crossref is a new strategy for performing tests when you want
to run a normal PyTorch API call, separately run some variation of
the API call (e.g., same thing but all the arguments are meta tensors)
and then cross-reference the results to see that they are consistent.
Any logic you add to CrossRefMode will get run on *every* PyTorch API
call that is called in the course of PyTorch's test suite. This can
be a good choice for correctness testing if OpInfo testing is not
exhaustive enough.
For now, the crossref test doesn't do anything except verify that
we can validly push a mode onto the torch function mode stack for all
functions.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyangfb.com>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/75988
Approved by: https://github.com/seemethere
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/74226
Update signature of `scatter_reduce_` to match `scatter_/scatter_add_`
`Tensor.scatter_reduce_(int64 dim, Tensor index, Tensor src, str reduce)`
- Add new reduction options in ScatterGatherKernel.cpp and update `scatter_reduce` to call into the cpu kernel for `scatter.reduce`
- `scatter_reduce` now has the same shape constraints as `scatter_` and `scatter_add_`
- Migrate `test/test_torch.py:test_scatter_reduce` to `test/test_scatter_gather_ops.py`
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D35222842
Pulled By: mikaylagawarecki
fbshipit-source-id: 84930add2ad30baf872c495251373313cb7428bd
(cherry picked from commit 1b45139482e22eb0dc8b6aec2a7b25a4b58e31df)
Summary:
This PR ports several tests in `test/test_torch.py` over to OpInfo ErrorInputs.
Some tests commented "convert to ErrorInputs" still remain in `test_torch.py`. They fall under two categories:
- Memory overlap tests which specifically test the in-place version of an operator (e.g. [this test](424a054d53/test/test_torch.py (L3788)) for index_add_).
- Tests with non-trivial behavior calling `torch.cuda.synchronize()` after calling the operator being tested (e.g. [this test](424a054d53/test/test_torch.py (L4948)) for torch.multinomial).
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/73981
Reviewed By: qihqi
Differential Revision: D35016669
Pulled By: saketh-are
fbshipit-source-id: bc0016d2b2bfb566a9dfef81ecf44e0adb9e4b14
(cherry picked from commit 99bcbdb05f2c10a717a269b0010aa3a3e24fe5c0)
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/67919
The compatibility check on `edge_order` in `pre_check_gradient` now looks only at dim argument if it is present, otherwise it checks all dimensions.
Previously, it would check all dimensions regardless of the dim argument and throw unnecessary errors.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/67926
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D33760621
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: d490cd8610c68ff3787e670fc947de3cbf2db062
(cherry picked from commit 45bc56de9e)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/65993
This PR attempts to port `index_add` to structured kernels, but does more than that:
* Adds an `out=` variant to `index_add`
* Revises `native_functions.yaml` registrations, to not have multiple entries and instead pass default value to `alpha`.
* Changes in `derivatives.yaml` file for autograd functioning
* Revises error messages, please see: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/65993#issuecomment-945441615
Follow-up PRs in near future will attempt to refactor the OpInfo test, and will give another look at tests in `test/test_torch.py` for this function. (hence the use of ghstack for this)
~This is WIP because there are tests failing for `Dimname` variant on mobile/android builds, and I'm working on fixing them.~
Issue tracker: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/55070
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: ejguan
Differential Revision: D32646426
fbshipit-source-id: b035ecf843a9a27d4d1e18b202b035adc2a49ab5
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/53647
With this if a test forgets to add `dtypes` while using `dtypesIf`, following error is raised
```
AssertionError: dtypes is mandatory when using dtypesIf however 'test_exponential_no_zero' didn't specify it
```
**Tested Locally**
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/68186
Reviewed By: VitalyFedyunin
Differential Revision: D32468581
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 805e0855f988b77a5d8d4cd52b31426c04c2200b
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/46741
pytorchbot
contributors: nickleus27, yanivsagy, and khanhthien123
SmrutiSikha this is mostly your work. We just did very minor clean up.
cc mruberry
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/67664
Reviewed By: gchanan
Differential Revision: D32311838
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 0e5d4d888caeccb0fd7c80e6ff11b1b1fa8e00d6
Summary:
Many thanks to Forest Yang (meowmix) from the forum for reporting it with a minimal reproduction.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/67829
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D32184786
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: b63dbd3148b5def2109deb2f4612c08f55f59dfb
Summary:
Partially fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/66066
This PR:
- cleans up op-specific testing from test_autograd. test_autograd should be reserved for testing generic autograd functionality
- tests related to an operator are better colocated
- see the tracker for details
What to think about when moving tests to their correct test suite:
- naming, make sure its not too generic
- how the test is parametrized, sometimes we need to add/remove a device/dtype parameter
- can this be merged with existing tests
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/67413
Reviewed By: jbschlosser, albanD
Differential Revision: D32031480
Pulled By: soulitzer
fbshipit-source-id: 8e13da1e58a38d5cecbfdfd4fe2b4fe6f816897f
Summary:
Adds mixed precision autocasting support between fp32/fp16 to torchscript/JIT. More in depth descriptoin can be found at [torch/csrc/jit/JIT-AUTOCAST.md](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63939/files#diff-1f1772aaa508841c5bb58b74ab98f49a1e577612cd9ea5c386c8714a75db830b)
This PR implemented an autocast optimization pass that inserts casting ops per AMP rule (torch/csrc/jit/passes/autocast.cpp), that mimics the behavior of eager autocast. The pass also takes into consideration the context of `torch.cuda.amp.autocast` and only inserts casting ops within the enabled context manager, giving feature parity as with eager amp autocast.
We currently provide JIT AMP autocast as a prototyping feature, so it is default off and could be turned on via `torch._C._jit_set_autocast_mode(True)`
The JIT support for autocast is subject to different constraints compared to the eager mode implementation (mostly related to the fact that TorchScript is statically typed), restriction on the user facing python code is described in doc torch/csrc/jit/JIT-AUTOCAST.md
This is a prototype, there are also implementation limitation that's necessary to keep this PR small and get something functioning quickly on upstream, so we can iterate on designs.
Few limitation/challenge that is not properly resolved in this PR:
1. Autocast inserts cast operation, which would have impact on scalar type of output tensor feeding downstream operations. We are not currently propagating the updated scalar types, this would give issues/wrong results on operations in promotion rules.
2. Backward for autodiff in JIT misses the casting of dgrad to input scalar type, as what autograd does in eager. This forces us to explicitly mark the casting operation for certain operations (e.g. binary ops), otherwise, we might be feeding dgrad with mismatch scalar type to input. This could potentially break gradient function consuming dgrad. (e.g. gemm backwards, which assumes grad_output to be of same scalar type as input')
3. `torch.autocast` api has an optional argument `dtype` which is not currently supported in the JIT autocast and we require a static value.
Credit goes mostly to:
tlemo
kevinstephano
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63939
Reviewed By: navahgar
Differential Revision: D31093381
Pulled By: eellison
fbshipit-source-id: da6e26c668c38b01e296f304507048d6c1794314
Summary:
CAFFE2 has been deprecated for a while, but still included in every PyTorch build.
We should stop building it by default, although CI should still validate that caffe2 code is buildable.
Build even fewer dependencies when compiling mobile builds without Caffe2
Introduce `TEST_CAFFE2` in torch.common.utils
Skip `TestQuantizedEmbeddingOps` and `TestJit.test_old_models_bc` is code is compiled without Caffe2
Should be landed after https://github.com/pytorch/builder/pull/864
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/66658
Reviewed By: driazati, seemethere, janeyx99
Differential Revision: D31669156
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 1cc45e2d402daf913a4685eb9f841cc3863e458d
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/64181
This PR replaces all the calls to:
- `transpose(-2, -1)` or `transpose(-1, -2)` by `mT()` in C++ and `mT` in Python
- `conj().transpose(-2, -1)` or `transpose(-2, -1).conj()` or `conj().transpose(-1, -2)` or `transpose(-1, -2).conj()` by `mH()` in C++ and `mH` in Python.
It also simplifies two pieces of code, and fixes one bug where a pair
of parentheses were missing in the function `make_symmetric_matrices`.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: H-Huang
Differential Revision: D31692896
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: e9112c42343663d442dc5bd53ff2b492094b434a
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/64883
Adds a `warn_only` kwarg to `use_deterministic_algorithms`. When enabled, calling an operation that does not have a deterministic implementation will raise a warning, rather than an error.
`torch.testing._internal.common_device_type.expectedAlertNondeterministic` is also refactored and documented in this PR to make it easier to use and understand.
cc mruberry kurtamohler
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/66233
Reviewed By: bdhirsh
Differential Revision: D31616481
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 059634a82d54407492b1d8df08f059c758d0a420
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/62030
Remove dtype tracking from Python Storage interface, remove all the different `<type>Storage` classes except for `ByteStorage`, and update serialization accordingly, while maintaining as much FC/BC as possible
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/47442
* **THE SERIALIZATION FORMAT IS FULLY FC/BC.** We worked very hard to make sure this is the case. We will probably want to break FC at some point to make the serialization structure of tensors make more sense, but not today.
* There is now only a single torch.ByteStorage class. Methods like `Tensor.set_` no longer check that the dtype of storage is appropriate.
* As we no longer know what dtype of a storage is, we've **removed** the size method from Storage, replacing it with nbytes. This is to help catch otherwise silent errors where you confuse number of elements with number of bytes.
* `Storage._new_shared` takes a `nbytes` kwarg and will reject previous positional only calls. `Storage._new_with_file` and `_set_from_file` require explicit element size arguments.
* It's no longer possible to convert storages to different types using the float/double/etc methods. Instead, do the conversion using a tensor.
* It's no longer possible to allocate a typed storage directly using FloatStorage/DoubleStorage/etc constructors. Instead, construct a tensor and extract its storage. The classes still exist but they are used purely for unpickling.
* The preexisting serialization format stores dtype with storage, and in fact this dtype is used to determine the dtype of the tensor overall.
To accommodate this case, we introduce a new TypedStorage concept that exists only during unpickling time which is used to temporarily store the dtype so we can construct a tensor. **If you overrode the handling of pickling/unpickling, you MUST add handling for TypedStorage** or your serialization code will degrade to standard file-based serialization.
Original pull request: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/59671
Reviewed By: soulitzer, ngimel
Differential Revision: D29466819
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 4a14e5d3c2b08e06e558683d97f7378a3180b00e
Summary:
Happy to get any feedback on how to make this code cleaner!
This:
- Fix Tensor attribute deepcopy BC-breaking?
- Add a test for Tensor attribute deepcopy
- Fix subclass deepcopy
- Moves the subclass serialization tests into their own class not to interfere with other serialization test logic
- Add a test for subclass deepcopy
cc ezyang gchanan
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/65584
Reviewed By: gchanan
Differential Revision: D31206590
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 74a8f0767f4933b9c941fbea880a8fd1b893ea2f
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/62793
This is mostly a quick fix. I think the more correct fix could be updating `unique_dim` to `_unique_dim` which could be BC-breaking for C++ users (� maybe). Maybe something else I am missing.
~~Not sure how to add a test for it.~~ Have tested it locally.
We can add a test like following. Tested this locally, it fails currently but passes with the fix.
