Summary:
Regularize mask handling for attn_mask and key_padding_mask
* Update documentation to remove reference to byte masks (which were deprecated long ago)
* Introduce check and warn about deprecation if attn_mask and key_padding_mask types mismatch
* Convert all masks to float before combining
* Combine by adding
Test Plan: sandcastle & github CI
Differential Revision: D42653215
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/92733
Approved by: https://github.com/ngimel, https://github.com/drisspg
# Summary
In preparation for pt 2.0 launch this PR updates SDPA's API and makes the function a nn.funcitonal public function.
## Changes
### API
Previously the the function signature was:
`scaled_dot_product_attention(query, key, value, attn_mask=None, need_attn_weights=False, dropout_p=0.0, is_causal=False) -> (Tensor, Tensor)`
Updated signature:
`scaled_dot_product_attention(query, key, value, attn_mask=None, dropout_p=0.0, is_causal=False) -> Tensor`
This PR removes the need_attn_weights optional boolean variable and updates the return type to a singular tensor.
#### Reasoning:
The main goal of this function is to provide an easy interface for users to call into fused attention kernels e.g. (FlashAttention). The fused kernels do not currently support arbitrary attn_mask or dropout but there is a PR to mem-efficient attention to enable these. We want to have the API surface ready for when the backing kernels get updated.
The fused kernels save on memory usage by not materializing the weights and it is unlikely that a fast fused implementation will enable this feature so we are removing.
Discussed with folks at FAIR/Xformers and +1 this API change.
#### Make function Public
In preparation for the pt 2.0 launch we make the function public to start to generate user feedback
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/92189
Approved by: https://github.com/cpuhrsch
We have known for a while that we should in principle support SymBool as a separate concept from SymInt and SymFloat ( in particular, every distinct numeric type should get its own API). However, recent work with unbacked SymInts in, e.g., https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/90985 have made this a priority to implement. The essential problem is that our logic for computing the contiguity of tensors performs branches on the passed in input sizes, and this causes us to require guards when constructing tensors from unbacked SymInts. Morally, this should not be a big deal because, we only really care about the regular (non-channels-last) contiguity of the tensor, which should be guaranteed since most people aren't calling `empty_strided` on the tensor, however, because we store a bool (not a SymBool, prior to this PR it doesn't exist) on TensorImpl, we are forced to *immediately* compute these values, even if the value ends up not being used at all. In particular, even when a user allocates a contiguous tensor, we still must compute channels-last contiguity (as some contiguous tensors are also channels-last contiguous, but others are not.)
This PR implements SymBool, and makes TensorImpl use SymBool to store the contiguity information in ExtraMeta. There are a number of knock on effects, which I now discuss below.
* I introduce a new C++ type SymBool, analogous to SymInt and SymFloat. This type supports logical and, logical or and logical negation. I support the bitwise operations on this class (but not the conventional logic operators) to make it clear that logical operations on SymBool are NOT short-circuiting. I also, for now, do NOT support implicit conversion of SymBool to bool (creating a guard in this case). This does matter too much in practice, as in this PR I did not modify the equality operations (e.g., `==` on SymInt) to return SymBool, so all preexisting implicit guards did not need to be changed. I also introduced symbolic comparison functions `sym_eq`, etc. on SymInt to make it possible to create SymBool. The current implementation of comparison functions makes it unfortunately easy to accidentally introduce guards when you do not mean to (as both `s0 == s1` and `s0.sym_eq(s1)` are valid spellings of equality operation); in the short term, I intend to prevent excess guarding in this situation by unit testing; in the long term making the equality operators return SymBool is probably the correct fix.
* ~~I modify TensorImpl to store SymBool for the `is_contiguous` fields and friends on `ExtraMeta`. In practice, this essentially meant reverting most of the changes from https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/85936 . In particular, the fields on ExtraMeta are no longer strongly typed; at the time I was particularly concerned about the giant lambda I was using as the setter getting a desynchronized argument order, but now that I have individual setters for each field the only "big list" of boolean arguments is in the constructor of ExtraMeta, which seems like an acceptable risk. The semantics of TensorImpl are now that we guard only when you actually attempt to access the contiguity of the tensor via, e.g., `is_contiguous`. By in large, the contiguity calculation in the implementations now needs to be duplicated (as the boolean version can short circuit, but the SymBool version cannot); you should carefully review the duplicate new implementations. I typically use the `identity` template to disambiguate which version of the function I need, and rely on overloading to allow for implementation sharing. The changes to the `compute_` functions are particularly interesting; for most of the functions, I preserved their original non-symbolic implementation, and then introduce a new symbolic implementation that is branch-less (making use of our new SymBool operations). However, `compute_non_overlapping_and_dense` is special, see next bullet.~~ This appears to cause performance problems, so I am leaving this to an update PR.
* (Update: the Python side pieces for this are still in this PR, but they are not wired up until later PRs.) While the contiguity calculations are relatively easy to write in a branch-free way, `compute_non_overlapping_and_dense` is not: it involves a sort on the strides. While in principle we can still make it go through by using a data oblivious sorting network, this seems like too much complication for a field that is likely never used (because typically, it will be obvious that a tensor is non overlapping and dense, because the tensor is contiguous.) So we take a different approach: instead of trying to trace through the logic computation of non-overlapping and dense, we instead introduce a new opaque operator IsNonOverlappingAndDenseIndicator which represents all of the compute that would have been done here. This function returns an integer 0 if `is_non_overlapping_and_dense` would have returned `False`, and an integer 1 otherwise, for technical reasons (Sympy does not easily allow defining custom functions that return booleans). The function itself only knows how to evaluate itself if all of its arguments are integers; otherwise it is left unevaluated. This means we can always guard on it (as `size_hint` will always be able to evaluate through it), but otherwise its insides are left a black box. We typically do NOT expect this custom function to show up in actual boolean expressions, because we will typically shortcut it due to the tensor being contiguous. It's possible we should apply this treatment to all of the other `compute_` operations, more investigation necessary. As a technical note, because this operator takes a pair of a list of SymInts, we need to support converting `ArrayRef<SymNode>` to Python, and I also unpack the pair of lists into a single list because I don't know if Sympy operations can actually validly take lists of Sympy expressions as inputs. See for example `_make_node_sizes_strides`
* On the Python side, we also introduce a SymBool class, and update SymNode to track bool as a valid pytype. There is some subtlety here: bool is a subclass of int, so one has to be careful about `isinstance` checks (in fact, in most cases I replaced `isinstance(x, int)` with `type(x) is int` for expressly this reason.) Additionally, unlike, C++, I do NOT define bitwise inverse on SymBool, because it does not do the correct thing when run on booleans, e.g., `~True` is `-2`. (For that matter, they don't do the right thing in C++ either, but at least in principle the compiler can warn you about it with `-Wbool-operation`, and so the rule is simple in C++; only use logical operations if the types are statically known to be SymBool). Alas, logical negation is not overrideable, so we have to introduce `sym_not` which must be used in place of `not` whenever a SymBool can turn up. To avoid confusion with `__not__` which may imply that `operators.__not__` might be acceptable to use (it isn't), our magic method is called `__sym_not__`. The other bitwise operators `&` and `|` do the right thing with booleans and are acceptable to use.
