mirror of
https://github.com/zebrajr/pytorch.git
synced 2025-12-06 12:20:52 +01:00
Add path optimize kwarg to einsum (#84890)
## This PR seeks to:
- [x] add c++ support for an optimize path
- [x] add python opt_einsum path passthrough
- [x] add opt_einsum to OSS requirements, but a soft one
- [x] show benchmark results here
Additional things I've explored + their conclusions:
- **Delaying the summing over dimensions** => added!
- The idea here is to not incur kernel calls to `sum` as we try to early sum out in einsum. Thus, we collect all the dimensions that need to be summed together in one contraction + sum at the end instead of summing as we go. While this optimization didn't feel like it made things faster for the random cases we've selected (they all summed 1 dim per contraction), it is a good principle and would help more common use cases that would reduce multiple dimensions at a time (like `bxy,xyi,xyj->bij`).
- **Caching contract_path based on equation and tensor sizes** => dropped :(
- The benchmarks were strictly worse for all the cases, and, from scanning the use cases, I observed people do not often call einsum on the same equation/tensor order enough for caching to be justified. I do think caching can be effective in the future, but it would require further investigation.
## Not a part of this PR (but are next steps):
- adding opt_einsum package to OSS CI
- adding it to internal CI
- potentially adding a kwarg path argument to the python API -- if the path is given, we wouldn't have to spend time calculating it, but there would be some time lost validating user input.
## Testing:
- Added more tests to CI
## Benchmarking:
**TL;DRs**
- **torch.einsum with opt_einsum is a definite win for the production case**.
- **torch.einsum with opt_einsum installed is consistently fast, but has an overhead** of needing to find the path. If the path is already found/optimal, it will be slightly slower.
- The einsum overhead decreases for bigger dimensions.
- **torch.einsum without opt_einsum installed is comparable to before this commit**, with occasional slowness potentially due to not reshaping/squeezing as we contract until the end.
- For many of the random generated cases, the dimensions were too similar and small where an optimal order wasn't that much more optimal than just going left to right. However, in production, dimensions are commonly quite distinct (batch size will be small, but the data will be huge).
- **torch.einsum opt is comparable (slightly faster overall) compared to numpy.einsum opt for the cpu case**. This is interesting given that torch.einsum currently spends time computing the path, but numpy.einsum takes it as input.
- **torch.einsum opt is significantly faster than numpy.einsum opt for the gpu case**. This is because numpy doesn't take advantage of GPUs.
The following benchmarks were done on an A100 GPU and Linux CPUs. The line in the first chart separates GPU (on top) from CPU, and the line in the second graph separates CPU (on top) and then GPU. Sorry it's flipped 😛 .
Production example (see [colab benchmark](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1V2s4v1dOOKwRvp5T_DC-PNUosOV9FFJx?authuser=1#scrollTo=WZoQkC8Mdt6I) for more context):
<img width="1176" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/31798555/192012636-9a68bfa7-2601-43b1-afeb-b4e0877db6a4.png">
Randomly generated examples (the same ones as in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/60191)
<img width="1176" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/31798555/192012804-1c639595-b3e6-48c9-a385-ad851c13e1c2.png">
Open below to see old + not super relevant benchmarking results:
<details>
Benchmark results BEFORE this PR (on Linux -- I will update devices so they are consistent later):
<img width="776" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/31798555/190807274-18f71fce-556e-47f4-b18c-e0f7d0c0d5aa.png">
Benchmark results with the code on this PR (on my x86 mac):
For the CPU internal use case --
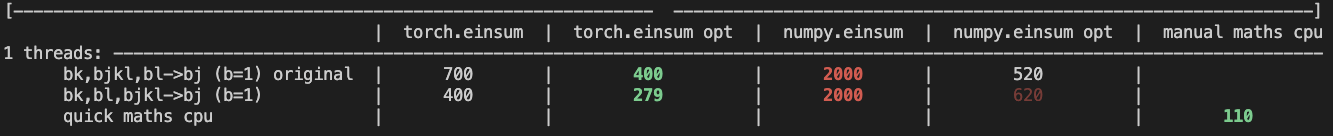
For the general use case --
It looks like numpy opt still does better in several of these random cases, but torch einsum opt is consistently faster than torch.einsum.