```python
def test_wildcard_import(self):
exec('from torch import *')
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63080
Reviewed By: gchanan
Differential Revision: D30738711
Pulled By: zou3519
fbshipit-source-id: b86d0190e45ba0b49fd2cffdcfd2e3a75cc2a35e
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/64813
Raises a TypeError when assigned value to a grad is not a Tensor or
None.
Adds tests.
cc ezyang gchanan
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/64876
Reviewed By: anjali411
Differential Revision: D30901678
Pulled By: soulitzer
fbshipit-source-id: dbb3cb5fd0bbac6918e0b2e2f51d340daa43dee0
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/64746
This extracts the error checking that used to be in the PR above.
We are not going to land the proposed fix there, but I think we want this error checking in right now as these would lead to respectively a memory leak and arbitrary memory read/write.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D30867569
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: bf468033fb8b49fcb26eed423f5fad82b4a46c56
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63554
Following https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/61840#issuecomment-884087809, this deprecates all the dtype getters publicly exposed in the `torch.testing` namespace. The reason for this twofold:
1. If someone is not familiar with the C++ dispatch macros PyTorch uses, the names are misleading. For example `torch.testing.floating_types()` will only give you `float32` and `float64` skipping `float16` and `bfloat16`.
2. The dtype getters provide very minimal functionality that can be easily emulated by downstream libraries.
We thought about [providing an replacement](https://gist.github.com/pmeier/3dfd2e105842ad0de4505068a1a0270a), but ultimately decided against it. The major problem is BC: by keeping it, either the namespace is getting messy again after a new dtype is added or we need to somehow version the return values of the getters.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: H-Huang
Differential Revision: D30662206
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: a2bdb10ab02ae665df1b5b76e8afa9af043bbf56
Summary:
Will add a description once this is ready for review.
cc: ysiraichi ezyang
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63312
Reviewed By: iramazanli
Differential Revision: D30597447
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: d36e59835c2f4b38e286032dd2a1111a7e16b7e5
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63572
Addresses #61906. Issue will be fixed later in the stack when `torch.testing.assert_close` got the same treatment.
cc ezyang gchanan
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: ezyang
Differential Revision: D30633527
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: c2002a4998a7a75cb2ab83f87190bde43a9d4f7c
Summary:
This PR implements the necessary hooks/stubs/enums/etc for complete ONNX Runtime (ORT) Eager Mode integration. The actual extension will live out of tree at https://github.com/pytorch/ort.
We have been [working on this at Microsoft](https://github.com/microsoft/onnxruntime-pytorch/tree/eager-ort/torch_onnxruntime) for the last few months, and are finally ready to contribute the PyTorch core changes upstream (nothing major or exciting, just the usual boilerplate for adding new backends).
The ORT backend will allow us to ferry [almost] all torch ops into granular ONNX kernels that ORT will eagerly execute against any devices it supports (therefore, we only need a single ORT backend from a PyTorch perspective).
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58248
Reviewed By: astaff
Differential Revision: D30344992
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 69082b32121246340d686e16653626114b7714b2
Summary:
This creates `torch.cuda.set_warn_on_synchronization()` function that would warn or error when synchronizing operation is performed. We could wrap it in a context manager for ease of use, but it would be a lie, because it sets global, and not thread-local state. Since it's intended for debugging, maybe that's ok though.
As all `torch.cuda.*` functions, it's going through CPython, not pybind, so the argument is converted to long before being passed to c10 function. I'll make python argument a python enum class, but without pybind it'll still have to go thourgh long conversion.
For a test script
```
import torch
torch.cuda.set_warn_on_synchronization(1)
x=torch.randn(10, device="cuda")
x.nonzero()
y=torch.randn((), device="cuda")
if y:
print("something")
torch.multinomial(x.abs(), 10, replacement=False)
torch.randperm(20000, device="cuda")
ind = torch.randint(10, (3,), device="cuda")
mask = torch.randint(2, (10,), device="cuda", dtype=torch.bool)
val = torch.randn((), device="cuda")
x[mask]=1.
x[mask] = val
torch.cuda.synchronize()
```
the output is
```
/../playground/sync_warn_test.py:4: UserWarning: called a synchronizing operation (Triggered internally at ../c10/cuda/CUDAFunctions.cpp:145.)
x.nonzero()
/../playground/sync_warn_test.py:7: UserWarning: called a synchronizing operation (Triggered internally at ../c10/cuda/CUDAFunctions.cpp:145.)
if y:
something
/../playground/sync_warn_test.py:9: UserWarning: called a synchronizing operation (Triggered internally at ../c10/cuda/CUDAFunctions.cpp:145.)
torch.multinomial(x.abs(), 10, replacement=False)
/../playground/sync_warn_test.py:15: UserWarning: called a synchronizing operation (Triggered internally at ../c10/cuda/CUDAFunctions.cpp:145.)
x[mask] = val
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/62092
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D29968792
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: cc6f817212c164727ed99ecf6ab050dc29631b9e
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/60959
Add TorchVitals for Dataloader, this indicates that the data loader was enabled.
This is a no-op if TORCH_VITALS environment variable is not set.
Test Plan: buck test mode/dbg caffe2/test:torch -- --regex vitals
Reviewed By: VitalyFedyunin
Differential Revision: D29445146
fbshipit-source-id: d5778fff3dafb3c0463fec7a498bff4905597518
Summary:
Based from https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/50466
Adds the initial implementation of `torch.cov` similar to `numpy.cov`. For simplicity, we removed support for many parameters in `numpy.cov` that are either redundant such as `bias`, or have simple workarounds such as `y` and `rowvar`.
cc PandaBoi
closes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/19037
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58311
Reviewed By: jbschlosser
Differential Revision: D29431651
Pulled By: heitorschueroff
fbshipit-source-id: 167dea880f534934b145ba94291a9d634c25b01b
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58059
Add CUDA.used vital sign which is true only if CUDA was "used" which technically means the context was created.
Also adds the following features:
- Force vitals to be written even if vitals are disabled, to enable testing when the env variable is not set from the start of execution
- Add a read_vitals call for python to read existing vital signs.
Test Plan: buck test mode/dbg caffe2/test:torch -- --regex basic_vitals
Reviewed By: xuzhao9
Differential Revision: D28357615
fbshipit-source-id: 681bf9ef63cb1458df9f1c241d301a3ddf1e5252
Summary:
Currently foreach `addcmul` and `addcdiv` cast scalar to float so that actual math is done in FP32 when tensor dtype is Float16/BFloat16 while regular `addcmul` and `addcdiv`, not.
### Reproducible steps to see the behavioral difference
```ipython
In [1]: import torch; torch.__version__
Out[1]: '1.9.0'
In [2]: a, b, c = torch.tensor([60000.0], device='cuda', dtype=torch.half), torch.tensor([60000.0], device='cuda', dtype=torch.half), torch.tensor([-1.0], device='cuda', dtype=torch.half)
In [4]: torch.addcmul(a, b, c, value=2)
Out[4]: tensor([-inf], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float16)
In [5]: torch._foreach_addcmul([a], [b], [c], value=2)[0]
Out[5]: tensor([-60000.], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float16)
```
### How foreach casts?
Foreach addcmul and addcdiv cast scalar to `opmath_t` (almost equivalent to acc_type) here: 42c8439b6e/aten/src/ATen/native/cuda/ForeachPointwiseOp.cu (L30) and cast inputs and results here:
42c8439b6e/aten/src/ATen/native/cuda/ForeachFunctors.cuh (L133-L135)
Related to https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/58833#60227https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/60454
cc ptrblck mcarilli ngimel
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/60715
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D29385715
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 8bb2db19ab66fc99d686de056a6ee60f9f71d603
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/56036
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/56130
* All the interior points are computed using second order accurate central differences method for gradient operator. However, currently we only have first order method computation for edge points. In this PR we are adding second order methods for edge points as well.
* Currently, there is no detailed description of how gradient operator computed using second order method, and how to use parameters correctly. We add detailed explanation of meaning of each parameter, and return of the gradient operator, meanwhile giving description of the second-order computation.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58165
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D29305321
Pulled By: iramazanli
fbshipit-source-id: 0e0e418eed801c8510b8babe2ad3d064479fb4d6
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/27655
This PR adds a C++ and Python version of ReflectionPad3d with structured kernels. The implementation uses lambdas extensively to better share code from the backward and forward pass.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/59791
Reviewed By: gchanan
Differential Revision: D29242015
Pulled By: jbschlosser
fbshipit-source-id: 18e692d3b49b74082be09f373fc95fb7891e1b56
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/59014Fixes#48401
`assert_no_overlap` currently has a false-negative where it recognizes
the transpose of a contiguous tensor as fully overlapping. This happens because
the memory regions do fully overlap, but of course the strides are different so
the actual elements don't all overlap.
This goes slightly in the other direction, by requiring strides to exactly
match we get false-positives for some unusual situations, e.g.
```
torch.add(a, a, out=a.view([1, *a.shape]))
```
Or replacing strides of length-1 dimensions, etc. However, I think these are
sufficiently obscure that it's okay to error and the common cases like
inplace operations still work as before.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: gchanan
Differential Revision: D29040928
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 5a636c67536a3809c83f0d3117d2fdf49c0a45e6
Summary:
Based from https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/50466
Adds the initial implementation of `torch.cov` similar to `numpy.cov`. For simplicity, we removed support for many parameters in `numpy.cov` that are either redundant such as `bias`, or have simple workarounds such as `y` and `rowvar`.
cc PandaBoi
TODO
- [x] Improve documentation
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58311
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D28994140
Pulled By: heitorschueroff
fbshipit-source-id: 1890166c0a9c01e0a536acd91571cd704d632f44
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/59596
Parallelize batch matmul across batch dim. This was found to improve perf for
some usecases on mobile.
ghstack-source-id: 130989569
Test Plan: CI unit tests
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D26833417
fbshipit-source-id: 9b84d89d29883a6c9d992d993844dd31a25f76b1
Summary:
Implements an idea by ngimel to improve the performance of `torch.flip` via a clever hack into TI to bypass the fact that TI is not designed to work with negative indices.
Something that might be added is vectorisation support on CPU, given how simple the implementation is now.
Some low-hanging fruits that I did not implement:
- Write it as a structured kernel
- Migrate the tests to opinfos
- Have a look at `cumsum_backward` and `cumprod_backward`, as I think that they could be implemented faster with `flip`, now that `flip` is fast.