* There is some annoyance working with booleans in Sympy. Unlike int and float, booleans live in their own algebra and they support less operations than regular numbers. In particular, `sympy.expand` does not work on them. To get around this, I introduce `safe_expand` which only calls expand on operations which are known to be expandable.
TODO: this PR appears to greatly regress performance of symbolic reasoning. In particular, `python test/functorch/test_aotdispatch.py -k max_pool2d` performs really poorly with these changes. Need to investigate.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@meta.com>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/92149
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD, https://github.com/Skylion007
`TORCH_CHECK_TENSOR_ALL(cond, ...)` is a wrapper around `TORCH_CHECK` which allows the condition argument to be a tensor, batched or unbatched. `cond` can be a boolean tensor of any size. If any element is False, or if `cond.numel() == 0`, then `TORCH_CHECK_TENSOR_ALL` raises an error
Part of #72948
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/89097
Approved by: https://github.com/zou3519
It turns out our old max/min implementation didn't do anything, because `__max__` and `__min__` are not actually magic methods in Python. So I give 'em the `sym_` treatment, similar to the other non-overrideable builtins.
NB: I would like to use `sym_max` when computing contiguous strides but this appears to make `python test/functorch/test_aotdispatch.py -v -k test_aot_autograd_symbolic_exhaustive_nn_functional_max_pool2d_cpu_float32` run extremely slowly. Needs investigating.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@meta.com>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/92107
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD, https://github.com/voznesenskym, https://github.com/Skylion007
This PR moves the definitions for:
* `sym_int`
* `sym_ceil` (used only for `sym_int`)
* `sym_floor` (used only for `sym_int`)
* `sym_float`
from `torch/fx/experimental/symbolic_shapes.py` to `torch/__init__.py`, where `SymInt` and `SymFloat` are already defined.
This removes the need for several in-line imports, and enables proper JIT script gating for #91318. I'm very open to doing this in a better way!
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/91317
Approved by: https://github.com/ezyang, https://github.com/anijain2305
Summary: Introduce causal mask
This PR introduces a causal mask option _causal_mask (as well as causal mask detection if attn_mask is provided), since current custom kernels do not support arbitrary masks.
Test Plan: sandcastle & github ci/cd
Differential Revision: D41723137
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/90508
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD
Continuation after https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/90163.
Here is a script I used to find all the non-existing arguments in the docstrings (the script can give false positives in presence of *args/**kwargs or decorators):
_Edit:_
I've realized that the indentation is wrong for the last `break` in the script, so the script only gives output for a function if the first docstring argument is wrong. I'll create a separate PR if I find more issues with corrected script.
``` python
import ast
import os
import docstring_parser
for root, dirs, files in os.walk('.'):
for name in files:
if root.startswith("./.git/") or root.startswith("./third_party/"):
continue
if name.endswith(".py"):
full_name = os.path.join(root, name)
with open(full_name, "r") as source:
tree = ast.parse(source.read())
for node in ast.walk(tree):
if isinstance(node, ast.FunctionDef):
all_node_args = node.args.args
if node.args.vararg is not None:
all_node_args.append(node.args.vararg)
if node.args.kwarg is not None:
all_node_args.append(node.args.kwarg)
if node.args.posonlyargs is not None:
all_node_args.extend(node.args.posonlyargs)
if node.args.kwonlyargs is not None:
all_node_args.extend(node.args.kwonlyargs)
args = [a.arg for a in all_node_args]
docstring = docstring_parser.parse(ast.get_docstring(node))
doc_args = [a.arg_name for a in docstring.params]
clean_doc_args = []
for a in doc_args:
clean_a = ""
for c in a.split()[0]:
if c.isalnum() or c == '_':
clean_a += c
if clean_a:
clean_doc_args.append(clean_a)
doc_args = clean_doc_args
for a in doc_args:
if a not in args:
print(full_name, node.lineno, args, doc_args)
break
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/90505
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet, https://github.com/ZainRizvi
`torch.compile` can be used either as decorator or to optimize model directly, for example:
```
@torch.compile
def foo(x):
return torch.sin(x) + x.max()
```
or
```
mod = torch.nn.ReLU()
optimized_mod = torch.compile(mod, mode="max-autotune")
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/89607
Approved by: https://github.com/soumith
Using the same repro from the issue (but with BatchNorm2D)
Rectifies native_batch_norm schema by splitting the schema into 2:
1. one will have NON-optional alias-able running_mean and running_var inputs
2. the other will just not have those parameters at all (no_stats variation)
**Calling for name suggestions!**
## test plan
I've added tests in test_functionalization.py as well as an entry in common_method_invocations.py for `native_batch_norm_legit`
CI should pass.
## next steps
Because of bc/fc reasons, we reroute native_batch_norm to call our new schemas ONLY through the python dispatcher, but in 2 weeks or so, we should make `native_batch_norm_legit` the official batch_norm.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/88697
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD
Summary: In order to make the layer normalization implementation for nested tensors public, it needs to be generalized to accept a normalized_shape argument instead of assuming it to be the last dimension of the nested_tensor. This commit does that, as well as adding extra unit tests to ensure the implementation is correct.
Test Plan:
All unit tests designed to test different ways of using the function work:
`buck test //caffe2/test:nested -- test_layer_norm`
Differential Revision: D40105207
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/86295
Approved by: https://github.com/drisspg
Based on @ezyang's suggestion, mode stack now has "one true mode" which is the _only_ mode that can ever be active at the C++ level. That mode's torch dispatch is just to take the top mode in the stack, reenable itself (if we aren't at the end of the mode stack), and run the top mode's torch_{dispatch|function}
This maintains that in the middle of a mode's torch dispatch, the mode itself will not be active. It changes the function the user has to call to see what the current mode is (no longer queries the C++, it's python only) but allows the user to also see the entire mode stack easily
Removes `enable_torch_dispatch_mode` and `.restore()` since neither makes sense in this new setup
### Background
Why do we want this? Well, a pretty common pattern that was coming up was that users had to do something like
```python
## PRE-PR UX
def f(mode):
with mode.restore(): # user needs to understand this restore thing?
