Fixes#102678Fixes#102629Fixes#102558
HipSOLVER performance on ROCm5.4.2 and later no longer serves as massive bottleneck. Additionally, using magma on rocm in this case caused test_compare_cpu_lialg_pinv_singular_cuda_float32 to fail. Using hipSOLVER, the test now passes.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/103540
Approved by: https://github.com/lezcano
Enables the hipSolver backend for ROCm builds
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Minimum ROCm version requirement - 5.3
- Introduces new macro USE_LINALG_SOLVER the controls enablement of both cuSOLVER and hipSOLVER
- Adds hipSOLVER API to hipification process
- combines hipSOLVER and hipSPARSE mappings into single SPECIAL map that takes priority among normal mappings
- Torch api to be moved to hipsolver backend (as opposed to magma) include: torch.svd(), torch.geqrf(), torch.orgqr(), torch.ormqr()
- Will enable 100+ linalg unit tests for ROCm
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/97370
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
Notes:
- No segfaults observed in any CI tests: dynamo unittests, inductor unittests, dynamo-wrapped pytorch tests. So we remove the warning that using dynamo 3.11 may result in segfaults.
- Some dynamo-wrapped pytorch tests hang. They will be skipped in the dynamo-wrapped test suite and will be addressed in a future PR
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99180
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
Issue: #93684
# Problem
Reduce graph breaks when dynamo compiles python functions containing numpy functions and ndarray operations.
# Design (as I know it)
* Use torch_np.ndarray(a wrapper of tensor) to back a `VariableTracker`: `NumpyTensorVariable`.
* Translate all attributes and methods calls, on ndarray, to torch_np.ndarray equivalent.
This PR adds `NumpyTensorVariable` and supports:
1. tensor to ndarray, ndarray to tensor
2. numpy functions such as numpy.meshgrid()
3. ndarray attributes such as `itemsize`, `stride`
Next PR will handle returning `np.ndarray` and add support for ndarray methods
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/95849
Approved by: https://github.com/ezyang
Add _int_mm primitive that binds cuBLAS int8@int8 -> int32 matmul and that translates to Triton based mm templates under max autotune. This is a very useful first step towards better supporting quantization on the GPU. This is a not a user facing API, but an internal primitive.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/94339
Approved by: https://github.com/ngimel, https://github.com/jansel
Currently, if we multiply a transposed batch of matrices with shape
[b, m, n] and a matrix with shape [n, k], when computing the gradient
of the matrix, we instantiate a matrix of shape [b, n, k]. This may be
a very large matrix. Instead, we fold the batch of matrices into a
matrix, which avoids creating any large intermediary tensor.
Note that multiplying a batch of matrices and a matrix naturally occurs
within an attention module, so this case surely happens in the wild.
In particular, this issue was found while investigating the OOMs caused by the
improved folding algorithm in the next PR of this stack. See https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/76828#issuecomment-1432359980
This PR fixes those OOMs and decreases the memory footprint of the
backward of matmul.
I understand this is a tricky one, so I put it on its own PR to discuss it.
Differential Revision: [D43541495](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D43541495)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/95261
Approved by: https://github.com/ezyang
Follow-up of #89582 to drop flags like `CUDA11OrLater` in tests. Note that in some places it appears that `TEST_WITH_ROCM` is _implicitly_ guarded against via the `CUDA11OrLater` version check, based on my best-guess of how `torch.version.cuda` would behave in ROCM builds, so I've added `not TEST_WITH_ROCM` in cases where ROCM wasn't previously explicitly allowed.
CC @ptrblck @malfet @ngimel
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/92605
Approved by: https://github.com/ngimel
This achieves the same things as https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/85908 but using backends instead of kwargs (which breaks torchscript unfortunately). This also does mean we let go of numpy compatibility BUT the wins here are that users can control what opt einsum they wanna do!
The backend allows for..well you should just read the docs:
```
.. attribute:: torch.backends.opteinsum.enabled
A :class:`bool` that controls whether opt_einsum is enabled (on by default). If so,
torch.einsum will use opt_einsum (https://optimized-einsum.readthedocs.io/en/stable/path_finding.html)
to calculate an optimal path of contraction for faster performance.
.. attribute:: torch.backends.opteinsum.strategy
A :class:`str` that specifies which strategies to try when `torch.backends.opteinsum.enabled` is True.
By default, torch.einsum will try the "auto" strategy, but the "greedy" and "optimal" strategies are
also supported. Note that the "optimal" strategy is factorial on the number of inputs as it tries all
possible paths. See more details in opt_einsum's docs
(https://optimized-einsum.readthedocs.io/en/stable/path_finding.html).
