(a, b):
|
|
# TODO: update this when promote_types supports bfloat16 and/or
|
|
# isclose supports bfloat16.
|
|
a_dtype = torch.float32 if a.dtype is torch.bfloat16 else a.dtype
|
|
b_dtype = torch.float32 if b.dtype is torch.bfloat16 else b.dtype
|
|
|
|
compare_dtype = torch.promote_types(a_dtype, b_dtype)
|
|
|
|
# non-CUDA (CPU, for example) float16 -> float32
|
|
# TODO: update this when isclose is implemented for CPU float16
|
|
if (compare_dtype is torch.float16 and
|
|
(a.device != b.device or a.device.type != 'cuda' or
|
|
b.device.type != 'cuda')):
|
|
compare_dtype = torch.float32
|
|
|
|
return compare_dtype
|
|
|
|
# This implements a variant of assertRaises/assertRaisesRegex where we first test
|
|
# if the exception is NotImplementedError, and if so just skip the test instead
|
|
# of failing it.
|
|
#
|
|
# This is implemented by inheriting from the (private) implementation of
|
|
# assertRaises from unittest.case, and slightly tweaking it for this new
|
|
# behavior. The year is 2021: this private class hierarchy hasn't changed since
|
|
# 2010, seems low risk to inherit from.
|
|
class AssertRaisesContextIgnoreNotImplementedError(unittest.case._AssertRaisesContext):
|
|
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, tb):
|
|
if exc_type is not None and issubclass(exc_type, NotImplementedError):
|
|
self.test_case.skipTest(f"not_implemented: {exc_value}") # type: ignore[attr-defined]
|
|
return super().__exit__(exc_type, exc_value, tb)
|
|
|
|
|
|
@contextmanager
|
|
def set_warn_always_context(new_val: bool):
|
|
old_val = torch.is_warn_always_enabled()
|
|
torch.set_warn_always(new_val)
|
|
try:
|
|
yield
|
|
finally:
|
|
torch.set_warn_always(old_val)
|
|
|
|
|
|
class TestCase(expecttest.TestCase):
|
|
# NOTE: "precision" lets classes and generated tests set minimum
|
|
# atol values when comparing tensors. Used by @precisionOverride and @toleranceOverride, for
|
|
# example.
|
|
# NOTE: "rel_tol" lets classes and generated tests set minimum
|
|
# rtol values when comparing tensors. Used by @toleranceOverride, for example.
|
|
_precision: float = 0
|
|
_rel_tol: float = 0
|
|
|
|
# checker to early terminate test suite if unrecoverable failure occurs.
|
|
def _should_stop_test_suite(self):
|
|
if torch.cuda.is_initialized():
|
|
# CUDA device side error will cause subsequence test cases to fail.
|
|
# stop entire test suite if catches RuntimeError during torch.cuda.synchronize().
|
|
try:
|
|
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
|
except RuntimeError as rte:
|
|
return True
|
|
return False
|
|
else:
|
|
return False
|
|
|
|
@property
|
|
def precision(self) -> float:
|
|
return self._precision
|
|
|
|
@precision.setter
|
|
def precision(self, prec: float) -> None:
|
|
self._precision = prec
|
|
|
|
@property
|
|
def rel_tol(self) -> float:
|
|
return self._rel_tol
|
|
|
|
@rel_tol.setter
|
|
def rel_tol(self, prec: float) -> None:
|
|
self._rel_tol = prec
|
|
|
|
_do_cuda_memory_leak_check = False
|
|
_do_cuda_non_default_stream = False
|
|
|
|
# When True, if a test case raises a NotImplementedError, instead of failing
|
|
# the test, skip it instead.
|
|
_ignore_not_implemented_error = False
|
|
|
|
def __init__(self, method_name='runTest'):
|
|
super().__init__(method_name)
|
|
|
|
test_method = getattr(self, method_name, None)
|
|
if test_method is not None:
|
|
# Wraps the tested method if we should do CUDA memory check.
|
|
if not TEST_SKIP_CUDA_MEM_LEAK_CHECK:
|
|
self._do_cuda_memory_leak_check &= getattr(test_method, '_do_cuda_memory_leak_check', True)
|
|
# FIXME: figure out the flaky -1024 anti-leaks on windows. See #8044
|
|
if self._do_cuda_memory_leak_check and not IS_WINDOWS:
|
|
self.wrap_with_cuda_policy(method_name, self.assertLeaksNoCudaTensors)
|
|
|
|
# Wraps the tested method if we should enforce non default CUDA stream.
|
|
self._do_cuda_non_default_stream &= getattr(test_method, '_do_cuda_non_default_stream', True)
|
|
if self._do_cuda_non_default_stream and not IS_WINDOWS:
|
|
self.wrap_with_cuda_policy(method_name, self.enforceNonDefaultStream)
|
|
|
|
if self._ignore_not_implemented_error:
|
|
self.wrap_with_policy(method_name, lambda: skip_exception_type(NotImplementedError))
|
|
|
|
def assertLeaksNoCudaTensors(self, name=None):
|
|
name = self.id() if name is None else name
|
|
return CudaMemoryLeakCheck(self, name)
|
|
|
|
def enforceNonDefaultStream(self):
|
|
return CudaNonDefaultStream()
|
|
|
|
def wrap_with_cuda_policy(self, method_name, policy):
|
|
test_method = getattr(self, method_name)
|
|
# the import below may initialize CUDA context, so we do it only if
|
|
# self._do_cuda_memory_leak_check or self._do_cuda_non_default_stream
|
|
# is True.
|
|
# TODO: sure looks like we unconditionally initialize the context here
|
|
# -- ezyang
|
|
from torch.testing._internal.common_cuda import TEST_CUDA
|
|
fullname = self.id().lower() # class_name.method_name
|
|
if TEST_CUDA and ('gpu' in fullname or 'cuda' in fullname):
|
|
setattr(self, method_name, self.wrap_method_with_policy(test_method, policy))
|
|
|
|
def wrap_with_policy(self, method_name, policy):
|
|
test_method = getattr(self, method_name)
|
|
setattr(self, method_name, self.wrap_method_with_policy(test_method, policy))
|
|
|
|
# A policy is a zero-argument function that returns a context manager.
|
|
# We don't take the context manager directly as it may be necessary to
|
|
# construct it once per test method
|
|
def wrap_method_with_policy(self, method, policy):
|
|
# Assumes that `method` is the tested function in `self`.
|
|
# NOTE: Python Exceptions (e.g., unittest.Skip) keeps objects in scope
|
|
# alive, so this cannot be done in setUp and tearDown because
|
|
# tearDown is run unconditionally no matter whether the test
|
|
# passes or not. For the same reason, we can't wrap the `method`
|
|
# call in try-finally and always do the check.
|
|
@wraps(method)
|
|
def wrapper(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
|
with policy():
|
|
method(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
return types.MethodType(wrapper, self)
|
|
|
|
def wrap_with_cuda_memory_check(self, method):
|
|
return self.wrap_method_with_policy(method, self.assertLeaksNoCudaTensors)
|
|
|
|
def run(self, result=None):
|
|
super().run(result=result)
|
|
# Early terminate test if necessary.
|
|
if self._should_stop_test_suite():
|
|
result.stop()
|
|
|
|
def setUp(self):
|
|
check_if_enable(self)
|
|
set_rng_seed(SEED)
|
|
|
|
@staticmethod
|
|
def _make_crow_indices(n_rows, n_cols, nnz,
|
|
*, device, dtype, random=True):
|
|
"""Return crow_indices of a CSR tensor with size (n_rows, n_cols) and
|
|
the number of specified elements nnz.
|
|
|
|
If random is True, the column counts of rows are in random
|
|
order. Otherwise, the column counts of rows are defined by the
|
|
used sampling method.
|
|
|
|
Sampling method
|
|
---------------
|
|
|
|
The used sampling method was introduced in
|
|
https://pearu.github.io/csr_sampling.html, and here we give
|
|
only an overall description of the method.
|
|
|
|
Notice that crow_indices can be defined as cumsum(counts)
|
|
where counts is a sequence of non-negative integers satisfying
|
|
the following conditions:
|
|
|
|
len(counts) == n_rows + 1
|
|
counts.max() <= n_cols
|
|
|
|
while counts[i + 1] is interpreted as the number of specified
|
|
elements in the i-th row.
|
|
|
|
The used sampling method aims at increasing the diversity of
|
|
CSR samples, that is, a CSR sample should contain (i) rows
|
|
that are all filled, (ii) rows with no elements at all, and
|
|
(iii) rows that are partially filled. At the same time and for
|
|
the given total number of specified elements (nnz), there
|
|
should be minimal preference to rows with a given number of
|
|
elements. To achieve this, the sampling method is built-up on
|
|
using a sawteeth model for counts. In the simplest case, we
|
|
would have
|
|
|
|
counts = arange(n_rows + 1) % (n_cols + 1)
|
|
|
|
that has equal number of all possible column counts per row.
|
|
This formula can be used only for specific input values of
|
|
n_rows, n_cols, and nnz. To generalize this model to any
|
|
combinations of inputs, the counts model above is extended
|
|
with an incomplete sawtooth, and the right and lower
|
|
rectangular parts that will guarantee that
|
|
|
|
counts.sum() == nnz
|
|
|
|
for any combination of n_rows, n_cols, and nnz. Basically,
|
|
we'll find a maximal window in (n_rows + 1, n_cols + 1)-grid
|
|
that is able to hold a sequence of sawteeth and so-called
|
|
final correction, while the external part of the window is
|
|
filled with counts to meet the nnz contraint exactly.