**Edit**
This operation already has OpInfos and it cannot be migrated to a structured kernel because it implements quantisation
Summary of the PR:
- x1.5-3 performance boost on CPU
- x1.5-2 performance boost on CUDA
- Comparable performance across dimensions, regardless of the strides (thanks TI)
- Simpler code
<details>
<summary>
Test Script
</summary>
```python
from itertools import product
import torch
from torch.utils.benchmark import Compare, Timer
def get_timer(size, dims, num_threads, device):
x = torch.rand(*size, device=device)
timer = Timer(
"torch.flip(x, dims=dims)",
globals={"x": x, "dims": dims},
label=f"Flip {device}",
description=f"dims: {dims}",
sub_label=f"size: {size}",
num_threads=num_threads,
)
return timer.blocked_autorange(min_run_time=5)
def get_params():
sizes = ((1000,)*2, (1000,)*3, (10000,)*2)
for size, device in product(sizes, ("cpu", "cuda")):
threads = (1, 2, 4) if device == "cpu" else (1,)
list_dims = [(0,), (1,), (0, 1)]
if len(size) == 3:
list_dims.append((0, 2))
for num_threads, dims in product(threads, list_dims):
yield size, dims, num_threads, device
def compare():
compare = Compare([get_timer(*params) for params in get_params()])
compare.trim_significant_figures()
compare.colorize()
compare.print()
compare()
```
</details>
<details>
<summary>
Benchmark PR
</summary>
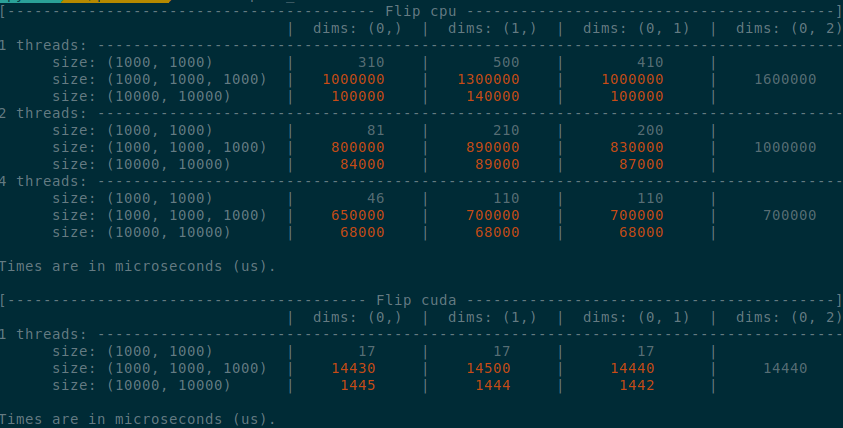
</details>
<details>
<summary>
Benchmark master
</summary>
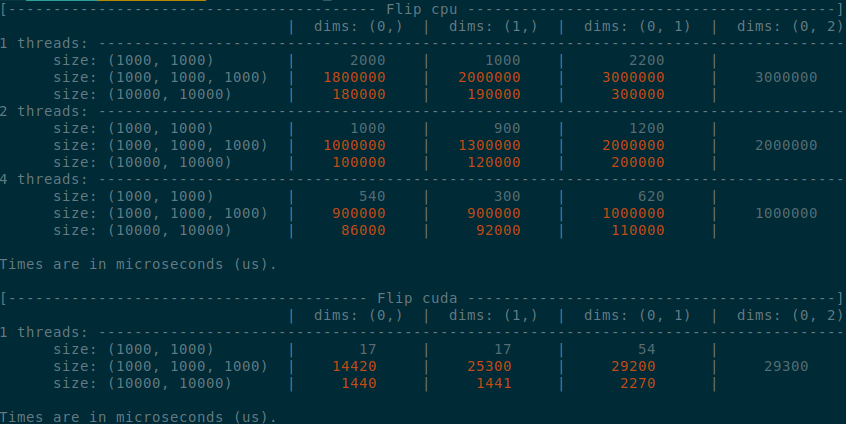
</details>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58747
Reviewed By: agolynski
Differential Revision: D28877076
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 4fa6eb519085950176cb3a9161eeb3b6289ec575
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/56017Fixes#55686
This patch is seemingly straightforward but some of the changes are very
subtle. For the general algorithmic approach, please first read the
quoted issue. Based on the algorithm, there are some fairly
straightforward changes:
- New boolean on TensorImpl tracking if we own the pyobj or not
- PythonHooks virtual interface for requesting deallocation of pyobj
when TensorImpl is being released and we own its pyobj, and
implementation of the hooks in python_tensor.cpp
- Modification of THPVariable to MaybeOwned its C++ tensor, directly
using swolchok's nice new class
And then, there is python_variable.cpp. Some of the changes follow the
general algorithmic approach:
- THPVariable_NewWithVar is simply adjusted to handle MaybeOwned and
initializes as owend (like before)
- THPVariable_Wrap adds the logic for reverting ownership back to
PyObject when we take out an owning reference to the Python object
- THPVariable_dealloc attempts to resurrect the Python object if
the C++ tensor is live, and otherwise does the same old implementation
as before
- THPVariable_tryResurrect implements the resurrection logic. It is
modeled after CPython code so read the cited logic and see if
it is faithfully replicated
- THPVariable_clear is slightly updated for MaybeOwned and also to
preserve the invariant that if owns_pyobj, then pyobj_ is not null.
This change is slightly dodgy: the previous implementation has a
comment mentioning that the pyobj nulling is required to ensure we
don't try to reuse the dead pyobj. I don't think, in this new world,
this is possible, because the invariant says that the pyobj only
dies if the C++ object is dead too. But I still unset the field
for safety.
And then... there is THPVariableMetaType. colesbury explained in the
issue why this is necessary: when destructing an object in Python, you
start off by running the tp_dealloc of the subclass before moving up
to the parent class (much in the same way C++ destructors work). The
deallocation process for a vanilla Python-defined class does irreparable
harm to the PyObject instance (e.g., the finalizers get run) making it
no longer valid attempt to resurrect later in the tp_dealloc chain.
(BTW, the fact that objects can resurrect but in an invalid state is
one of the reasons why it's so frickin' hard to write correct __del__
implementations). So we need to make sure that we actually override
the tp_dealloc of the bottom most *subclass* of Tensor to make sure
we attempt a resurrection before we start finalizing. To do this,
we need to define a metaclass for Tensor that can override tp_dealloc
whenever we create a new subclass of Tensor. By the way, it was totally
not documented how to create metaclasses in the C++ API, and it took
a good bit of trial error to figure it out (and the answer is now
immortalized in https://stackoverflow.com/q/67077317/23845 -- the things
that I got wrong in earlier versions of the PR included setting
tp_basicsize incorrectly, incorrectly setting Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_GC on
the metaclass--you want to leave it unset so that it inherits, and
determining that tp_init is what actually gets called when you construct
a class, not tp_call as another not-to-be-named StackOverflow question
suggests).
Aside: Ordinarily, adding a metaclass to a class is a user visible
change, as it means that it is no longer valid to mixin another class
with a different metaclass. However, because _C._TensorBase is a C
extension object, it will typically conflict with most other
metaclasses, so this is not BC breaking.
The desired new behavior of a subclass tp_dealloc is to first test if
we should resurrect, and otherwise do the same old behavior. In an
initial implementation of this patch, I implemented this by saving the
original tp_dealloc (which references subtype_dealloc, the "standard"
dealloc for all Python defined classes) and invoking it. However, this
results in an infinite loop, as it attempts to call the dealloc function
of the base type, but incorrectly chooses subclass type (because it is
not a subtype_dealloc, as we have overridden it; see
b38601d496/Objects/typeobject.c (L1261) )
So, with great reluctance, I must duplicate the behavior of
subtype_dealloc in our implementation. Note that this is not entirely
unheard of in Python binding code; for example, Cython
c25c3ccc4b/Cython/Compiler/ModuleNode.py (L1560)
also does similar things. This logic makes up the bulk of
THPVariable_subclass_dealloc
To review this, you should pull up the CPython copy of subtype_dealloc
b38601d496/Objects/typeobject.c (L1230)
and verify that I have specialized the implementation for our case
appropriately. Among the simplifications I made:
- I assume PyType_IS_GC, because I assume that Tensor subclasses are
only ever done in Python and those classes are always subject to GC.
(BTW, yes! This means I have broken anyone who has extend PyTorch
tensor from C API directly. I'm going to guess no one has actually
done this.)
- I don't bother walking up the type bases to find the parent dealloc;
I know it is always THPVariable_dealloc. Similarly, I can get rid
of some parent type tests based on knowledge of how
THPVariable_dealloc is defined
- The CPython version calls some private APIs which I can't call, so
I use the public PyObject_GC_UnTrack APIs.
- I don't allow the finalizer of a Tensor to change its type (but
more on this shortly)
One alternative I discussed with colesbury was instead of copy pasting
the subtype_dealloc, we could transmute the type of the object that was
dying to turn it into a different object whose tp_dealloc is
subtype_dealloc, so the stock subtype_dealloc would then be applicable.
We decided this would be kind of weird and didn't do it that way.
TODO:
- More code comments
- Figure out how not to increase the size of TensorImpl with the new
bool field
- Add some torture tests for the THPVariable_subclass_dealloc, e.g.,
involving subclasses of Tensors that do strange things with finalizers
- Benchmark the impact of taking the GIL to release C++ side tensors
(e.g., from autograd)
- Benchmark the impact of adding a new metaclass to Tensor (probably
will be done by separating out the metaclass change into its own
change)
- Benchmark the impact of changing THPVariable to conditionally own
Tensor (as opposed to unconditionally owning it, as before)
- Add tests that this actually indeed preserves the Python object
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D27765125
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 857f14bdcca2900727412aff4c2e2d7f0af1415a
Summary:
1) remove pushing back to strides vector for 1D tensors, those strides are never used in the loop anyway
2) avoid calling get_data_ptrs unless necessary
3) don't call into assert_no_partial_overlap if tensorImpls are the same (assert_no_partial_overlap has this comparison too, but after a couple of nested function calls)
4) is_non_overlapping_and_dense instead of is_contiguous in memory overlap (which, for some reason, is faster than is_contiguous, though I hoped after is_contiguous is non-virtualized, it should be the same).
Altogether, brings instruction count down from ~110K to 102735 for the following binary inplace benchmark:
```
In [2]: timer = Timer("m1.add_(b);", setup="at::Tensor m1=torch::empty({1}); at::Tensor b = torch::empty({1});", language="c++", timer=timeit.default_timer)
...: stats=timer.collect_callgrind(number=30, repeats=3)
...: print(stats[1].as_standardized().stats(inclusive=False))
```
similar improvements for unary inplace.
Upd: returned stride packing for now, counts is now 104295, so packing is worth ~ 52 instructions, we should think about how to remove it safely.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58810
Reviewed By: bhosmer
Differential Revision: D28664514
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 2e03cf90b37a411d9994a7607402645f1d8f3c93
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58881
recently added new parameter to the function with PR: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58417
However, this introduced ambiguity when making call below:
some_tensor.repeat_interleave(some_integer_value)
Making it optional to avoid the issue.
Reviewed By: ezyang, ngimel
Differential Revision: D28653820
fbshipit-source-id: 5bc0b1f326f069ff505554b51e3b24d60e69c843
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58417
Same as title.
Test Plan:
Rely on CI signal.
Update unit test to exercise new code path as well.
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D28482927
fbshipit-source-id: 3ec8682810ed5c8547b1e8d3869924480ce63dcd
Summary:
This adds the methods `Tensor.cfloat()` and `Tensor.cdouble()`.