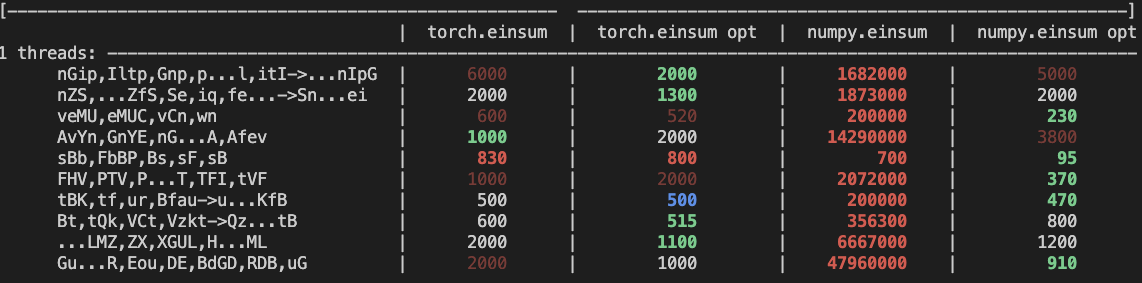
<details>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/84890
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD, https://github.com/soulitzer
This commit is contained in:
parent
e78e00f4d9
commit
e7e1cd945f
2
.github/ci_commit_pins/xla.txt
vendored
2
.github/ci_commit_pins/xla.txt
vendored
|
|
@ -1 +1 @@
|
|||
revert-4019-revert-3913-ceil_forr_round_trunc_int
|
||||
einsum-path
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -344,7 +344,7 @@ TORCH_LIBRARY_IMPL(aten, Autocast, m) {
|
|||
KERNEL(ADD_NS(addmv), "addmv", Tensor (const Tensor &, const Tensor &, const Tensor &, const Scalar&, const Scalar&), lower_precision_fp)
|
||||
KERNEL(ADD_NS(addr), "addr", Tensor (const Tensor &, const Tensor &, const Tensor &, const Scalar&, const Scalar&), lower_precision_fp)
|
||||
KERNEL(ADD_NS(matmul), "matmul", Tensor (const Tensor &, const Tensor &), lower_precision_fp)
|
||||
KERNEL(ADD_NS(einsum), "einsum", Tensor (c10::string_view, TensorList), lower_precision_fp)
|
||||
KERNEL(ADD_NS(einsum), "einsum", Tensor (c10::string_view, TensorList, OptionalIntArrayRef), lower_precision_fp)
|
||||
KERNEL(ADD_NS(mm), "mm", Tensor (const Tensor &, const Tensor &), lower_precision_fp)
|
||||
KERNEL(ADD_NS(mv), "mv", Tensor (const Tensor &, const Tensor &), lower_precision_fp)
|
||||
KERNEL(ADD_NS(linear), "linear", Tensor (const Tensor &, const Tensor &, const c10::optional<Tensor>&), lower_precision_fp)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -2,6 +2,7 @@
|
|||
#include <ATen/native/Resize.h>
|
||||
#include <ATen/NativeFunctions.h>
|
||||
#include <ATen/native/xnnpack/Engine.h>
|
||||
#include <ATen/SmallVector.h>
|
||||
#include <ATen/WrapDimUtilsMulti.h>
|
||||
#include <c10/macros/Macros.h>
|
||||
#include <c10/util/irange.h>
|
||||
|
|
@ -93,8 +94,8 @@ static Tensor sumproduct_pair(const Tensor& left_, const Tensor& right_, IntArra
|
|||
Tensor left = left_;
|
||||
Tensor right = right_;
|
||||
for (const auto i : c10::irange(dim)) {
|
||||
auto sl = left.size(i)>1;
|
||||
auto sr = right.size(i)>1;
|
||||
auto sl = left.size(i)!=1;
|
||||
auto sr = right.size(i)!=1;
|
||||
if (sum_dims[i]) { // first dimensions that will be summed over after multiplication
|
||||
if (sl && sr) { // dimensions nontrivially in both left and right must be of the same size
|
||||
TORCH_CHECK(left.size(i)==right.size(i), "non-broadcast dimensions must match");
|
||||
|
|
@ -184,8 +185,19 @@ static Tensor sumproduct_pair(const Tensor& left_, const Tensor& right_, IntArra
|
|||
// 2. Unsqueeze missing dimensions from input operands and permute to align them
|
||||
// 3. Compute result by multiplying input operands and summing contraction
|
||||
// dimensions We do the last part by reducing to bmm.