|
|
"""
|
|
assert 0 <= nnz <= n_rows * n_cols
|
|
|
|
def sawteeth(n, m):
|
|
# return the total number of counts in the sequence of
|
|
# sawteeth where n and m define a window in (n_rows+1,
|
|
# n_cols+1) rectangle where the sequence of sawteeth
|
|
# perfectly fit.
|
|
M = (n_cols - m) * (n_cols - m + 1) // 2
|
|
K = (n_rows - n) % (n_cols - m + 1)
|
|
return M * ((n_rows - n) // (n_cols - m + 1)) + K * (K - 1) // 2
|
|
|
|
# Different from the original method description, here counts
|
|
# has leading 0 required by crow_indices:
|
|
counts = torch.zeros(n_rows + 1, dtype=dtype, device=torch.device('cpu'))
|
|
|
|
n = m = 0
|
|
N = sawteeth(n, m)
|
|
if N and nnz >= max(N, n_cols):
|
|
# determine the width of the sawteeth window. We use bisection to solve
|
|
# N(n, 0) == 0 or nnz - n * n_cols < max(N(n, 0), n_cols)
|
|
# for n
|
|
n_left = n
|
|
n_right = n_rows - 1
|
|
N_right = sawteeth(n_right, m)
|
|
while n_right - n_left > 1:
|
|
n_middle = (n_left + n_right) // 2
|
|
N_middle = sawteeth(n_middle, m)
|
|
if N_middle == 0 or nnz - n_middle * n_cols < max(N_middle, n_cols):
|
|
n_right, N_right = n_middle, N_middle
|
|
else:
|
|
n_left = n_middle
|
|
n, N = n_right, N_right
|
|
# fill the right rectangle with counts:
|
|
assert n
|
|
counts[-n:].fill_(n_cols)
|
|
|
|
if N and nnz - n * n_cols >= max(N, n_rows - n):
|
|
# determine the height of the sawteeth window. We use bisection to solve
|
|
# N(n, m) == 0 or nnz - n * n_cols - m * (n_rows - n) < max(N(n, m), n_rows - n)
|
|
# for m.
|
|
m_left = m
|
|
m_right = n_cols - 1
|
|
N_right = sawteeth(n, m_right)
|
|
while m_right - m_left > 1:
|
|
m_middle = (m_left + m_right) // 2
|
|
N_middle = sawteeth(n, m_middle)
|
|
if N_middle == 0 or nnz - n * n_cols - m_middle * (n_rows - n) < max(N_middle, n_rows - n):
|
|
m_right, N_right = m_middle, N_middle
|
|
else:
|
|
m_left = m_middle
|
|
m, N = m_right, N_right
|
|
# fill the bottom rectangle with counts:
|
|
assert m
|
|
counts[1:n_rows - n + 1].fill_(m)
|
|
|
|
if N:
|
|
# fill the sawteeth window with counts
|
|
q, r = divmod(nnz - n * n_cols - m * (n_rows - n),
|
|
(n_cols - m) * (n_cols - m + 1) // 2)
|
|
p = 1 + q * (n_cols - m + 1)
|
|
if sys.version_info >= (3, 8):
|
|
k = math.isqrt(2 * r)
|
|
else:
|
|
# math.isqrt(x) is available starting from Python 3.8.
|
|
# Here we use int(math.sqrt(x)) as an approximation
|
|
# that appers to give exaxt result for all x values
|
|
# less than 2**35, at least, the upper limit of x is
|
|
# TBD.
|
|
k = int(math.sqrt(2 * r))
|
|
if k * (k + 1) > 2 * r:
|
|
k -= 1
|
|
corr = r - k * (k + 1) // 2
|
|
assert not ((p > 1) and (m > 0)) # full sawteeth are never on top of a bottom rectangle
|
|
# sequence of full sawteeth:
|
|
counts[1:p] = torch.arange(p - 1, dtype=dtype, device=counts.device) % (n_cols - m + 1)
|
|
# incomplete sawtooth:
|
|
counts[p:p + k + 1] += torch.arange(k + 1, dtype=dtype, device=counts.device)
|
|
else:
|
|
# given input does not support sawteeth
|
|
p = 1
|
|
corr = nnz - n * n_cols - m * (n_rows - n)
|
|
|
|
# correction that will guarantee counts.sum() == nnz:
|
|
counts[p] += corr
|
|
|
|
if random:
|
|
# randomize crow_indices by shuffling the sawteeth
|
|
# sequence:
|
|
perm = torch.randperm(n_rows, device=counts.device)
|
|
counts[1:] = counts[1:][perm]
|
|
|
|
# compute crow_indices:
|
|
crow_indices = counts
|
|
crow_indices.cumsum_(dim=0)
|
|
return crow_indices.to(device=device)
|
|
|
|
def genSparseCSRTensor(self, size, nnz, *, device, dtype, index_dtype):
|
|
sparse_dim = 2
|
|
assert all(size[d] > 0 for d in range(sparse_dim)) or nnz == 0, 'invalid arguments'
|
|
assert len(size) == sparse_dim
|
|
|
|
def random_sparse_csr(n_rows, n_cols, nnz):
|
|
crow_indices = self._make_crow_indices(n_rows, n_cols, nnz, device=device, dtype=index_dtype)
|
|
col_indices = torch.zeros(nnz, dtype=index_dtype, device=device)
|
|
for i in range(n_rows):
|
|
count = crow_indices[i + 1] - crow_indices[i]
|
|
col_indices[crow_indices[i]:crow_indices[i + 1]], _ = torch.sort(
|
|
torch.randperm(n_cols, dtype=index_dtype, device=device)[:count])
|
|
values = make_tensor([nnz], device=device, dtype=dtype, low=-1, high=1)
|
|
return values, crow_indices, col_indices
|
|
|
|
values, crow_indices, col_indices = random_sparse_csr(size[0], size[1], nnz)
|
|
return torch.sparse_csr_tensor(crow_indices,
|
|
col_indices,
|
|
values, size=size, dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
|
|
def genSparseTensor(self, size, sparse_dim, nnz, is_uncoalesced, device, dtype):
|
|
# Assert not given impossible combination, where the sparse dims have
|
|
# empty numel, but nnz > 0 makes the indices containing values.
|
|
assert all(size[d] > 0 for d in range(sparse_dim)) or nnz == 0, 'invalid arguments'
|
|
|
|
v_size = [nnz] + list(size[sparse_dim:])
|
|
v = make_tensor(v_size, device=device, dtype=dtype, low=-1, high=1)
|
|
i = torch.rand(sparse_dim, nnz, device=device)
|
|
i.mul_(torch.tensor(size[:sparse_dim]).unsqueeze(1).to(i))
|
|
i = i.to(torch.long)
|
|
if is_uncoalesced:
|
|
v = torch.cat([v, torch.randn_like(v)], 0)
|
|
i = torch.cat([i, i], 1)
|
|
x = torch.sparse_coo_tensor(i, v, torch.Size(size), dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
|
|
if not is_uncoalesced:
|
|
x = x.coalesce()
|
|
else:
|
|
# FIXME: `x` is a sparse view of `v`. Currently rebase_history for
|
|
# sparse views is not implemented, so this workaround is
|
|
# needed for inplace operations done on `x`, e.g., copy_().
|
|
# Remove after implementing something equivalent to CopySlice
|
|
# for sparse views.
|
|
# NOTE: We do clone() after detach() here because we need to be able to change size/storage of x afterwards
|
|
x = x.detach().clone()
|
|
return x, x._indices().clone(), x._values().clone()
|
|
|
|
def safeToDense(self, t):
|
|
return t.coalesce().to_dense()
|
|
|
|
# Compares torch function with reference function for given sample input (object of SampleInput)
|
|
# Note: only values are compared, type comparison is not done here
|
|
def compare_with_reference(self, torch_fn, ref_fn, sample_input, **kwargs):
|
|
n_inp, n_args, n_kwargs = sample_input.numpy()
|
|
t_inp, t_args, t_kwargs = sample_input.input, sample_input.args, sample_input.kwargs
|
|
|
|
actual = torch_fn(t_inp, *t_args, **t_kwargs)
|
|
expected = ref_fn(n_inp, *n_args, **n_kwargs)
|
|
|
|
self.assertEqual(actual, expected, exact_device=False)
|
|
|
|
# Compares the given Torch and NumPy functions on the given tensor-like object.
|
|
# NOTE: both torch_fn and np_fn should be functions that take a single
|
|
# tensor (array). If the torch and/or NumPy function require additional
|
|
# arguments then wrap the function in a lambda or pass a partial function.
|
|
# TODO: add args/kwargs for passing to assertEqual (e.g. rtol, atol)
|
|
def compare_with_numpy(self, torch_fn, np_fn, tensor_like,
|
|
device=None, dtype=None, **kwargs):
|
|
assert TEST_NUMPY
|
|
|
|
if isinstance(tensor_like, torch.Tensor):
|
|
assert device is None
|
|
assert dtype is None
|
|
t_cpu = tensor_like.detach().cpu()
|
|
if t_cpu.dtype is torch.bfloat16:
|
|
t_cpu = t_cpu.float()
|
|
a = t_cpu.numpy()
|
|
t = tensor_like
|
|
else:
|
|
d = copy.copy(torch_to_numpy_dtype_dict)
|
|
d[torch.bfloat16] = np.float32
|
|
a = np.array(tensor_like, dtype=d[dtype])
|
|
t = torch.tensor(tensor_like, device=device, dtype=dtype)
|
|
|
|
np_result = np_fn(a)
|
|
torch_result = torch_fn(t).cpu()
|
|
|
|
# Converts arrays to tensors
|
|
if isinstance(np_result, np.ndarray):
|
|
try:
|
|
np_result = torch.from_numpy(np_result)
|
|
except Exception:
|
|
# NOTE: copying an array before conversion is necessary when,
|
|
# for example, the array has negative strides.
|
|
np_result = torch.from_numpy(np_result.copy())
|
|
if t.dtype is torch.bfloat16 and torch_result.dtype is torch.bfloat16 and np_result.dtype is torch.float:
|
|
torch_result = torch_result.to(torch.float)
|
|
|
|
self.assertEqual(np_result, torch_result, **kwargs)
|
|
|
|
# Some analysis of tolerance by logging tests from test_torch.py can be found
|
|
# in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/32538.
|
|
# dtype name : (rtol, atol)
|
|
dtype_precisions = {
|
|
torch.float16 : (0.001, 1e-5),
|
|
torch.bfloat16 : (0.016, 1e-5),
|
|
torch.float32 : (1.3e-6, 1e-5),
|
|
torch.float64 : (1e-7, 1e-7),
|
|
torch.complex32 : (0.001, 1e-5),
|
|
torch.complex64 : (1.3e-6, 1e-5),
|
|
torch.complex128 : (1e-7, 1e-7),
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
# Returns the "default" rtol and atol for comparing scalars or
|
|
# tensors of the given dtypes.
|
|
def _getDefaultRtolAndAtol(self, dtype0, dtype1):
|
|
rtol = max(self.dtype_precisions.get(dtype0, (0, 0))[0],
|
|
self.dtype_precisions.get(dtype1, (0, 0))[0])
|
|
atol = max(self.dtype_precisions.get(dtype0, (0, 0))[1],
|
|
self.dtype_precisions.get(dtype1, (0, 0))[1])
|
|
|
|
return rtol, atol
|
|
|
|
# Checks if two dense tensors are equal(-ish), returning (True, None)
|
|
# when they are and (False, debug_msg) when they are not.
|
|
# If exact_dtype is true both tensors must have the same dtype.
|
|
# If exact_device is true both tensors must be on the same device.
|
|
# See the "Test Framework Tensor 'Equality'" note for more details.
|
|
# NOTE: tensors on different devices are moved to the CPU to be compared when
|
|
# exact_device is False.
|
|
# NOTE: this function checks the tensors' devices, sizes, and dtypes
|
|
# and acquires the appropriate device, dtype, rtol and atol to compare
|
|
# them with. It then calls _compare_tensors_internal.
|
|
def _compareTensors(self, a, b, *, rtol: Optional[float] = None, atol=None, equal_nan=True,
|
|
exact_dtype=True, exact_device=False) -> _compare_return_type:
|
|
assert (atol is None) == (rtol is None)
|
|
if not isinstance(a, torch.Tensor):
|
|
return (False, "argument a, {0}, to _compareTensors is not a tensor!".format(a))
|
|
if not isinstance(b, torch.Tensor):
|
|
return (False, "argument b, {0}, to _compareTensors is not a tensor!".format(b))
|
|
|
|
# Validates tensors are on the same device
|
|
if exact_device and a.device != b.device:
|
|
return (False, ("Attempted to compare equality of tensors on "
|
|
"different devices! Got devices {0} and "
|
|
"{1}.".format(a.device, b.device)))
|
|
|
|
# Compares tensors of different devices on the CPU
|
|
if a.device != b.device:
|
|
a = a.cpu()
|
|
b = b.cpu()
|
|
|
|
# Checks size matches
|
|
if a.size() != b.size():
|
|
return (False, ("Attempted to compare equality of tensors with "
|
|
"different sizes. Got sizes {0} and {1}.").format(a.size(), b.size()))
|
|
|
|
# Checks dtype (if exact_dtype)
|
|
if exact_dtype and a.dtype is not b.dtype:
|
|
return (False, ("Attempted to compare equality of tensors with "
|
|
"different dtypes. Got dtypes {0} and {1}.").format(a.dtype, b.dtype))
|
|
|
|
# Acquires rtol and atol
|
|
if rtol is None:
|
|
rtol, atol = self._getDefaultRtolAndAtol(a.dtype, b.dtype)
|
|
|
|
atol = max(atol, self.precision)
|
|
rtol = max(rtol, self.rel_tol)
|
|
|
|
# Converts to comparison dtype
|
|
dtype = get_comparison_dtype(a, b)
|
|
a = a.to(dtype)
|
|
b = b.to(dtype)
|
|
|
|
return _compare_tensors_internal(a, b, rtol=rtol, atol=atol, equal_nan=equal_nan)
|
|
|
|
# Checks if two scalars are equal(-ish), returning (True, None)
|
|
# when they are and (False, debug_msg) when they are not.
|
|
# NOTE: this function just acquires rtol and atol
|
|
# before calling _compare_scalars_internal.
|
|
def _compareScalars(self, a, b, *,
|
|
rtol: Optional[float] = None, atol: Optional[float] = None, equal_nan=True) -> _compare_return_type:
|
|
# Acquires rtol and atol
|
|
assert (atol is None) == (rtol is None)
|
|
if rtol is None:
|
|
if isinstance(a, complex) or isinstance(b, complex):
|
|
rtol, atol = self._getDefaultRtolAndAtol(torch.complex64, torch.complex64)
|
|
elif isinstance(a, float) or isinstance(b, float):
|
|
rtol, atol = self._getDefaultRtolAndAtol(torch.float32, torch.float32)
|
|
else:
|
|
rtol, atol = 0, 0
|
|
rtol = cast(float, rtol)
|
|
atol = cast(float, atol)
|
|
assert atol is not None
|
|
atol = max(atol, self.precision)
|
|
rtol = max(rtol, self.rel_tol)
|
|
|
|
return _compare_scalars_internal(a, b, rtol=rtol, atol=atol, equal_nan=equal_nan)
|
|
|
|
# Construct assert messages basd on internal debug message and user provided message.
|
|
def _get_assert_msg(self, msg, debug_msg=None):
|
|
if msg is None:
|
|
return debug_msg
|
|
else:
|
|
return f"\n{msg}" if debug_msg is None else f"{debug_msg}\n{msg}"
|
|
|
|
def assertEqualIgnoreType(self, *args, **kwargs) -> None:
|
|
# If you are seeing this function used, that means test is written wrongly
|
|
# and deserves detailed investigation
|
|
return self.assertEqual(*args, exact_dtype=False, **kwargs)
|
|
|
|
def _is_dict(self, obj):
|
|
return isinstance(obj, (dict, torch._C.ScriptDict)) # type: ignore[attr-defined]
|
|
|
|
# Compares x and y
|
|
# TODO: default exact_device to True
|
|
def assertEqual(self, x, y, msg: Optional[str] = None, *,
|
|
atol: Optional[float] = None, rtol: Optional[float] = None,
|
|
equal_nan=True, exact_dtype=True, exact_device=False) -> None:
|
|
assert (atol is None) == (rtol is None), "If one of atol or rtol is specified, then the other must be too"
|
|
debug_msg: Optional[str] = None
|
|
|
|
# Tensor x Number and Number x Tensor comparisons
|
|
if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) and isinstance(y, Number):
|
|
self.assertEqual(x.item(), y, atol=atol, rtol=rtol, msg=msg,
|
|
exact_dtype=exact_dtype, exact_device=exact_device)
|
|
elif isinstance(y, torch.Tensor) and isinstance(x, Number):
|
|
self.assertEqual(x, y.item(), atol=atol, rtol=rtol, msg=msg,
|
|
exact_dtype=exact_dtype, exact_device=exact_device)
|
|
# Tensor x np.bool
|
|
elif isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) and isinstance(y, np.bool_):
|
|
self.assertEqual(x.item(), y, atol=atol, rtol=rtol, msg=msg,
|
|
exact_dtype=exact_dtype, exact_device=exact_device)
|
|
elif isinstance(y, torch.Tensor) and isinstance(x, np.bool_):
|
|
self.assertEqual(x, y.item(), atol=atol, rtol=rtol, msg=msg,
|
|
exact_dtype=exact_dtype, exact_device=exact_device)
|
|
|
|
# Tensor x Tensor
|
|
elif isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) and isinstance(y, torch.Tensor):
|
|
debug_msg = ("Attempted to compare with different is_sparse settings: "
|
|
f"Expected: {x.is_sparse}; Actual: {y.is_sparse}.")
|
|
super().assertEqual(x.is_sparse, y.is_sparse, msg=self._get_assert_msg(msg=msg, debug_msg=debug_msg))
|
|
debug_msg = ("Attempted to compare with different is_quantized settings: "
|
|
f"Expected: {x.is_quantized}; Actual: {y.is_quantized}.")
|
|
super().assertEqual(x.is_quantized, y.is_quantized, msg=self._get_assert_msg(msg=msg, debug_msg=debug_msg))
|
|
if x.is_sparse:
|
|
if x.size() != y.size():
|
|
debug_msg_sparse = ("Attempted to compare equality of tensors with different sizes: "
|
|
f"Expected: {x.size()}; Actual: {y.size()}.")
