- This PR defines a new `api.py` meant to hold the public API for FSDP (minus `FullyShardedDataParallel` itself). This is needed because several of the `_<...>_utils.py` files rely on the public API, and we cannot import from `torch.distributed.fsdp.fully_sharded_data_parallel` without a circular import. Calling the file `api.py` follows the convention used by `ShardedTensor`.
- This PR cleans up the wording in the `BackwardPrefetch`, `ShardingStrategy`, `MixedPrecision`, and `CPUOffload` docstrings.
- This PR adds the aforementioned classes to `fsdp.rst` to have them rendered in public docs.
- To abide by the public bindings contract (`test_public_bindings.py`), the aforementioned classes are removed from `fully_sharded_data_parallel.py`'s `__all__`. This is technically BC breaking if someone uses `from torch.distributed.fsdp.fully_sharded_data_parallel import *`; however, that does not happen in any of our own external or internal code.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/87917
Approved by: https://github.com/mrshenli
# Summary
Add in a torch.backends.cuda flag and update context manager to pic between the three implementations of the scaled_dot_product_attention.
cc @cpuhrsch @jbschlosser @bhosmer @mikaylagawarecki
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/87946
Approved by: https://github.com/cpuhrsch
This refactor was prompted by challenges handling mixed int/float
operations in C++. A previous version of this patch
added overloads for each permutation of int/float and was unwieldy
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/87722/ This PR takes a different
approach.
The general outline of the patch is to combine the C++ types SymIntNode
and SymFloatNode into a single type, SymNode. This is type erased; we
no longer know statically at C++ if we have an int/float and have to test
it with the is_int()/is_float() virtual methods. This has a number of
knock on effects.
- We no longer have C++ classes to bind to Python. Instead, we take an
entirely new approach to our Python API, where we have a SymInt/SymFloat
class defined entirely in Python, which hold a SymNode (which corresponds
to the C++ SymNode). However, SymNode is not pybind11-bound; instead,
it lives as-is in Python, and is wrapped into C++ SymNode using PythonSymNode
when it goes into C++. This implies a userland rename.
In principle, it is also possible for the canonical implementation of SymNode
to be written in C++, and then bound to Python with pybind11 (we have
this code, although it is commented out.) However, I did not implement
this as we currently have no C++ implementations of SymNode.
Because we do return SymInt/SymFloat from C++ bindings, the C++ binding
code needs to know how to find these classes. Currently, this is done
just by manually importing torch and getting the attributes.
- Because SymInt/SymFloat are easy Python wrappers, __sym_dispatch__ now
takes SymInt/SymFloat, rather than SymNode, bringing it in line with how
__torch_dispatch__ works.
Some miscellaneous improvements:
- SymInt now has a constructor that takes SymNode. Note that this
constructor is ambiguous if you pass in a subclass of SymNode,
so an explicit downcast is necessary. This means toSymFloat/toSymInt
are no more. This is a mild optimization as it means rvalue reference
works automatically.
- We uniformly use the caster for c10::SymInt/SymFloat, rather than
going the long way via the SymIntNode/SymFloatNode.
- Removed some unnecessary toSymInt/toSymFloat calls in normalize_*
functions, pretty sure this doesn't do anything.
- guard_int is now a free function, since to guard on an int you cannot
assume the method exists. A function can handle both int and SymInt
inputs.
- We clean up the magic method definition code for SymInt/SymFloat/SymNode.
ONLY the user classes (SymInt/SymFloat) get magic methods; SymNode gets
plain methods; this is to help avoid confusion between the two types.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
cc @jansel @mlazos @soumith @voznesenskym @yanboliang @penguinwu @anijain2305
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/87817
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD, https://github.com/anjali411
Fixes#83973 (This is a substitute PR for https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/85024)
First of all, thanks for your invaluable contributions to PyTorch everyone!
Given how extensively `torch.cuda.is_available` is used in the PyTorch ecosystem, IMHO it's worthwhile to provide downstream libraries/frameworks/users the ability to alter the default behavior of `torch.cuda.is_available` in the context of their PyTorch usage.
I'm confident there are many current and future such use cases which could benefit from leveraging a weakened, NVML-based `torch.cuda.is_available` assessment at a downstream framework's explicit direction (thanks @malfet 81da50a972 !). Though one could always patch out the `torch.cuda.is_available` function with another implementation in a downstream library, I think this environmental variable based configuration option is more convenient and the cost to including the option is quite low.
As discussed in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/85024#issuecomment-1261542045, this PR gates new non-default NVML-based CUDA behavior with an environmental variable (PYTORCH_NVML_BASED_CUDA_CHK) that allows a user/framework to invoke non-default, NVML-based `is_available()` assessments if desired.
Thanks again for your work everyone!
@ngimel @malfet @awaelchli
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/85951
Approved by: https://github.com/ngimel
`Sparsity` as a term doesn't reflect the tools that are developed by the AO. The `torch/ao/sparsity` also has utilities for structured pruning, which internally we always referred to as just "pruning". To avoid any confusion, we renamed `Sparsity` to `Prune`. We will not be introducing the backwards compatibility, as so far this toolset was kept under silent development.
This change will reflect the changes in the documentation as well.
**TODO:**
- [ ] Change the tutorials
- [ ] Confirm no bc-breakages
- [ ] Reflect the changes in the trackers and RFC docs
Fixes #ISSUE_NUMBER
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/84867
Approved by: https://github.com/supriyar
This achieves the same things as https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/85908 but using backends instead of kwargs (which breaks torchscript unfortunately). This also does mean we let go of numpy compatibility BUT the wins here are that users can control what opt einsum they wanna do!
The backend allows for..well you should just read the docs:
```
.. attribute:: torch.backends.opteinsum.enabled
A :class:`bool` that controls whether opt_einsum is enabled (on by default). If so,
torch.einsum will use opt_einsum (https://optimized-einsum.readthedocs.io/en/stable/path_finding.html)
to calculate an optimal path of contraction for faster performance.
.. attribute:: torch.backends.opteinsum.strategy
A :class:`str` that specifies which strategies to try when `torch.backends.opteinsum.enabled` is True.
By default, torch.einsum will try the "auto" strategy, but the "greedy" and "optimal" strategies are
also supported. Note that the "optimal" strategy is factorial on the number of inputs as it tries all
possible paths. See more details in opt_einsum's docs
(https://optimized-einsum.readthedocs.io/en/stable/path_finding.html).
