Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/61903
### Remaining Tasks
- [ ] Collate results of benchmarks on two Intel Xeon machines (with & without CUDA, to check if CPU throttling causes issues with GPUs) - make graphs, including Roofline model plots (Intel Advisor can't make them with libgomp, though, but with Intel OpenMP).
### Summary
1. This draft PR produces binaries with with 3 types of ATen kernels - default, AVX2, AVX512 . Using the environment variable `ATEN_AVX512_256=TRUE` also results in 3 types of kernels, but the compiler can use 32 ymm registers for AVX2, instead of the default 16. ATen kernels for `CPU_CAPABILITY_AVX` have been removed.
2. `nansum` is not using AVX512 kernel right now, as it has poorer accuracy for Float16, than does AVX2 or DEFAULT, whose respective accuracies aren't very good either (#59415).
It was more convenient to disable AVX512 dispatch for all dtypes of `nansum` for now.
3. On Windows , ATen Quantized AVX512 kernels are not being used, as quantization tests are flaky. If `--continue-through-failure` is used, then `test_compare_model_outputs_functional_static` fails. But if this test is skipped, `test_compare_model_outputs_conv_static` fails. If both these tests are skipped, then a third one fails. These are hard to debug right now due to not having access to a Windows machine with AVX512 support, so it was more convenient to disable AVX512 dispatch of all ATen Quantized kernels on Windows for now.
4. One test is currently being skipped -
[test_lstm` in `quantization.bc](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/59098) - It fails only on Cascade Lake machines, irrespective of the `ATEN_CPU_CAPABILITY` used, because FBGEMM uses `AVX512_VNNI` on machines that support it. The value of `reduce_range` should be used as `False` on such machines.
The list of the changes is at https://gist.github.com/imaginary-person/4b4fda660534f0493bf9573d511a878d.
Credits to ezyang for proposing `AVX512_256` - these use AVX2 intrinsics but benefit from 32 registers, instead of the 16 ymm registers that AVX2 uses.
Credits to limo1996 for the initial proposal, and for optimizing `hsub_pd` & `hadd_pd`, which didn't have direct AVX512 equivalents, and are being used in some kernels. He also refactored `vec/functional.h` to remove duplicated code.
Credits to quickwritereader for helping fix 4 failing complex multiplication & division tests.
### Testing
1. `vec_test_all_types` was modified to test basic AVX512 support, as tests already existed for AVX2.
Only one test had to be modified, as it was hardcoded for AVX2.
2. `pytorch_linux_bionic_py3_8_gcc9_coverage_test1` & `pytorch_linux_bionic_py3_8_gcc9_coverage_test2` are now using `linux.2xlarge` instances, as they support AVX512. They were used for testing AVX512 kernels, as AVX512 kernels are being used by default in both of the CI checks. Windows CI checks had already been using machines with AVX512 support.
### Would the downclocking caused by AVX512 pose an issue?
I think it's important to note that AVX2 causes downclocking as well, and the additional downclocking caused by AVX512 may not hamper performance on some Skylake machines & beyond, because of the double vector-size. I think that [this post with verifiable references is a must-read](https://community.intel.com/t5/Software-Tuning-Performance/Unexpected-power-vs-cores-profile-for-MKL-kernels-on-modern-Xeon/m-p/1133869/highlight/true#M6450). Also, AVX512 would _probably not_ hurt performance on a high-end machine, [but measurements are recommended](https://lemire.me/blog/2018/09/07/avx-512-when-and-how-to-use-these-new-instructions/). In case it does, `ATEN_AVX512_256=TRUE` can be used for building PyTorch, as AVX2 can then use 32 ymm registers instead of the default 16. [FBGEMM uses `AVX512_256` only on Xeon D processors](https://github.com/pytorch/FBGEMM/pull/209), which are said to have poor AVX512 performance.
This [official data](https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/specification-updates/xeon-scalable-spec-update.pdf) is for the Intel Skylake family, and the first link helps understand its significance. Cascade Lake & Ice Lake SP Xeon processors are said to be even better when it comes to AVX512 performance.