```
In trying (and failing) to land 85908, I discovered that jit script does NOT actually pull from python's version of einsum (because it cannot support variadic args nor kwargs). Thus I learned that jitted einsum does not subscribe to the new opt_einsum path calculation. Overall, this is fine since jit script is getting deprecated, but where is the best place to document this?
## Test plan:
- added tests to CI
- locally tested that trying to set the strategy to something invalid will error properly
- locally tested that tests will pass even if you don't have opt-einsum
- locally tested that setting the strategy when opt-einsum is not there will also error properly
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/86219
Approved by: https://github.com/soulitzer, https://github.com/malfet
## This PR seeks to:
- [x] add c++ support for an optimize path
- [x] add python opt_einsum path passthrough
- [x] add opt_einsum to OSS requirements, but a soft one
- [x] show benchmark results here
Additional things I've explored + their conclusions:
- **Delaying the summing over dimensions** => added!
- The idea here is to not incur kernel calls to `sum` as we try to early sum out in einsum. Thus, we collect all the dimensions that need to be summed together in one contraction + sum at the end instead of summing as we go. While this optimization didn't feel like it made things faster for the random cases we've selected (they all summed 1 dim per contraction), it is a good principle and would help more common use cases that would reduce multiple dimensions at a time (like `bxy,xyi,xyj->bij`).
- **Caching contract_path based on equation and tensor sizes** => dropped :(
- The benchmarks were strictly worse for all the cases, and, from scanning the use cases, I observed people do not often call einsum on the same equation/tensor order enough for caching to be justified. I do think caching can be effective in the future, but it would require further investigation.
## Not a part of this PR (but are next steps):
- adding opt_einsum package to OSS CI
- adding it to internal CI
- potentially adding a kwarg path argument to the python API -- if the path is given, we wouldn't have to spend time calculating it, but there would be some time lost validating user input.
## Testing:
- Added more tests to CI
## Benchmarking:
**TL;DRs**
- **torch.einsum with opt_einsum is a definite win for the production case**.
- **torch.einsum with opt_einsum installed is consistently fast, but has an overhead** of needing to find the path. If the path is already found/optimal, it will be slightly slower.
- The einsum overhead decreases for bigger dimensions.
- **torch.einsum without opt_einsum installed is comparable to before this commit**, with occasional slowness potentially due to not reshaping/squeezing as we contract until the end.
- For many of the random generated cases, the dimensions were too similar and small where an optimal order wasn't that much more optimal than just going left to right. However, in production, dimensions are commonly quite distinct (batch size will be small, but the data will be huge).
- **torch.einsum opt is comparable (slightly faster overall) compared to numpy.einsum opt for the cpu case**. This is interesting given that torch.einsum currently spends time computing the path, but numpy.einsum takes it as input.
- **torch.einsum opt is significantly faster than numpy.einsum opt for the gpu case**. This is because numpy doesn't take advantage of GPUs.
The following benchmarks were done on an A100 GPU and Linux CPUs. The line in the first chart separates GPU (on top) from CPU, and the line in the second graph separates CPU (on top) and then GPU. Sorry it's flipped 😛 .
Production example (see [colab benchmark](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1V2s4v1dOOKwRvp5T_DC-PNUosOV9FFJx?authuser=1#scrollTo=WZoQkC8Mdt6I) for more context):
<img width="1176" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/31798555/192012636-9a68bfa7-2601-43b1-afeb-b4e0877db6a4.png">
Randomly generated examples (the same ones as in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/60191)
<img width="1176" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/31798555/192012804-1c639595-b3e6-48c9-a385-ad851c13e1c2.png">
Open below to see old + not super relevant benchmarking results:
<details>
Benchmark results BEFORE this PR (on Linux -- I will update devices so they are consistent later):
<img width="776" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/31798555/190807274-18f71fce-556e-47f4-b18c-e0f7d0c0d5aa.png">
Benchmark results with the code on this PR (on my x86 mac):
For the CPU internal use case --
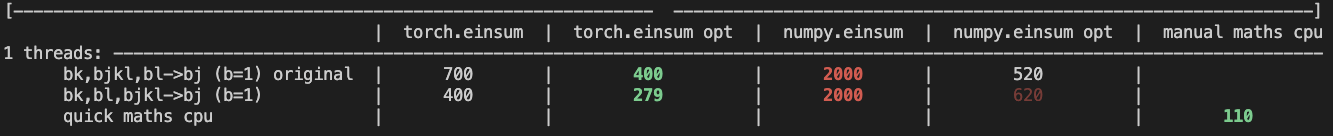
For the general use case --
It looks like numpy opt still does better in several of these random cases, but torch einsum opt is consistently faster than torch.einsum.