I was not able to find the tests for `.float()` functions. I'd be happy to add similar tests for these functions once someone points me to them.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/56014
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58137
Reviewed By: ejguan
Differential Revision: D28412288
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: ff3653cb3516bcb3d26a97b9ec3d314f1f42f83d
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58144
reland D28291041 (14badd9929), which was reverted due to a type error from Tuple[torch.Tensor], seems that mypy requires Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]
Test Plan:
buck test mode/opt //caffe2/test:torch_cuda -- test_index_copy_deterministic
✓ ListingSuccess: caffe2/test:torch_cuda - main (9.229)
✓ Pass: caffe2/test:torch_cuda - test_index_copy_deterministic_cuda (test_torch.TestTorchDeviceTypeCUDA) (25.750)
✓ Pass: caffe2/test:torch_cuda - main (25.750)
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D28383178
fbshipit-source-id: 38896fd6ddd670cfcce36e079aee7ad52adc2a28
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/57544
Instead of removing tp_new from the superclass (which causes
super().__new__ to not work), I now still install tp_new on the
superclass, but verify that you are not trying to directly
construct _TensorBase.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/57421
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D28189475
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 9397a3842a77f5428d182dd62244b42425bca827
Summary:
This PR also removes qr and eig tests from test/test_torch.py. They were not skipped if compiled without LAPACK and they are now replaced with OpInfos.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/55929
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/56284
Reviewed By: ejguan
Differential Revision: D27827077
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 1dceb955810a9fa34bb6baaccbaf0c8229444d3a
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/55090
I included the header directly, but I am not sure if we should add this as a git submodule, what do you guys think?
Also regarding the implementation, in ATen lanes seems not to be supported, but from CuPy complex types are exported with 2 lanes, I am not sure wether this is correct or not. However, in PyTorch this seems to be working properly, so I forgive 2 lanes for complex datatypes.
TODO: add tests for complex and bfloat
Easy test script against cupy
```python
import cupy
import torch
from torch.utils.dlpack import to_dlpack
from torch.utils.dlpack import from_dlpack
# Create a PyTorch tensor.
tx1 = torch.tensor(
[2 + 1j, 3 + 2j, 4 + 3j, 5 + 4j], dtype=torch.complex128
).cuda()
# Convert it into a DLPack tensor.
dx = to_dlpack(tx1)
# Convert it into a CuPy array.
cx = cupy.fromDlpack(dx)
# Convert it back to a PyTorch tensor.
tx2 = from_dlpack(cx.toDlpack())
torch.testing.assert_allclose(tx1, tx2)
```
Thanks to leofang who updated CuPy's dlpack version and his PR served me as the guide for this one.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/55365
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D27724923
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 481eadb882ff3dd31e7664e08e8908c60a960f66
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/56150
See #56017 for full context; the short story is that by making
it illegal to directly construct _TensorBase, we need only
write a *single* tp_dealloc function which will work universally
for all _TensorBase subclasses, rather than having to write two
versions, one for _TensorBase itself, and others for Python subclasses
of _TensorBase. This means simpler code.
The subtlety here is that we only install our custom `tp_new` for direct subclasses of TensorBase. This is important, because overriding the `tp_new` also overrides any user defined constructor. Fortunately class Tensor(_TensorBase) has no nontrivial constructors and doesn't mind, but other subclasses like Parameter definitely mind!
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: H-Huang
Differential Revision: D28028746
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 3c03a14666ad1ded1145fe676afb0a7623cdb9bb
Summary:
The test seems to be failing in ROCM 4.1 on CI node. Disabling the same for now. The test will be re-enabled for ROCM when CI transitions to 4.2.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/56951
Reviewed By: zou3519
Differential Revision: D28059808
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: a9b064b7525ae6dce89c51fe29ff07f37b7ac796
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/46702
- fails on probability distribution with odd items
- trying to access an `acc_type` (`float`) in a `scalar_t` (`float16`) aligned memory
- produce unrepeatable result for large input tensor
- parallel cumsum not monotonic at some positions
### Fixes
- computing cumsum on `acc_type` (`float`) instead of using `scalar_t` (`float16`) fixed both issues
- the non-monotonic behavior may happen even using `float`, though
- in these cases, deterministic behavior may be achieved by eliminating the race condition when writing the result, using the atomic function `atomicMax`
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/55364
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D28031666
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 0fc6289e0b9ea2d31ef3771e7ca370de8f5c02de
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/55102
To avoid casting a tensor to `.long()`, we introduce support for int32 in `torch.repeat_interleave`.
Reviewed By: ezyang
Differential Revision: D27478235
fbshipit-source-id: 08b4cce65fe94ff10535ddc07e1ba2bacea6a2cf
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/53238
There is a tension for the Vitals design: (1) we want a macro based logging API for C++ and (2) we want a clean python API. Furthermore, we want to this to work with "print on destruction" semantics.
The unfortunate resolution is that there are (2) ways to define vitals:
(1) Use the macros for local use only within C++ - this keeps the semantics people enjoy
(2) For vitals to be used through either C++ or Python, we use a global VitalsAPI object.
Both these go to the same place for the user: printing to stdout as the globals are destructed.
The long history on this diff shows many different ways to try to avoid having 2 different paths... we tried weak pointers & shared pointers, verbose switch cases, etc. Ultimately each ran into an ugly trade-off and this cuts the difference better the alternatives.
Test Plan:
buck test mode/dev caffe2/test:torch -- --regex vital
buck test //caffe2/aten:vitals
Reviewed By: orionr
Differential Revision: D26736443
fbshipit-source-id: ccab464224913edd07c1e8532093f673cdcb789f
Summary:
#### Reason for relanding
Line 1607 of `torch/testing/_internal/common_methods_invocations.py` of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/50999 had `dtype` instead of `dtype=torch.bool`, so 4 of the 9 sample inputs for `bool` had incorrect dtype. This bug was caught by https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/54949.
1. Added support for pow() on CPU for `float16` (`Half`) and `bfloat16` types.
Both `pow(Tensor, Scalar)` and `pow(Tensor, Tensor)` are now supported for the aforementioned types.
However autograd isn't supported for `Float16` on CPU yet, as `log_vml_cpu` can't be enabled for it.
2. heitorschueroff added `pow_tensor_scalar_optimized_kernel` to refactor & simplify `PowKernel.cpp`.
It provides a common path for all the complex types & floating point types (except Float16, due to lack of complete AVX2 vectorization support for it). It replaced code that had previously been duplicated for (float, double) and complex types,
so PowKernel.cpp looks a lot cleaner now.
3. Enabled (unskipped) some tests for `erf`, `erfc`,`erfinv`, `tan` and `linalg.vector.norm` which were being skipped earlier due to `pow()` not having been implemented for `float16` & `bfloat16`.
4. Added an OpInfo for `pow()` & enabled some test cases for `pow()`.
5. Extended the coverage of existing tests for `pow` in `test_binary_ufuncs.py` in order to enable comparison with `numpy`, even with discontiguous tensors, and added a test to ensure that a runtime error is raised for `pow`'s inplace variant if resizing the base tensor is required during its invocation.
6. Added `float16` & `bfloat16` to `square`'s dtype lists in its `UnaryUfuncInfo`.
7. Removed redundant `dtypesIfCPU` and `dtypesIfCUDA` from `OpInfo`s where they are equal to `dtypes`.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/55280
Reviewed By: jbschlosser
Differential Revision: D27591772
Pulled By: heitorschueroff
fbshipit-source-id: c7420811b32595bb3353149a61e54a73f2eb352b
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/55150
Somehow I forgot to add these checks. Now they're in here. Thanks
ngimel for noticing.
This is probably a slight efficiency hit on TensorIterator, which is
probably already doing all these checks. Would be good to follow up
on this, though it may not be easily fixable with the TI rewrite.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: zhangguanheng66
Differential Revision: D27523879
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 458e617dbc6de6fcfa9e5841148b30b99f52e001
Summary:
Added the functionality desired in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/50789.
1. Added support for pow() on CPU for `float16` (`Half`) and `bfloat16` types.
Both `pow(Tensor, Scalar)` and `pow(Tensor, Tensor)` are now supported for the aforementioned types.
However autograd isn't supported for `Float16` on CPU yet, as `log_vml_cpu` can't be enabled for it.
2. heitorschueroff added `pow_tensor_scalar_optimized_kernel` to refactor & simplify `PowKernel.cpp`.
It provides a common path for all the complex types & floating point types (except Float16, due to lack of complete AVX2 vectorization support for it). It replaced code that had previously been duplicated for (float, double) and complex types,
so PowKernel.cpp looks a lot cleaner now.
3. Enabled (unskipped) some tests for `erf`, `erfc`,`erfinv`, `linalg.norm` and `linalg.vector.norm` which were being skipped earlier due to `pow()` not having been implemented for `float16` & `bfloat16`.
4. Added an OpInfo for `pow()` & enabled some test cases for `pow()`.
5. Extended the coverage of existing tests for `pow` in `test_binary_ufuncs.py` in order to enable comparison with `numpy`, even with discontiguous tensors, and added a test to ensure that a runtime error is raised for `pow`'s inplace variant if resizing the base tensor is required during its invocation.
6. Added `float16` & `bfloat16` to `square`'s dtype lists in its `UnaryUfuncInfo`.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/50999
Reviewed By: zou3519
Differential Revision: D27478225
Pulled By: heitorschueroff
fbshipit-source-id: d309dd98d5a96d0cb9b08281757bb1c65266d011
Summary:
- Corrected a few errata in the SVD docs
- Made the notation more uniform (refer to `Vh` in `linalg.svd`, always use double tilts...)
- Wrote a better explanation about why the gradients of `U` and `V` are not well-defined when the input is complex or real but has repeated singular values. The previous one pointed to a somewhat obscure post on gauge theory.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/54002
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D27459502
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: f5c35eca02d35dadd2fc0eeadfacc8824f409400
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/54901
Some subtleties:
- Need to make sure not to clobber composite definitions when
deciding when to generate
- I was lazy and so I didn't make inplace on TensorList work,
nor did I make inplace functions that returned void work
- A few tests started complaining that these noop meta functions
weren't raising the errors they needed. This is tracked
in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/54897
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: jbschlosser
Differential Revision: D27407232
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 5e706a267496368acdafd128942c310954e43d29
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/53973
Two parts to this PR; I had to put them together because adding support for X causes more test code to be exercised, which in turn may require a fix for Y.
The first part is restoring the concept of storage to meta tensors. Previously, meta tensors had a nullptr storage (e.g., `meta_tensor.storage()` is an error.) As I was increasing the coverage of meta tensors, I started running into test cases (specifically memory overlap tests) that were failing because not having storage meant I couldn't check for memory overlap. After some discussion, we decided that it would make sense for meta tensors to model this as well (we already model strides, so getting accurate view information also seems useful). This PR does that by:
* Rewrite all of the factory functions in MetaTensor.cpp to use the generic versions (which are very carefully written to not actually poke at the data pointer, so everything works out). The key idea here is we give meta tensors a special allocator, MetaAllocator, which always returns a nullptr even if you ask for a nonzero number of bytes. resize_ is also made generic; the normal variant can be used directly rather than having to instruct it to avoid resizing storage
* Turn on memory overlap checking in TensorIterator even for meta tensors
* Although meta tensors now have storage, the concept of meta storage is NOT exposed to Python land (as it would imply I would have to codegen MetaFloatStorage, MetaDoubleStorage, etc. classes). So `x.storage()` still raises an error and I have a cludge in `__deepcopy__` to break storage sharing upon deep copy (this is wrong, but no tests exercise this at the moment).