|
|
super().assertTrue(False, msg=self._get_assert_msg(msg=msg, debug_msg=debug_msg_sparse))
|
|
|
|
x = x.coalesce()
|
|
y = y.coalesce()
|
|
indices_result, debug_msg_indices = self._compareTensors(x._indices(), y._indices(),
|
|
rtol=rtol, atol=atol,
|
|
equal_nan=equal_nan, exact_dtype=exact_dtype,
|
|
exact_device=exact_device)
|
|
|
|
if not indices_result:
|
|
assert debug_msg_indices is not None
|
|
debug_msg = "Sparse tensor indices failed to compare as equal! " + debug_msg_indices
|
|
super().assertTrue(indices_result, msg=self._get_assert_msg(msg, debug_msg=debug_msg))
|
|
|
|
values_result, debug_msg_values = self._compareTensors(x._values(), y._values(),
|
|
rtol=rtol, atol=atol,
|
|
equal_nan=equal_nan, exact_dtype=exact_dtype,
|
|
exact_device=exact_device)
|
|
|
|
if not values_result:
|
|
assert debug_msg_values is not None
|
|
debug_msg = "Sparse tensor values failed to compare as equal! " + debug_msg_values
|
|
super().assertTrue(values_result, msg=self._get_assert_msg(msg, debug_msg=debug_msg))
|
|
elif x.is_quantized and y.is_quantized:
|
|
self.assertEqual(x.qscheme(), y.qscheme(), atol=atol, rtol=rtol,
|
|
msg=msg, exact_dtype=exact_dtype,
|
|
exact_device=exact_device)
|
|
|
|
if x.qscheme() == torch.per_tensor_affine:
|
|
self.assertEqual(x.q_scale(), y.q_scale(), atol=atol, rtol=rtol,
|
|
msg=msg, exact_dtype=exact_dtype,
|
|
exact_device=exact_device)
|
|
self.assertEqual(x.q_zero_point(), y.q_zero_point(),
|
|
atol=atol, rtol=rtol, msg=msg,
|
|
exact_dtype=exact_dtype, exact_device=exact_device)
|
|
elif x.qscheme() == torch.per_channel_affine:
|
|
self.assertEqual(x.q_per_channel_scales(), y.q_per_channel_scales(), atol=atol, rtol=rtol,
|
|
msg=msg, exact_dtype=exact_dtype,
|
|
exact_device=exact_device)
|
|
self.assertEqual(x.q_per_channel_zero_points(), y.q_per_channel_zero_points(),
|
|
atol=atol, rtol=rtol, msg=msg,
|
|
exact_dtype=exact_dtype, exact_device=exact_device)
|
|
self.assertEqual(x.q_per_channel_axis(), y.q_per_channel_axis(),
|
|
atol=atol, rtol=rtol, msg=msg,
|
|
exact_dtype=exact_dtype, exact_device=exact_device)
|
|
|
|
result, debug_msg_compare = self._compareTensors(x.int_repr().to(torch.int32),
|
|
y.int_repr().to(torch.int32),
|
|
atol=atol, rtol=rtol,
|
|
exact_dtype=exact_dtype,
|
|
exact_device=exact_device)
|
|
|
|
if not result:
|
|
assert debug_msg_compare is not None
|
|
debug_msg = "Quantized representations failed to compare as equal! " + debug_msg_compare
|
|
super().assertTrue(result, msg=self._get_assert_msg(msg, debug_msg=debug_msg))
|
|
else:
|
|
result, debug_msg_generic = self._compareTensors(x, y, rtol=rtol, atol=atol,
|
|
equal_nan=equal_nan, exact_dtype=exact_dtype,
|
|
exact_device=exact_device)
|
|
|
|
if not result:
|
|
assert debug_msg_generic is not None
|
|
debug_msg = "Tensors failed to compare as equal!" + debug_msg_generic
|
|
super().assertTrue(result, msg=self._get_assert_msg(msg, debug_msg=debug_msg))
|
|
elif isinstance(x, (np.ndarray, torch.Tensor)) or isinstance(y, (np.ndarray, torch.Tensor)):
|
|
def maybe_to_tensor(a: Union[np.ndarray, torch.Tensor]) -> Union[np.ndarray, torch.Tensor]:
|
|
if not isinstance(a, np.ndarray):
|
|
return a
|
|
|
|
try:
|
|
return torch.from_numpy(a)
|
|
except TypeError:
|
|
# This happens if the dtype is non-numeric or not supported by torch
|
|
return a
|
|
|
|
def maybe_to_list(a: Any) -> Any:
|
|
if not isinstance(a, (np.ndarray, torch.Tensor)):
|
|
return a
|
|
|
|
return a.tolist()
|
|
|
|
x = maybe_to_tensor(x)
|
|
y = maybe_to_tensor(y)
|
|
|
|
if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) and isinstance(y, torch.Tensor):
|
|
self.assertEqual(
|
|
x, y, atol=atol, rtol=rtol, msg=msg, exact_dtype=exact_dtype, exact_device=exact_device
|
|
)
|
|
else:
|
|
# In case we can't convert the array to a tensor, we fall back to comparing x and y as iterables
|
|
self.assertEqual(
|
|
maybe_to_list(x),
|
|
maybe_to_list(y),
|
|
atol=atol,
|
|
rtol=rtol,
|
|
msg=msg,
|
|
exact_dtype=exact_dtype,
|
|
exact_device=exact_device
|
|
)
|
|
elif isinstance(x, string_classes) and isinstance(y, string_classes):
|
|
debug_msg = ("Attempted to compare [string] types: "
|
|
f"Expected: {repr(x)}; Actual: {repr(y)}.")
|
|
super().assertEqual(x, y, msg=self._get_assert_msg(msg, debug_msg=debug_msg))
|
|
elif type(x) == set and type(y) == set:
|
|
debug_msg = ("Attempted to compare [set] types: "
|
|
f"Expected: {x}; Actual: {y}.")
|
|
super().assertEqual(x, y, msg=self._get_assert_msg(msg, debug_msg=debug_msg))
|
|
elif self._is_dict(x) and self._is_dict(y):
|
|
if isinstance(x, OrderedDict) and isinstance(y, OrderedDict):
|
|
self.assertEqual(x.items(), y.items(), atol=atol, rtol=rtol,
|
|
msg=msg, exact_dtype=exact_dtype,
|
|
exact_device=exact_device)
|
|
else:
|
|
self.assertEqual(set(x.keys()), set(y.keys()), atol=atol, rtol=rtol,
|
|
msg=msg, exact_dtype=exact_dtype,
|
|
exact_device=exact_device)
|
|
key_list = list(x.keys())
|
|
self.assertEqual([x[k] for k in key_list],
|
|
[y[k] for k in key_list],
|
|
atol=atol, rtol=rtol, msg=msg,
|
|
exact_dtype=exact_dtype, exact_device=exact_device)
|
|
elif isinstance(x, type) and isinstance(y, type):
|
|
# See TestTorch.test_assert_equal_generic_meta
|
|
debug_msg = ("Attempted to compare [type] types: "
|
|
f"Expected: {x}; Actual: {y}.")
|
|
super().assertEqual(x, y, msg=self._get_assert_msg(msg, debug_msg=debug_msg))
|
|
elif is_iterable(x) and is_iterable(y):
|
|
debug_msg = ("Attempted to compare the lengths of [iterable] types: "
|
|
f"Expected: {len(x)}; Actual: {len(y)}.")
|
|
super().assertEqual(len(x), len(y), msg=self._get_assert_msg(msg, debug_msg=debug_msg))
|
|
for x_, y_ in zip(x, y):
|
|
self.assertEqual(x_, y_, atol=atol, rtol=rtol, msg=msg,
|
|
exact_dtype=exact_dtype, exact_device=exact_device)
|
|
elif isinstance(x, bool) and isinstance(y, bool):
|
|
super().assertTrue(x == y, msg=msg)
|
|
|
|
# Scalar x Scalar
|
|
elif isinstance(x, Number) and isinstance(y, Number):
|
|
result, debug_msg_scalars = self._compareScalars(x, y, rtol=rtol, atol=atol,
|
|
equal_nan=equal_nan)
|
|
if not result:
|
|
assert debug_msg_scalars is not None
|
|
debug_msg = "Scalars failed to compare as equal! " + debug_msg_scalars
|
|
super().assertTrue(result, msg=self._get_assert_msg(msg, debug_msg=debug_msg))
|
|
else:
|
|
super().assertEqual(x, y, msg=msg)
|
|
|
|
def assertNotEqual(self, x, y, msg: Optional[str] = None, *, # type: ignore[override]
|
|
atol: Optional[float] = None, rtol: Optional[float] = None, **kwargs) -> None:
|
|
with self.assertRaises(AssertionError, msg=msg):
|
|
self.assertEqual(x, y, msg, atol=atol, rtol=rtol, **kwargs)
|
|
|
|
def assertEqualTypeString(self, x, y) -> None:
|
|
# This API is used simulate deprecated x.type() == y.type()
|
|
self.assertEqual(x.device, y.device)
|
|
self.assertEqual(x.dtype, y.dtype)
|
|
self.assertEqual(x.is_sparse, y.is_sparse)
|
|
|
|
def assertObjectIn(self, obj: Any, iterable: Iterable[Any]) -> None:
|
|
for elem in iterable:
|
|
if id(obj) == id(elem):
|
|
return
|
|
raise AssertionError("object not found in iterable")
|
|
|
|
# Reimplemented to provide special behavior when
|
|
# _ignore_not_implemented_error is True
|
|
def assertRaises(self, expected_exception, *args, **kwargs):
|
|
if self._ignore_not_implemented_error:
|
|
context: Optional[AssertRaisesContextIgnoreNotImplementedError] = \
|
|
AssertRaisesContextIgnoreNotImplementedError(expected_exception, self) # type: ignore[call-arg]
|
|
try:
|
|
return context.handle('assertRaises', args, kwargs) # type: ignore[union-attr]
|
|
finally:
|
|
# see https://bugs.python.org/issue23890
|
|
context = None
|
|
else:
|
|
return super().assertRaises(expected_exception, *args, **kwargs)
|
|
|
|
# Reimplemented to provide special behavior when
|
|
# _ignore_not_implemented_error is True
|
|
def assertRaisesRegex(self, expected_exception, expected_regex, *args, **kwargs):
|
|
if self._ignore_not_implemented_error:
|
|
context = AssertRaisesContextIgnoreNotImplementedError( # type: ignore[call-arg]
|
|
expected_exception, self, expected_regex)
|
|
return context.handle('assertRaisesRegex', args, kwargs) # type: ignore[attr-defined]
|
|
else:
|
|
return super().assertRaisesRegex(expected_exception, expected_regex, *args, **kwargs)
|
|
|
|
# TODO: Support context manager interface
|
|
# NB: The kwargs forwarding to callable robs the 'subname' parameter.
|
|
# If you need it, manually apply your callable in a lambda instead.
|
|
def assertExpectedRaises(self, exc_type, callable, *args, **kwargs):
|
|
subname = None
|
|
if 'subname' in kwargs:
|
|
subname = kwargs['subname']
|
|
del kwargs['subname']
|
|
try:
|
|
callable(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
except exc_type as e:
|
|
self.assertExpected(str(e), subname)
|
|
return
|
|
# Don't put this in the try block; the AssertionError will catch it
|
|
self.fail(msg="Did not raise when expected to")
|
|
|
|
def assertNotWarn(self, callable, msg=''):
|
|
r"""
|
|
Test if :attr:`callable` does not raise a warning.