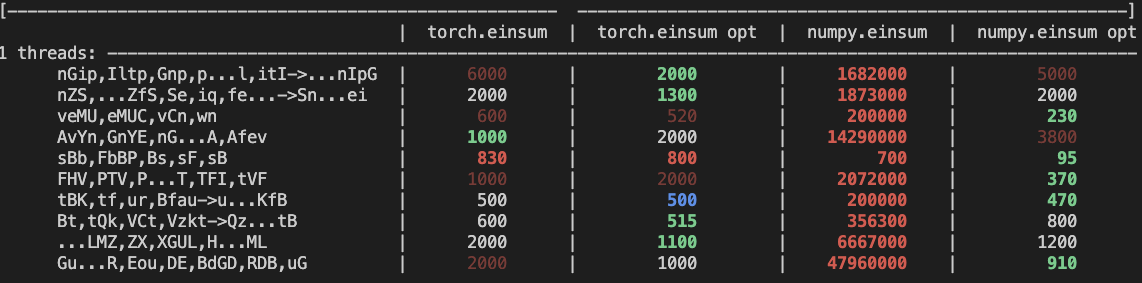
<details>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/84890
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD, https://github.com/soulitzer
Summary: test_inverse_errors_large and test_linalg_solve_triangular fail for dtype=float64 when invoked on GPUs on Meta internal testing infra. Skip in Meta internal testing.
Test Plan: (observe tests skipped on Meta internal infra)
Reviewed By: mikekgfb
Differential Revision: D39785331
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/85577
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
Summary:
Re-submit for approved PR that was then reverted: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/85084
Create unit test to detect cuBLAS breakage via large differences between CPU and GPU addmm invocations
Test Plan:
Sample unit test output --
[...]
test_cublas_addmm_size_10000_cpu_bfloat16 (test_linalg.TestLinalgCPU) ... ok
test_cublas_addmm_size_10000_cpu_float16 (test_linalg.TestLinalgCPU) ... ok
test_cublas_addmm_size_10000_cpu_float32 (test_linalg.TestLinalgCPU) ... ok
test_cublas_addmm_size_1000_cpu_bfloat16 (test_linalg.TestLinalgCPU) ... ok
test_cublas_addmm_size_1000_cpu_float16 (test_linalg.TestLinalgCPU) ... ok
test_cublas_addmm_size_1000_cpu_float32 (test_linalg.TestLinalgCPU) ... ok
test_cublas_addmm_size_100_cpu_bfloat16 (test_linalg.TestLinalgCPU) ... ok
test_cublas_addmm_size_100_cpu_float16 (test_linalg.TestLinalgCPU) ... ok
test_cublas_addmm_size_100_cpu_float32 (test_linalg.TestLinalgCPU) ... ok
[...]
Reviewed By: mikekgfb
Differential Revision: D39433029
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/85432
Approved by: https://github.com/zrphercule
Summary: Create unit test to detect cuBLAS breakage via large differences between CPU and GPU addmm invocations
Test Plan:
Sample unit test output --
[...]
test_cublas_addmm_size_10000_cpu_bfloat16 (test_linalg.TestLinalgCPU) ... ok
test_cublas_addmm_size_10000_cpu_float16 (test_linalg.TestLinalgCPU) ... ok
test_cublas_addmm_size_10000_cpu_float32 (test_linalg.TestLinalgCPU) ... ok
test_cublas_addmm_size_1000_cpu_bfloat16 (test_linalg.TestLinalgCPU) ... ok
test_cublas_addmm_size_1000_cpu_float16 (test_linalg.TestLinalgCPU) ... ok
test_cublas_addmm_size_1000_cpu_float32 (test_linalg.TestLinalgCPU) ... ok
test_cublas_addmm_size_100_cpu_bfloat16 (test_linalg.TestLinalgCPU) ... ok
test_cublas_addmm_size_100_cpu_float16 (test_linalg.TestLinalgCPU) ... ok
test_cublas_addmm_size_100_cpu_float32 (test_linalg.TestLinalgCPU) ... ok
[...]
Reviewed By: mikekgfb
Differential Revision: D39433029
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/85084
Approved by: https://github.com/zrphercule
`torch.norm` is very odd. Some notable issues are:
- The default value of `"fro"` in `torch.norm` has an odd behaviour when `dim=None`. This is handled in the new dispatch
- The treatment of the `dtype` argument in `torch.norm` was completely wrong. This should fix it
- Some `out=` variants in the previous implementation were also wrong. This should fix those.