The second part is adding more support for the most used functions in the test suite.
* Inplace operations have very simple meta functions. I added `fill_`, `zero_`, `random_`, `uniform_` and `normal_`. In the case of random, I take advantage of pbelevich's templates for defining random kernels, so that I can reuse the common scaffolding, and then just register a noop stub that actually does the RNG. (Look, another structured kernels tiny variant!)
* `copy_` is now implemented. Copying into a meta tensor is always OK, but copying out of a meta tensor raises an error (as we don't know what the "correct" data to copy out is in this case)
* `empty_strided` usage from structured kernels now is implemented (TBH, this could have been done as soon as `empty_strided` was added)
* Meta was missing in a few places in TensorOptions/DispatchKey utility functions, so I added them
* Autograd engine now correctly homes meta tensors with CPU tensors (they have -1 device index so CUDA queues wouldn't work anyway)
* `apply_`, `map_` and `map2_` are special cased to no-op on meta tensor self. These count as inplace operations too but they are implemented a little differently.
Getting more meta function support triggers a number of bugs in the test suite, which I then fix:
- Linear algebra functions sometimes don't report NotImplementedError because they get swallowed by catch all try blocks. This is tracked in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/53739
- dlpack obviously doesn't work with meta tensors, I just disabled the test
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Differential Revision: D27036572
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: agolynski, bdhirsh
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 7005ecf4feb92a643c37389fdfbd852dbf00ac78
Summary:
```
index_add(Tensor self, int dim, Tensor index, Tensor source) -> Tensor
```
now becomes
```
index_add(Tensor self, int dim, Tensor index, Tensor source, Scalar alpha=1) -> Tensor
```
Generally, this sounds useful and harmless, and inside PyTorch, we are already needing this feature in `add_out_dense_sparse_cuda`, see the `SparseCUDATensorMath.cu` change in this PR.
**Test not added yet. Will add if after discussion we believe this is a good idea.**
- [ ] TODO: add test
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/54176
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D27319198
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: fe43be082d1230c87c5313458213d5252be2ff23
Summary:
Added the support for half / bfloat / bool for `index_select`, as suggested by ngimel in
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/49707#issuecomment-788140578
For the tests to pass, I also added the support for `index_add`.
I added `OpInfo` tests for `index_add` and more thorough forward tests for `index_select` to test these changes.
While doing so, I found that the support for scalar types in the derivative of `index_add` was not correct, so I corrected it.
Resolves https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/49707
It should also resolve similar issues that I encountered when porting `index_copy`, `take` and `put`.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/53898
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D27193294
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 5a0af2c62a0cf24f3cc9c74f230ab4f3712bbb7a
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/54079
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/53815
Instead of testing if something is CUDA, we instead test if something
is not CPU. This in the general theming of "Don't be so darn CUDA
centric".
Intruigingly, we didn't have a is_cpu() method on Tensor. Which seems
like a big oversight and one of the reasons how we ended up in this
mess. So in it goes. Maybe we should also get this for Python bindings
as well (but in that case, should probably look into redoing all of the
is_X bindings so they aren't done manually).
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D27109507
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: abbe72c2e688c452ffe098d206cb79938b5824b1
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/53759Fixes#53587, see issue for in-depth explanation of the bug.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D26971342
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 805983fed2658e27fb033f36a71fd30950a29328
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/53665
ngimel pointed out to me where we already test the behavior of the `Upsample` ops in `test_nn.py`. This PR deleting my bespoke tests in `test_torch.py` and updates those in `test_nn.py` to test memory format properly.
There were two reasons the original test didn't pick up on a memory format regression:
- They didn't test the memory format of the output tensor explicitly, i.e. `output.is_contiguous(memory_format=...)`
- Even with that change, the test tensors were to simple to fail the tests. From some trial and error, it looks like one of the first two dimensions in the inputs needs to be > 1 in order for the `channels_last` memory format to actually re-order the strides.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D26929683
Pulled By: bdhirsh
fbshipit-source-id: d17bc660ff031e9b3e2c93c60a9e9308e56ea612
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/48841 for half datatype (it was fixed for other datatypes before).
The reason for https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/48841 happening for half was that `exponential_` for half was producing 0s.
Exponential distribution implementation on cuda is here e08aae2613/aten/src/ATen/native/cuda/DistributionTemplates.h (L535-L545)
with `transformation::exponential` defined here
e08aae2613/aten/src/ATen/core/TransformationHelper.h (L113-L123)
It takes a uniformly distributed random number and takes `log` of it. If necessary, the result is then converted to low precision datatype (half). To avoid 0's, before applying `log`, ones are replaced with std::nextafter(1,0). This seems fine, because log(1-eps) is still representable in half precision (`torch.tensor([1.], device="cuda").nextafter(torch.tensor([0.], device="cuda")).log().half()` produces 5.96e-8) , so casting to `scalar_t` should work. However, since fast log approximation is used (`__logf`), the log result is ~3e-9 instead of more accurate 5.96e-8, and underflows when casting to half. Using `::log` instead of fast approximation fixes it, however, it comes with ~20% perf penalty on exponential kernel for fp32 datatype, probably more for half.
Edit: alternative approach used now is to filter all small values returned by transformation. The result is equivalent to squashing of 1's to 1-eps that was used before, and computing correct log of 1-eps (which is -eps, exactly equal even for doubles). This doesn't incur noticeable performance hit.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/53480
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D26924622
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: dc1329e4773bf91f26af23c8afa0ae845cfb0937
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/53535
During the port to structured kernels for upsample kernels, I missed that a subset of them explicitly pass `memory_format` information from the input to the output tensors.
Note 1:
I added the logic into the `meta` function of each op, which feels morally correct since this logic affects the output shape/metadata. One consequence is that all backend implementations will get the logic. I synced with fmassa that this seems reasonable.
Note 2:
This logic used to happen in the following operators, which this PR fixes:
- upsample_nearest3d
- upsample_trilinear3d
- upsample_nearest2d
- upsample_bilinear2d
I explicitly didn't patch the other upsample kernels, which look like they never forwarded memory_format information:
- `upsample_bicubic2d` (maybe this should though? `UpSampleBicubic2d.cpp` isn't currently written to do anything different for `channels_last` tensors)
- All of the `upsample_{mode}1d` operators. Probably because, afaik, channels_last isn't supported for 3d tensors
- The corresponding backwards operator for every upsample op.
Note 3:
I'm also wondering why memory_format isn't just directly a part of the `tensor::options()` method, which would cause all ops to universally forward memory_format information from input to output tensors, rather than just the upsample ops. My guess is:
- BC-breakage. I'm not sure whether this would really *break* people, but it's an API change
- performance. `tensor::options()` is called everywhere, and adding a call to `suggest_memory_format()` would probably noticeably hit microbenchmarks. We could probably deal with that by making `memory_format` a precomputed field on the tensor?
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: H-Huang
Differential Revision: D26891540
Pulled By: bdhirsh
fbshipit-source-id: b3845f4dd5646b88bf738b9e41fe829be6b0e5cf
Summary:
Helps make master green by removing this hefty memory allocating from CPU test.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/53561
Reviewed By: malfet, albanD
Differential Revision: D26897941
Pulled By: janeyx99
fbshipit-source-id: 9f6c2d55f4eea1ab48665f7819fc113f21991036
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/53276
- One of the tests had a syntax error (but the test
wasn't fine grained enough to catch this; any error
was a pass)
- Doesn't work on ROCm
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Differential Revision: D26820048
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: mruberry
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: b02c4252d10191c3b1b78f141d008084dc860c45
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/53143
Meta is now an honest to goodness device type, like cpu, so you can use
device='meta' to trigger allocation of meta tensors. This way better
than empty_meta since we now have working API for most factory functions
(they don't necessarily work yet, though, because need to register Meta
versions of those functions.)
Some subtleties:
- I decided to drop the concept of CPU versus CUDA meta tensors; meta
tensors are device agnostic. It's hard to say exactly what the
correct level of abstraction here is, but in this particular case
implementation considerations trump semantic considerations: it
is way easier to have just a meta device, than to have a meta device
AND a cpu device AND a cuda device. This may limit the applicability
of meta tensors for tracing models that do explicit cpu()/cuda()
conversions (unless, perhaps, we make those operations no-ops on meta
tensors).
- I noticed that the DeviceType uppercase strings are kind of weird.
Are they really supposed to be all caps? That's weird.
- I moved the Meta dispatch key to live with the rest of the "device"
dispatch keys.
- I intentionally did NOT add a Backend for Meta. For now, I'm going to
hope meta tensors never exercise any of the Backend conversion code;
even if it does, better to fix the code to just stop converting to and
from Backend.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: samestep
Differential Revision: D26763552
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 14633b6ca738e60b921db66a763155d01795480d
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/52213
Nans were previously inconsistently propagated due to std::min always returning first argument if one of the args in nan
when reduction functor was called on 2 `-inf` arguments, `std::min(x,y) - std::max(x,y)` resulted in `-inf - (-inf)` = nan, even though logcumsumexp is well defined for `-inf, -inf` pair.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/52947
Reviewed By: H-Huang
Differential Revision: D26718456
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: a44433889da352cc959786dd15b6361a68fcfed7
Summary:
This PR adds functionality to skip a test based on CUDA version.
This way, we can be more specific when skipping a test, such as when the test only fails for a particular CUDA version.
This allows us to add back the skipped tests for CUDA 11.2 for other CUDA versions, such as 10.1 and 11.1.
I tested this locally (by using 11.0 instead of 11.2), but will run all the CI to make sure it works.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/52359
Reviewed By: walterddr
Differential Revision: D26487951
Pulled By: janeyx99
fbshipit-source-id: 45c71cc6105ffd9985054880009cf68ea5ef3f6a
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/51719, https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/28142
**Change**
- Update `torch.Tensor.unflatten` to support users pass`-1` as the inferred size for both tensors and named tensors.
- Examples of using `-1` in the `unflatten` function are added to the docs.
- Fix the rendered issue of original `unflatten` docs by removing a blank line between its example section.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/51955
Reviewed By: agolynski
Differential Revision: D26467198
Pulled By: zou3519
fbshipit-source-id: 6a3ede25561223187273796427ad0cb63f125364
Summary:
Reference: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/50006
We should probably add aliases for these operators to be consistent with NumPy names i.e. `np.degrees` and `np.radians`.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/51283
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D26171163
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 1869604ed400820d95f6ff50a0e3cba1de1ffa84
Summary:
Adding CUDA 11.2 to Windows CI.
Disabled tests:
The following ran into `CUDA error: misaligned address` for CUDA 11.2: (issue linked below)
`test_where_scalar_valid_combination_cuda_complex128` in test_torch.py
`test_sgn_complex_cuda` in test_autograd.py
The following ran into `CUDA error: too many resources requested for launch` for CUDA 11.2: (https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/52002)
test_EmbeddingBag_per_sample_weights_and_new_offsets_cuda_int64_float64
test_EmbeddingBag_per_sample_weights_and_offsets_cuda_int64_float64
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/51598
Reviewed By: mrshenli
Differential Revision: D26344965
Pulled By: janeyx99
fbshipit-source-id: 3c9a4ed16d748969e96593220ec0a9f33e1ffcef
Summary:
Toward fixing https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/47624
~Step 1: add `TORCH_WARN_MAYBE` which can either warn once or every time in c++, and add a c++ function to toggle the value.