```
In trying (and failing) to land 85908, I discovered that jit script does NOT actually pull from python's version of einsum (because it cannot support variadic args nor kwargs). Thus I learned that jitted einsum does not subscribe to the new opt_einsum path calculation. Overall, this is fine since jit script is getting deprecated, but where is the best place to document this?
## Test plan:
- added tests to CI
- locally tested that trying to set the strategy to something invalid will error properly
- locally tested that tests will pass even if you don't have opt-einsum
- locally tested that setting the strategy when opt-einsum is not there will also error properly
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/86219
Approved by: https://github.com/soulitzer, https://github.com/malfet
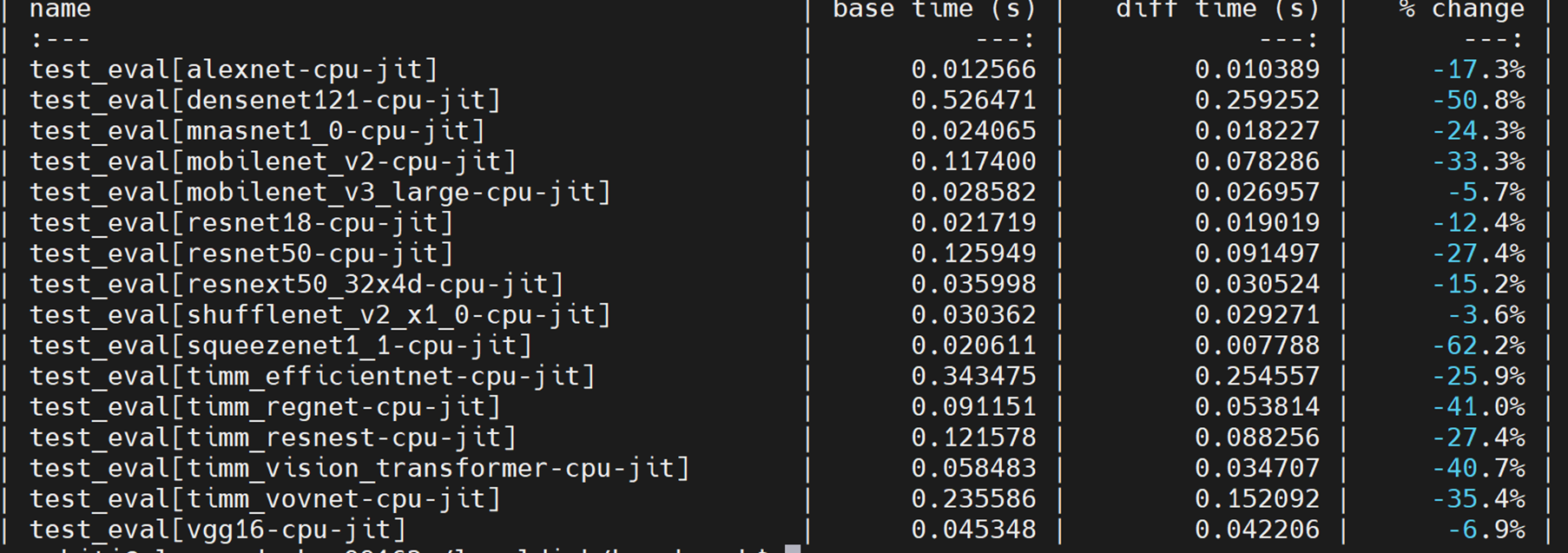
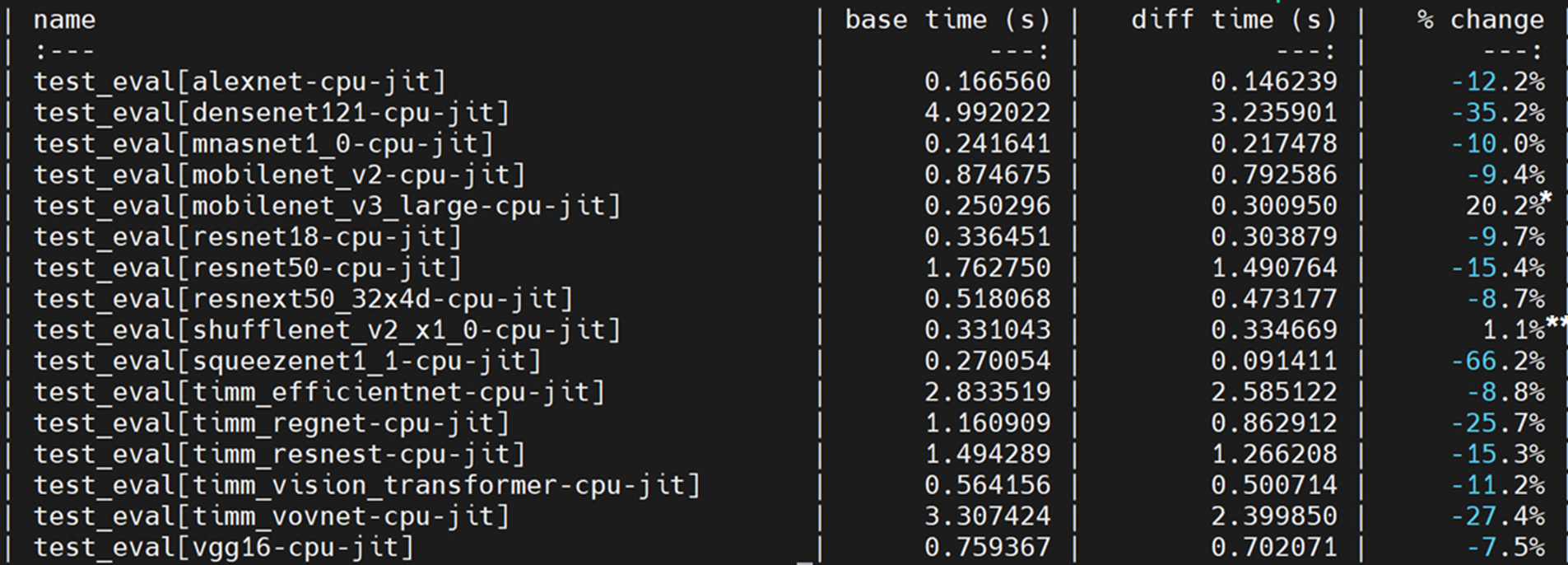
# Summary
- This code creates the runtime dispatch system for choosing a performant fused SDP kernel. The only choice of fused kernel is flash_attention. It also creates python flags and a context manager that can be used to turn off and on behavior for dispatch.