- This new dispatch should make some paths much faster. For example, `torch.norm(x)` where `x` is complex.
I'll try to make the changes in these PRs as incremental as possible as this is a tricky one.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/81761
Approved by: https://github.com/ngimel
As per title. I corrected a thing or two from my previous implementation
to make for better errors in some weird edge-cases and have a more clear
understanding of when does this function support low_precision types and
when it doesn't.
We also use the optimisation for bfloat16 within `vector_norm` within
this function.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/81113
Approved by: https://github.com/ngimel
This PR also adds complex support for logdet, and makes all these
functions support out= and be composite depending on one function. We
also extend the support of `logdet` to complex numbers and improve the
docs of all these functions.
We also use `linalg_lu_factor_ex` in these functions, so we remove the
synchronisation present before.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/79742
Approved by: https://github.com/IvanYashchuk, https://github.com/albanD
This PR heavily simplifies the code of `linalg.solve`. At the same time,
this implementation saves quite a few copies of the input data in some
cases (e.g. A is contiguous)
We also implement it in such a way that the derivative goes from
computing two LU decompositions and two LU solves to no LU
decompositions and one LU solves. It also avoids a number of unnecessary
copies the derivative was unnecessarily performing (at least the copy of
two matrices).
On top of this, we add a `left` kw-only arg that allows the user to
solve `XA = B` rather concisely.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/74046
Approved by: https://github.com/nikitaved, https://github.com/IvanYashchuk, https://github.com/mruberry
This PR simplifies the logic of `linalg.qr` using structured kernels. I
also took this chance and merged a few `copy_` operations with other
ops.
This PR removes a the previous magma implementation as is never faster
than that of cusolver and it's rather buggy. This has the side-effect
that now `qr` is not supported in Rocm. Ivan confirmed that this is
fine, given how incredibly slow was QR on Rocm anyway (we were marking
some tests as slow because of this...).
This PR also corrects the dispatch in geqrf. Before, if we called it
with a matrix for which `input.size(-2) <= 256 && batchCount(input) >= std::max<int64_t>(2, input.size(-2) / 16)` is false, and we have cublas but not cusolver, we would end up calling magma rather than cublas. This is not what the heuristic suggested.
Probaly we should benchmark these heuristics again, but that's beyond the scope of this PR.
Note. It looks like `torch.geqrf` maybe broken in MAGMA as per the
previous comment in `linalg_qr_helper_magma`. IvanYashchuk wdyt?
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/79054
Approved by: https://github.com/IvanYashchuk, https://github.com/ezyang
**BC-breaking note**:
This PR deprecates `torch.lu` in favor of `torch.linalg.lu_factor`.
A upgrade guide is added to the documentation for `torch.lu`.
Note this PR DOES NOT remove `torch.lu`.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/77636
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
This PR adds `linalg.lu_solve`. While doing so, I found a bug in MAGMA
when calling the batched MAGMA backend with trans=True. We work around
that by solving the system solving two triangular systems.
We also update the heuristics for this function, as they were fairly
updated. We found that cuSolver is king, so luckily we do not need to
rely on the buggy backend from magma for this function.
We added tests testing this function left and right. We also added tests
for the different backends. We also activated the tests for AMD, as
those should work as well.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/61657
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/77634
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
This PR does a number of things:
- Move linalg.vector_norm to structured kernels and simplify the logic
- Fixes a number of prexisting issues with the dtype kwarg of these ops
- Heavily simplifies and corrects the logic of `linalg.matrix_norm` and `linalg.norm` to be consistent with the docs
- Before the `_out` versions of these functions were incorrect
- Their implementation is now as efficient as expected, as it avoids reimplementing these operations whenever possible.
- Deprecates `torch.frobenius_norm` and `torch.nuclear_norm`, as they were exposed in the API and they are apparently being used in mobile (??!!) even though they were not documented and their implementation was slow.
- I'd love to get rid of these functions already, but I guess we have to go through their deprecation.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/76547
Approved by: https://github.com/mruberry
This PR adds `linalg.lu_solve`. While doing so, I found a bug in MAGMA
when calling the batched MAGMA backend with trans=True. We work around
that by solving the system solving two triangular systems.
We also update the heuristics for this function, as they were fairly
updated. We found that cuSolver is king, so luckily we do not need to
rely on the buggy backend from magma for this function.