Here is the corresponding data for [Cascade Lake](https://cdrdv2.intel.com/v1/dl/getContent/338848) -
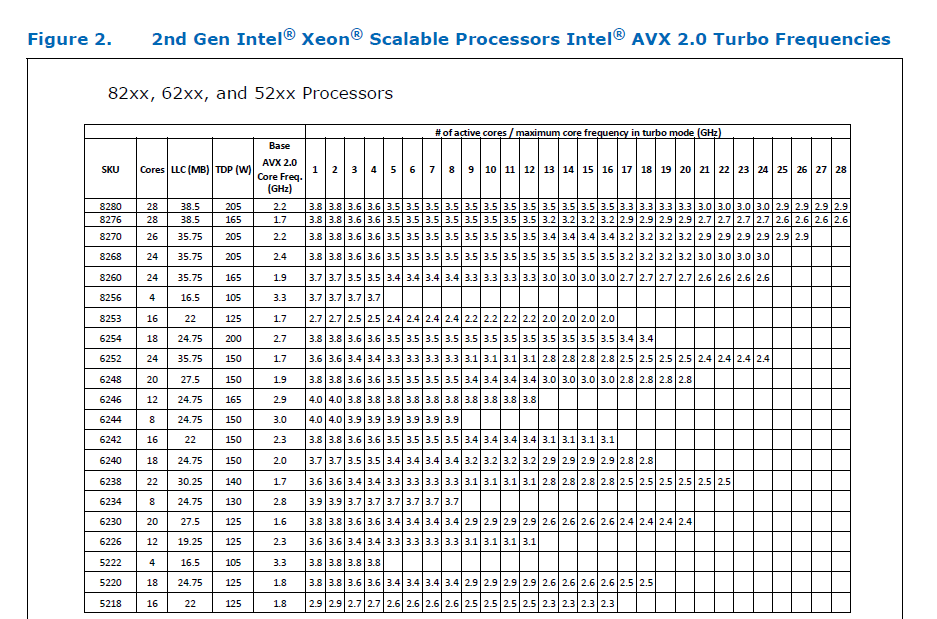
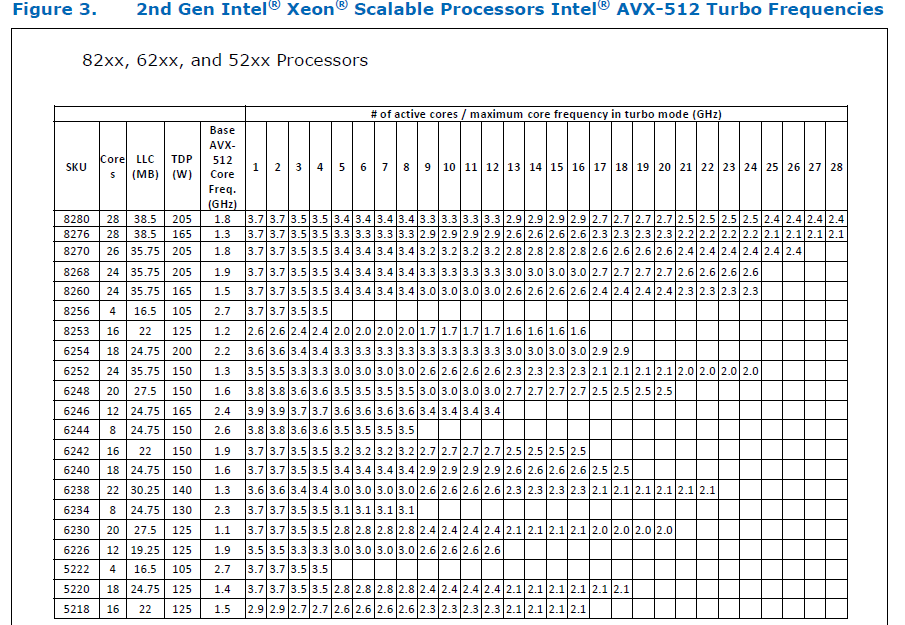
The corresponding data isn't publicly available for Intel Xeon SP 3rd gen (Ice Lake SP), but [Intel mentioned that the 3rd gen has frequency improvements pertaining to AVX512](https://newsroom.intel.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/11/2021/04/3rd-Gen-Intel-Xeon-Scalable-Platform-Press-Presentation-281884.pdf). Ice Lake SP machines also have 48 KB L1D caches, so that's another reason for AVX512 performance to be better on them.