|
||||
Tensor einsum(c10::string_view equation, TensorList operands) {
|
||||
Tensor einsum(c10::string_view equation, TensorList operands, at::OptionalIntArrayRef path) {
|
||||
TORCH_CHECK(!operands.empty(), "einsum(): must provide at least one operand");
|
||||
const auto num_ops = operands.size();
|
||||
|
||||
if (path.has_value()) {
|
||||
const auto path_size = num_ops == 1 ? 1 : (num_ops - 1) * 2;
|
||||
TORCH_CHECK(
|
||||
path->size() == path_size,
|
||||
"einsum(): expected contraction path given in path parameter to have size ",
|
||||
path_size,
|
||||
" but got ",
|
||||
path->size());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Labels must be in range [A-Za-z]
|
||||
constexpr uint8_t NUM_OF_LETTERS = 'z' - 'a' + 1;
|
||||
|
|
@ -208,12 +220,10 @@ Tensor einsum(c10::string_view equation, TensorList operands) {
|
|||
const auto arrow_pos = equation.find("->");
|
||||
const auto lhs = equation.substr(0, arrow_pos);
|
||||
|
||||
const auto num_ops = operands.size();
|
||||
|
||||
// Convert labels for input operands into an index in [0, 52) and store
|
||||
// them in op_labels for each operand along with ELLIPSIS if present.
|
||||
std::vector<std::vector<uint8_t>> op_labels(num_ops);
|
||||
bool found_ell = false;
|
||||
bool ell_in_input = false;
|
||||
std::size_t curr_op = 0;
|
||||
for (auto i = decltype(lhs.length()){0}; i < lhs.length(); ++i) {
|
||||
const unsigned char label = lhs[i];
|
||||
|
|
@ -225,7 +235,7 @@ Tensor einsum(c10::string_view equation, TensorList operands) {
|
|||
case '.':
|
||||
TORCH_CHECK(
|
||||
// Only one ellipsis per operand can be given
|
||||
!found_ell,
|
||||
!ell_in_input,
|
||||
"einsum(): found \'.\' for operand ",
|
||||
curr_op,
|
||||
" for which an ellipsis was already found");
|
||||
|
|
@ -236,7 +246,7 @@ Tensor einsum(c10::string_view equation, TensorList operands) {
|
|||
curr_op,
|
||||
" that is not part of any ellipsis");
|
||||
op_labels[curr_op].push_back(ELLIPSIS);
|
||||
found_ell = true;
|
||||
ell_in_input = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case ',':
|
||||
|
|
@ -245,7 +255,7 @@ Tensor einsum(c10::string_view equation, TensorList operands) {
|
|||
TORCH_CHECK(
|
||||
curr_op < num_ops,
|
||||
"einsum(): fewer operands were provided than specified in the equation");
|
||||
found_ell = false;
|
||||
ell_in_input = false;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
default:
|
||||
|
|
@ -311,12 +321,13 @@ Tensor einsum(c10::string_view equation, TensorList operands) {
|
|||
|
||||
// Start index of ellipsis dimensions in the permuted shape
|
||||
int64_t ell_index = 0;
|
||||
found_ell = false;
|
||||
bool ell_in_output = false;
|
||||
|
||||
if (arrow_pos == std::string::npos) {
|
||||
// Implicit output is ellipsis (...) + labels seen only once
|
||||
perm_index = ell_num_dim;
|
||||
found_ell = true;
|
||||
// ell_in_output is used to stop us from reducing ellipses dims later
|
||||
ell_in_output = true;
|
||||
for (const auto label : c10::irange(TOTAL_LABELS)) {