...
with Mode() as m:
pass
f(m)
```
Many users were getting error from forgetting to call `.restore` or from forgetting to add the (tbh weird) "mode instantiation" step where they use the mode as a context manager with an empty body. Really, they wanted to treat modes like context managers and just write
```python
## FROM FEEDBACK, USER DESIRED CODE. POSSIBLE POST-PR
def f(mode):
with mode:
...
f(Mode())
```
** Technical Details **
With the old mode stack, we basically had a linked list so the mode itself could only be used once and had a fixed parent. In this new design, the mode stack is just a python list that we're pushing to and popping from. There's only one mode that's ever active at the C++ level and it runs the next mode in the Python list. The modes don't have state on them anymore
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/84774
Approved by: https://github.com/ezyang, https://github.com/zou3519
As per the title. Fixes: #81161
- [x] add ErrorInputs
- ~[ ] dtype argument?~
- ~[ ] casting argument?~
As discussed offline with @kshitij12345, we can currently ignore `dtype` and `casting` arguments.
cc: @kshitij12345!
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/82946
Approved by: https://github.com/mruberry
unflatten now has a free function version in torch.flatten in addition to
the method in torch.Tensor.flatten.
Updated docs to reflect this and polished them a little.
For consistency, changed the signature of the int version of unflatten in
native_functions.yaml.
Some override tests were failing because unflatten has unusual
characteristics in terms of the .int and .Dimname versions having
different number of arguments so this required some changes
to test/test_override.py
Removed support for using mix of integer and string arguments
when specifying dimensions in unflatten.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/81399
Approved by: https://github.com/Lezcano, https://github.com/ngimel
Currently we have 2 ways of doing the same thing for torch dispatch and function modes:
`with push_torch_dispatch_mode(X)` or `with X.push(...)`
is now the equivalent of doing
`with X()`
This removes the first API (which is older and private so we don't need to go through a deprecation cycle)
There is some risk here that this might land race with a PR that uses the old API but in general it seems like most are using the `with X()` API or `enable_torch_dispatch_mode(X())` which isn't getting removed.
EDIT: left the `with X.push(...)` API since there were ~3 land races with that over the past day or so. But made it give a warning and ask users to use the other API
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78215
Approved by: https://github.com/ezyang
This PR adds support for `SymInt`s in python. Namely,
* `THPVariable_size` now returns `sym_sizes()`
* python arg parser is modified to parse PyObjects into ints and `SymbolicIntNode`s
* pybind11 bindings for `SymbolicIntNode` are added, so size expressions can be traced
* a large number of tests added to demonstrate how to implement python symints.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78135
Approved by: https://github.com/ezyang
This PR heavily simplifies the code of `linalg.solve`. At the same time,
this implementation saves quite a few copies of the input data in some
cases (e.g. A is contiguous)
We also implement it in such a way that the derivative goes from
computing two LU decompositions and two LU solves to no LU
decompositions and one LU solves. It also avoids a number of unnecessary
copies the derivative was unnecessarily performing (at least the copy of
two matrices).
On top of this, we add a `left` kw-only arg that allows the user to
solve `XA = B` rather concisely.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/74046
Approved by: https://github.com/nikitaved, https://github.com/IvanYashchuk, https://github.com/mruberry
This PR adds `linalg.lu_solve`. While doing so, I found a bug in MAGMA
when calling the batched MAGMA backend with trans=True. We work around
that by solving the system solving two triangular systems.
We also update the heuristics for this function, as they were fairly
updated. We found that cuSolver is king, so luckily we do not need to
rely on the buggy backend from magma for this function.
We added tests testing this function left and right. We also added tests
for the different backends. We also activated the tests for AMD, as
those should work as well.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/61657
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/77634
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
```Python
chebyshev_polynomial_v(input, n, *, out=None) -> Tensor
```
Chebyshev polynomial of the third kind $V_{n}(\text{input})$.
```Python
chebyshev_polynomial_w(input, n, *, out=None) -> Tensor
```
Chebyshev polynomial of the fourth kind $W_{n}(\text{input})$.
```Python
legendre_polynomial_p(input, n, *, out=None) -> Tensor
```
Legendre polynomial $P_{n}(\text{input})$.
```Python
shifted_chebyshev_polynomial_t(input, n, *, out=None) -> Tensor
```
Shifted Chebyshev polynomial of the first kind $T_{n}^{\ast}(\text{input})$.
```Python
shifted_chebyshev_polynomial_u(input, n, *, out=None) -> Tensor
```
Shifted Chebyshev polynomial of the second kind $U_{n}^{\ast}(\text{input})$.
```Python
shifted_chebyshev_polynomial_v(input, n, *, out=None) -> Tensor
```
Shifted Chebyshev polynomial of the third kind $V_{n}^{\ast}(\text{input})$.
```Python
shifted_chebyshev_polynomial_w(input, n, *, out=None) -> Tensor
```
Shifted Chebyshev polynomial of the fourth kind $W_{n}^{\ast}(\text{input})$.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78304
Approved by: https://github.com/mruberry
Adds:
```Python
bessel_j0(input, *, out=None) -> Tensor
```
Bessel function of the first kind of order $0$, $J_{0}(\text{input})$.
```Python
bessel_j1(input, *, out=None) -> Tensor
```
Bessel function of the first kind of order $1$, $J_{1}(\text{input})$.
```Python
bessel_j0(input, *, out=None) -> Tensor
```
Bessel function of the second kind of order $0$, $Y_{0}(\text{input})$.
```Python
bessel_j1(input, *, out=None) -> Tensor
```
Bessel function of the second kind of order $1$, $Y_{1}(\text{input})$.
```Python
modified_bessel_i0(input, *, out=None) -> Tensor
```
Modified Bessel function of the first kind of order $0$, $I_{0}(\text{input})$.
```Python
modified_bessel_i1(input, *, out=None) -> Tensor
```
Modified Bessel function of the first kind of order $1$, $I_{1}(\text{input})$.
```Python
modified_bessel_k0(input, *, out=None) -> Tensor
```
Modified Bessel function of the second kind of order $0$, $K_{0}(\text{input})$.
```Python
modified_bessel_k1(input, *, out=None) -> Tensor
```
Modified Bessel function of the second kind of order $1$, $K_{1}(\text{input})$.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78451
Approved by: https://github.com/mruberry
Adds:
```Python
chebyshev_polynomial_t(input, n, *, out=None) -> Tensor
```
Chebyshev polynomial of the first kind $T_{n}(\text{input})$.
If $n = 0$, $1$ is returned. If $n = 1$, $\text{input}$ is returned. If $n < 6$ or $|\text{input}| > 1$ the recursion:
$$T_{n + 1}(\text{input}) = 2 \times \text{input} \times T_{n}(\text{input}) - T_{n - 1}(\text{input})$$
is evaluated. Otherwise, the explicit trigonometric formula:
$$T_{n}(\text{input}) = \text{cos}(n \times \text{arccos}(x))$$
is evaluated.
## Derivatives
Recommended $k$-derivative formula with respect to $\text{input}$:
$$2^{-1 + k} \times n \times \Gamma(k) \times C_{-k + n}^{k}(\text{input})$$
where $C$ is the Gegenbauer polynomial.