### Is PyTorch always faster with AVX512?
No, but then PyTorch is not always faster with AVX2 either. Please refer to #60202. The benefit from vectorization is apparent with with small tensors that fit in caches or in kernels that are more compute heavy. For instance, AVX512 or AVX2 would yield no benefit for adding two 64 MB tensors, but adding two 1 MB tensors would do well with AVX2, and even more so with AVX512.
It seems that memory-bound computations, such as adding two 64 MB tensors can be slow with vectorization (depending upon the number of threads used), as the effects of downclocking can then be observed.
Original pull request: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/56992
Reviewed By: soulitzer
Differential Revision: D29266289
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 2d5e8d1c2307252f22423bbc14f136c67c3e6184
Summary:
it should not error out if the file is not found.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/61610
Reviewed By: samestep
Differential Revision: D29687958
Pulled By: walterddr
fbshipit-source-id: 17cacba8daa131df9bfb37fd58d6e4870ff75198
Summary:
and into tools/ folder
Currently run_tests.py invokes tools/test_selections.py
1. download and analyze what test_file to run
2. download and parse S3 stats and pass the info to local files.
3. common_utils.py uses download S3 stats to determine what test cases to run.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/61479
Reviewed By: janeyx99
Differential Revision: D29661986
Pulled By: walterddr
fbshipit-source-id: bebd8c474bcc2444e135bfd2fa4bdd1eefafe595
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/60990
This makes the breakpad build more explicit in its messaging and hints to cmake where to look for the library (it wasn't able to find it without `PATHS` on CI even though that works locally). This also adds a smoke test that will fail if breakpad isn't present on a CI job where it is expected (e.g. binary builds).
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D29514316
Pulled By: driazati
fbshipit-source-id: 79514363334788f311ba5d4f25deed3452f0c3eb
Summary:
This PR will ideally add `ref` argument to `OpInfo` base class. The idea is to add reference checks for all the ops _eligible_. For more discussion, please check https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/58294
* [x] Migrate (but not removing yet) and modify helper functions from `UnaryUfuncOpInfo` class to `OpInfo` base class.
* [x] Test the reference checks for multiple ops. (also decide a list of different and eligible ops for this)
* [x] Handle possible edge cases (for example: `uint64` isn't implemented in PyTorch but is there in NumPy, and this needs to be handled -- more on this later) -- _Update_: We decided that these reference tests should only test for values and not types.
* [x] Create a sample PR for a single (of all different categories?) on adding reference functions to the eligible ops. -- _Update_: This is being done in this PR only.
* [x] ~Remove reference tests from `test_unary_ufuncs.py` and test to make sure that nothing breaks.~ (*Update*: We won't be touching Unary Ufunc reference tests in this PR)
* [x] Add comments, remove unnecessary prints/comments (added for debugging).
Note: To keep the PR description short, examples of edge cases encountered have been mentioned in the comments below.
cc: mruberry pmeier kshitij12345
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/59369
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D29347252
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 69719deddb1d23c53db45287a7e66c1bfe7e65bb
Summary:
`IS_PYTORCH_CI` and `IN_CI` are used randomly, however in some cases IN_CI is not currently set because it only exist in .circleci/scripts/setup_ci_environment.sh. This cleans up the 2 flags and only use IN_CI
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/60279
Test Plan: CI
Reviewed By: seemethere
Differential Revision: D29239545
Pulled By: walterddr
fbshipit-source-id: a069424a2bb8790a3adfdaf0dc460301026bf8c7
Summary:
During development it is common practice to put `type: ignore` comments on lines that are correct, but `mypy` doesn't recognize this. This often stems from the fact, that the used `mypy` version wasn't able to handle the used pattern.
With every new release `mypy` gets better at handling complex code. In addition to fix all the previously accepted but now failing patterns, we should also revisit all `type: ignore` comments to see if they are still needed or not. Fortunately, we don't need to do it manually: by adding `warn_unused_ignores = True` to the configuration, `mypy` will error out in case it encounters an `type: ignore` that is no longer needed.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/60006
Reviewed By: jbschlosser, malfet
Differential Revision: D29133237
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 41e82edc5cd5affa7ccedad044b59b94dad4425a
Summary:
Do not reorder tests unless they are in IN_CI, this causes local development test ordering indeterministic. most of use branch out from viable strict not head of master.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/59565
Reviewed By: ejguan
Differential Revision: D28943906
Pulled By: walterddr
fbshipit-source-id: e742e7ce4b3fc017d7563b01e93c4cd774d0a537
Summary:
The run-specified-test-cases option would allow us to specify a list of test cases to run by having a CSV with minimally two columns: test_filename and test_case_name.