We added tests testing this function left and right. We also added tests
for the different backends. We also activated the tests for AMD, as
those should work as well.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/61657
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72935
Approved by: https://github.com/IvanYashchuk, https://github.com/mruberry
This PR modifies `lu_unpack` by:
- Using less memory when unpacking `L` and `U`
- Fuse the subtraction by `-1` with `unpack_pivots_stub`
- Define tensors of the correct types to avoid copies
- Port `lu_unpack` to be a strucutred kernel so that its `_out` version
does not incur on extra copies
Then we implement `linalg.lu` as a structured kernel, as we want to
compute its derivative manually. We do so because composing the
derivatives of `torch.lu_factor` and `torch.lu_unpack` would be less efficient.
This new function and `lu_unpack` comes with all the things it can come:
forward and backward ad, decent docs, correctness tests, OpInfo, complex support,
support for metatensors and support for vmap and vmap over the gradients.
I really hope we don't continue adding more features.
This PR also avoids saving some of the tensors that were previously
saved unnecessarily for the backward in `lu_factor_ex_backward` and
`lu_backward` and does some other general improvements here and there
to the forward and backward AD formulae of other related functions.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/67833
Approved by: https://github.com/IvanYashchuk, https://github.com/nikitaved, https://github.com/mruberry
We derive and implement a more concise rule for the forward and backward
derivatives of the QR decomposition. While doing this we:
- Fix the composite compliance of `linalg.qr` and we make it support batches
- Improve the performance and simplify the implementation of both foward and backward
- Avoid saving the input matrix for the backward computation.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/76115
Approved by: https://github.com/nikitaved, https://github.com/albanD
Let's make sure we don't break anything in the next PRs of the stack.
Also some comprehensive testing of matmul on CPU and CUDA was long due.
Running this tests we see that the `out=` variant of matmul is broken
when used on 4D tensors. This hints what would be the amount of people
that use out= variants...
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/75193
Approved by: https://github.com/ngimel
This PR adds a function for computing the LDL decomposition and a function that can solve systems of linear equations using this decomposition. The result of `torch.linalg.ldl_factor_ex` is in a compact form and it's required to use it only through `torch.linalg.ldl_solve`. In the future, we could provide `ldl_unpack` function that transforms the compact representation into explicit matrices.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/54847.
cc @jianyuh @nikitaved @pearu @mruberry @walterddr @IvanYashchuk @xwang233 @Lezcano
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69828
Approved by: https://github.com/Lezcano, https://github.com/mruberry, https://github.com/albanD
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/73748
This adds CPU-only slow test jobs, which previously would never run.
Includes fixes/skips for slow tests which fail (they need to be skipped now because they used to never run)
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D34628803
Pulled By: davidberard98
fbshipit-source-id: c090ab7bf7bda9e24ec5cdefa6fd35c6310dbac0
(cherry picked from commit 06f7a94a57cc7023e9c5442be8298d20cd011144)
Summary:
Previous PR with the same content: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69752. Opening a new PR by request: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69752#issuecomment-1020829812.
------
Previously for single input matrix A and batched matrix B, matrix A was expanded and cloned before computing the LU decomposition and solving the linear system.
With this PR the LU decomposition is computed once for a single matrix and then expanded&cloned if required by a backend library call for the linear system solving.
Here's a basic comparison:
```python
# BEFORE THE PR
In [1]: import torch
In [2]: a = torch.randn(256, 256)
In [3]: b = torch.randn(1024, 256, 2)
In [4]: %%timeit
...: torch.linalg.solve(a, b)
...:
...:
329 ms ± 17.4 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)
# WITH THIS PR
In [1]: import torch
In [2]: a = torch.randn(256, 256)
In [3]: b = torch.randn(1024, 256, 2)
In [4]: %%timeit
...: torch.linalg.solve(a, b)
...:
...:
21.4 ms ± 23 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)
```
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/71406, fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/71610
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/71756
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D33771981
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 0917ee36a3eb622ff75d54787b1bffe26b41cb4a
(cherry picked from commit 9c30a05aaa972bc02dfc94c3d2463f0c5ee0c58c)
Summary:
This PR was opened as copy of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/68812 by request https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/68812#issuecomment-1030215862.
-----
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/67693.
Reference LAPACK (used in OpenBLAS) changed info error code for svd when inputs contain non-finite numbers. In PyTorch, we raise an internal assert error for negative `info` error codes because usually, it would indicate the wrong implementation. However, this is not the case with SVD now in newer versions of LAPACK. MKL (tried 2021.4.0) still gives a positive error code for this kind of input. This change aligns with the OpenBLAS and MKL behavior in our code.
MKL 2022 has uses the latest reference LAPACK behavior and returns the same `info` as OpenBLAS 0.3.15+
This PR also fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/71645 that is due to the updated MKL version in CI.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72357
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D34012245
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 2b66c173cc3458d8c766b542d0d569191cdce310
(cherry picked from commit fa29e65611)