Recommended $k$-derivative formula with respect to $\text{n}$:
$$\text{arccos}(\text{input})^{k} \times \text{cos}(\frac{k \times \pi}{2} + n \times \text{arccos}(\text{input})).$$
## Example
```Python
x = torch.linspace(-1, 1, 256)
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, torch.special.chebyshev_polynomial_t(x, 10))
```
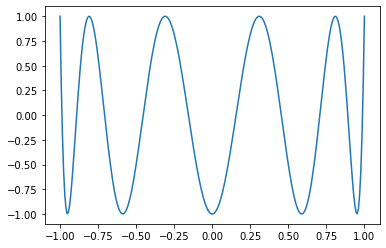
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78196
Approved by: https://github.com/mruberry
Euler beta function:
```Python
torch.special.beta(input, other, *, out=None) → Tensor
```
`reentrant_gamma` and `reentrant_ln_gamma` implementations (using Stirling’s approximation) are provided. I started working on this before I realized we were missing a gamma implementation (despite providing incomplete gamma implementations). Uses the coefficients computed by Steve Moshier to replicate SciPy’s implementation. Likewise, it mimics SciPy’s behavior (instead of the behavior in Cephes).
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78031
Approved by: https://github.com/mruberry
We don't have any coverage for meta tensor correctness for backwards
because torch function mode can only allow us to interpose on
Python torch API calls, but backwards invocations happen from C++.
To make this possible, I add torch_dispatch_meta test which runs the
tests with __torch_dispatch__
While doing this, I needed to generate fresh expected failure / skip
lists for the new test suite, and I discovered that my original
scaffolding for this purpose was woefully insufficient. So I rewrote
how the test framework worked, and at the same time rewrote the
__torch_function__ code to also use the new logic. Here's whats
new:
- Expected failure / skip is now done on a per function call basis,
rather than the entire test. This means that separate OpInfo
samples for a function don't affect each other.
- There are now only two lists: expect failure list (where the test
consistently fails on all runs) and skip list (where the test
sometimes passes and fails.
- We explicitly notate the dtype that failed. I considered detecting
when something failed on all dtypes, but this was complicated and
listing everything out seemed to be nice and simple. To keep the
dtypes short, I introduce a shorthand notation for dtypes.
- Conversion to meta tensors is factored into its own class
MetaConverter
- To regenerate the expected failure / skip lists, just run with
PYTORCH_COLLECT_EXPECT and filter on a specific test type
(test_meta or test_dispatch_meta) for whichever you want to update.
Other misc fixes:
- Fix max_pool1d to work with BFloat16 in all circumstances, by making
it dispatch and then fixing a minor compile error (constexpr doesn't
work with BFloat16)
- Add resolve_name for turning random torch API functions into string
names
- Add push classmethod to the Mode classes, so that you can more easily
push a mode onto the mode stack
- Add some more skips for missing LAPACK
- Added an API to let you query if there's already a registration for
a function, added a test to check that we register_meta for all
decompositions (except detach, that decomp is wrong lol), and then
update all the necessary sites to make the test pass.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyangfb.com>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/77477
Approved by: https://github.com/zou3519
This PR adds `linalg.vander`, the linalg version of `torch.vander`.
We add autograd support and support for batched inputs.
We also take this chance to improve the docs (TODO: Check that they
render correctly!) and add an OpInfo.
**Discussion**: The current default for the `increasing` kwargs is extremely
odd as it is the opposite of the classical definition (see
[wiki](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vandermonde_matrix)). This is
reflected in the docs, where I explicit both the odd defaults that we
use and the classical definition. See also [this stackoverflow
post](https://stackoverflow.com/a/71758047/5280578), which shows how
people are confused by this defaults.
My take on this would be to correct the default to be `increasing=True`
and document the divergence with NumPy (as we do for other `linalg`
functions) as:
- It is what people expect
- It gives the correct determinant called "the Vandermonde determinant" rather than (-1)^{n-1} times the Vandermonde det (ugh).
- [Minor] It is more efficient (no `flip` needed)
- Since it's under `linalg.vander`, it's strictly not a drop-in replacement for `np.vander`.
We will deprecate `torch.vander` in a PR after this one in this stack
(once we settle on what's the correct default).
Thoughts? mruberry
cc kgryte rgommers as they might have some context for the defaults of
NumPy.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/60197
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/76303
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD, https://github.com/mruberry
This PR adds `linalg.lu_solve`. While doing so, I found a bug in MAGMA
when calling the batched MAGMA backend with trans=True. We work around
that by solving the system solving two triangular systems.
We also update the heuristics for this function, as they were fairly
updated. We found that cuSolver is king, so luckily we do not need to
rely on the buggy backend from magma for this function.
We added tests testing this function left and right. We also added tests
for the different backends. We also activated the tests for AMD, as
those should work as well.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/61657
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72935
Approved by: https://github.com/IvanYashchuk, https://github.com/mruberry
This PR modifies `lu_unpack` by:
- Using less memory when unpacking `L` and `U`
- Fuse the subtraction by `-1` with `unpack_pivots_stub`
- Define tensors of the correct types to avoid copies
- Port `lu_unpack` to be a strucutred kernel so that its `_out` version
does not incur on extra copies
Then we implement `linalg.lu` as a structured kernel, as we want to
compute its derivative manually. We do so because composing the
derivatives of `torch.lu_factor` and `torch.lu_unpack` would be less efficient.
This new function and `lu_unpack` comes with all the things it can come:
forward and backward ad, decent docs, correctness tests, OpInfo, complex support,
support for metatensors and support for vmap and vmap over the gradients.
I really hope we don't continue adding more features.
This PR also avoids saving some of the tensors that were previously
saved unnecessarily for the backward in `lu_factor_ex_backward` and
`lu_backward` and does some other general improvements here and there
to the forward and backward AD formulae of other related functions.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/67833
Approved by: https://github.com/IvanYashchuk, https://github.com/nikitaved, https://github.com/mruberry
This PR adds `linalg.vander`, the linalg version of `torch.vander`.
We add autograd support and support for batched inputs.
We also take this chance to improve the docs (TODO: Check that they
render correctly!) and add an OpInfo.
**Discussion**: The current default for the `increasing` kwargs is extremely
odd as it is the opposite of the classical definition (see
[wiki](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vandermonde_matrix)). This is
reflected in the docs, where I explicit both the odd defaults that we
use and the classical definition. See also [this stackoverflow
post](https://stackoverflow.com/a/71758047/5280578), which shows how
people are confused by this defaults.
My take on this would be to correct the default to be `increasing=True`
and document the divergence with NumPy (as we do for other `linalg`
functions) as:
- It is what people expect
- It gives the correct determinant called "the Vandermonde determinant" rather than (-1)^{n-1} times the Vandermonde det (ugh).
- [Minor] It is more efficient (no `flip` needed)
- Since it's under `linalg.vander`, it's strictly not a drop-in replacement for `np.vander`.