This PR also adds .json to some files we use for better clarity.
Usage:
`python test/run_test.py --run-specified-test-cases <csv_file>` where the csv file can look like:
```
test_filename,test_case_name,test_total_time,windows_only_failure_sha_count,total_sha_count,windows_failure_count,linux_failure_count,windows_total_count,linux_total_count
test_cuda,test_cudnn_multiple_threads_same_device,8068.8409659525,46,3768,53,0,2181,6750
test_utils,test_load_standalone,8308.8062920459,14,4630,65,0,2718,8729
test_ops,test_forward_mode_AD_acosh_cuda_complex128,91.652619369806,11,1971,26,1,1197,3825
test_ops,test_forward_mode_AD_acos_cuda_complex128,91.825633094915,11,1971,26,1,1197,3825
test_profiler,test_source,60.93786725749,9,4656,21,3,2742,8805
test_profiler,test_profiler_tracing,203.09352795241,9,4662,21,3,2737,8807
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/59487
Test Plan:
Without specifying the option, everything should be as they were before.
Running `python test/run_test.py --run-specified-test-cases windows_smoke_tests.csv` resulted in this paste P420276949 (you can see internally). A snippet looks like:
```
(pytorch) janeyx@janeyx-mbp pytorch % python test/run_test.py --run-specified-test-cases windows_smoke_tests.csv
Loading specified test cases to run from windows_smoke_tests.csv.
Processed 28 test cases.
Running test_cpp_extensions_jit ... [2021-06-04 17:24:41.213644]
Executing ['/Users/janeyx/miniconda3/envs/pytorch/bin/python', 'test_cpp_extensions_jit.py', '-k', 'test_jit_cuda_archflags'] ... [2021-06-04 17:24:41.213781]
s
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 1 test in 0.000s
OK (skipped=1)
...
```
With pytest, an example executable would be:
`Running test_dataloader ... [2021-06-04 17:37:57.643039]
Executing ['/Users/janeyx/miniconda3/envs/pytorch/bin/python', '-m', 'pytest', 'test_dataloader.py', '-v', '-k', 'test_segfault or test_timeout'] ... [2021-06-04 17:37:57.643327]`
Reviewed By: samestep
Differential Revision: D28913223
Pulled By: janeyx99
fbshipit-source-id: 0d1f9910973426b8756815c697b483160517b127
Summary:
Implements an idea by ngimel to improve the performance of `torch.flip` via a clever hack into TI to bypass the fact that TI is not designed to work with negative indices.
Something that might be added is vectorisation support on CPU, given how simple the implementation is now.
Some low-hanging fruits that I did not implement:
- Write it as a structured kernel
- Migrate the tests to opinfos
- Have a look at `cumsum_backward` and `cumprod_backward`, as I think that they could be implemented faster with `flip`, now that `flip` is fast.