|
|
"""
|
|
with warnings.catch_warnings(record=True) as ws:
|
|
warnings.simplefilter("always") # allow any warning to be raised
|
|
with set_warn_always_context(True):
|
|
callable()
|
|
self.assertTrue(len(ws) == 0, msg)
|
|
|
|
@contextmanager
|
|
def assertWarnsOnceRegex(self, category, regex=''):
|
|
"""Context manager for code that *must always* warn
|
|
|
|
This filters expected warnings from the test and fails if
|
|
the expected warning is not caught. It uses set_warn_always() to force
|
|
TORCH_WARN_ONCE to behave like TORCH_WARN
|
|
"""
|
|
pattern = re.compile(regex)
|
|
with warnings.catch_warnings(record=True) as ws:
|
|
warnings.simplefilter("always") # allow any warning to be raised
|
|
with set_warn_always_context(True):
|
|
yield
|
|
if len(ws) == 0:
|
|
self.fail('no warning caught')
|
|
self.assertTrue(any([type(w.message) is category for w in ws]))
|
|
self.assertTrue(
|
|
any([re.match(pattern, str(w.message)) for w in ws]),
|
|
f'{pattern}, {[w.message for w in ws if type(w.message) is category]}')
|
|
|
|
def assertExpected(self, s, subname=None):
|
|
r"""
|
|
Test that a string matches the recorded contents of a file
|
|
derived from the name of this test and subname. This file
|
|
is placed in the 'expect' directory in the same directory
|
|
as the test script. You can automatically update the recorded test
|
|
output using --accept.
|
|
|
|
If you call this multiple times in a single function, you must
|
|
give a unique subname each time.
|
|
"""
|
|
if not isinstance(s, str):
|
|
raise TypeError("assertExpected is strings only")
|
|
|
|
def remove_prefix(text, prefix):
|
|
if text.startswith(prefix):
|
|
return text[len(prefix):]
|
|
return text
|
|
# NB: we take __file__ from the module that defined the test
|
|
# class, so we place the expect directory where the test script
|
|
# lives, NOT where test/common_utils.py lives. This doesn't matter in
|
|
# PyTorch where all test scripts are in the same directory as
|
|
# test/common_utils.py, but it matters in onnx-pytorch
|
|
module_id = self.__class__.__module__
|
|
munged_id = remove_prefix(self.id(), module_id + ".")
|
|
test_file = os.path.realpath(sys.modules[module_id].__file__)
|
|
expected_file = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(test_file),
|
|
"expect",
|
|
munged_id)
|
|
|
|
subname_output = ""
|
|
if subname:
|
|
expected_file += "-" + subname
|
|
subname_output = " ({})".format(subname)
|
|
expected_file += ".expect"
|
|
expected = None
|
|
|
|
def accept_output(update_type):
|
|
print("Accepting {} for {}{}:\n\n{}".format(update_type, munged_id, subname_output, s))
|
|
with open(expected_file, 'w') as f:
|
|
# Adjust for producer_version, leave s unmodified
|
|
s_tag = re.sub(r'(producer_version): "[0-9.]*"',
|
|
r'\1producer_version: "CURRENT_VERSION"', s)
|
|
f.write(s_tag)
|
|
|
|
try:
|
|
with open(expected_file) as f:
|
|
expected = f.read()
|
|
except IOError as e:
|
|
if e.errno != errno.ENOENT:
|
|
raise
|
|
elif expecttest.ACCEPT:
|
|
return accept_output("output")
|
|
else:
|
|
raise RuntimeError(
|
|
("I got this output for {}{}:\n\n{}\n\n"
|
|
"No expect file exists; to accept the current output, run:\n"
|
|
"python {} {} --accept").format(munged_id, subname_output, s, __main__.__file__, munged_id)) from None
|
|
|
|
# a hack for JIT tests
|
|
if IS_WINDOWS:
|
|
expected = re.sub(r'CppOp\[(.+?)\]', 'CppOp[]', expected)
|
|
s = re.sub(r'CppOp\[(.+?)\]', 'CppOp[]', s)
|
|
|
|
# Adjust for producer_version
|
|
expected = expected.replace(
|
|
'producer_version: "CURRENT_VERSION"',
|
|
'producer_version: "{}"'.format(torch.onnx.producer_version)
|
|
)
|
|
if expecttest.ACCEPT:
|
|
if expected != s:
|
|
return accept_output("updated output")
|
|
else:
|
|
if hasattr(self, "assertMultiLineEqual"):
|
|
# Python 2.7 only
|
|
# NB: Python considers lhs "old" and rhs "new".
|
|
self.assertMultiLineEqual(expected, s)
|
|
else:
|
|
self.assertEqual(s, expected)
|
|
|
|
def assertExpectedStripMangled(self, s, subname=None):
|
|
s = re.sub(r'__torch__[^ ]+', '', s)
|
|
self.assertExpected(s, subname)
|
|
|
|
def assertGreaterAlmostEqual(self, first, second, places=None, msg=None, delta=None):
|
|
"""Assert that ``first`` is greater than or almost equal to ``second``.
|
|
|
|
The equality of ``first`` and ``second`` is determined in a similar way to
|
|
the ``assertAlmostEqual`` function of the standard library.
|
|
"""
|
|
if delta is not None and places is not None:
|
|
raise TypeError("specify delta or places not both")
|
|
|
|
if first >= second:
|
|
return
|
|
|
|
diff = second - first
|
|
if delta is not None:
|
|
if diff <= delta:
|
|
return
|
|
|
|
standardMsg = f"{first} not greater than or equal to {second} within {delta} delta"
|
|
else:
|
|
if places is None:
|
|
places = 7
|
|
|
|
if round(diff, places) == 0:
|
|
return
|
|
|
|
standardMsg = f"{first} not greater than or equal to {second} within {places} places"
|
|
|
|
msg = self._formatMessage(msg, standardMsg)
|
|
raise self.failureException(msg)
|
|
|
|
# run code in subprocess and capture exceptions.
|
|
@staticmethod
|
|
def run_process_no_exception(code, env=None):
|
|
import subprocess
|
|
|
|
popen = subprocess.Popen(
|
|
[sys.executable, '-c', code],
|
|
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
|
|
stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
|
|
env=env)
|
|
(stdout, stderr) = popen.communicate()
|
|
return (stdout, stderr)
|
|
|
|
# returns captured stderr
|
|
@staticmethod
|
|
def runWithPytorchAPIUsageStderr(code):
|
|
env = os.environ.copy()
|
|
env["PYTORCH_API_USAGE_STDERR"] = "1"
|
|
# remove IN_CI flag since this is a wrapped test process.
|
|
# IN_CI flag should be set in the parent process only.
|
|
if "IN_CI" in env.keys():
|
|
del env["IN_CI"]
|
|
(stdout, stderr) = TestCase.run_process_no_exception(code, env=env)
|
|
return stderr.decode('ascii')
|
|
|
|
|
|
def download_file(url, binary=True):
|
|
from urllib.parse import urlsplit
|
|
from urllib import request, error
|
|
|
|
filename = os.path.basename(urlsplit(url)[2])
|
|
data_dir = get_writable_path(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'data'))
|
|
path = os.path.join(data_dir, filename)
|
|
|
|
if os.path.exists(path):
|
|
return path
|
|
try:
|
|
data = request.urlopen(url, timeout=15).read()
|
|
with open(path, 'wb' if binary else 'w') as f:
|
|
f.write(data)
|
|
return path
|
|
except error.URLError as e:
|
|
msg = "could not download test file '{}'".format(url)
|
|
warnings.warn(msg, RuntimeWarning)
|
|
raise unittest.SkipTest(msg) from e
|
|
|
|
def find_free_port():
|
|
with closing(socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)) as sock:
|
|
sock.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
|
|
sock.bind(('localhost', 0))
|
|
_, port = sock.getsockname()
|
|
return port
|
|
|
|
# Errors that we can get in c10d initialization for which we should retry tests for.
|
|
ADDRESS_IN_USE = "Address already in use"
|
|
CONNECT_TIMEOUT = "connect() timed out."
|
|
|
|
def retry_on_connect_failures(func=None, connect_errors=(ADDRESS_IN_USE)):
|
|
"""Reruns a test if the test returns a RuntimeError and the exception
|
|
matches exactly with one of the strings in connect_errors."""