- This also adds support for flash_attention with dense tensors.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/85984
Approved by: https://github.com/cpuhrsch
Summary:
Added an additional roundup knob( ``roundup_bypass_threshold_mb``) to bypass rounding the requested allocation size, for allocation requests larger than the threshold value (in MB). This can help reduce the memory footprint when making large allocations that are expected to be persistent or have a large lifetime.
Differential Revision: D39868104
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/85940
Approved by: https://github.com/zdevito
### Deprecation reasons:
- For most users training is on one GPU per process so these APIs are rarely used
- They added one more API dimension
- They can be expressed in a composed manner
- They are not abstracted – specific to GPU
- They caused backend APIs and implementations to have nested `std::vector<std::vector<Tensor>>`, which is hard to read or maintain
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/85961
Approved by: https://github.com/XilunWu, https://github.com/H-Huang
As per request from Vision team, adding `collate` function with an extra argument of `collate_fn_map` to dispatch custom collate functions for non-collection objects and specific objects.
If the type of batch element is not present in`collate_fn_map`, it will go through all keys in the insertion order to check if the type is a subclass of the key. If so, it will invoke the corresponding collate functions.
And, `default_collate` will utilize the `collate` function with a few by default collate function for `int`, `float`, `str` and `numpy object`.
Benefit:
- Domain teams can register their own `collate` function to handle their specific type of objects
- Easier for users to extend from the `collate` function.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/85748
Approved by: https://github.com/NivekT, https://github.com/pmeier
Add unit tests and docstrings corresponding to PR https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63289
UT:
1. `test_profiler_emit_itt` in `test/test_autograd.py`. This test is merely intended to catch if emit_itt breaks on construction.
2. Test `torch.profiler.itt` functions in `test/test_itt.py`
3. Only testing that emit_itt runs when `record_shapes` option is enabled in `test/test_profiler.py`.
Docstring:
1. add ITT related info into `docs/source/bottleneck.rst`
4. add `torch.profiler.itt` functions to `docs/source/profiler.rst`
5. add docstring to `torch.profiler.itt` functions in `torch/profiler/itt.py`
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/84848
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
### Description
- This PR renames `_all_gather_base` to `all_gather_into_tensor` so that it is clearer in meaning.
- The `all_gather_into_tensor` API differs from the `all_gather` API in the output it accepts -- a single, large tensor instead of a list of tensors.
- This PR also adds deprecation warning to `_all_gather_base`.
### Issue
`_all_gather_base` was implemented in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/33924 to avoid unnecessary flattening. There was previous effort (#82639) to merge `_all_gather_base` with the existing `all_gather` API by detecting the parameter type passed in for the output.
There are, however, two "blockers" that make the merge difficult:
(i) The merge leads to backward compatibility break. We would need to change the parameter name `tensor_list` in `all_gather` to a general name `output` that can cover both tensor and tensor list.
(ii) Recently, the `all_gather` API has added uneven tensor support, utilizing the tensor boundaries implied by the list. We are, however, not sure to add such support to the `_all_gather_base` function, because that would require users to pass in additional tensor boundary information.
In view of the above, we decided to productize `_all_gather_base` as a separate function, but with a clearer name.
### Testing
Added tests:
- `test_all_gather_into_cat_tensor_cuda` -- output form as with `torch.cat`. For example:
```
>>> tensor_in
tensor([1, 2], device='cuda:0') # Rank 0
tensor([3, 4], device='cuda:1') # Rank 1
>>> tensor_out
tensor([1, 2, 3, 4], device='cuda:0') # Rank 0
tensor([1, 2, 3, 4], device='cuda:1') # Rank 1
```
- `test_all_gather_into_stack_tensor_cuda` -- output form as with `torch.stack`. For example:
```
>>> tensor_out2
tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]], device='cuda:0') # Rank 0
tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]], device='cuda:1') # Rank 1
```
The output form is determined by the shape of the output tensor passed by the user, no flag used.
Cc @rohan-varma @mrshenli @crcrpar @ptrblck @H-Huang
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/85686
Approved by: https://github.com/rohan-varma, https://github.com/crcrpar
Small rework of how the error message is formatted, introduces a distinction between the arguments and the output of kernels. Verified manually on multiple examples that the message is printed as expected.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/85008
Approved by: https://github.com/lw
As per the title. Fixes: #81161
- [x] add ErrorInputs
- ~[ ] dtype argument?~
- ~[ ] casting argument?~
As discussed offline with @kshitij12345, we can currently ignore `dtype` and `casting` arguments.
cc: @kshitij12345!
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/82946
Approved by: https://github.com/mruberry
Fixes#83363
This is not a full update yet, but fixes some obvious things: missing modules (torchrec, sparse) and brings a few people from merge_rules.json who are working on the respective modules. There are still discrepancies - e.g. Intel CPU work is split in many categories in merge_rules, but it's better to improve things incrementally.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/84772
Approved by: https://github.com/b0noI, https://github.com/malfet
Summary:
Some more clarifications for the arguments, including linking to object docs (QConfigMapping, BackendConfig) and adding types
in the doc
Test Plan:
```
cd docs
make html
```
and
visual inspection for the generated docs
Reviewers:
Subscribers:
Tasks:
Tags:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/84587
Approved by: https://github.com/vkuzo
Context: In order to avoid the cluttering of the `torch.nn` namespace
the quantized modules namespace is moved to `torch.ao.nn`.
The list of the `nn.quantized` files that are being migrated:
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.functional` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.functional`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.dynamic`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized._reference` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized._reference`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantizable` → `torch.ao.nn.quantizable`
- [X] [Current PR] `torch.nn.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.qat`
- [X] `torch.nn.qat.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.modules`
- [X] `torch.nn.qat.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.dynamic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.qat`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic`
Majority of the files are just moved to the new location.
However, specific files need to be double checked:
- None
Differential Revision: [D36861197](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36861197/)
**NOTE FOR REVIEWERS**: This PR has internal Facebook specific changes or comments, please review them on [Phabricator](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36861197/)!
Differential Revision: [D36861197](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36861197)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78716
Approved by: https://github.com/jerryzh168
Context: In order to avoid the cluttering of the `torch.nn` namespace
the quantized modules namespace is moved to `torch.ao.nn`.
The list of the `nn.quantized` files that are being migrated:
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.functional` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.functional`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.dynamic`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized._reference` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized._reference`
- [X] [Current PR] `torch.nn.quantizable` → `torch.ao.nn.quantizable`
- [ ] `torch.nn.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.qat`
- [ ] `torch.nn.qat.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.qat.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.dynamic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.qat`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic`
Majority of the files are just moved to the new location.