**Edit**
This operation already has OpInfos and it cannot be migrated to a structured kernel because it implements quantisation
Summary of the PR:
- x1.5-3 performance boost on CPU
- x1.5-2 performance boost on CUDA
- Comparable performance across dimensions, regardless of the strides (thanks TI)
- Simpler code
<details>
<summary>
Test Script
</summary>
```python
from itertools import product
import torch
from torch.utils.benchmark import Compare, Timer
def get_timer(size, dims, num_threads, device):
x = torch.rand(*size, device=device)
timer = Timer(
"torch.flip(x, dims=dims)",
globals={"x": x, "dims": dims},
label=f"Flip {device}",
description=f"dims: {dims}",
sub_label=f"size: {size}",
num_threads=num_threads,
)
return timer.blocked_autorange(min_run_time=5)
def get_params():
sizes = ((1000,)*2, (1000,)*3, (10000,)*2)
for size, device in product(sizes, ("cpu", "cuda")):
threads = (1, 2, 4) if device == "cpu" else (1,)
list_dims = [(0,), (1,), (0, 1)]
if len(size) == 3:
list_dims.append((0, 2))
for num_threads, dims in product(threads, list_dims):
yield size, dims, num_threads, device
def compare():
compare = Compare([get_timer(*params) for params in get_params()])
compare.trim_significant_figures()
compare.colorize()
compare.print()
compare()
```
</details>
<details>
<summary>
Benchmark PR
</summary>
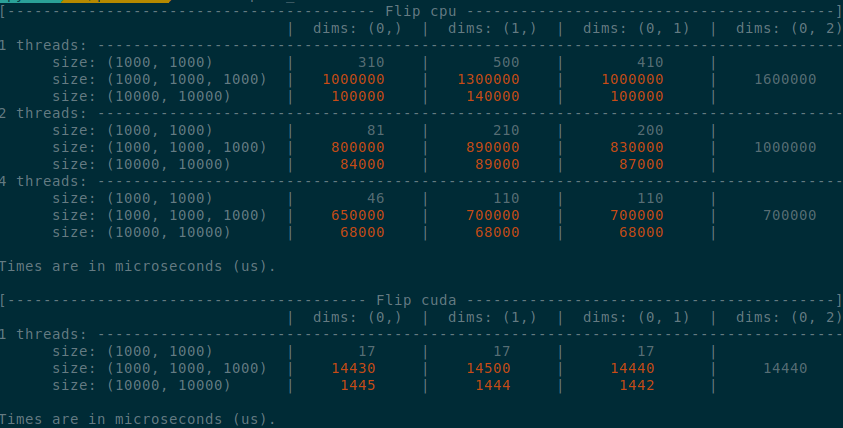
</details>
<details>
<summary>
Benchmark master
</summary>
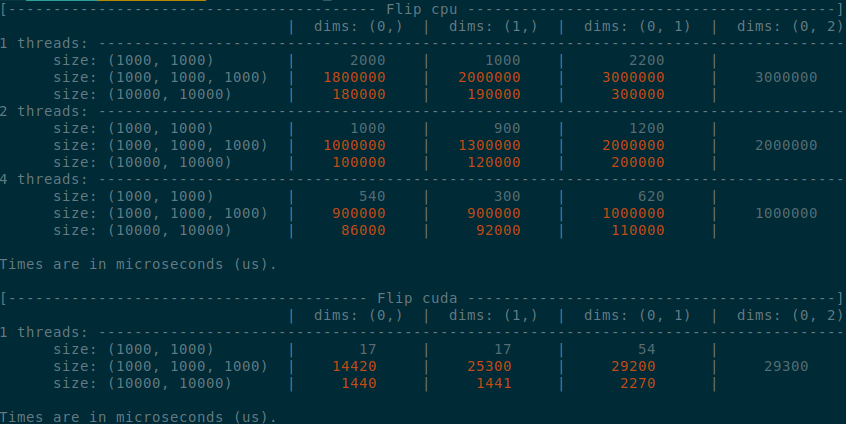
</details>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58747
Reviewed By: agolynski
Differential Revision: D28877076
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 4fa6eb519085950176cb3a9161eeb3b6289ec575
Summary:
There are two main changes here:
- THPVariable will actually visit their grad_fn if there are no other reference to the c++ Tensor and no other reference to the grad_fn. The critical observation compared to the existing comment (thanks Ed!) is that if we also check that the c++ Tensor object is not referenced somewhere else, we're sure that no one can change the grad_fn refcount between the traverse and the clear.
- THPVariable don't need a special clear for this new cases as we're the only owner of the c++ Tensor and so the cdata.reset() will necessarily free the Tensor and all its resources.
The two tests are to ensure:
- That the cycles are indeed collectible by the gc
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58271
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D28796461
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 62c05930ddd0c48422c79b03118db41a73c1355d
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/52659
**Summary**
This commit adds `torch._C.ScriptDict`, a dictionary type that has reference
semantics across the Python/TorchScript boundary. That is, modifications
made to instances of `torch._C.ScriptDict` in TorchScript are visible in
Python even when it is not returned from the function. Instances can be
constructed by passing an instance of a Python dictionary to
`torch.jit.script`. In the case of an empty dictionary, its type is
assumed to be `Dict[str, Tensor]` to be consistent with the handling of
empty dictionaries in TorchScript source code.