|
||||
if (label_count[label] == 1) {
|
||||
label_perm_index[label] = perm_index++;
|
||||
|
|
@ -335,7 +346,7 @@ Tensor einsum(c10::string_view equation, TensorList operands) {
|
|||
case '.':
|
||||
TORCH_CHECK(
|
||||
// There can only be one ellipsis in the output
|
||||
!found_ell,
|
||||
!ell_in_output,
|
||||
"einsum(): found \'.\' for output but an ellipsis (...) was already found");
|
||||
TORCH_CHECK(
|
||||
// Ensure ellipsis is correct
|
||||
|
|
@ -343,7 +354,7 @@ Tensor einsum(c10::string_view equation, TensorList operands) {
|
|||
"einsum(): found \'.\' for output that is not part of any ellipsis (...)");
|
||||
ell_index = perm_index;
|
||||
perm_index += ell_num_dim;
|
||||
found_ell = true;
|
||||
ell_in_output = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
default:
|
||||
|
|
@ -367,11 +378,11 @@ Tensor einsum(c10::string_view equation, TensorList operands) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Save output size before adding contraction dims (dims to sum out)
|
||||
const int64_t out_size = perm_index;
|
||||
// Save number of dimensions in output before adding contraction dims (dims to sum out)
|
||||
const int64_t out_num_dim = perm_index;
|
||||
|
||||
// If ellipsis is not part of the output, add to contraction dimensions
|
||||
if (!found_ell) {
|
||||
if (!ell_in_output) {
|
||||
ell_index = perm_index;
|
||||
perm_index += ell_num_dim;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -383,144 +394,156 @@ Tensor einsum(c10::string_view equation, TensorList operands) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Here we unsqueeze missing dimensions to make all operands have the same
|
||||
// number of dimensions. We take diagonals for repeated labels within the
|
||||
// same operand. Finally we permute the operands to align dimensions as
|
||||
// per the perm_out_index we computed above.
|
||||
std::vector<Tensor> permuted_operands;
|
||||
for (const auto i: c10::irange(num_ops)) {
|
||||
std::vector<int64_t> perm_shape(perm_index, -1);
|
||||
std::vector<int64_t> label_dim(TOTAL_LABELS, -1);
|
||||
Tensor operand = operands[i];
|
||||
const auto labels = op_labels[i];
|
||||
const auto original_sizes = operand.sizes();
|
||||
|
||||
int64_t j = 0;
|
||||
for (const auto& label : labels) {
|
||||
if (label == ELLIPSIS) {
|
||||
// Add missing dimensions covered by the ellipsis
|
||||
const auto num_missing_dim =
|
||||
ell_num_dim - (original_sizes.size() - labels.size() + 1);
|
||||
for (const auto k : c10::irange(num_missing_dim)) {
|
||||
(void)k; //Suppress unused warning
|
||||
operand = operand.unsqueeze(j);
|
||||
// Next we check the sizes, take diagonals for repeated labels, unsqueeze
|
||||
// missing dimensions so all operands have the same dimensions and permute
|
||||
// the operands to align the dimensions following the indices compute above.
|
||||
// We also count how many operands have dimension with size > 1 for each
|
||||
// label used to identify which dimensions can be contracted.