We will deprecate `torch.vander` in a PR after this one in this stack
(once we settle on what's the correct default).
Thoughts? mruberry
cc kgryte rgommers as they might have some context for the defaults of
NumPy.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/60197
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/76303
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD
This PR adds a function for computing the LDL decomposition and a function that can solve systems of linear equations using this decomposition. The result of `torch.linalg.ldl_factor_ex` is in a compact form and it's required to use it only through `torch.linalg.ldl_solve`. In the future, we could provide `ldl_unpack` function that transforms the compact representation into explicit matrices.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/54847.
cc @jianyuh @nikitaved @pearu @mruberry @walterddr @IvanYashchuk @xwang233 @Lezcano
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69828
Approved by: https://github.com/Lezcano, https://github.com/mruberry, https://github.com/albanD
crossref is a new strategy for performing tests when you want
to run a normal PyTorch API call, separately run some variation of
the API call (e.g., same thing but all the arguments are meta tensors)
and then cross-reference the results to see that they are consistent.
Any logic you add to CrossRefMode will get run on *every* PyTorch API
call that is called in the course of PyTorch's test suite. This can
be a good choice for correctness testing if OpInfo testing is not
exhaustive enough.
For now, the crossref test doesn't do anything except verify that
we can validly push a mode onto the torch function mode stack for all
functions.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyangfb.com>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/75988
Approved by: https://github.com/seemethere
I figured these out by unconditionally turning on a no-op torch function
mode on the test suite and then fixing errors as they showed up. Here's
what I found:
- _parse_to failed internal assert when __torch_function__'ed because it
claims its name is "to" to the argument parser; added a name override
so we know how to find the correct name
- Infix operator magic methods on Tensor did not uniformly handle
__torch_function__ and TypeError to NotImplemented. Now, we always
do the __torch_function__ handling in
_wrap_type_error_to_not_implemented and your implementation of
__torch_function__ gets its TypeErrors converted to NotImplemented
(for better or for worse; see
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/75462 )
- A few cases where code was incorrectly testing if a Tensor was
Tensor-like in the wrong way, now use is_tensor_like (in grad
and in distributions). Also update docs for has_torch_function to
push people to use is_tensor_like.
- is_grads_batched was dropped from grad in handle_torch_function, now
fixed
- Report that you have a torch function even if torch function is
disabled if a mode is enabled. This makes it possible for a mode
to return NotImplemented, pass to a subclass which does some
processing and then pass back to the mode even after the subclass
disables __torch_function__ (so the tensors are treated "as if"
they are regular Tensors). This brings the C++ handling behavior
in line with the Python behavior.
- Make the Python implementation of overloaded types computation match
the C++ version: when torch function is disabled, there are no
overloaded types (because they all report they are not overloaded).
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyangfb.com>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/75484
Approved by: https://github.com/zou3519
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/74226
Update signature of `scatter_reduce_` to match `scatter_/scatter_add_`
`Tensor.scatter_reduce_(int64 dim, Tensor index, Tensor src, str reduce)`
- Add new reduction options in ScatterGatherKernel.cpp and update `scatter_reduce` to call into the cpu kernel for `scatter.reduce`
- `scatter_reduce` now has the same shape constraints as `scatter_` and `scatter_add_`
- Migrate `test/test_torch.py:test_scatter_reduce` to `test/test_scatter_gather_ops.py`
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D35222842
Pulled By: mikaylagawarecki
fbshipit-source-id: 84930add2ad30baf872c495251373313cb7428bd
(cherry picked from commit 1b45139482e22eb0dc8b6aec2a7b25a4b58e31df)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/74691
The wrapper just called through to methods on the underlying Tensor.
ghstack-source-id: 152433754
Test Plan: existing tests
Reviewed By: ezyang
Differential Revision: D34689789
fbshipit-source-id: cf53476780cf3ed00a3aa4add441300bfe8e27ce
(cherry picked from commit 5a9e5eb6bc13eb30be6e3c3bc4ac954c92704198)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/73999
Seems to be the typical way to detect a flavor of TensorImpl.
ghstack-source-id: 151440167
Test Plan: Existing tests?
Reviewed By: ezyang
Differential Revision: D34665269
fbshipit-source-id: 5081a00928933e0c5252eeddca43bae0b026013d
(cherry picked from commit 7cf62a3f69f158a33c5108f7e96ea4c5520f0f15)
I was working on an explanation of how to call into the "super"
implementation of some given ATen operation inside of __torch_dispatch__
(https://github.com/albanD/subclass_zoo/blob/main/trivial_tensors.py)
and I kept thinking to myself "Why doesn't just calling super() on
__torch_dispatch__ work"? Well, after this patch, it does! The idea
is if you don't actually unwrap the input tensors, you can call
super().__torch_dispatch__ to get at the original behavior.
Internally, this is implemented by disabling PythonKey and then
redispatching. This implementation of disabled_torch_dispatch is
not /quite/ right, and some reasons why are commented in the code.
There is then some extra work I have to do to make sure we recognize
disabled_torch_dispatch as the "default" implementation (so we don't
start slapping PythonKey on all tensors, including base Tensors),
which is modeled the same way as how disabled_torch_function is done.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyangfb.com>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/73684
Approved by: albanD
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72944
Doesn't make sense to develop it in core right now.
ghstack-source-id: 149456040
Test Plan:
CI
run MHA benchmark in benchmark_transformers.py to make sure it doesn't crash
Reviewed By: zrphercule
Differential Revision: D34283104
fbshipit-source-id: 4f0c7a6bc066f938ceac891320d4cf4c3f8a9cd6
(cherry picked from commit b9df65e97c)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72200
This op should still remain private in release 1.11, add underscore before op name to make it happens
Test Plan: buck run mode/opt -c fbcode.enable_gpu_sections=true pytext/fb/tools:benchmark_transformers -- mha --batch-size=10 --max-sequence-length=16
Reviewed By: bdhirsh
Differential Revision: D33952191
fbshipit-source-id: 3f8525ac9c23bb286f51476342113ebc31b8ed59
(cherry picked from commit 6e41bfa4fc)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/70649
As described in https://fb.quip.com/oxpiA1uDBjgP
This implements the first parts of the RFC, and is a rough draft showing the approach. The idea is that for the first cut we can maintain very close (identical I believe in this diff) numerical equivalence to the existing nn.MHA implementation, which is what this diff attempts to do. In subsequent implementations, once we have a working and adopted native self-attention implementation, we could then explore alternative implementations, etc.
The current implementation is similar to existing dedicated implementations such as LightSeq/FasterTransformer/DeepSpeed, and for MHA on both CPUs and GPUs is between 1.2x and 2x faster depending on the setting. It makes some approximations/restrictions (doesn't handle masking in masked softmax, etc), but these shouldn't materially impact performance.