|
|
# This if block is executed when using this function as a decorator with arguments.
|
|
if func is None:
|
|
return partial(retry_on_connect_failures, connect_errors=connect_errors)
|
|
|
|
@wraps(func)
|
|
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
|
|
tries_remaining = 10
|
|
while True:
|
|
try:
|
|
return func(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
except RuntimeError as error:
|
|
if str(error) in connect_errors:
|
|
tries_remaining -= 1
|
|
if tries_remaining == 0:
|
|
raise
|
|
time.sleep(random.random())
|
|
continue
|
|
raise
|
|
return wrapper
|
|
|
|
|
|
# Decorator to retry upon certain Exceptions.
|
|
def retry(ExceptionToCheck, tries=3, delay=3, skip_after_retries=False):
|
|
def deco_retry(f):
|
|
@wraps(f)
|
|
def f_retry(*args, **kwargs):
|
|
mtries, mdelay = tries, delay
|
|
while mtries > 1:
|
|
try:
|
|
return f(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
except ExceptionToCheck as e:
|
|
msg = "%s, Retrying in %d seconds..." % (str(e), mdelay)
|
|
print(msg)
|
|
time.sleep(mdelay)
|
|
mtries -= 1
|
|
try:
|
|
return f(*args, **kwargs)
|
|
except ExceptionToCheck as e:
|
|
raise unittest.SkipTest(f"Skipping after {tries} consecutive {str(e)}") from e if skip_after_retries else e
|
|
return f_retry # true decorator
|
|
return deco_retry
|
|
|
|
|
|
# Methods for matrix and tensor generation
|
|
|
|
def make_tensor(size, device: torch.device, dtype: torch.dtype, *, low=None, high=None,
|
|
requires_grad: bool = False, noncontiguous: bool = False,
|
|
exclude_zero: bool = False) -> torch.Tensor:
|
|
""" Creates a random tensor with the given size, device and dtype.
|
|
|
|
By default, the tensor's values are in the range [-9, 9] for most dtypes. If low
|
|
and/or high are specified then the values will be in the range [max(-9, low), min(9, high)].
|
|
|
|
For unsigned types the values are in the range[0, 9] and for complex types the real and imaginary
|
|
parts are each in the range [-9, 9].
|
|
|
|
If noncontiguous=True, a noncontiguous tensor with the given size will be returned unless the size
|
|
specifies a tensor with a 1 or 0 elements in which case the noncontiguous parameter is ignored because
|
|
it is not possible to create a noncontiguous Tensor with a single element.
|
|
|
|
If exclude_zero is passed with True (default is False), all the matching values (with zero) in
|
|
created tensor are replaced with an epsilon value if floating type, [`eps + `eps`.j] if
|
|
complex type and 1 if integer/boolean type.
|
|
"""
|
|
|
|
assert low is None or low < 9, "low value too high!"
|
|
assert high is None or high > -9, "high value too low!"
|
|
|
|
if dtype is torch.bool:
|
|
result = torch.randint(0, 2, size, device=device, dtype=dtype)
|
|
elif dtype is torch.uint8:
|
|
low = math.floor(0 if low is None else max(low, 0))
|
|
high = math.ceil(10 if high is None else min(high, 10))
|
|
result = torch.randint(low, high, size, device=device, dtype=dtype)
|
|
elif dtype in integral_types():
|
|
low = math.floor(-9 if low is None else max(low, -9))
|
|
high = math.ceil(10 if high is None else min(high, 10))
|
|
result = torch.randint(low, high, size, device=device, dtype=dtype)
|
|
elif dtype in floating_types_and(torch.half, torch.bfloat16):
|
|
low = -9 if low is None else max(low, -9)
|
|
high = 9 if high is None else min(high, 10)
|
|
span = high - low
|
|
# Windows doesn't support torch.rand(bfloat16) on CUDA
|
|
if IS_WINDOWS and torch.device(device).type == 'cuda' and dtype is torch.bfloat16:
|
|
result = (torch.rand(size, device=device, dtype=torch.float32) * span + low).to(torch.bfloat16)
|
|
else:
|
|
result = torch.rand(size, device=device, dtype=dtype) * span + low
|
|
else:
|
|
assert dtype in complex_types()
|
|
low = -9 if low is None else max(low, -9)
|
|
high = 9 if high is None else min(high, 10)
|
|
span = high - low
|
|
float_dtype = torch.float if dtype is torch.cfloat else torch.double
|
|
real = torch.rand(size, device=device, dtype=float_dtype) * span + low
|
|
imag = torch.rand(size, device=device, dtype=float_dtype) * span + low
|
|
result = torch.complex(real, imag)
|
|
|
|
if noncontiguous and result.numel() > 1:
|
|
result = torch.repeat_interleave(result, 2, dim=-1)
|
|
result = result[..., ::2]
|
|
|
|
if exclude_zero:
|
|
if dtype in integral_types() or dtype is torch.bool:
|
|
replace_with = torch.tensor(1, device=device, dtype=dtype)
|
|
elif dtype in floating_types_and(torch.half, torch.bfloat16):
|
|
replace_with = torch.tensor(torch.finfo(dtype).eps, device=device, dtype=dtype)
|
|
else:
|
|
assert dtype in complex_types()
|
|
float_dtype = torch.float if dtype is torch.cfloat else torch.double
|
|
float_eps = torch.tensor(torch.finfo(float_dtype).eps, device=device, dtype=float_dtype)
|
|
replace_with = torch.complex(float_eps, float_eps)
|
|
result[result == 0] = replace_with
|
|
|
|
if dtype in floating_types_and(torch.half, torch.bfloat16) or\
|
|
dtype in complex_types():
|
|
result.requires_grad = requires_grad
|
|
|
|
return result
|
|
|
|
def random_square_matrix_of_rank(l, rank, dtype=torch.double, device='cpu'):
|
|
assert rank <= l
|
|
A = torch.randn(l, l, dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
u, s, vh = torch.linalg.svd(A, full_matrices=False)
|
|
for i in range(l):
|
|
if i >= rank:
|
|
s[i] = 0
|
|
elif s[i] == 0:
|
|
s[i] = 1
|
|
return (u * s.to(dtype).unsqueeze(-2)) @ vh
|
|
|
|
def random_well_conditioned_matrix(*shape, dtype, device, mean=1.0, sigma=0.001):
|
|
"""
|
|
Returns a random rectangular matrix (batch of matrices)
|
|
with singular values sampled from a Gaussian with
|
|
mean `mean` and standard deviation `sigma`.
|
|
The smaller the `sigma`, the better conditioned
|
|
the output matrix is.
|
|
"""
|
|
primitive_dtype = {
|
|
torch.float: torch.float,
|
|
torch.double: torch.double,
|
|
torch.cfloat: torch.float,
|
|
torch.cdouble: torch.double
|
|
}
|
|
x = torch.rand(shape, dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
m = x.size(-2)
|
|
n = x.size(-1)
|
|
u, _, vh = torch.linalg.svd(x, full_matrices=False)
|
|
s = (torch.randn(*(shape[:-2] + (min(m, n),)), dtype=primitive_dtype[dtype], device=device) * sigma + mean) \
|
|
.sort(-1, descending=True).values.to(dtype)
|
|
return (u * s.unsqueeze(-2)) @ vh
|
|
|
|
# TODO: remove this (prefer make_symmetric_matrices below)
|
|
def random_symmetric_matrix(l, *batches, **kwargs):
|
|
dtype = kwargs.get('dtype', torch.double)
|
|
device = kwargs.get('device', 'cpu')
|
|
A = torch.randn(*(batches + (l, l)), dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
A = (A + A.transpose(-2, -1)).div_(2)
|
|
return A
|
|
|
|
# Creates a symmetric matrix or batch of symmetric matrices
|
|
# Shape must be a square matrix or batch of square matrices
|
|
def make_symmetric_matrices(*shape, device, dtype):
|
|
assert shape[-1] == shape[-2]
|
|
t = make_tensor(shape, device=device, dtype=dtype)
|
|
t = t + t.transpose(-2, -1).div_(2)
|
|
return t
|
|
|
|
def random_hermitian_matrix(l, *batches, **kwargs):
|
|
dtype = kwargs.get('dtype', torch.double)
|
|
device = kwargs.get('device', 'cpu')
|
|
A = torch.randn(*(batches + (l, l)), dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
A = (A + A.transpose(-2, -1).conj()).div_(2)
|
|
return A
|
|
|
|
|
|
def random_symmetric_psd_matrix(l, *batches, **kwargs):
|
|
dtype = kwargs.get('dtype', torch.double)
|
|
device = kwargs.get('device', 'cpu')
|
|
A = torch.randn(*(batches + (l, l)), dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
return torch.matmul(A, A.transpose(-2, -1))
|
|
|
|
|
|
def random_hermitian_psd_matrix(matrix_size, *batch_dims, dtype=torch.double, device='cpu'):
|
|
"""
|
|
Returns a batch of random Hermitian semi-positive-definite matrices.
|
|
The shape of the result is batch_dims + (matrix_size, matrix_size)
|
|
The following example creates a tensor of size 2 x 4 x 3 x 3
|
|
>>> matrices = random_hermitian_psd_matrix(3, 2, 4, dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
"""
|
|
A = torch.randn(*(batch_dims + (matrix_size, matrix_size)), dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
return torch.matmul(A, A.conj().transpose(-2, -1))
|
|
|
|
|
|
# TODO: remove this (prefer make_symmetric_pd_matrices below)
|
|
def random_symmetric_pd_matrix(matrix_size, *batch_dims, **kwargs):
|
|
dtype = kwargs.get('dtype', torch.double)
|
|
device = kwargs.get('device', 'cpu')
|
|
A = torch.randn(*(batch_dims + (matrix_size, matrix_size)),
|
|
dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
return torch.matmul(A, A.transpose(-2, -1)) \
|
|
+ torch.eye(matrix_size, dtype=dtype, device=device) * 1e-5
|
|
|
|
|
|
# Creates a symmetric positive-definite matrix or batch of
|
|
# such matrices
|
|
def make_symmetric_pd_matrices(*shape, device, dtype):
|
|
assert shape[-1] == shape[-2]
|
|
t = make_tensor(shape, device=device, dtype=dtype)
|
|
t = torch.matmul(t, t.transpose(-2, -1))
|
|
i = torch.eye(shape[-1], device=device, dtype=dtype) * 1e-5
|
|
return t + i
|
|
|
|
def random_hermitian_pd_matrix(matrix_size, *batch_dims, dtype, device):
|
|
"""
|
|
Returns a batch of random Hermitian positive-definite matrices.