However, specific files need to be double checked:
- `torch/ao/nn/__init__.py` → Changing the imports to lazy.
Differential Revision: [D36861090](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36861090/)
**NOTE FOR REVIEWERS**: This PR has internal Facebook specific changes or comments, please review them on [Phabricator](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36861090/)!
Differential Revision: [D36861090](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36861090)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78717
Approved by: https://github.com/jerryzh168
Context: In order to avoid the cluttering of the `torch.nn` namespace
the quantized modules namespace is moved to `torch.ao.nn`.
The list of the `nn.quantized` files that are being migrated:
- [ ] `torch.nn.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.functional` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.functional`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules`
- [X] [Current PR] `torch.nn.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.dynamic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.quantized._reference` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized._reference`
- [ ] `torch.nn.quantizable` → `torch.ao.nn.quantizable`
- [ ] `torch.nn.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.qat`
- [ ] `torch.nn.qat.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.qat.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.dynamic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.qat`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic`
Majority of the files are just moved to the new location.
However, specific files need to be double checked:
- [Documentation](docs/source/quantization-support.rst) @vkuzo
- [Public API test list](test/allowlist_for_publicAPI.json) @peterbell10
- [BC test](test/quantization/bc/test_backward_compatibility.py) @vkuzo
- [IR emitter](torch/csrc/jit/frontend/ir_emitter.cpp) @jamesr66a
- [JIT serialization](torch/csrc/jit/serialization/import_source.cpp) @IvanKobzarev @jamesr66a
Differential Revision: [D36860660](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36860660/)
**NOTE FOR REVIEWERS**: This PR has internal Facebook specific changes or comments, please review them on [Phabricator](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36860660/)!
Differential Revision: [D36860660](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36860660)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78714
Approved by: https://github.com/jerryzh168
Summary:
This diff implements a named pipe based watchdog timer (`FileTimerClient` and `FileTimerServer`). This is similar to the existing `LocalTimerClient` and `LocalTimerServer` (https://fburl.com/code/j4b9pyya).
The motivation is from the need of handling various timeout issues. The training process occasionally get stuck. We need a proper watchdog to monitor the liveness of the training processes. This timer allows the TorchElastic agent (as the watchdog) to monitor the progress of the training processes that it spawned. If a timeout occurred, he TorchElastic agent can take some action to kill the stuck process and creating a core dump for it.
`LocalTimerClient` and `LocalTimerServer` require a `multiprocessing.Queue()` to work. So they can only be used between `multiprocessing` parent and child processes.
`FileTimerClient` and `FileTimerServer` does not have such limitation.
Test Plan:
### Unit Test
```
buck test mode/opt caffe2/test/distributed/elastic/timer:file_based_timer_test
```
```
RemoteExecution session id: reSessionID-06d70a77-043c-4d9d-b0f2-94c24460740a-tpx
Started reporting to test run: https://www.internalfb.com/intern/testinfra/testrun/844425186732666
✓ ListingSuccess: caffe2/test/distributed/elastic/timer:file_based_timer_test : 12 tests discovered (2.177)
✓ Pass: caffe2/test/distributed/elastic/timer:file_based_timer_test - test_happy_path (file_based_local_timer_test.FileTimerTest) (2.463)
✓ Pass: caffe2/test/distributed/elastic/timer:file_based_timer_test - test_expired_timers (file_based_local_timer_test.FileTimerServerTest) (1.889)
✓ Pass: caffe2/test/distributed/elastic/timer:file_based_timer_test - test_send_request_release (file_based_local_timer_test.FileTimerServerTest) (1.700)
✓ Pass: caffe2/test/distributed/elastic/timer:file_based_timer_test - test_valid_timers (file_based_local_timer_test.FileTimerServerTest) (1.873)
✓ Pass: caffe2/test/distributed/elastic/timer:file_based_timer_test - test_watchdog_call_count (file_based_local_timer_test.FileTimerServerTest) (1.715)
✓ Pass: caffe2/test/distributed/elastic/timer:file_based_timer_test - test_watchdog_empty_queue (file_based_local_timer_test.FileTimerServerTest) (1.609)
✓ Pass: caffe2/test/distributed/elastic/timer:file_based_timer_test - test_exception_propagation (file_based_local_timer_test.FileTimerTest) (1.633)
✓ Pass: caffe2/test/distributed/elastic/timer:file_based_timer_test - test_multiple_clients_interaction (file_based_local_timer_test.FileTimerTest) (2.189)
✓ Pass: caffe2/test/distributed/elastic/timer:file_based_timer_test - test_get_timer_recursive (file_based_local_timer_test.FileTimerTest) (2.295)
✓ Pass: caffe2/test/distributed/elastic/timer:file_based_timer_test - test_no_client (file_based_local_timer_test.FileTimerTest) (1.753)
✓ Pass: caffe2/test/distributed/elastic/timer:file_based_timer_test - test_timer (file_based_local_timer_test.FileTimerTest) (2.151)
✓ Pass: caffe2/test/distributed/elastic/timer:file_based_timer_test - test_client_interaction (file_based_local_timer_test.FileTimerTest) (1.895)
Summary
Pass: 12
ListingSuccess: 1
Finished test run: https://www.internalfb.com/intern/testinfra/testrun/844425186732666
```
Differential Revision: D38604238
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/83695
Approved by: https://github.com/d4l3k
Context: In order to avoid the cluttering of the `torch.nn` namespace
the quantized modules namespace is moved to `torch.ao.nn`.
The list of the `nn.quantized` files that are being migrated:
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.functional` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.functional`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.dynamic`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized._reference` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized._reference`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantizable` → `torch.ao.nn.quantizable`
- [X] [Current PR] `torch.nn.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.qat`
- [X] `torch.nn.qat.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.modules`
- [X] `torch.nn.qat.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.dynamic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.qat`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic`
Majority of the files are just moved to the new location.
However, specific files need to be double checked:
- None
Differential Revision: [D36861197](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36861197/)
**NOTE FOR REVIEWERS**: This PR has internal Facebook specific changes or comments, please review them on [Phabricator](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36861197/)!
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78716
Approved by: https://github.com/jerryzh168
Context: In order to avoid the cluttering of the `torch.nn` namespace
the quantized modules namespace is moved to `torch.ao.nn`.