This does the first few items:
* add native_multi_head_attention(...) , native_multi_head_attention_backward(..) to native_functions.yaml
* Implement native_multi_head_attention(..) on GPU, extracting bits and pieces out of LS/DS/FT as appropriate
* Implement native_multi_head_attention(..) on CPU
The backward implementation is still WIP, but the idea would be to:
* Hook these up in derivatives.yaml
Implement native_multi_head_attention_backward(..) on GPU, extracting out bits and pieces out of LS/DS (not FT since it’s inference only)
* Implement native_multi_head_attention_backward(..) on CPU
* In torch.nn.functional.multi_head_attention_forward 23321ba7a3/torch/nn/functional.py (L4953), add some conditionals to check if we are being called in a BERT/ViT-style encoder fashion, and invoke the native function directly.
Test Plan: TODO
Reviewed By: mikekgfb
Differential Revision: D31829981
fbshipit-source-id: c430344d91ba7a5fbee3138e50b3e62efbb33d96
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/66933
This PR exposes `torch.lu` as `torch.linalg.lu_factor` and
`torch.linalg.lu_factor_ex`.
This PR also adds support for matrices with zero elements both in
the size of the matrix and the batch. Note that this function simply
returns empty tensors of the correct size in this case.
We add a test and an OpInfo for the new function.
This PR also adds documentation for this new function in line of
the documentation in the rest of `torch.linalg`.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/56590
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/64014
cc jianyuh nikitaved pearu mruberry walterddr IvanYashchuk xwang233 Lezcano
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: gchanan
Differential Revision: D32834069
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 51ef12535fa91d292f419acf83b800b86ee9c7eb
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69327
Original commit changeset: d44096d88265
Original Phabricator Diff: D32144240 (668574af4a)
Test Plan:
CI
original diff failed 175 builds in CI
Reviewed By: airboyang, anjali411
Differential Revision: D32809407
fbshipit-source-id: c7c8e69bcee0274992e2d5da901f035332e60071
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/66933
This PR exposes `torch.lu` as `torch.linalg.lu_factor` and
`torch.linalg.lu_factor_ex`.
This PR also adds support for matrices with zero elements both in
the size of the matrix and the batch. Note that this function simply
returns empty tensors of the correct size in this case.
We add a test and an OpInfo for the new function.
This PR also adds documentation for this new function in line of
the documentation in the rest of `torch.linalg`.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/56590
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/64014
cc jianyuh nikitaved pearu mruberry walterddr IvanYashchuk xwang233 Lezcano
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D32521980
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 26a49ebd87f8a41472f8cd4e9de4ddfb7f5581fb
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63568
This PR adds the first solver with structure to `linalg`. This solver
has an API compatible with that of `linalg.solve` preparing these for a
possible future merge of the APIs. The new API:
- Just returns the solution, rather than the solution and a copy of `A`
- Removes the confusing `transpose` argument and replaces it by a
correct handling of conj and strides within the call
- Adds a `left=True` kwarg. This can be achieved via transposes of the
inputs and the result, but it's exposed for convenience.
This PR also implements a dataflow that minimises the number of copies
needed before calling LAPACK / MAGMA / cuBLAS and takes advantage of the
conjugate and neg bits.
This algorithm is implemented for `solve_triangular` (which, for this, is
the most complex of all the solvers due to the `upper` parameters).
Once more solvers are added, we will factor out this calling algorithm,
so that all of them can take advantage of it.
Given the complexity of this algorithm, we implement some thorough
testing. We also added tests for all the backends, which was not done
before.
We also add forward AD support for `linalg.solve_triangular` and improve the
docs of `linalg.solve_triangular`. We also fix a few issues with those of
`torch.triangular_solve`.
Resolves https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/54258
Resolves https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/56327
Resolves https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/45734
cc jianyuh nikitaved pearu mruberry walterddr IvanYashchuk xwang233 Lezcano
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: jbschlosser
Differential Revision: D32588230
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 69e484849deb9ad7bb992cc97905df29c8915910
Summary:
Adds native_dropout to have a reasonable target for torchscript in auto diff. native_dropout has scale and train as arguments in its signature, this makes native_dropout more consistent with other operators and removes conditionals in the autodiff definition.
cc gmagogsfm
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63937
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D32477657
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: d37b137a37acafa50990f60c77f5cea2818454e4
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63568
This PR adds the first solver with structure to `linalg`. This solver
has an API compatible with that of `linalg.solve` preparing these for a
possible future merge of the APIs. The new API:
- Just returns the solution, rather than the solution and a copy of `A`
- Removes the confusing `transpose` argument and replaces it by a
correct handling of conj and strides within the call
- Adds a `left=True` kwarg. This can be achieved via transposes of the
inputs and the result, but it's exposed for convenience.
This PR also implements a dataflow that minimises the number of copies
needed before calling LAPACK / MAGMA / cuBLAS and takes advantage of the
conjugate and neg bits.
This algorithm is implemented for `solve_triangular` (which, for this, is
the most complex of all the solvers due to the `upper` parameters).
Once more solvers are added, we will factor out this calling algorithm,
so that all of them can take advantage of it.
Given the complexity of this algorithm, we implement some thorough
testing. We also added tests for all the backends, which was not done
before.
We also add forward AD support for `linalg.solve_triangular` and improve the
docs of `linalg.solve_triangular`. We also fix a few issues with those of
`torch.triangular_solve`.
Resolves https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/54258
Resolves https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/56327
Resolves https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/45734
cc jianyuh nikitaved pearu mruberry walterddr IvanYashchuk xwang233 Lezcano
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: zou3519, JacobSzwejbka
Differential Revision: D32283178
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: deb672e6e52f58b76536ab4158073927a35e43a8
Summary:
### Create `linalg.cross`
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/62810
As discussed in the corresponding issue, this PR adds `cross` to the `linalg` namespace (**Note**: There is no method variant) which is slightly different in behaviour compared to `torch.cross`.
**Note**: this is NOT an alias as suggested in mruberry's [https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/62810 comment](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/62810#issuecomment-897504372) below
> linalg.cross being consistent with the Python Array API (over NumPy) makes sense because NumPy has no linalg.cross. I also think we can implement linalg.cross without immediately deprecating torch.cross, although we should definitely refer users to linalg.cross. Deprecating torch.cross will require additional review. While it's not used often it is used, and it's unclear if users are relying on its unique behavior or not.
The current default implementation of `torch.cross` is extremely weird and confusing. This has also been reported multiple times previously. (See https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/17229, https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/39310, https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/41850, https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/50273)
- [x] Add `torch.linalg.cross` with default `dim=-1`
- [x] Add OpInfo and other tests for `torch.linalg.cross`
- [x] Add broadcasting support to `torch.cross` and `torch.linalg.cross`
- [x] Remove out skip from `torch.cross` OpInfo
- [x] Add docs for `torch.linalg.cross`. Improve docs for `torch.cross` mentioning `linalg.cross` and the difference between the two. Also adds a warning to `torch.cross`, that it may change in the future (we might want to deprecate it later)
---
### Additional Fixes to `torch.cross`
- [x] Fix Doc for Tensor.cross
- [x] Fix torch.cross in `torch/overridres.py`
While working on `linalg.cross` I noticed these small issues with `torch.cross` itself.