|
||||
std::vector<int64_t> label_size(TOTAL_LABELS, 1);
|
||||
std::vector<int64_t> ell_sizes(ell_num_dim, 1);
|
||||
std::vector<uint64_t> dim_counts(perm_index, 0);
|
||||
std::vector<Tensor> ops;
|
||||
for (const auto i : irange(num_ops)) {
|
||||
auto op = operands[i];
|
||||
std::vector<int64_t> permutation(perm_index, -1);
|
||||
std::int64_t dim = 0;
|
||||
for (const auto s : op_labels[i]) {
|
||||
if (s == ELLIPSIS) {
|
||||
// Iterate over each dimension covered by ellipsis
|
||||
const auto ndim = operands[i].ndimension() - (static_cast<int64_t>(op_labels[i].size()) - 1);
|
||||
for (auto j = ell_num_dim - ndim; j < ell_num_dim; ++j) {
|
||||
if (op.size(dim) != 1) {
|
||||
// Update ellipsis size
|
||||
TORCH_CHECK(
|
||||
ell_sizes[j] == 1 || ell_sizes[j] == op.size(dim),
|
||||
"einsum(): dimension ",
|
||||
dim,
|
||||
" covered by ellipsis in operand ",
|
||||
i,
|
||||
"has size ",
|
||||
op.size(dim),
|
||||
" which does not broadcast with previously seen ellipsis with size ",
|
||||
ell_sizes[j],
|
||||
" for the respective dimension");
|
||||
ell_sizes[j] = op.size(dim);
|
||||
++dim_counts[ell_index + j];
|
||||
}
|
||||
permutation[ell_index + j] = dim++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (const auto k : c10::irange(ell_num_dim)) {
|
||||
perm_shape[ell_index + k] = j++;
|
||||
} else if (permutation[label_perm_index[s]] == -1) {
|
||||
if (op.size(dim) != 1) {
|
||||
// Update subscript
|
||||
TORCH_CHECK(
|
||||
label_size[s] == 1 || label_size[s] == op.size(dim),
|
||||
"einsum(): subscript ",
|
||||
subscript_to_label(s),
|
||||
" has size ",
|
||||
op.size(dim),
|
||||
" for operand ",
|
||||
i,
|
||||
" which does not broadcast with previously seen size ",
|
||||
label_size[s]);
|
||||
label_size[s] = op.size(dim);
|
||||
++dim_counts[label_perm_index[s]];
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if (label_dim[label] != -1) {
|
||||
permutation[label_perm_index[s]] = dim++;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Repeated label, take diagonal
|
||||
const auto dim = label_dim[label];
|
||||
const auto prev_dim = permutation[label_perm_index[s]];
|
||||
TORCH_CHECK(
|
||||
operand.size(j) == operand.size(dim),
|
||||
op.size(dim) == op.size(prev_dim),
|
||||
"einsum(): subscript ",
|
||||
subscript_to_label(label),
|
||||
subscript_to_label(s),
|
||||
" is repeated for operand ",
|
||||
i,
|
||||
" but the sizes don't match, ",
|
||||
operand.size(j),
|
||||
op.size(dim),
|
||||
" != ",
|
||||
operand.size(dim));
|
||||
operand = operand.diagonal(0, dim, j).movedim(-1, dim);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Lookup output index for label
|
||||
label_dim[label] = j;
|
||||
perm_shape[label_perm_index[label]] = j++;
|
||||
op.size(prev_dim));
|
||||
op = op.diagonal(0, prev_dim, dim).movedim(-1, prev_dim);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add dimensions for missing labels
|
||||
for (int64_t& index : perm_shape) {
|
||||
if (index == -1) {
|
||||
operand = operand.unsqueeze(-1);
|
||||
index = j++;
|
||||
for (auto& val : permutation) {
|
||||
if (val == -1) {
|
||||
op = op.unsqueeze(dim);
|
||||
val = dim++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
permuted_operands.push_back(operand.permute(perm_shape));
|
||||
ops.emplace_back(op.permute(permutation));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Check if operands broadcast and keep track of last operand with
|
||||
// dimension size != 1 for optimizing reductions
|
||||
std::vector<std::size_t> dim_last_op(perm_index, 0);
|
||||
bool has_zero_size_dim = false;
|
||||
for (const auto dim : c10::irange(perm_index)) {
|
||||
auto broadcast_size = permuted_operands[0].size(dim);
|
||||
for (const auto i: c10::irange(1, num_ops)) {
|
||||
const auto dim_size = permuted_operands[i].size(dim);
|
||||
if (broadcast_size != dim_size && broadcast_size != 1 && dim_size != 1) {
|
||||
std::ostringstream msg;
|
||||
msg << "einsum(): operands do not broadcast with remapped shapes [original->remapped]:";
|
||||
for (const auto j: c10::irange(num_ops)) {
|
||||
msg << " " << operands[j].sizes() << "->"
|
||||
<< permuted_operands[j].sizes();
|
||||
}
|
||||
TORCH_CHECK(false, msg.str());
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (dim_size != 1) {
|
||||