The list of the `nn.quantized` files that are being migrated:
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.functional` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.functional`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.dynamic`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized._reference` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized._reference`
- [X] [Current PR] `torch.nn.quantizable` → `torch.ao.nn.quantizable`
- [ ] `torch.nn.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.qat`
- [ ] `torch.nn.qat.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.qat.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.dynamic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.qat`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic`
Majority of the files are just moved to the new location.
However, specific files need to be double checked:
- None
Differential Revision: [D36861090](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36861090/)
**NOTE FOR REVIEWERS**: This PR has internal Facebook specific changes or comments, please review them on [Phabricator](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36861090/)!
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78717
Approved by: https://github.com/jerryzh168
Context: In order to avoid the cluttering of the `torch.nn` namespace
the quantized modules namespace is moved to `torch.ao.nn`.
The list of the `nn.quantized` files that are being migrated:
- [ ] `torch.nn.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.functional` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.functional`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules`
- [X] [Current PR] `torch.nn.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.dynamic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.quantized._reference` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized._reference`
- [ ] `torch.nn.quantizable` → `torch.ao.nn.quantizable`
- [ ] `torch.nn.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.qat`
- [ ] `torch.nn.qat.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.qat.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.dynamic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.qat`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic`
Majority of the files are just moved to the new location.
However, specific files need to be double checked:
- [Documentation](docs/source/quantization-support.rst) @vkuzo
- [Public API test list](test/allowlist_for_publicAPI.json) @peterbell10
- [BC test](test/quantization/bc/test_backward_compatibility.py) @vkuzo
- [IR emitter](torch/csrc/jit/frontend/ir_emitter.cpp) @jamesr66a
- [JIT serialization](torch/csrc/jit/serialization/import_source.cpp) @IvanKobzarev @jamesr66a
Differential Revision: [D36860660](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36860660/)
**NOTE FOR REVIEWERS**: This PR has internal Facebook specific changes or comments, please review them on [Phabricator](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36860660/)!
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78714
Approved by: https://github.com/jerryzh168
Context: In order to avoid the cluttering of the `torch.nn` namespace
the quantized modules namespace is moved to `torch.ao.nn`.
The list of the `nn.quantized` files that are being migrated:
- [ ] `torch.nn.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized`
- [X] [Current PR] `torch.nn.quantized.functional` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.functional`
- [ ] `torch.nn.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.dynamic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.quantized._reference` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized._reference`
- [ ] `torch.nn.quantizable` → `torch.ao.nn.quantizable`
- [ ] `torch.nn.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.qat`
- [ ] `torch.nn.qat.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.qat.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.dynamic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.qat`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic`
Majority of the files are just moved to the new location.
However, specific files need to be double checked:
- [Documentation](docs/source/quantization-support.rst) @vkuzo
- [Public API test list](test/allowlist_for_publicAPI.json) @peterbell10
Differential Revision: [D36792967](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36792967/)
**NOTE FOR REVIEWERS**: This PR has internal Facebook specific changes or comments, please review them on [Phabricator](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36792967/)!
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78712
Approved by: https://github.com/jerryzh168
This is a new version of #15648 based on the latest master branch.
Unlike the previous PR where I fixed a lot of the doctests in addition to integrating xdoctest, I'm going to reduce the scope here. I'm simply going to integrate xdoctest, and then I'm going to mark all of the failing tests as "SKIP". This will let xdoctest run on the dashboards, provide some value, and still let the dashboards pass. I'll leave fixing the doctests themselves to another PR.
In my initial commit, I do the bare minimum to get something running with failing dashboards. The few tests that I marked as skip are causing segfaults. Running xdoctest results in 293 failed, 201 passed tests. The next commits will be to disable those tests. (unfortunately I don't have a tool that will insert the `#xdoctest: +SKIP` directive over every failing test, so I'm going to do this mostly manually.)
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/71105
@ezyang
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/82797
Approved by: https://github.com/ezyang
Changes:
* form for topics proposals for Core maintainers review been added
* merge_rules.json file specified as spruce of truth for the list of maintainers (since it is the file that actually defines permissions)
* responsibilities of the module maintainers are added (as per the last core maintainers meeting)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/82736
Approved by: https://github.com/svekars, https://github.com/soumith
Re-land #81953
Add `_type_utils` for handling data type conversion among JIT, torch and ONNX.
- Replace dictionary / list indexing with methods in ScalarType
- Breaking: **Remove ScalarType from `symbolic_helper`** and move it to `_type_utils`
- Deprecated: "cast_pytorch_to_onnx", "pytorch_name_to_type", "scalar_name_to_pytorch", "scalar_type_to_onnx", "scalar_type_to_pytorch_type" in `symbolic_helper`
- Deprecate the type mappings and lists. Remove all internal references
- Move _cast_func_template to opset 9 and remove its reference elsewhere (clean up). Added documentation for easy discovery
Why: List / dictionary indexing and lookup are error-prone and convoluted.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/82995
Approved by: https://github.com/kit1980
Add `_type_utils` for handling data type conversion among JIT, torch and ONNX.
- Replace dictionary / list indexing with methods in ScalarType
- Breaking: **Remove ScalarType from `symbolic_helper`** and move it to `_type_utils`
- Breaking: **Remove "cast_pytorch_to_onnx", "pytorch_name_to_type", "scalar_name_to_pytorch", "scalar_type_to_onnx", "scalar_type_to_pytorch_type"** from `symbolic_helper`
- Deprecate the type mappings and lists. Remove all internal references
- Move _cast_func_template to opset 9 and remove its reference elsewhere (clean up). Added documentation for easy discovery
Why: List / dictionary indexing and lookup are error-prone and convoluted.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/81953
Approved by: https://github.com/AllenTiTaiWang, https://github.com/BowenBao
Add flag (inline_autograd) to enable inline export of model consisting of autograd functions. Currently, this flag should only be used in TrainingMode.EVAL and not for training.
An example:
If a model containing ``autograd.Function`` is as follows
```
class AutogradFunc(torch.autograd.Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, i):
result = i.exp()
result = result.log()
ctx.save_for_backward(result)
return result
```
Then the model is exported as
```
graph(%0 : Float):
%1 : Float = ^AutogradFunc(%0)
return (%1)
```
If inline_autograd is set to True, this will be exported as
```
graph(%0 : Float):
%1 : Float = onnx::Exp(%0)
%2 : Float = onnx::Log(%1)
return (%2)
```
If one of the ops within the autograd module is not supported, that particular node is exported as is mirroring ONNX_FALLTHROUGH mode
Fixes: #61813
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/74765
Approved by: https://github.com/BowenBao, https://github.com/malfet
### Description
Since the major changes for `_TypedStorage` and `_UntypedStorage` are now complete, they can be renamed to be public.