`torch._C.ScriptDict` is implemented using a modified version of pybind's `stl_bind.h`-style bindings attached to `ScriptDict`, `ScriptDictIterator` and `ScriptDictKeyIterator`, wrapper classes around `c10::impl::GenericDict` and `c10::impl::GenericDict::iterator`. These bindings allow instances of `torch._C.ScriptDict` to be used as if it were a regular `dict` Python. Reference semantics are achieved by simply retrieving the `IValue` contained in `ScriptDict` in `toIValue` (invoked when converting Python arguments to `IValues` before calling TorchScript code).
**Test Plan**
This commit adds `TestScriptDict` to `test_list_dict.py`, a set of tests
that check that all of the common dictionary operations are supported
and that instances have reference semantics across the
Python/TorchScript boundary.
Differential Revision:
D27211605
D27211605
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: gmagogsfm
Pulled By: SplitInfinity
fbshipit-source-id: 446d4e5328375791aa73eb9e8b04dfe3465af960
Summary:
This PR adds a note to the documentation that torch.svd is deprecated together with an upgrade guide on how to use `torch.linalg.svd` and `torch.linalg.svdvals` (Lezcano's instructions from https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/57549).
In addition, all usage of the old svd function is replaced with a new one from torch.linalg module, except for the `at::linalg_pinv` function, that fails the XLA CI build (https://github.com/pytorch/xla/issues/2755, see failure in draft PR https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/57772).
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/57981
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D28345558
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 02dd9ae6efe975026e80ca128e9b91dfc65d7213
Summary:
Downloading slow_test list on SC causes timeout, this is even a bigger issue since `common_utils.py` is reused in many internal projects/modules.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/57953
Test Plan: CI
Reviewed By: janeyx99
Differential Revision: D28325527
fbshipit-source-id: ae47c9e43ad6f416008005bb26ceb2f3d6966f2e
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/55237
In this PR, we reenable fast-gradcheck and resolve misc issues that arise:
Before landing this PR, land #55182 so that slow tests are still being run periodically.
Bolded indicates the issue is handled in this PR, otherwise it is handled in a previous PR.
**Non-determinism issues**:
- ops that do not have deterministic implementation (as documented https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.use_deterministic_algorithms.html#torch.use_deterministic_algorithms)
- test_pad_cuda (replication_pad2d) (test_nn)
- interpolate (test_nn)
- cummin, cummax (scatter_add_cuda_kernel) (test_ops)
- test_fn_gradgrad_prod_cpu_float64 (test_ops)
Randomness:
- RRelu (new module tests) - we fix by using our own generator as to avoid messing with user RNG state (handled in #54480)
Numerical precision issues:
- jacobian mismatch: test_gelu (test_nn, float32, not able to replicate locally) - we fixed this by disabling for float32 (handled in previous PR)
- cholesky_solve (test_linalg): #56235 handled in previous PR
- **cumprod** (test_ops) - #56275 disabled fast gradcheck
Not yet replicated:
- test_relaxed_one_hot_categorical_2d (test_distributions)
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D27920906
fbshipit-source-id: 894dd7bf20b74f1a91a5bc24fe56794b4ee24656
Summary:
Under this setting the job should run 3 times a day.
When the environment variable, `PYTORCH_TEST_WITH_SLOW_GRADCHECK` is set to `ON`, set the default value for `fast_mode` in gradchack wrapper as False. This would be overriden by whatever value the user explicitly passes in.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/55182
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D27919236
Pulled By: soulitzer
fbshipit-source-id: 3a55ec6edcfc6e65fbc3a8a09c63aaea1bd1c5bf
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/56434
If we hit multiple TORCH_WARN from different sources when running the
statement, it makes more sense to me that we want to check the regex is
met in any one of the warning messages instead of all messages.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D27871946
Pulled By: ailzhang
fbshipit-source-id: 5940a8e43e4cc91aef213ef01e48d506fd9a1132
Summary:
As this diff shows, currently there are a couple hundred instances of raw `noqa` in the codebase, which just ignore all errors on a given line. That isn't great, so this PR changes all existing instances of that antipattern to qualify the `noqa` with respect to a specific error code, and adds a lint to prevent more of this from happening in the future.
Interestingly, some of the examples the `noqa` lint catches are genuine attempts to qualify the `noqa` with a specific error code, such as these two:
```
test/jit/test_misc.py:27: print(f"{hello + ' ' + test}, I'm a {test}") # noqa E999
test/jit/test_misc.py:28: print(f"format blank") # noqa F541
```
However, those are still wrong because they are [missing a colon](https://flake8.pycqa.org/en/3.9.1/user/violations.html#in-line-ignoring-errors), which actually causes the error code to be completely ignored:
- If you change them to anything else, the warnings will still be suppressed.