[Tensor.cross docs](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Tensor.cross.html) still mentions `dim=-1` default which is actually wrong. It should be `dim=None` after the behaviour was updated in PR https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/17582 but the documentation for the `method` or `function` variant wasn’t updated. Later PR https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/41850 updated the documentation for the `function` variant i.e `torch.cross` and also added the following warning about the weird behaviour.
> If `dim` is not given, it defaults to the first dimension found with the size 3. Note that this might be unexpected.
But still, the `Tensor.cross` docs were missed and remained outdated. I’m finally fixing that here. Also fixing `torch/overrides.py` for `torch.cross` as well now, with `dim=None`.
To verify according to the docs the default behaviour of `dim=-1` should raise, you can try the following.
```python
a = torch.randn(3, 4)
b = torch.randn(3, 4)
b.cross(a) # this works because the implementation finds 3 in the first dimension and the default behaviour as shown in documentation is actually not true.
>>> tensor([[ 0.7171, -1.1059, 0.4162, 1.3026],
[ 0.4320, -2.1591, -1.1423, 1.2314],
[-0.6034, -1.6592, -0.8016, 1.6467]])
b.cross(a, dim=-1) # this raises as expected since the last dimension doesn't have a 3
>>> RuntimeError: dimension -1 does not have size 3
```
Please take a closer look (particularly the autograd part, this is the first time I'm dealing with `derivatives.yaml`). If there is something missing, wrong or needs more explanation, please let me know. Looking forward to the feedback.
cc mruberry Lezcano IvanYashchuk rgommers
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63285
Reviewed By: gchanan
Differential Revision: D32313346
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: e68c2687c57367274e8ddb7ef28ee92dcd4c9f2c
Summary:
Adds `torch.argwhere` as an alias to `torch.nonzero`
Currently, `torch.nonzero` is actually provides equivalent functionality to `np.argwhere`.
From NumPy docs,
> np.argwhere(a) is almost the same as np.transpose(np.nonzero(a)), but produces a result of the correct shape for a 0D array.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/64257
Reviewed By: qihqi
Differential Revision: D32049884
Pulled By: saketh-are
fbshipit-source-id: 016e49884698daa53b83e384435c3f8f6b5bf6bb
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/64430
The functionalization pass needs `{view}_scatter` versions of the slice/select/diagonal ops in order to correctly propagate mutations from a view to its base. On top of that, the implementations need to be primitive w.r.t. autograd, because they look something like `...slice().copy_()`, and the functionalization pass can't use views + mutations inside of it's own alias-removal machinery!
I added some basic tests that I tried to base off of existing tests for views (particularly around testing the derivative formulas), but I'm wondering if I should add something more comprehensive.
Also, as_strided fits into this category - the functionalization pass will need an `as_strided_scatter` op that's primitive w.r.t. autograd. I didn't add it for now, because it'll involve duplicating a bunch of logic from the current `as_strided_backward()` function, and also writing a derivative formula that I wasn't sure how to write :)
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D31942092
Pulled By: bdhirsh
fbshipit-source-id: c702a57c2748a7c771c14e4bcc3e996b48fcc4c8
Summary:
Adds mixed precision autocasting support between fp32/fp16 to torchscript/JIT. More in depth descriptoin can be found at [torch/csrc/jit/JIT-AUTOCAST.md](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63939/files#diff-1f1772aaa508841c5bb58b74ab98f49a1e577612cd9ea5c386c8714a75db830b)
This PR implemented an autocast optimization pass that inserts casting ops per AMP rule (torch/csrc/jit/passes/autocast.cpp), that mimics the behavior of eager autocast. The pass also takes into consideration the context of `torch.cuda.amp.autocast` and only inserts casting ops within the enabled context manager, giving feature parity as with eager amp autocast.
We currently provide JIT AMP autocast as a prototyping feature, so it is default off and could be turned on via `torch._C._jit_set_autocast_mode(True)`
The JIT support for autocast is subject to different constraints compared to the eager mode implementation (mostly related to the fact that TorchScript is statically typed), restriction on the user facing python code is described in doc torch/csrc/jit/JIT-AUTOCAST.md
This is a prototype, there are also implementation limitation that's necessary to keep this PR small and get something functioning quickly on upstream, so we can iterate on designs.
Few limitation/challenge that is not properly resolved in this PR:
1. Autocast inserts cast operation, which would have impact on scalar type of output tensor feeding downstream operations. We are not currently propagating the updated scalar types, this would give issues/wrong results on operations in promotion rules.
2. Backward for autodiff in JIT misses the casting of dgrad to input scalar type, as what autograd does in eager. This forces us to explicitly mark the casting operation for certain operations (e.g. binary ops), otherwise, we might be feeding dgrad with mismatch scalar type to input. This could potentially break gradient function consuming dgrad. (e.g. gemm backwards, which assumes grad_output to be of same scalar type as input')
3. `torch.autocast` api has an optional argument `dtype` which is not currently supported in the JIT autocast and we require a static value.
Credit goes mostly to:
tlemo
kevinstephano
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63939
Reviewed By: navahgar
Differential Revision: D31093381
Pulled By: eellison
fbshipit-source-id: da6e26c668c38b01e296f304507048d6c1794314
Summary:
Adds `torch.argwhere` as an alias to `torch.nonzero`
Currently, `torch.nonzero` is actually provides equivalent functionality to `np.argwhere`.
From NumPy docs,
> np.argwhere(a) is almost the same as np.transpose(np.nonzero(a)), but produces a result of the correct shape for a 0D array.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/64257
Reviewed By: dagitses
Differential Revision: D31474901
Pulled By: saketh-are
fbshipit-source-id: 335327a4986fa327da74e1fb8624cc1e56959c70
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/62030
Remove dtype tracking from Python Storage interface, remove all the different `<type>Storage` classes except for `ByteStorage`, and update serialization accordingly, while maintaining as much FC/BC as possible
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/47442
* **THE SERIALIZATION FORMAT IS FULLY FC/BC.** We worked very hard to make sure this is the case. We will probably want to break FC at some point to make the serialization structure of tensors make more sense, but not today.
* There is now only a single torch.ByteStorage class. Methods like `Tensor.set_` no longer check that the dtype of storage is appropriate.
* As we no longer know what dtype of a storage is, we've **removed** the size method from Storage, replacing it with nbytes. This is to help catch otherwise silent errors where you confuse number of elements with number of bytes.