`TypedStorage._untyped()` is renamed to `TypedStorage.untyped()`.
Documentation for storages is improved as well.
### Issue
Fixes#82436
### Testing
N/A
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/82438
Approved by: https://github.com/ezyang
unflatten now has a free function version in torch.flatten in addition to
the method in torch.Tensor.flatten.
Updated docs to reflect this and polished them a little.
For consistency, changed the signature of the int version of unflatten in
native_functions.yaml.
Some override tests were failing because unflatten has unusual
characteristics in terms of the .int and .Dimname versions having
different number of arguments so this required some changes
to test/test_override.py
Removed support for using mix of integer and string arguments
when specifying dimensions in unflatten.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/81399
Approved by: https://github.com/Lezcano, https://github.com/ngimel
Done via
```
git grep -l 'SymbolicIntNode' | xargs sed -i 's/SymbolicIntNode/SymIntNodeImpl/g'
```
Reasoning for the change:
* Sym is shorter than Symbolic, and consistent with SymInt
* You usually will deal in shared_ptr<...>, so we're going to
reserve the shorter name (SymIntNode) for the shared pointer.
But I don't want to update the Python name, so afterwards I ran
```
git grep -l _C.SymIntNodeImpl | xargs sed -i 's/_C.SymIntNodeImpl/_C.SymIntNode/'
```
and manually fixed up the binding code
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/82350
Approved by: https://github.com/Krovatkin
**RFC:
Problem statement**
Intel oneMKL and oneDNN are used to accelerate performance on Intel platforms. Both these 2 libraries provide verbose functionality to dump detailed operator execution information as well as execution time. These verbose messages are very helpful to performance profiling. However, the verbose functionality works for the entire execution. In many scenarios, though, we only would like to profile partial of the execution process. This feature is to expose PyTorch API functions to control oneDNN and oneMKL verbose functionality in runtime.
**Additional context**
The most used performance profiling steps are shown as the following code snippet:
```
def inference(model, inputs):
# step0 (optional): jit
model = torch.jit.trace(model, inputs)
# step1: warmup
for _ in range(100):
model(inputs)
# step2: performance profiling. We only care the profiling result, as well as oneDNN and oneMKL verbose messages, of this step
model(inputs)
# step3 (optional): benchmarking
t0 = time.time()
for _ in range(100):
model(inputs)
t1 = time.time()
print(‘dur: {}’.format((t1-t0)/100))
return model(inputs)
```
Since environment variables MKL_VERBOSE and DNNL_VERBOSE will be effect to the entire progress, we will get a great number of verbose messages for all of 101 iterations (if step3 is not involved). However, we only care about the verbose messages dumped in step2. It is very difficult to filter unnecessary verbose messages out if we are running into a complicated usages scenario. Also, jit trace will also bring more undesired verbose messages.
Furthermore, there are more complicated topologies or usages like cascaded topologies as below:
```
model1 = Model1()
model2 = Model2()
model3 = Model3()
x1 = inference(model1, x)
x2 = inference(model2, x1)
y = inference(model3, x2)
```
There are many cases that it is very hard to split these child topologies out. In this scenario, it is not possible to investigate performance of each individual topology with `DNNL_VERBOSE` and `MKL_VERBOSE`.
To solve this issue, oneDNN and oneMKL provide API functions to make it possible to control verbose functionality in runtime.
```
int mkl_verbose (int enable)
status dnnl::set_verbose(int level)
```
oneDNN and oneMKL print verbose messages to stdout when oneMKL or oneDNN ops are executed.
Sample verbose messages:
```
MKL_VERBOSE SGEMM(t,n,768,2048,3072,0x7fff64115800,0x7fa1aca58040,3072,0x1041f5c0,3072,0x7fff64115820,0x981f0c0,768) 8.52ms CNR:OFF Dyn:1 FastMM:1 TID:0 NThr:44
dnnl_verbose,exec,cpu,inner_product,brgemm:avx512_core,forward_training,src_f32::blocked:ab:f0 wei_f32::blocked:AB16b64a:f0 bia_f32::blocked:a:f0 dst_f32::blocked:ab:f0,,,mb16ic768oc768,0.0839844
```
**Design and implementation**
The design is to make python-interfaced wrap functions to invoke mkl_verbose and dnnl::set_verbose functions.
**Design concern**
- Need to add wrapper C++ functions for mkl_verbose and dnnl::set_verbose functions in torch/csrc and aten/csrc.
- Python API functions will be added to device-specific backends
- with torch.backends.mkl.verbose(1):
- with torch.backends.mkldnn.verbose(1):
**Use cases**
```
def inference(model, inputs):
# step0 (optional): jit
model = torch.jit.trace(model, inputs)
# step1: warmup
for _ in range(100):
model(inputs)
# step2: performance profiling
with torch.backends.mkl.verbose(1), torch.backends.mkldnn.verbose(1):
model(inputs)
# step3 (optional): benchmarking
t0 = time.time()
for _ in range(100):
model(inputs)
t1 = time.time()
print(‘dur: {}’.format((t1-t0)/100))
return model(inputs)
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63212
Approved by: https://github.com/VitalyFedyunin, https://github.com/malfet
Summary: There is currently per channel quantization support for Conv1d,
however this was not highlighted by the documentation for quantization
when discussion which modules have per channel quantization support.
This adds that there is exisiting support for Conv1d, with evidence
reproducable through the test plan below.
Test Plan:
```
class SingleLayerModel(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv1d = torch.nn.Conv1d(5, 5, 1).to(dtype=torch.float)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1d(x)
return x
def get_example_inputs(self):
return (torch.rand(5, 5, 1),)
torch.backends.quantized.engine = "fbgemm"
model = SingleLayerModel()
example_input = model.get_example_inputs()[0]
q_config = q_config_mapping = QConfigMapping()
q_config_mapping.set_global(torch.ao.quantization.get_default_qconfig(torch.backends.quantized.engine))
prepared = quantize_fx.prepare_fx(model, q_config_mapping, example_input)
print(prepared.conv1d.qconfig.weight.p.func)
```
Printing the above lines shows that the Conv1d has a
PerChannelMinMaxObserver. To show that this doesn't work for everything,
if you replace the Conv1d with a ConvTranspose1d, you will see running
the same code above that there is an error thrown about lack of support.