- If you add the necessary colons then it is revealed that `E261` was also being suppressed, unintentionally:
```
test/jit/test_misc.py:27:57: E261 at least two spaces before inline comment
test/jit/test_misc.py:28:35: E261 at least two spaces before inline comment
```
I did try using [flake8-noqa](https://pypi.org/project/flake8-noqa/) instead of a custom `git grep` lint, but it didn't seem to work. This PR is definitely missing some of the functionality that flake8-noqa is supposed to provide, though, so if someone can figure out how to use it, we should do that instead.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/56272
Test Plan:
CI should pass on the tip of this PR, and we know that the lint works because the following CI run (before this PR was finished) failed:
- https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/runs/2365189927
Reviewed By: janeyx99
Differential Revision: D27830127
Pulled By: samestep
fbshipit-source-id: d6dcf4f945ebd18cd76c46a07f3b408296864fcb
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/50699.
The root cause was that some floating-point assertions had a "greater than or **equal to**" condition. The "equal to" part was causing flakiness due to strict equality check (`==`) in `TestCase.assertGreaterEqual()`. This PR introduces a new assertion method called `assertGreaterAlmostEqual()` in `common_utils.py` that mitigates the problem by behaving similar to `TestCase.assertAlmostEqual()`.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/56192
Reviewed By: zhaojuanmao
Differential Revision: D27804724
Pulled By: cbalioglu
fbshipit-source-id: bc44a41ca4ce45dfee62fb3769fb47bfd9028831
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/55682Fixes#55648
For now it downloads and writes the relevant files to the system's temp dir and marks it as valid for 3 hours.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: malfet, nikithamalgifb
Differential Revision: D27685616
Pulled By: driazati
fbshipit-source-id: 27469b85fe4b6b4addde6b22bf795bca3d4990ef
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/54769
Follow-up to #53820. This
- makes the `asserts.py` module private as per suggestion from rgommers in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/53820#issuecomment-802661387. With this the functions should only be accessible through `torch.testing`, giving us the option the change the underlying structure later.
- moves the code from `torch/testing/__init__.py` to `torch/testing/_core.py` (happy to accept other name suggestions). Otherwise we can't import the new `_asserts.py` in `torch/testing/__init__.py` due to circular imports.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: mrshenli
Differential Revision: D27438451
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: c7292b4d5709185b42b4aac8016648562688040e
Summary:
Stack:
* https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/54954 Fixed OpInfo jit tests failing for TensorList inputs
* __#54922 Added support for TensorList inputs in OpInfo__
Updated OpInfo to accept either a `Tensor` or `TensorList` as `sample.input` and added workarounds to make this work with gradcheck.
Note: JIT testing support for TensorList inputs will be added in a follow up PR.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/51996
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/54922
Reviewed By: H-Huang
Differential Revision: D27448952
Pulled By: heitorschueroff
fbshipit-source-id: 3f24a56f6180eb2d044dcfc89ba59fce8acfe278
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/53511
torch.det does depend on torch.prod, which in turn depends on several other functions, and they also depend on torch.prod, so there is a circular relationship, hence this PR will enable complex backward support for several functions at once.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/48125
Reviewed By: pbelevich
Differential Revision: D27188589
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: bbb80f8ecb83a0c3bea2b917627d3cd3b84eb09a
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/53682
With this, under the meta device, 101 tests passed and 16953 skipped.
It ain't much, but it's a start.
Some various bits and bobs:
- NotImplementedError suppression at test level is implemented
in the same way as CUDA memory leak check, i.e., by wrapping
test methods and monkeypatching them back in.
- I had to reimplement assertRaises/assertRaisesRegex from scratch to
ignore NotImplementedError when _ignore_not_implemented_error is True.
The implementation relies on a small amount of private API that hasn't
changed since 2010
- expectedAlertNondeterministic doesn't really work so I skipped them
all; there's probably a way to do it better
I tested this using `pytest --disable-warnings --tb=native -k meta --sw
test/*.py` and a pile of extra patches to make collection actually work
(lol).
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D26955539
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: ac21c8734562497fdcca3b614a28010bc4c03d74