Step 2 will be to expose this to python for tests. Should I continue in this PR or should we take a different approach: add the python level exposure without changing any c++ code and then over a series of PRs change each call site to use the new macro and change the tests to make sure it is being checked?~
Step 1: add a python and c++ toggle to convert TORCH_WARN_ONCE into TORCH_WARN so the warnings can be caught in tests
Step 2: add a python-level decorator to use this toggle in tests
Step 3: (in future PRs): use the decorator to catch the warnings instead of `maybeWarnsRegex`
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/48560
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D26171175
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: d83c18f131d282474a24c50f70a6eee82687158f
Summary:
Implements `np.diff` for single order differences only:
- method and function variants for `diff` and function variant for `diff_out`
- supports out variant, but not in-place since shape changes
- adds OpInfo entry, and test in `test_torch`
- automatic autograd because we are using the `Math` dispatch
_Update: we only support Tensors for prepend and append in this PR. See discussion below and comments for more details._
Currently there is a quirk in the c++ API based on how this is implemented: it is not possible to specify scalar prepend and appends without also specifying all 4 arguments.
That is because the goal is to match NumPy's diff signature of `diff(int n=1, int dim=-1, Union[Scalar, Tensor] prepend=None, Union[Scalar, Tensor] append)=None` where all arguments are optional, positional and in the correct order.
There are a couple blockers. One is c++ ambiguity. This prevents us from simply doing `diff(int n=1, int dim=-1, Scalar? prepend=None, Tensor? append=None)` etc for all combinations of {Tensor, Scalar} x {Tensor, Scalar}.
Why not have append, prepend not have default args and then write out the whole power set of {Tensor, Scalar, omitted} x {Tensor, Scalar, omitted} you might ask. Aside from having to write 18 overloads, this is actually illegal because arguments with defaults must come after arguments without defaults. This would mean having to write `diff(prepend, append, n, dim)` which is not desired. Finally writing out the entire power set of all arguments n, dim, prepend, append is out of the question because that would actually involve 2 * 2 * 3 * 3 = 36 combinations. And if we include the out variant, that would be 72 overloads!
With this in mind, the current way this is implemented is actually to still do `diff(int n=1, int dim=-1, Scalar? prepend=None, Tensor? append=None)`. But also make use of `cpp_no_default_args`. The idea is to only have one of the 4 {Tensor, Scalar} x {Tensor, Scalar} provide default arguments for the c++ api, and add `cpp_no_default_args` for the remaining 3 overloads. With this, Python api works as expected, but some calls such as `diff(prepend=1)` won't work on c++ api.
We can optionally add 18 more overloads that cover the {dim, n, no-args} x {scalar-tensor, tensor-scalar, scalar-scalar} x {out, non-out} cases for c++ api. _[edit: counting is hard - just realized this number is still wrong. We should try to count the cases we do cover instead and subtract that from the total: (2 * 2 * 3 * 3) - (3 + 2^4) = 17. 3 comes from the 3 of 4 combinations of {tensor, scalar}^2 that we declare to be `cpp_no_default_args`, and the one remaining case that has default arguments has covers 2^4 cases. So actual count is 34 additional overloads to support all possible calls]_
_[edit: thanks to https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/50767 hacky_wrapper is no longer necessary; it is removed in the latest commit]_
hacky_wrapper was also necessary here because `Tensor?` will cause dispatch to look for the `const optional<Tensor>&` schema but also generate a `const Tensor&` declaration in Functions.h. hacky_wrapper allows us to define our function as `const Tensor&` but wraps it in optional for us, so this avoids both the errors while linking and loading.
_[edit: rewrote the above to improve clarity and correct the fact that we actually need 18 more overloads (26 total), not 18 in total to complete the c++ api]_
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/50569
Reviewed By: H-Huang
Differential Revision: D26176105
Pulled By: soulitzer
fbshipit-source-id: cd8e77cc2de1117c876cd71c29b312887daca33f
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/51578https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/49710 introduced an edge case in which
drawing a single sample resulted in ignoring the `dtype` arg to `draw`. This
fixes this and adds a unit test to cover this behavior.
Test Plan: Unit tests
Reviewed By: danielrjiang
Differential Revision: D26204393
fbshipit-source-id: 441a44dc035002e7bbe6b662bf6d1af0e2cd88f4
Summary:
Performs the update that was suggested in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/41489
Adjust the functionality to largely match that pf the scipy companion PR https://github.com/scipy/scipy/pull/10844/, including
- a new `draw_base2` method
- include zero as the first point in the (unscrambled) Sobol sequence
The scipy PR is also quite opinionated if the `draw` method doesn't get called with a base 2 number (for which the resulting sequence has nice properties, see the scipy PR for a comprehensive discussion of this).
Note that this update is a **breaking change** in the sense that sequences generated with the same parameters after as before will not be identical! They will have the same (better, arguably) distributional properties, but calling the engine with the same seed will result in different numbers in the sequence.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/49710
Test Plan:
```
from torch.quasirandom import SobolEngine
sobol = SobolEngine(3)
sobol.draw(4)
sobol = SobolEngine(4, scramble=True)
sobol.draw(5)
sobol = SobolEngine(4, scramble=True)
sobol.draw_base2(2)
```
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D25657233
Pulled By: Balandat
fbshipit-source-id: 9df50a14631092b176cc692b6024aa62a639ef61
Summary:
Reference: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/33152
Changes
* Enable complex support for masked_scatter
* Enable half support for masked_scatter CPU
* Enable complex autograd support for masked_scatter CPU and masked_select (both CPU and CUDA).
**Note**:
Complex Support for masked_scatter CUDA is disabled as it depends on `masked_fill` which is yet to be ported to ATen.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/51281
Reviewed By: ailzhang
Differential Revision: D26127561
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: 6284926b934942213c5dfc24b5bcc8538d0231af
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/3307
Previously, `self.grad` was not ~cloned~ deepcopied to the returned tensor in `deepcopy`. Added a test and an implementation.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/50663
Reviewed By: heitorschueroff
Differential Revision: D26074811
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 536dad36415f1d03714b4ce57453f406ad802b8c
Summary:
All these Unary operators have been an entry in OpInfo DB.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/50096
Reviewed By: zhangguanheng66
Differential Revision: D25870048
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: b64e06d5b9ab5a03a202cda8c22fdb7e4ae8adf8
Summary:
Based on ngimel's (Thank you!) feedback, cpu half was only accidental, so I'm removing it.
This lets us ditch the old codepath for without replacement in favour of the new, better one.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/50063
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D25772449
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 608729c32237de4ee6d1acf7e316a6e878dac7f0
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/49552
This PR:
1. Migrates independent autograd test for `hstack`, `dstack`, `vstack`, `movedim`, `moveaxis` from `test_autograd.py` to the new `OpInfo` based tests.
2. Migrates autograd test for `gather`, `index_select` from the method_tests to the new `OpInfo` based tests.
2. Enables complex backward for `stack, gather, index_select, index_add_` and adds tests for complex autograd for all the above mentioned ops.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D25682511
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: 5d8f89db4a9ec340ab99a6196987d44a23e2c6c6
Summary:
**BC-breaking Note:**
This PR updates PyTorch's digamma function to be consistent with SciPy's special.digamma function. This changes the result of the digamma function on the nonpositive integers, where the gamma function is not defined. Since the gamma function is undefined at these points, the (typical) derivative of the logarithm of the gamma function is also undefined at these points, and for negative integers this PR updates digamma to return NaN. For zero, however, it returns -inf to be consistent with SciPy.
Interestingly, SciPy made a similar change, which was noticed by at least one user: https://github.com/scipy/scipy/issues/9663#issue-396587679.
SciPy's returning of negative infinity at zero is intentional:
59347ae8b8/scipy/special/cephes/psi.c (L163)
This change is consistent with the C++ standard for the gamma function:
https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/numeric/math/tgamma
**PR Summary:**
Reference https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/42515
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/48302
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D25664087
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 1168e81e218bf9fe5b849db0e07e7b22e590cf73
Summary:
**BC-Breaking Note:**
This PR updates PyTorch's angle operator to be consistent with NumPy's. Previously angle would return zero for all floating point values (including NaN). Now angle returns `pi` for negative floating point values, zero for non-negative floating point values, and propagates NaNs.
**PR Summary:**
Reference: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/42515
TODO:
* [x] Add BC-Breaking Note (Prev all real numbers returned `0` (even `nan`)) -> Fixed to match the correct behavior of NumPy.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/49163
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D25681758
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 54143fe6bccbae044427ff15d8daaed3596f9685
Summary:
This replaces the narrow character set APIs with the wide character set ones in `THAllocator.cpp`. This fixes the potential crashes caused by passing non-ASCII characters in `torch::from_file` on Windows.
See: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/47422
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/47905
Reviewed By: zhangguanheng66
Differential Revision: D25399146
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 0a183b65de171c48ed1718fa71e773224eaf196f
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/45964
Indexing operators e.g. `scatter`/`gather` use tensor restriding so the `TensorIterator` built in overlap checking needs to be disabled. This adds the missing overlap checks for these operators.
In addition, some indexing operators don't work will with `MemOverlapStatus::FULL` which is explicitly allowed by `assert_no_partial_overlap`. So, I've introduced `assert_no_overlap` that will raise an error on partial _or_ full overlap.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/48651
Reviewed By: zhangguanheng66
Differential Revision: D25401047
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 53abb41ac63c4283f3f1b10a0abb037169f20b89
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/48116
If you port kernels to be structured, you get Meta kernels automatically
generated for you. This is one payoff of structured kernels.
Code generation was mercifully really simple, although at risk of
"swiss cheese" syndrome: there's two new conditionals in the codegen
to tweak behavior when generating for meta keys. It's not too bad
right now but there's a risk of things getting out of hand. One
way to rationalize the logic here would be to transmit "TensorMeta-ness"
inside the TensorOptions (so tensor_from_meta can deal with it); then
the "Meta" kernel magic would literally just be generating empty
out_impls to call after all the scaffolding is done. But I didn't
do this because it seemed like it would be more annoying short term.
Also had to teach resize_ to work on meta tensors, since we use them
to implement the out kernels.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: bhosmer, ailzhang
Differential Revision: D25056640
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: f8fcfa0dbb58a94d9b4196748f56e155f83b1521
Summary:
Creates multiple new test suites to have fewer tests in test_torch.py, consistent with previous test suite creation like test_unary_ufuncs.py and test_linalg.py.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/47356
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D25202268
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 75fde3ca76545d1b32b86d432a5cb7a5ba8f5bb6
Summary:
Quiet errors from flake8. Only a couple of code changes for deprecated Python syntax from before 2.4. The rest is just adding noqa markers.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/48453
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D25181871
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: f8d7298aae783b1bce2a46827b088fc390970641
Summary:
Adding Unary Ufunc Test entry for `erf` variants.