broadcast_size = dim_size;
|
||||
dim_last_op[dim] = i;
|
||||
const auto contract_path = path.value_or(std::vector<int64_t>{});
|
||||
auto it = contract_path.begin();
|
||||
|
||||
// Contract
|
||||
while (ops.size() > 1) {
|
||||
int64_t i = 0;
|
||||
int64_t j = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
if (path.has_value()) {
|
||||
i = *it++;
|
||||
j = *it++;
|
||||
if (j < i) {
|
||||
std::swap(i, j);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TORCH_CHECK(
|
||||
i != j && i >= 0 && j < static_cast<int64_t>(ops.size()),
|
||||
"einsum(): invalid contraction (",
|
||||
i,
|
||||
", ",
|
||||
j,
|
||||
i == j ? ") cannot contract an operand with itself"
|
||||
: ") operand index is out of bounds");
|
||||
}
|
||||
has_zero_size_dim |= broadcast_size == 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute result
|
||||
Tensor result = permuted_operands[0];
|
||||
auto a = ops[i];
|
||||
auto b = ops[j];
|
||||
ops.erase(ops.begin() + j);
|
||||
ops.erase(ops.begin() + i);
|
||||
|
||||
// Fast path for when an operand has zero sized dim
|
||||
if (has_zero_size_dim) {
|
||||
std::vector<int64_t> out_shape(out_size);
|
||||
for (const auto i : c10::irange(out_size)) {
|
||||
out_shape[i] = permuted_operands[dim_last_op[i]].size(i);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return at::zeros(out_shape, result.options());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Sum out or squeeze dimensions that are size 1 for all later operands
|
||||
int64_t dim = out_size;
|
||||
for (int64_t i = dim; i < perm_index; ++i, ++dim) {
|
||||
if (dim_last_op[i] == 0) {
|
||||
if (result.size(dim) == 1) {
|
||||
result = result.squeeze(dim--);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
result = result.sum(dim--);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (const auto i: c10::irange(1, num_ops)) {
|
||||
Tensor operand = permuted_operands[i];
|
||||
// Collect dimensions that can be summed now
|
||||
std::vector<int64_t> sum_dims;
|
||||
|
||||
// Sum out or squeeze dimensions that are size 1 for all later operands
|
||||
dim = out_size;
|
||||
for (int64_t j = dim; j < perm_index; ++j, ++dim) {
|
||||
if (dim_last_op[j] < i) {
|
||||
operand = operand.squeeze(dim);
|
||||
--dim;
|
||||
} else if (dim_last_op[j] == i) {
|
||||
if (result.size(dim) == 1) {
|
||||
operand = operand.sum(dim);
|
||||
result = result.squeeze(dim);
|
||||
--dim;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SmallVector<int64_t, 5> a_dims_to_sum;
|
||||
SmallVector<int64_t, 5> b_dims_to_sum;
|
||||
for (auto dim = out_num_dim; dim < perm_index; ++dim) {
|
||||
if (a.size(dim) != 1 && b.size(dim) != 1) {
|
||||
if (--dim_counts[dim] == 1) {
|
||||
sum_dims.push_back(dim);
|
||||
dim_counts[dim] = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if (dim_counts[dim] == 1) {
|
||||
if (a.size(dim) != 1) {
|
||||
a_dims_to_sum.push_back(dim);
|
||||
dim_counts[dim] = 0;
|
||||
} else if (b.size(dim) != 1) {
|
||||
b_dims_to_sum.push_back(dim);
|
||||
dim_counts[dim] = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Multiply tensors and sum out dimensions in sum_dims
|
||||
if (sum_dims.empty()) {
|
||||
result = result.mul(operand);
|
||||
} else if (sum_dims.size() == result.sizes().size()) {
|
||||
result = result.flatten().dot(operand.flatten());
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
result = sumproduct_pair(result, operand, sum_dims, false);
|
||||
// Sum multiple dims at a time to minimize the number of kernel calls to sum
|
||||
if (!a_dims_to_sum.empty()) {
|
||||
a = a.sum(a_dims_to_sum, true);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (!b_dims_to_sum.empty()) {
|
||||
b = b.sum(b_dims_to_sum, true);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ops.emplace_back(sumproduct_pair(a, b, sum_dims, true));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
// Sum out contraction dims
|
||||
if (perm_index - out_num_dim > 0) {
|
||||
std::vector<int64_t> sum_dims(perm_index - out_num_dim);
|
||||
std::iota(sum_dims.begin(), sum_dims.end(), out_num_dim);
|
||||
ops[0] = ops[0].sum(sum_dims);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return ops[0];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// _trilinear computes a trilinear einstein sum with an unrolled dimension