Reviewers:
Subscribers:
Tasks:
Tags:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/81349
Approved by: https://github.com/andrewor14
adding a quick link to nvfuser README.md in jit doc
Note that for 1.12 release, we probably want to have the link pointed to the doc in the release code base. I don't know if we have a tag for 1.12 release candidate yet, so we might want to update that.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/77780
Approved by: https://github.com/davidberard98
Similar to [scipy.sparse.spdiags](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.sparse.spdiags.html#scipy-sparse-spdiags)
Part of #70926
In other functions (ie (torch.diagonal)[https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.diagonal.html#torch.diagonal]) diagonals of a tensor are referenced using the offset and the two dimensions that the diagonal is taken with respect to.
Here the reference implementation from scipy is only considering matrix output, so even if we only support 2-d output at first. It may be useful to consider how the dimensions corresponding to each diagonal would be specified for higher dimensional output.
The proposed torch signature implies that all offsets refer to the diagonals with respect to the only two dimensions of the output:
```
torch.sparse.spdiags(Tensor diagonals, IntTensor offsets, int[] shape, Layout? layout=None) -> SparseTensor
```
Above it is required that: `diagonals.ndimension() == 2`, `offsets.ndimensions() == 1`, `offsets.shape[0] == diagonals.shape[0]` and `len(shape) == 2`.
This would need to be altered for the case where `len(shape)` > 2. One options is:
```
torch.sparse.spdiags(Tensor[] diagonals, IntTensor[] offsets, IntTensor dims, int[] shape, Layout? layout=None) -> SparseTensor
```
Here `offsets` and `diagonals` becomes lists of tensors, and the `IntTensor dims` argument is introduced. This would require that `len(diagonals) == len(offsets) == dims.shape[0]`, `dims.ndimension() == 2` and `dims.shape[1] == 2` also the same restrictions as the 2d case above apply to the elements of `diagonals` and `offsets` pairwise (that is `diagonals[i].ndimension() == 2`, `offsets[i].ndimension() == 1` and `offsets[i].shape[0] == diagonals[i].shape[0]` for all i). This form of the signature would construct the sparse result by placing the values from `diagonals[i][j]` into the diagonal with offset `offset[i][j]` taken with respect to dimensions `dims[i]`. The specialization back to the original signature for the 2d case could be seen as allowing the single row of dims to default to `[0, 1]` when there is only one `diagonals`, `offsets` provided, and shape is `2-d`. This option allows the rows of an input element `diagonals[i]` to have a different length which may be appropriate as the max length of a diagonal along different dimension pairs will be different.
Another option is to specify the dimensions the diagonal is taken with respect to for each offset. This signature would look like:
```
torch.sparse.spdiags(Tensor diagonals, IntTensor offsets, IntTensor dims, int[] shape, Layout? layout=None) -> SparseTensor
```
Here, `diagonals` is still 2-D with dimension 0 matching the length of 1-D `offsets` and the tensor input `dims` is also 2-D with dimension 0 matching the length of 1-D `offsets` and the second dimension being fixed at `2` in this case the sparse result is constructed by placing the elements from `diagonals[i]` into the output diagonal `output.diagonal(offset[i], dim0=dims[i][0], dim1=dims[i][1])` (with some additional consideration that makes it more complicated than simply asigning to that view). The specialization from this back to the 2-D form could be seen as assuming `dims = [[0, 1], [0, 1]... len(offsets) times ]` when `len shape==2`.
In both proposed signatures for the N-D case the specialization back to the 2-D signature is a bit of a stretch for your typical default arguments logic, however I think the first is better choice as it offers more flexibility.
I think some discussion is required about:
- [x] Should the N-D output case be implemented from the outset
- [x] If not, should the future addition of the N-D output case be considered when designing the interface.
- [x] Other thoughts on the signature which includes the `dims` information for the N-D output case.
**Resolution**: Since no one has offered a request for N-D output support, I think is fine to restrict this to sparse matrix generation. Should a request for N-D support come later, an overload accepting the additional `dims` could be added.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78439
Approved by: https://github.com/nikitaved, https://github.com/cpuhrsch, https://github.com/pearu
Similar to [scipy.sparse.spdiags](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.sparse.spdiags.html#scipy-sparse-spdiags)
Part of #70926
In other functions (ie (torch.diagonal)[https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.diagonal.html#torch.diagonal]) diagonals of a tensor are referenced using the offset and the two dimensions that the diagonal is taken with respect to.
Here the reference implementation from scipy is only considering matrix output, so even if we only support 2-d output at first. It may be useful to consider how the dimensions corresponding to each diagonal would be specified for higher dimensional output.
The proposed torch signature implies that all offsets refer to the diagonals with respect to the only two dimensions of the output:
```
torch.sparse.spdiags(Tensor diagonals, IntTensor offsets, int[] shape, Layout? layout=None) -> SparseTensor
```
Above it is required that: `diagonals.ndimension() == 2`, `offsets.ndimensions() == 1`, `offsets.shape[0] == diagonals.shape[0]` and `len(shape) == 2`.
This would need to be altered for the case where `len(shape)` > 2. One options is:
```
torch.sparse.spdiags(Tensor[] diagonals, IntTensor[] offsets, IntTensor dims, int[] shape, Layout? layout=None) -> SparseTensor
```
Here `offsets` and `diagonals` becomes lists of tensors, and the `IntTensor dims` argument is introduced. This would require that `len(diagonals) == len(offsets) == dims.shape[0]`, `dims.ndimension() == 2` and `dims.shape[1] == 2` also the same restrictions as the 2d case above apply to the elements of `diagonals` and `offsets` pairwise (that is `diagonals[i].ndimension() == 2`, `offsets[i].ndimension() == 1` and `offsets[i].shape[0] == diagonals[i].shape[0]` for all i). This form of the signature would construct the sparse result by placing the values from `diagonals[i][j]` into the diagonal with offset `offset[i][j]` taken with respect to dimensions `dims[i]`. The specialization back to the original signature for the 2d case could be seen as allowing the single row of dims to default to `[0, 1]` when there is only one `diagonals`, `offsets` provided, and shape is `2-d`. This option allows the rows of an input element `diagonals[i]` to have a different length which may be appropriate as the max length of a diagonal along different dimension pairs will be different.
Another option is to specify the dimensions the diagonal is taken with respect to for each offset. This signature would look like:
```
torch.sparse.spdiags(Tensor diagonals, IntTensor offsets, IntTensor dims, int[] shape, Layout? layout=None) -> SparseTensor
```
Here, `diagonals` is still 2-D with dimension 0 matching the length of 1-D `offsets` and the tensor input `dims` is also 2-D with dimension 0 matching the length of 1-D `offsets` and the second dimension being fixed at `2` in this case the sparse result is constructed by placing the elements from `diagonals[i]` into the output diagonal `output.diagonal(offset[i], dim0=dims[i][0], dim1=dims[i][1])` (with some additional consideration that makes it more complicated than simply asigning to that view). The specialization from this back to the 2-D form could be seen as assuming `dims = [[0, 1], [0, 1]... len(offsets) times ]` when `len shape==2`.