|
|
The shape of the result is batch_dims + (matrix_size, matrix_size)
|
|
The following example creates a tensor of size 2 x 4 x 3 x 3
|
|
>>> matrices = random_hermitian_pd_matrix(3, 2, 4, dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
"""
|
|
A = torch.randn(*(batch_dims + (matrix_size, matrix_size)),
|
|
dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
return torch.matmul(A, A.transpose(-2, -1).conj()) \
|
|
+ torch.eye(matrix_size, dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
|
|
|
|
# TODO: remove this (prefer make_fullrank_matrices_with_distinct_singular_values below)
|
|
def random_fullrank_matrix_distinct_singular_value(matrix_size, *batch_dims,
|
|
**kwargs):
|
|
dtype = kwargs.get('dtype', torch.double)
|
|
device = kwargs.get('device', 'cpu')
|
|
silent = kwargs.get("silent", False)
|
|
if silent and not torch._C.has_lapack:
|
|
return torch.ones(matrix_size, matrix_size, dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
|
|
A = torch.randn(batch_dims + (matrix_size, matrix_size), dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
u, _, vh = torch.linalg.svd(A, full_matrices=False)
|
|
real_dtype = A.real.dtype if A.dtype.is_complex else A.dtype
|
|
s = torch.arange(1., matrix_size + 1, dtype=real_dtype, device=device).mul_(1.0 / (matrix_size + 1))
|
|
return (u * s.to(A.dtype)) @ vh
|
|
|
|
|
|
# Creates a full rank matrix with distinct signular values or
|
|
# a batch of such matrices
|
|
# Shape must be a square matrix or batch of square matrices
|
|
def make_fullrank_matrices_with_distinct_singular_values(*shape, device, dtype):
|
|
assert shape[-1] == shape[-2]
|
|
t = make_tensor(shape, device=device, dtype=dtype)
|
|
u, _, vh = torch.linalg.svd(t, full_matrices=False)
|
|
# TODO: improve the handling of complex tensors here
|
|
real_dtype = t.real.dtype if t.dtype.is_complex else t.dtype
|
|
s = torch.arange(1., shape[-1] + 1, dtype=real_dtype, device=device).mul_(1.0 / (shape[-1] + 1))
|
|
return (u * s.to(dtype)) @ vh
|
|
|
|
|
|
def random_matrix(rows, columns, *batch_dims, **kwargs):
|
|
"""Return rectangular matrix or batches of rectangular matrices.
|
|
|
|
Parameters:
|
|
dtype - the data type
|
|
device - the device kind
|
|
singular - when True, the output will be singular
|
|
"""
|
|
dtype = kwargs.get('dtype', torch.double)
|
|
device = kwargs.get('device', 'cpu')
|
|
silent = kwargs.get("silent", False)
|
|
singular = kwargs.get("singular", False)
|
|
if silent and not torch._C.has_lapack:
|
|
return torch.ones(rows, columns, dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
|
|
A = torch.randn(batch_dims + (rows, columns), dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
u, _, vh = torch.linalg.svd(A, full_matrices=False)
|
|
k = min(rows, columns)
|
|
s = torch.linspace(1 / (k + 1), 1, k, dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
if singular:
|
|
# make matrix singular
|
|
s[k - 1] = 0
|
|
if k > 2:
|
|
# increase the order of singularity so that the pivoting
|
|
# in LU factorization will be non-trivial
|
|
s[0] = 0
|
|
return (u * s.unsqueeze(-2)) @ vh
|
|
|
|
|
|
def random_lowrank_matrix(rank, rows, columns, *batch_dims, **kwargs):
|
|
"""Return rectangular matrix or batches of rectangular matrices with
|
|
given rank.
|
|
"""
|
|
B = random_matrix(rows, rank, *batch_dims, **kwargs)
|
|
C = random_matrix(rank, columns, *batch_dims, **kwargs)
|
|
return B.matmul(C)
|
|
|
|
|
|
def random_sparse_matrix(rows, columns, density=0.01, **kwargs):
|
|
"""Return rectangular random sparse matrix within given density.
|
|
|
|
The density of the result approaches to given density as the size
|
|
of the matrix is increased and a relatively small value of density
|
|
is specified but higher than min(rows, columns)/(rows * columns)
|
|
for non-singular matrices.
|
|
"""
|
|
dtype = kwargs.get('dtype', torch.double)
|
|
device = kwargs.get('device', 'cpu')
|
|
singular = kwargs.get("singular", False)
|
|
|
|
k = min(rows, columns)
|
|
nonzero_elements = max(min(rows, columns), int(rows * columns * density))
|
|
|
|
row_indices = [i % rows for i in range(nonzero_elements)]
|
|
column_indices = [i % columns for i in range(nonzero_elements)]
|
|
random.shuffle(column_indices)
|
|
indices = [row_indices, column_indices]
|
|
values = torch.randn(nonzero_elements, dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
# ensure that the diagonal dominates
|
|
values *= torch.tensor([-float(i - j)**2 for i, j in zip(*indices)], dtype=dtype, device=device).exp()
|
|
indices_tensor = torch.tensor(indices)
|
|
A = torch.sparse_coo_tensor(indices_tensor, values, (rows, columns), device=device)
|
|
return A.coalesce()
|
|
|
|
|
|
def random_sparse_pd_matrix(matrix_size, density=0.01, **kwargs):
|
|
"""Return random sparse positive-definite matrix with given density.
|
|
|
|
The eigenvalues of the matrix are defined as::
|
|
arange(1, matrix_size+1)/matrix_size
|
|
|
|
Algorithm:
|
|
A = diag(arange(1, matrix_size+1)/matrix_size)
|
|
while <A density is smaller than required>:
|
|
<choose random i, j in range(matrix_size), theta in [0, 2*pi]>
|
|
R = <rotation matrix (i,j,theta)>
|
|
A = R^T A R
|
|
"""
|
|
import math
|
|
torch = kwargs.get('torch', globals()['torch'])
|
|
dtype = kwargs.get('dtype', torch.double)
|
|
device = kwargs.get('device', 'cpu')
|
|
data = dict([((i, i), float(i + 1) / matrix_size)
|
|
for i in range(matrix_size)])
|
|
|
|
|
|
def multiply(data, N, i, j, cs, sn, left=True):
|
|
for k in range(N):
|
|
if left:
|
|
ik, jk = (k, i), (k, j)
|
|
else:
|
|
ik, jk = (i, k), (j, k)
|
|
aik, ajk = data.get(ik, 0), data.get(jk, 0)
|
|
aik, ajk = cs * aik + sn * ajk, -sn * aik + cs * ajk
|
|
if aik:
|
|
data[ik] = aik
|
|
else:
|
|
data.pop(ik, None)
|
|
if ajk:
|
|
data[jk] = ajk
|
|
else:
|
|
data.pop(jk, None)
|
|
|
|
target_nnz = density * matrix_size * matrix_size
|
|
while len(data) < target_nnz:
|
|
i = random.randint(0, matrix_size - 1)
|
|
j = random.randint(0, matrix_size - 1)
|
|
if i != j:
|
|
theta = random.uniform(0, 2 * math.pi)
|
|
cs = math.cos(theta)
|
|
sn = math.sin(theta)
|
|
multiply(data, matrix_size, i, j, cs, sn, left=True)
|
|
multiply(data, matrix_size, i, j, cs, sn, left=False)
|
|
icoords, jcoords, values = [], [], []
|
|
for (i, j), v in sorted(data.items()):
|
|
icoords.append(i)
|
|
jcoords.append(j)
|
|
values.append(v)
|
|
indices_tensor = torch.tensor([icoords, jcoords])
|
|
return torch.sparse_coo_tensor(indices_tensor, values, (matrix_size, matrix_size), dtype=dtype, device=device)
|
|
|
|
|
|
def do_test_dtypes(self, dtypes, layout, device):
|
|
for dtype in dtypes:
|
|
if dtype != torch.float16:
|
|
out = torch.zeros((2, 3), dtype=dtype, layout=layout, device=device)
|
|
self.assertIs(dtype, out.dtype)
|
|
self.assertIs(layout, out.layout)
|
|
self.assertEqual(device, out.device)
|
|
|
|
|
|
def do_test_empty_full(self, dtypes, layout, device):
|
|
shape = torch.Size([2, 3])
|
|
|
|
def check_value(tensor, dtype, layout, device, value, requires_grad):
|
|
self.assertEqual(shape, tensor.shape)
|
|
self.assertIs(dtype, tensor.dtype)
|
|
self.assertIs(layout, tensor.layout)
|
|
self.assertEqual(tensor.requires_grad, requires_grad)
|
|
if tensor.is_cuda and device is not None:
|
|
self.assertEqual(device, tensor.device)
|
|
if value is not None:
|
|
fill = tensor.new(shape).fill_(value)
|
|
self.assertEqual(tensor, fill)
|
|
|
|
def get_int64_dtype(dtype):
|
|
module = '.'.join(str(dtype).split('.')[1:-1])
|
|
if not module:
|
|
return torch.int64
|
|
return operator.attrgetter(module)(torch).int64
|
|
|
|
default_dtype = torch.get_default_dtype()
|
|
check_value(torch.empty(shape), default_dtype, torch.strided, -1, None, False)
|
|
check_value(torch.full(shape, -5.), default_dtype, torch.strided, -1, None, False)
|
|
for dtype in dtypes:
|
|
for rg in {dtype.is_floating_point, False}:
|
|
int64_dtype = get_int64_dtype(dtype)
|
|