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1995,7 +1995,7 @@
|
|||
dispatch:
|
||||
CompositeExplicitAutograd: vdot_out
|
||||
|
||||
- func: einsum(str equation, Tensor[] tensors) -> Tensor
|
||||
- func: einsum(str equation, Tensor[] tensors, *, int[]? path=None) -> Tensor
|
||||
|
||||
- func: embedding(Tensor weight, Tensor indices, int padding_idx=-1, bool scale_grad_by_freq=False, bool sparse=False) -> Tensor
|
||||
dispatch:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
5
setup.py
5
setup.py
|
|
@ -989,6 +989,10 @@ def main():
|
|||
|
||||
install_requires += extra_install_requires
|
||||
|
||||
extras_require = {
|
||||
'opt-einsum': ['opt-einsum>=3.3']
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Read in README.md for our long_description
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(cwd, "README.md"), encoding="utf-8") as f:
|
||||
long_description = f.read()
|
||||
|
|
@ -1168,6 +1172,7 @@ def main():
|
|||
packages=packages,
|
||||
entry_points=entry_points,
|
||||
install_requires=install_requires,
|
||||
extras_require=extras_require,
|
||||
package_data={
|
||||
'torch': torch_package_data,
|
||||
'torchgen': torchgen_package_data,
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -3776,9 +3776,9 @@ class TestLinalg(TestCase):
|
|||
|
||||
def test(n=10, # how many tests to generate
|
||||
n_labels=5, # how many labels available
|
||||
min_ops=1, max_ops=3, # min and max number of operands per test
|
||||
min_ops=1, max_ops=4, # min and max number of operands per test
|
||||
min_dims=1, max_dims=3, # min and max number of dimensions per operand
|
||||
min_size=1, max_size=8, # min and max size of each dimension
|
||||
min_size=1, max_size=8, # min and max size of each dimension
|
||||
max_out_dim=3, # max number of dimensions for the output
|
||||
enable_diagonals=True, # controls if labels can be repeated for diagonals
|
||||
ellipsis_prob=0.5, # probability of including ellipsis in operand
|
||||
|
|
@ -3867,7 +3867,7 @@ class TestLinalg(TestCase):
|
|||
args.append(out_sublist)
|
||||
self._check_einsum(*args, np_args=(equation, *np_operands))
|
||||
|
||||
test(100)
|
||||
test(500)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_einsum_corner_cases(self, device):
|
||||
def check(equation, *operands, expected_output):
|
||||
|
|
@ -3935,8 +3935,10 @@ class TestLinalg(TestCase):
|
|||
check('a->aa', [x], regex=r'output subscript a appears more than once in the output')
|
||||
check('a->i', [x], regex=r'output subscript i does not appear in the equation for any input operand')
|
||||
check('aa', [y], regex=r'subscript a is repeated for operand 0 but the sizes don\'t match, 3 != 2')
|
||||
check('a, ba', [x, y], regex=r'operands do not broadcast with remapped shapes \[original->remapped\]: '
|
||||
r'\[2\]->\[1, 2\] \[2, 3\]->\[2, 3\]')
|
||||
check('...,...', [x, y], regex=r'does not broadcast')
|
||||
check('a,a', [x, make_tensor((3,), dtype=torch.float32, device=device)], regex=r'does not broadcast')
|
||||
check('a, ba', [x, y], regex=r'subscript a has size 3 for operand 1 which does not broadcast with previously'
|
||||
r' seen size 2')
|
||||
|
||||
check(x, [-1], regex=r'not within the valid range \[0, 52\)', exception=ValueError)
|
||||
check(x, [52], regex=r'not within the valid range \[0, 52\)', exception=ValueError)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,6 +15,14 @@ from ._jit_internal import _overload as overload
|
|||
Tensor = torch.Tensor
|
||||
from torch import _VF
|
||||
|
||||
# Set a global declaring that we have opt_einsum
|
||||
from importlib.util import find_spec as _find_spec
|
||||
if _find_spec('opt_einsum') is not None:
|
||||
import opt_einsum as _opt_einsum # type: ignore[import]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
_opt_einsum = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = [
|
||||
'atleast_1d',
|
||||
'atleast_2d',
|
||||
|
|
@ -238,9 +246,10 @@ def einsum(*args: Any) -> Tensor:
|
|||
|
||||
.. note::
|
||||
|
||||
This function does not optimize the given expression, so a different formula for the same computation may
|
||||
run faster or consume less memory. Projects like opt_einsum (https://optimized-einsum.readthedocs.io/en/stable/)
|
||||
can optimize the formula for you.