We use scipy functions for reference implementation.
We can later update the tests once these functions will update integer input to float.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/47155
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D25176654
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: cb08efed1468b27650cec4f87a9a34e999ebd810
Summary:
The approach is to simply reuse `torch.repeat` but adding one more functionality to tile, which is to prepend 1's to reps arrays if there are more dimensions to the tensors than the reps given in input. Thus for a tensor of shape (64, 3, 24, 24) and reps of (2, 2) will become (1, 1, 2, 2), which is what NumPy does.
I've encountered some instability with the test on my end, where I could get a random failure of the test (due to, sometimes, random value of `self.dim()`, and sometimes, segfaults). I'd appreciate any feedback on the test or an explanation for this instability so I can this.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/47974
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D25148963
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: bf63b72c6fe3d3998a682822e669666f7cc97c58
Summary:
Adds ldexp operator for https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/38349
I'm not entirely sure the changes to `NamedRegistrations.cpp` were needed but I saw other operators in there so I added it.
Normally the ldexp operator is used along with the frexp to construct and deconstruct floating point values. This is useful for performing operations on either the mantissa and exponent portions of floating point values.
Sleef, std math.h, and cuda support both ldexp and frexp but not for all data types. I wasn't able to figure out how to get the iterators to play nicely with a vectorized kernel so I have left this with just the normal CPU kernel for now.
This is the first operator I'm adding so please review with an eye for errors.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/45370
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D24333516
Pulled By: ranman
fbshipit-source-id: 2df78088f00aa9789aae1124eda399771e120d3f
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/48113
Fix is simple: just treat Meta as a backend covered by AutogradOther.
This semantically makes sense, since meta kernels are just like regular
CPU/CUDA kernels, they just don't do any compute.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: zhangguanheng66
Differential Revision: D25056641
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 7b68911982352b3e0ee8616b38cd9c70bd58a740
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/47023
DeviceType pretty clearly only needs 1 byte. DeviceIndex only needs 1 byte given that machines don't have anywhere near 255 GPUs in them as far as I know.
ghstack-source-id: 116901430
Test Plan: Existing tests, added assertion to catch if my assumption about DeviceIndex is incorrect
Reviewed By: dzhulgakov
Differential Revision: D24605460
fbshipit-source-id: 7c9a89027fcf8eebd623b7cdbf6302162c981cd2
Summary:
Reference https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/38349
Delegates to `torch.transpose` (not sure what is the best way to alias)
TODO:
* [x] Add test
* [x] Add documentation
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/46041
Reviewed By: gchanan
Differential Revision: D25022816
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: c80223d081cef84f523ef9b23fbedeb2f8c1efc5
Summary:
Now when https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/42553 is merged we can delete a bit of code from the tests and enable some of the skipped complex tests.
Unfortunately, `test_pinverse_complex_xfailed` and `test_symeig_complex_xfailed` had bugs and it wasn't caught automatically that these tests xpass. Need to be careful next time with `unittest.expectedFailure`.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/47910
Reviewed By: zhangguanheng66
Differential Revision: D25052130
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 29512995c024b882f9cb78b7bede77733d5762d0
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/48042
Moving scalar test to a separate method so the XLA team can continue to test for the other cases without failing. Requested here https://github.com/pytorch/xla/issues/2620#issuecomment-725696108
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: zhangguanheng66
Differential Revision: D25055677
Pulled By: heitorschueroff
fbshipit-source-id: 5da66bac78ea197821fee0b9b8a213ff2dc19c67
Summary:
`torch.lu_solve` now works for complex inputs both on CPU and GPU.
I moved the existing tests to `test_linalg.py` and modified them to test complex dtypes, but I didn't modify/improve the body of the tests.
Ref. https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/33152
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/46862
Reviewed By: nikithamalgifb
Differential Revision: D24543682
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: 165bde39ef95cafebf976c5ba4b487297efe8433
Summary:
Fixed test:
- `test_is_nonzero`, this is asserting exact match, which is flaky when `TORCH_SHOW_CPP_STACKTRACES=1`, I changed this to non-exact assert
- `test_pinverse` TF32
- `test_symeig` TF32
- `test_triangular_solve_batched_many_batches_cpu_float64` precision on CPU BLAS
- `test_qr` TF32, as well as the tensor factory forgets a `dtype=dtype`
- `test_lu` TF32
- `ConvTranspose2d` TF32
- `Conv3d_1x1x1_no_bias` TF32
- `Transformer*` TF32
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/46941
Reviewed By: heitorschueroff
Differential Revision: D24852725
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: ccd4740cc643476178d81059d1c78da34e5082ed
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/42553
Ports `torch.bmm` and `torch.baddbmm` from TH to ATen, as well as adds support for complex dtypes. Also removes dead TH code for Level 2 functions.
Closes#24539
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: ansley
Differential Revision: D24893511
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: 0eba3f2aec99c48b3018a5264ee7789279cfab58
Summary:
`torch.triangular_solve` now works for complex inputs on GPU.
I moved the existing tests to `test_linalg.py` and modified them to test complex and float32 dtypes.
Ref. https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/33152
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/46916
Reviewed By: navahgar, agolynski
Differential Revision: D24706647
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: fe780eac93d2ae1b2549539bb385e5fac25213b3
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/46398
This PR makes torch.einsum compatible with numpy.einsum except for the sublist input option as requested here https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/21412. It also fixed 2 performance issues linked below and adds a check for reducing to torch.dot instead of torch.bmm which is faster in some cases.
fixes#45854, #37628, #30194, #15671fixes#41467 with benchmark below
```python
import torch
from torch.utils.benchmark import Timer
a = torch.randn(10000, 100, 101, device='cuda')
b = torch.randn(10000, 101, 3, device='cuda')
c = torch.randn(10000, 100, 1, device='cuda')
d = torch.randn(10000, 100, 1, 3, device='cuda')
print(Timer(
stmt='torch.einsum("bij,bjf->bif", a, b)',
globals={'a': a, 'b': b}
).blocked_autorange())
print()
print(Timer(
stmt='torch.einsum("bic,bicf->bif", c, d)',
globals={'c': c, 'd': d}
).blocked_autorange())
```
```
<torch.utils.benchmark.utils.common.Measurement object at 0x7fa37c413850>
torch.einsum("bij,bjf->bif", a, b)
Median: 4.53 ms
IQR: 0.00 ms (4.53 to 4.53)
45 measurements, 1 runs per measurement, 1 thread
<torch.utils.benchmark.utils.common.Measurement object at 0x7fa37c413700>
torch.einsum("bic,bicf->bif", c, d)
Median: 63.86 us
IQR: 1.52 us (63.22 to 64.73)
4 measurements, 1000 runs per measurement, 1 thread
```
fixes#32591 with benchmark below
```python
import torch
from torch.utils.benchmark import Timer
a = torch.rand(1, 1, 16, 2, 16, 2, 16, 2, 2, 2, 2, device="cuda")
b = torch.rand(729, 1, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, device="cuda")
print(Timer(
stmt='(a * b).sum(dim = (-3, -2, -1))',
globals={'a': a, 'b': b}
).blocked_autorange())
print()
print(Timer(
stmt='torch.einsum("...ijk, ...ijk -> ...", a, b)',
globals={'a': a, 'b': b}
).blocked_autorange())
```
```
<torch.utils.benchmark.utils.common.Measurement object at 0x7efe0de28850>
(a * b).sum(dim = (-3, -2, -1))
Median: 17.86 ms
2 measurements, 10 runs per measurement, 1 thread
<torch.utils.benchmark.utils.common.Measurement object at 0x7efe0de286a0>
torch.einsum("...ijk, ...ijk -> ...", a, b)
Median: 296.11 us
IQR: 1.38 us (295.42 to 296.81)
662 measurements, 1 runs per measurement, 1 thread
```
TODO
- [x] add support for ellipsis broadcasting
- [x] fix corner case issues with sumproduct_pair
- [x] update docs and add more comments
- [x] add tests for error cases
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D24860367
Pulled By: heitorschueroff
fbshipit-source-id: 31110ee598fd598a43acccf07929b67daee160f9
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/45092
Adding two operators
1. at::float_to_half -> Converts FP32 tensor to FP16 tensor
2. at::half_to_float -> Converts FP16 tensor to FP32 tensor.
These operators internally use the kernel provided by FBGeMM. Both C2 and PT will use the same FBGeMM kernel underneath.
Test Plan:
buck test //caffe2/test:torch -- .*test_half_tensor.*
Run benchmark locally using
```
buck run //caffe2/benchmarks/operator_benchmark/pt:tensor_to_test
```
AI Bench results are pending. I expect that not to finish as we have large queue with jobs pending for 2+ days.
Benchmark for 512x512 tensor with FbGeMM implementation
```
# ----------------------------------------
# PyTorch/Caffe2 Operator Micro-benchmarks
# ----------------------------------------
# Tag : short
# Benchmarking PyTorch: FloatToHalfTensorConversionBenchmark
# Mode: Eager
# Name: FloatToHalfTensorConversionBenchmark_M512_N512_cpu
# Input: M: 512, N: 512, device: cpu
Forward Execution Time (us) : 1246.332
# Benchmarking PyTorch: HalfToFloatTensorConversionBenchmark
# Mode: Eager
# Name: HalfToFloatTensorConversionBenchmark_M512_N512_cpu
# Input: M: 512, N: 512, device: cpu
Forward Execution Time (us) : 1734.304
```
Benchmark for 512x512 tensor trunk with no FbGeMM integration.
```
# ----------------------------------------
# PyTorch/Caffe2 Operator Micro-benchmarks
# ----------------------------------------
# Tag : short
# Benchmarking PyTorch: FloatToHalfTensorConversionBenchmark
# Mode: Eager
# Name: FloatToHalfTensorConversionBenchmark_M512_N512_cpu
# Input: M: 512, N: 512, device: cpu
Forward Execution Time (us) : 169045.724
# Benchmarking PyTorch: HalfToFloatTensorConversionBenchmark
# Mode: Eager
# Name: HalfToFloatTensorConversionBenchmark_M512_N512_cpu
# Input: M: 512, N: 512, device: cpu
Forward Execution Time (us) : 152382.494
```
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D23824869
fbshipit-source-id: ef044459b6c8c6e5ddded72080204c6a0ab4582c
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/47305
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/47127.
Ideally this would just use diag and sum (as the CUDA implementation does), but that seems to have performance problems, which I'll link in the github PR.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: zou3519
Differential Revision: D24729627
Pulled By: gchanan
fbshipit-source-id: 151b786b53e7b958f0929c803dbf8e95981c6884
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/47474
After enabling GPU/Re, some issues were specific to those runs
Test Plan:
```
buck test -c test.external_runner=tpx mode/opt //caffe2/test:torch_cuda -- --use-remote-execution --force-tpx --run-disabled
```
Reviewed By: malfet, janeyx99
Differential Revision: D24771578
fbshipit-source-id: 1ada79dae12c8cb6f795a0d261c60f038eee2dfb
Summary:
`torch.inverse` now works for complex inputs on GPU.
Test cases with complex matrices are xfailed for now. For example, batched matmul does not work with complex yet.