* `Storage._new_shared` takes a `nbytes` kwarg and will reject previous positional only calls. `Storage._new_with_file` and `_set_from_file` require explicit element size arguments.
* It's no longer possible to convert storages to different types using the float/double/etc methods. Instead, do the conversion using a tensor.
* It's no longer possible to allocate a typed storage directly using FloatStorage/DoubleStorage/etc constructors. Instead, construct a tensor and extract its storage. The classes still exist but they are used purely for unpickling.
* The preexisting serialization format stores dtype with storage, and in fact this dtype is used to determine the dtype of the tensor overall.
To accommodate this case, we introduce a new TypedStorage concept that exists only during unpickling time which is used to temporarily store the dtype so we can construct a tensor. **If you overrode the handling of pickling/unpickling, you MUST add handling for TypedStorage** or your serialization code will degrade to standard file-based serialization.
Original pull request: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/59671
Reviewed By: soulitzer, ngimel
Differential Revision: D29466819
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 4a14e5d3c2b08e06e558683d97f7378a3180b00e
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/65621
Add a new attribute to the FusedMovingAvgObsFakeQuantize that controls if the Fake Quant operation should be applied at the output of a particular layer. The motivation is to give the users additional control to control the numerics of the fake_quant operators during training. It defaults to always fake quant the output (True).
Note: We will still observer the tensors as before (only the fake_quant operation is controlled using this flag)
For example
```
input model
x -> fc1 -> fc2 -> non_quantizable_op -> fc3
After fake_quant
x -> fake_quant(x) -> fc1 -> fake_quant(fc1) -> fc2 -> fake_quant(fc2) -> non_quantizable_op -> fake_quant() -> fc3 -> fake_quantize(fc3)
With output_fake_quant disabled at the output of fc2 and fc3 (since their outputs are non-quantizable)
x -> fake_quant(x) -> fc1 -> fake_quant(fc1) -> fc2 -> non_quantizable_op -> fake_quant() -> fc3
```
Test Plan: ./buck-out/gen/caffe2/test/quantization_fx\#binary.par -r test_disable_output_fake_quant
Reviewed By: jerryzh168
Differential Revision: D31174526
fbshipit-source-id: bffe776216d041fb09133a6fb09bfc2c0bb46b89
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/65340
I thought about a few possible ways of doing this. The main hazard is
that if I create a CPU tensor that doesn't have any real storage, the
moment I actually try to access the data on the tensor I will segfault.
So I don't want to use _make_subclass on a "cpu meta tensor" because
the CPU meta tensor (with no subclass) is radioactive: printing it
will immediately cause a segfault. So instead, I have to create
the CPU meta tensor AND subclass all in one go, and that means I need
another function for it. One downside to doing it this way is
I need another overload for explicit strides, and in general it is
difficult to get the view relationships to all work out properly;
tracked at https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/65339
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/62972
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/62730
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D31057231
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 73522769e093ae8a1bf0c7f7e594659bfb827b28
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/62671
Very crude first implementation of `torch.nanmean`. The current reduction kernels do not have good support for implementing nan* variants. Rather than implementing new kernels for each nan* operator, I will work on new reduction kernels with support for a `nan_policy` flag and then I will port `nanmean` to use that.
**TODO**
- [x] Fix autograd issue
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D30515181
Pulled By: heitorschueroff
fbshipit-source-id: 303004ebd7ac9cf963dc4f8e2553eaded5f013f0
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/64689
This brings it in line with the C++ implementation.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/64687
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D30816215
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: ed36af6c35467ae678d9548197efd97c36d38dec
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63552
In this PR, we want to exclude these 2 cases in the `Autocast` weight cache usages:
- Using `torch.jit.trace` under the `Autocast`
As report in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/50231 and several other discussions, using `torch.jit.trace` under the `Autocast`, the trace process would hit Autocast's weight cache and fails. So we should disable weight cache under the trace process.
- Using `Autocast` with `Grad mode`
- Usually we are using `Grad mode` for training. Since in the training phase, the weight will change in every step. So we doesn't need to cache the weight.
- For the recommended `Autocast` training case in the [doc](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/amp.html), `Autocast` will clear the cache every step leaving the context. We should disable it to save the clear operations.
```
model = Net().cuda()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), ...)
for input, target in data:
optimizer.zero_grad()
with autocast():
output = model(input)
loss = loss_fn(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
```
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: mrshenli
Differential Revision: D30644913
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: ad7bc87372e554e7aa1aa0795e9676871b3974e7
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/62811
Add `torch.linalg.matmul` alias to `torch.matmul`. Note that the `linalg.matmul` doesn't have a `method` variant.
Also cleaning up `torch/_torch_docs.py` when formatting is not needed.
cc IvanYashchuk Lezcano mruberry rgommers
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63227
Reviewed By: mrshenli
Differential Revision: D30770235
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: bfba77dfcbb61fcd44f22ba41bd8d84c21132403
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/61767
## Changes
- [x] Add `torch.concat` alias to `torch.cat`
- [x] Add OpInfo for `cat`/`concat`
- [x] Fix `test_out` skips (Use `at::native::resize_output` or `at::native::resize_output_check`)
- [x] `cat`/`concat`
- [x] `stack`
- [x] `hstack`
- [x] `dstack`
- [x] `vstack`/`row_stack`
- [x] Remove redundant tests for `cat`/`stack`
~I've not added `cat`/`concat` to OpInfo `op_db` yet, since cat is a little more tricky than other OpInfos (should have a lot of tests) and currently there are no OpInfos for that. I can try to add that in a subsequent PR or maybe here itself, whatever is suggested.~
**Edit**: cat/concat OpInfo has been added.
**Note**: I've added the named tensor support for `concat` alias as well, maybe that's out of spec in `array-api` but it is still useful for consistency in PyTorch.
Thanks to krshrimali for guidance on my first PR :))
cc mruberry rgommers pmeier asmeurer leofang AnirudhDagar asi1024 emcastillo kmaehashi heitorschueroff krshrimali
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/62560
Reviewed By: saketh-are
Differential Revision: D30762069
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 6985159d1d9756238890488a0ab3ae7699d94337
Summary:
This PR implements the necessary hooks/stubs/enums/etc for complete ONNX Runtime (ORT) Eager Mode integration. The actual extension will live out of tree at https://github.com/pytorch/ort.
We have been [working on this at Microsoft](https://github.com/microsoft/onnxruntime-pytorch/tree/eager-ort/torch_onnxruntime) for the last few months, and are finally ready to contribute the PyTorch core changes upstream (nothing major or exciting, just the usual boilerplate for adding new backends).
The ORT backend will allow us to ferry [almost] all torch ops into granular ONNX kernels that ORT will eagerly execute against any devices it supports (therefore, we only need a single ORT backend from a PyTorch perspective).
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58248
Reviewed By: astaff
Differential Revision: D30344992
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 69082b32121246340d686e16653626114b7714b2