|
||||
This function uses opt_einsum (https://optimized-einsum.readthedocs.io/en/stable/) to speed up computation or to
|
||||
consume less memory by optimizing contraction order. Note that finding _the_ optimal path is an NP-hard problem,
|
||||
thus, opt_einsum relies on different heuristics to achieve near-optimal results. If opt_einsum is not available,
|
||||
the default order is to contract from left to right.
|
||||
|
||||
.. note::
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -361,7 +370,16 @@ def einsum(*args: Any) -> Tensor:
|
|||
# in the original implementation this line is omitted
|
||||
return einsum(equation, *_operands)
|
||||
|
||||
return _VF.einsum(equation, operands) # type: ignore[attr-defined]
|
||||
if len(operands) <= 2:
|
||||
# the path for contracting 0 or 1 time(s) is already optimized
|
||||
return _VF.einsum(equation, operands) # type: ignore[attr-defined]
|
||||
|
||||
path = None
|
||||
if _opt_einsum is not None:
|
||||
tupled_path = _opt_einsum.contract_path(equation, *operands)[0]
|
||||
# flatten path for dispatching to C++
|
||||
path = [item for pair in tupled_path for item in pair]
|
||||
return _VF.einsum(equation, operands, path=path) # type: ignore[attr-defined]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# This wrapper exists to support variadic args.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ _onnx_symbolic = functools.partial(registration.onnx_symbolic, opset=12)
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
@_beartype.beartype
|
||||
def _einsum_helper(g, equation, tensors):
|
||||
def _einsum_helper(g, equation, tensors, path=None):
|
||||
if not tensors:
|
||||
raise RuntimeError("Einsum inputs are empty.")
|
||||
# ONNX does not support bool for Einsum inputs.
|
||||
|
|
@ -54,19 +54,19 @@ def _einsum_helper(g, equation, tensors):
|
|||
]
|
||||
return g.op(
|
||||
"Cast",
|
||||
g.op("Einsum", *tensors, equation_s=equation),
|
||||
g.op("Einsum", *tensors, equation_s=equation, path_is=path),
|
||||
to_i=_C_onnx.TensorProtoDataType.BOOL,
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return g.op("Einsum", *tensors, equation_s=equation)
|
||||
return g.op("Einsum", *tensors, equation_s=equation, path_is=path)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@_onnx_symbolic("aten::einsum")
|
||||
@symbolic_helper.parse_args("s", "v")
|
||||
@symbolic_helper.parse_args("s", "v", "is")
|
||||
@_beartype.beartype
|
||||
def einsum(g, equation, tensor_list):
|
||||
def einsum(g, equation, tensor_list, path=None):
|
||||
tensors = symbolic_helper._unpack_list(tensor_list)
|
||||
return _einsum_helper(g, equation, tensors)
|
||||
return _einsum_helper(g, equation, tensors, path)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@_onnx_symbolic("aten::outer")
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user