Ref. https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/33152
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/45034
Reviewed By: zou3519
Differential Revision: D24730264
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: b9c94ec463012913c117278a884adeee96ea02aa
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/46758
It's in general helpful to support int32 indices and offsets, especially when such tensors are large and need to be transferred to accelerator backends. Since it may not be very useful to support the combination of int32 indices and int64 offsets, here we enforce that these two must have the same type.
Test Plan: unit tests
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D24470808
fbshipit-source-id: 94b8a1d0b7fc9fe3d128247aa042c04d7c227f0b
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/47126
Context
-------
This PR is a rebase of shihongzhi's https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/35360.
I forgot to merge it back when it was submitted so I rebased it and ran new benchmarks on it.
Benchmarks
----------
TL;DR: The op has more overhead than the TH version but for larger shapes the overhead disappears.
```
import torch
shapes = [
[1, 1],
[100, 100],
[1000, 1000],
[10000, 10000],
[100000, 100000],
]
for shape in shapes:
x = torch.ones(shape)
%timeit x.trace()
Before:
1.83 µs ± 42.4 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000000 loops each)
1.98 µs ± 48.2 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
3.19 µs ± 10.7 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
85.2 µs ± 700 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
1.23 ms ± 4.34 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
After:
2.16 µs ± 325 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000000 loops each)
2.08 µs ± 275 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
4.45 µs ± 19.2 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
81.8 µs ± 766 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
1.27 ms ± 6.75 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
```
Future work
-----------
Things that can be done after this PR:
- add complex tensor support
- Fix the type promotion discrepancy between CPU and CUDA
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: mrshenli
Differential Revision: D24683259
Pulled By: zou3519
fbshipit-source-id: f92b566ad0d58b72663ab64899d209c96edb78eb
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/47125
We didn't actually have any tests for torch.trace. The tests expose a
discrepancy between the behavior of torch.trace on CPU and CUDA that
I'll file an issue for.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D24683260
Pulled By: zou3519
fbshipit-source-id: 71dd3af62bc98c6b9b0ba2bf2923cb6d44daa640
Summary:
Related https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/38349
This PR implements `column_stack` as the composite ops of `torch.reshape` and `torch.hstack`, and makes `row_stack` as the alias of `torch.vstack`.
Todo
- [x] docs
- [x] alias pattern for `row_stack`
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/46313
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D24585471
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 62fc0ffd43d051dc3ecf386a3e9c0b89086c1d1c
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/41768
The fault was that a NULL `tau` would get passed to LAPACK function. This PR fixes that by checking whether the `tau` contains 0 elements at the beginning of the function.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/46700
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D24616427
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 92e8f1489b113c0ceeca6e54dea8b810a51a63c3
Summary:
Looks like this op is never tested for the support of different dtypes?
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/45155
Reviewed By: zou3519
Differential Revision: D24438839
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 103ff609e11811a0705d04520c2b97c456b623ef
Summary:
Follow-up of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/46461 with a similar goal
Makes them more readable and possibly faster. Care has to be taken because `map` applies the function immediately while `(x for x in xs)` is a generator expression which gets evaluated later. This is a benefit in some cases where it is not required to actually create the list of values in memory (e.g. when passing to `tuple` or `extend` or `join`)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/46462
Reviewed By: zou3519
Differential Revision: D24422343
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 252e33499c92ac0b15238f2df32681dbbda2b237
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/46046
*_like functions are used in pytorch to create a new tensor with the same shape of the input tensor. But we don’t always preserve the layout permutation of the tensor. Current behavior is that, for a dense and non-overlapping tensor, its layout permutation is preserved. For eg. passing a channel last contiguous tensor t with ‘shape/stride’ (2, 4, 3, 2)/(24, 1, 8, 4) to empty_like(t) function will create a new tensor with exactly the same ‘shape/stride’ as the input tensor t. However, if the input tensor is non-dense or has overlap, we simply create a contiguous tensor based on input tensor’s shape, so the tensor layout permutation is lost.
This PR preserves the layout permutation for non-dense or overlapping tensor. The strides propagation rule that used in this PR is exactly the same as what is being used in TensorIterator. The behavior changes are listed below:
| code | old | new |
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------|
| #strided tensors<br>a=torch.randn(2,3,8)[:,:,::2].permute(2,0,1)<br>print(a.stride())<br>print(a.exp().stride())<br>print((a+a).stride())<br>out = torch.empty(0)<br>torch.add(a,a,out=out)<br>print(out.stride()) | (2, 24, 8) <br>(6, 3, 1) <br>(1, 12, 4) <br>(6, 3, 1) | (2, 24, 8)<br>(1, 12, 4)<br>(1, 12, 4)<br>(1, 12, 4) |
| #memory dense tensors<br>a=torch.randn(3,1,1).as_strided((3,1,1), (1,3,3))<br>print(a.stride(), (a+torch.randn(1)).stride())<br>a=torch.randn(2,3,4).permute(2,0,1)<br>print(a.stride())<br>print(a.exp().stride())<br>print((a+a).stride())<br>out = torch.empty(0)<br>torch.add(a,a,out=out)<br>print(out.stride()) | (1, 3, 3) (1, 1, 1)<br>(1, 12, 4)<br>(6, 3, 1)<br>(1, 12, 4)<br>(6, 3, 1) | (1, 3, 3) (1, 3, 3)<br>(1, 12, 4)<br>(1, 12, 4)<br>(1, 12, 4)<br>(1, 12, 4) |
This is to solve the non-dense tensor layout problem in #45505
TODO:
- [x] Fix all the BC broken test cases in pytorch
- [ ] Investigate if any fb internal tests are broken
This change will cover all kinds of non-dense tensors.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: ezyang
Differential Revision: D24288970
Pulled By: glaringlee
fbshipit-source-id: 320fd4e0d1a810a12abfb1441472298c983a368d
Summary:
As per title. LU decomposition is used for computing determinants, and I need this functionality to implement the matrix square root. Next PR on my list is to enable `torch.det` on CUDA with complex input.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/45898
Reviewed By: heitorschueroff
Differential Revision: D24306951
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: 168f578fe65ae1b978617a66741aa27e72b2172b
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/46037
I now isolated the special case to be only between cuda tensor bases and cpu tensor exponents. My previous fix was not a complete fix--it fixed some stuff but broke others. The current fix is a more complete fix:
```
In [1]: import torch
In [2]: a=torch.randn(3)
In [3]: b=torch.tensor(2, device="cuda")
In [4]: torch.pow(a,b) #should not work and throws exception now!
In [5]: a=torch.tensor(3, device="cuda")
In [6]: b=torch.tensor(2)
In [7]: torch.pow(a,b) #should work, and now does
In [8]: a=torch.randn(3, device="cuda")
In [9]: torch.pow(a,b) # yeah, that one is fixed and still works
```
To add a test case to reflect the change, I had to modify the existing setup a little bit. I think it is an improvement but would appreciate any tips on how to make it better!
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/46320
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D24306610
Pulled By: janeyx99
fbshipit-source-id: cc74c61373d1adc2892a7a31226f38895b83066a
Summary:
This PR adds support for complex-valued input for `torch.pinverse`.
Fixed cuda SVD implementation to return singular values with real dtype.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/45385.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/45819
Reviewed By: heitorschueroff
Differential Revision: D24306539
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: 2fe19bc630de528e0643132689e1bc5ffeaa162a
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/46037
I'm not sure this is the most performant solution, but this works:
torch.pow(cuda_tensor, 5) should work and worked before.
torch.pow(cuda_tensor, torch.tensor(5)), should work **and works now!**
torch.pow(cuda_tensor, torch.tensor((5,))), should NOT work and complain the tensors are on different devices and indeed continues to complain.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/46185
Reviewed By: glaringlee, malfet
Differential Revision: D24257687
Pulled By: janeyx99
fbshipit-source-id: 2daf235d62ec5886d7c153da05445c2ec71dec98
Summary:
* Removes incorrect statement that "the vector norm will be applied to the last dimension".
* More clearly describe each different combination of `p`, `ord`, and input size.
* Moves norm tests from `test/test_torch.py` to `test/test_linalg.py`
* Adds test ensuring that `p='fro'` and `p=2` give same results for mutually valid inputs
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/41388
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/42696
Reviewed By: bwasti
Differential Revision: D23876862
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 36f33ccb6706d5fe13f6acf3de8ae14d7fbdff85
Summary:
`TCPStoreTest.test_numkeys_delkeys` takes 5+ min (mostly in idle wait for socket timeout)
`TestDataLoader.test_proper_exit` and `TestDataLoaderPersistentWorkers.test_proper_exit` take 2.5 min each
`TestXNNPACKConv1dTransformPass.test_conv1d_with_relu_fc` takes 2 min to finish
Add option to skip reporting test classes that run for less than a second to `print_test_stats.py` and speed up `TestTorchDeviceTypeCUDA.test_matmul_45724_cuda`
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/46068
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D24208660
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 780e0d8be4f0cf69ea28de79e423291a1f3349b7
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/45847
Original PR here https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/45084. Created this one because I was having problems with ghstack.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D24136629
Pulled By: heitorschueroff
fbshipit-source-id: dd7c7540a33f6a19e1ad70ba2479d5de44abbdf9
Summary:
This test is changed one day before the landing of the tf32 tests PR, therefore the fix for this is not included in that PR.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/45492
Reviewed By: ezyang
Differential Revision: D24101876
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: cb3615b2fb8acf17abe54cd18b1faec26582d6b6
Summary:
**BC-breaking note**
For ease of exposition let a_min be the value of the "min" argument to clamp, and a_max be the value of the "max" argument to clamp.
This PR changes the behavior of torch.clamp to always compute min(max(a, a_min), a_max). torch.clamp currently computes this in its vectorized CPU specializations:
78b95b6204/aten/src/ATen/cpu/vec256/vec256_double.h (L304)
but in other places it clamps differently:
78b95b6204/aten/src/ATen/cpu/vec256/vec256_base.h (L624)78b95b6204/aten/src/ATen/native/cuda/UnaryOpsKernel.cu (L160)
These implementations are the same when a_min < a_max, but divergent when a_min > a_max. This divergence is easily triggered:
```
t = torch.arange(200).to(torch.float)
torch.clamp(t, 4, 2)[0]
: tensor(2.)
torch.clamp(t.cuda(), 4, 2)[0]
: tensor(4., device='cuda:0')
torch.clamp(torch.tensor(0), 4, 2)
: tensor(4)
```
This PR makes the behavior consistent with NumPy's clip. C++'s std::clamp's behavior is undefined when a_min > a_max, but Clang's std::clamp will return 10 in this case (although the program, per the above comment, is in error). Python has no standard clamp implementation.
**PR Summary**
Fixes discrepancy between AVX, CUDA, and base vector implementation for clamp, such that all implementations are consistent and use min(max_vec, max(min_vec, x) formula, thus making it equivalent to numpy.clip in all implementations.
The same fix as in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/32587 but isolated to the kernel change only, so that the internal team can benchmark.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/43288
Reviewed By: colesbury
Differential Revision: D24079453
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 67f30d2f2c86bbd3e87080b32f00e8fb131a53f7