v = torch.empty(shape, dtype=dtype, device=device, layout=layout, requires_grad=rg)
|
|
check_value(v, dtype, layout, device, None, rg)
|
|
out = v.new()
|
|
check_value(torch.empty(shape, out=out, device=device, layout=layout, requires_grad=rg),
|
|
dtype, layout, device, None, rg)
|
|
check_value(v.new_empty(shape), dtype, layout, device, None, False)
|
|
check_value(v.new_empty(shape, dtype=int64_dtype, device=device, requires_grad=False),
|
|
int64_dtype, layout, device, None, False)
|
|
check_value(torch.empty_like(v), dtype, layout, device, None, False)
|
|
check_value(torch.empty_like(v, dtype=int64_dtype, layout=layout, device=device, requires_grad=False),
|
|
int64_dtype, layout, device, None, False)
|
|
|
|
if dtype is not torch.float16 and layout != torch.sparse_coo:
|
|
fv = 3
|
|
v = torch.full(shape, fv, dtype=dtype, layout=layout, device=device, requires_grad=rg)
|
|
check_value(v, dtype, layout, device, fv, rg)
|
|
check_value(v.new_full(shape, fv + 1), dtype, layout, device, fv + 1, False)
|
|
out = v.new()
|
|
check_value(torch.full(shape, fv + 2, out=out, device=device, layout=layout, requires_grad=rg),
|
|
dtype, layout, device, fv + 2, rg)
|
|
check_value(v.new_full(shape, fv + 3, dtype=int64_dtype, device=device, requires_grad=False),
|
|
int64_dtype, layout, device, fv + 3, False)
|
|
check_value(torch.full_like(v, fv + 4), dtype, layout, device, fv + 4, False)
|
|
check_value(torch.full_like(v, fv + 5,
|
|
dtype=int64_dtype, layout=layout, device=device, requires_grad=False),
|
|
int64_dtype, layout, device, fv + 5, False)
|
|
|
|
# this helper method is to recursively
|
|
# clone the tensor-type input of operators tested by OpInfo
|
|
def clone_input_helper(input):
|
|
if isinstance(input, torch.Tensor):
|
|
return torch.clone(input)
|
|
|
|
if isinstance(input, Sequence):
|
|
return tuple(map(clone_input_helper, input))
|
|
|
|
return input
|
|
|
|
THESE_TAKE_WAY_TOO_LONG = {
|
|
'test_Conv3d_groups',
|
|
'test_conv_double_backward',
|
|
'test_conv_double_backward_groups',
|
|
'test_Conv3d_dilated',
|
|
'test_Conv3d_stride_padding',
|
|
'test_Conv3d_dilated_strided',
|
|
'test_Conv3d',
|
|
'test_Conv2d_dilated',
|
|
'test_ConvTranspose3d_dilated',
|
|
'test_ConvTranspose2d_dilated',
|
|
'test_snli',
|
|
'test_Conv2d',
|
|
'test_Conv2d_padding',
|
|
'test_ConvTranspose2d_no_bias',
|
|
'test_ConvTranspose2d',
|
|
'test_ConvTranspose3d',
|
|
'test_Conv2d_no_bias',
|
|
'test_matmul_4d_4d',
|
|
'test_multinomial_invalid_probs',
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
running_script_path = None
|
|
|
|
|
|
def set_running_script_path():
|
|
global running_script_path
|
|
try:
|
|
running_file = os.path.abspath(os.path.realpath(sys.argv[0]))
|
|
if running_file.endswith('.py'): # skip if the running file is not a script
|
|
running_script_path = running_file
|
|
except Exception:
|
|
pass
|
|
|
|
|
|
def check_test_defined_in_running_script(test_case):
|
|
if running_script_path is None:
|
|
return
|
|
test_case_class_file = os.path.abspath(os.path.realpath(inspect.getfile(test_case.__class__)))
|
|
assert test_case_class_file == running_script_path, "Class of loaded TestCase \"{}\" " \
|
|
"is not defined in the running script \"{}\", but in \"{}\". Did you " \
|
|
"accidentally import a unittest.TestCase from another file?".format(
|
|
test_case.id(), running_script_path, test_case_class_file)
|
|
|
|
|
|
def load_tests(loader, tests, pattern):
|
|
set_running_script_path()
|
|
test_suite = unittest.TestSuite()
|
|
for test_group in tests:
|
|
for test in test_group:
|
|
check_test_defined_in_running_script(test)
|
|
test_suite.addTest(test)
|
|
return test_suite
|
|
|
|
|
|
class BytesIOContext(io.BytesIO):
|
|
def __enter__(self):
|
|
return self
|
|
|
|
def __exit__(self, *args):
|
|
pass
|
|
|
|
# Tentative value for nondet_tol for gradcheck when backward implementation
|
|
# relies on nondeterministic operations, i.e., those listed here:
|
|
# https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.use_deterministic_algorithms.html
|
|
#
|
|
# For more information see https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/56202
|
|
GRADCHECK_NONDET_TOL = 1e-12
|
|
|
|
def gradcheck(fn, inputs, **kwargs):
|
|
# Wrapper around gradcheck that enables certain keys by default.
|
|
# Use this testing-internal gradcheck instead of autograd.gradcheck so that new features like vmap and
|
|
# forward-mode AD are tested by default. We create this wrapper because we'd like to keep new checks
|
|
# to be disabled to default for the public-facing api to avoid breaking user code.
|
|
#
|
|
# All PyTorch devs doing testing should use this wrapper instead of autograd.gradcheck.
|
|
default_values = {
|
|
"check_batched_grad": True,
|
|
"fast_mode": True,
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
if os.environ.get('PYTORCH_TEST_WITH_SLOW_GRADCHECK', "0FF") == "ON":
|
|
default_values["fast_mode"] = False
|
|
|
|
for key, value in default_values.items():
|
|
# default value override values explicitly set to None
|
|
k = kwargs.get(key, None)
|
|
kwargs[key] = k if k is not None else value
|
|
|
|
return torch.autograd.gradcheck(fn, inputs, **kwargs)
|
|
|
|
def gradgradcheck(fn, inputs, grad_outputs=None, **kwargs):
|
|
# Wrapper around gradgradcheck that enables certain keys by default
|
|
# See gradcheck above for an explanation of why we need something like this.
|
|
#
|
|
# All PyTorch devs doing testing should use this wrapper instead of autograd.gradgradcheck
|
|
default_values = {
|
|
"check_batched_grad": True,
|
|
"fast_mode": True,
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
if os.environ.get('PYTORCH_TEST_WITH_SLOW_GRADCHECK', "0FF") == "ON":
|
|
default_values["fast_mode"] = False
|
|
|
|
for key, value in default_values.items():
|
|
# default value override values explicitly set to None
|
|
k = kwargs.get(key, None)
|
|
kwargs[key] = k if k is not None else value
|
|
|
|
return torch.autograd.gradgradcheck(fn, inputs, grad_outputs, **kwargs)
|
|
|
|
|
|
def _assertGradAndGradgradChecks(test_case, apply_fn, inputs, **kwargs):
|
|
# call assert function rather than returning a bool since it's nicer
|
|
# if we get whether this failed on the gradcheck or the gradgradcheck.
|
|
test_case.assertTrue(gradcheck(apply_fn, inputs, **kwargs))
|
|
test_case.assertTrue(gradgradcheck(apply_fn, inputs, **kwargs))
|
|
|
|
|
|
@contextmanager
|
|
def set_cwd(path: str) -> Iterator[None]:
|
|
old_cwd = os.getcwd()
|
|
try:
|
|
os.chdir(path)
|
|
yield
|
|
finally:
|
|
os.chdir(old_cwd)
|
|
|
|
|
|
# Using @precisionOverride specific to your test is the recommended way
|
|
# of doing this. These are just some values that worked for test_nn.
|
|
dtype2prec_DONTUSE = {torch.float: 1e-5,
|
|
torch.double: 1e-5,
|
|
torch.half: 1e-2,
|
|
torch.bfloat16: 1e-1}
|
|
|
|
|
|
def _wrap_warn_once(regex):
|
|
def decorator(fn):
|
|
def inner(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
|
with self.assertWarnsOnceRegex(UserWarning, regex):
|
|
fn(self, *args, **kwargs)
|
|
return inner
|
|
return decorator
|
|
|
|
# This is a wrapper that wraps a test to run this test twice, one with
|
|
# coalesced=True, another with coalesced=False for coalesced/uncoalesced sparse tensors.
|
|
def coalescedonoff(f):
|
|
@wraps(f)
|
|
def wrapped(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
|
f(self, *args, **kwargs, coalesced=True)
|
|
f(self, *args, **kwargs, coalesced=False)
|
|
return wrapped
|
|
|
|
|
|
@contextlib.contextmanager
|
|
def disable_gc():
|
|
if gc.isenabled():
|
|
try:
|
|
gc.disable()
|
|
yield
|
|
finally:
|
|
gc.enable()
|
|
else:
|
|
yield
|
|
|
|
def has_breakpad() -> bool:
|
|
# If not on a special build, check that the library was actually linked in
|
|
try:
|
|
torch._C._get_minidump_directory() # type: ignore[attr-defined]
|
|
return True
|
|
except RuntimeError as e:
|
|
return False
|