In both proposed signatures for the N-D case the specialization back to the 2-D signature is a bit of a stretch for your typical default arguments logic, however I think the first is better choice as it offers more flexibility.
I think some discussion is required about:
- [x] Should the N-D output case be implemented from the outset
- [x] If not, should the future addition of the N-D output case be considered when designing the interface.
- [x] Other thoughts on the signature which includes the `dims` information for the N-D output case.
**Resolution**: Since no one has offered a request for N-D output support, I think is fine to restrict this to sparse matrix generation. Should a request for N-D support come later, an overload accepting the additional `dims` could be added.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78439
Approved by: https://github.com/nikitaved, https://github.com/cpuhrsch, https://github.com/pearu
Create Z3 types. In particular, dynamic dimensions, dynamic tensor type and tensor types up to size 4. Note that for Z3 decidability reasons, we are using uninterpreted functions for tensor types, which means we must explicitly define tensor constructors with a concrete size (for now, upto size 4). We defer lifting this requirement to future work.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/80084
Approved by: https://github.com/anijain2305
This PR introduces two components.
CapabilityBasedPartitioner for FX graph: given a list of supported operators, this partitioner tries to forms the largest subgraphs that only contain the supported ops.
Fuser utility: given a list of nodes in FX graph, it lifts them as a sub-GraphModule in the original graph.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/79439
Approved by: https://github.com/jjsjann123, https://github.com/davidberard98
The BaseDataScheduler is the abstract scheduler class specifically for the
BaseDataSparsifier class. This class controls a specific hyperparameter of
the sparsifier class and varies it across the training process (or across time).
Args:
data_sparsifier (instance of BaseDataSparsifier)
Implemented class data sparsifier class wherein the update_mask is implemented
schedule_param (str)
A specific hyperparameter of the passed sparsifier that needs to be scheduled/varied
last_epoch (int, default=-1)
This is specifically is passed when training needs to be resumed from a particular
point.
verbose (bool, default=False)
Verbosity of the BaseDataScheduler
The *get_schedule_param()* function needs to be implemented by the user.
Test Plan:
```python test/test_ao_sparsity.py TestBaseDataScheduler```
Differential Revision: [D37358608](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D37358608)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/79817
Approved by: https://github.com/jerryzh168, https://github.com/z-a-f
Summary: per https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/79135 the code
snippets in the docs don't run. This is a recurring problem since
previously there was no unit test to check that these code snippets
actually ran. This PR adds support for such a test, importing the
snippet as a string and evaluating it to make sure that it actually runs
if the code snippet has user defined code, you can pass in dummy
versions using global_inputs. Sometimes the imports of the code snippets
behave oddly but you can pass them in as in test_quantization_doc_custom
where nnq is passed in.
Test Plan: python test/test_quantization.py TestQuantizationDocs
also see https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/79994 to see what shows up in CI when the docs get broken
Reviewers:
Subscribers:
Tasks:
Tags:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/79923
Approved by: https://github.com/z-a-f, https://github.com/vspenubarthi
This PR addresses issue address #75666.
Stateful communication hook now can be saved and reloaded to resume training.
Current PR adds the functionality for PowerSGD communication hook and tests that communication hook can be properly saved and restored.
PowerSGD implementation uses ``__slots__``, as a result introduced __getstate__ and __setstate__ methods are implemented to work with `__slots__` and not` __dict__`.
`__getstate__ `
Returns:
A dictionary that represents a ``PowerSGDState`` which will be pickled and saved.
``process_group`` is non-serializable and excluded from a returned state.
`__setstate__`
Takes a provided ``state`` and retrieves ``PowerSGDState``.
``process_group`` is set to default with a proper warning issued to a user.
Unit test
A hook-independent `_test_hook_pickling` is added with this PR, as well as `test_ddp_hook_pickling_powerSGD`, which tests `powerSGD`’s ability to be saved and reloaded.
Currently, the test creates a ddp model with a provided hook, trains it for 10 epochs and saves model’s state and hook’s state.
During reloading, unit test makes sure that a warning was logged (only one warning and the proper one). It then proceeds to check that reloaded hook and original hook are the same. Finally, it checks that a hook’s state was properly initialized:
- it compares slot values (all, but 2: `process_group` and `rng`) for original and reloaded state
- it checks that process group was set to a default group
- it checks that a random state was restored properly with np.testing.assert_array_equal, because `rng` is an instance of `np.random.RandomState`, represented by a tuple. One of entries is of `ndarray dtype[uint32]` type and `np.testing.assert_array_equal` is used for assertion.
Future To-Do:
- Implement similar __getstate__ and __setstate__ for other stateful communication hooks
- Add appropriate tests
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/79334
Approved by: https://github.com/rohan-varma, https://github.com/awgu
Base Data Sparsifier class for all Data sparsifiers.
The abstract class accepts raw torch tensors / embedding / embedding bags (refer to SUPPORTED_TYPES above)
to prepare for sparsification.
In this case, mask (and parametrizations) is owned by the class and not by the user.
Specifically, the container object inside the class maintains the mask and parametrizations of the input data
Test Plan:
```python test/test_ao_sparsity.py TestBaseDataSparsifier```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/79251
Approved by: https://github.com/z-a-f, https://github.com/HDCharles
This PR adds support for `SymInt`s in python. Namely,
* `THPVariable_size` now returns `sym_sizes()`
* python arg parser is modified to parse PyObjects into ints and `SymbolicIntNode`s
* pybind11 bindings for `SymbolicIntNode` are added, so size expressions can be traced
* a large number of tests added to demonstrate how to implement python symints.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78135
Approved by: https://github.com/ezyang
adding a link to github 1.12 release branch nvfuser README.md in jit doc
Note that this PR is intended to be cherry-picked by 1.12 release, we'll have a follow up PR to update the link once this PR is merged.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78160
Approved by: https://github.com/davidberard98
This PR adds `linalg.lu_solve`. While doing so, I found a bug in MAGMA
when calling the batched MAGMA backend with trans=True. We work around
that by solving the system solving two triangular systems.
We also update the heuristics for this function, as they were fairly
updated. We found that cuSolver is king, so luckily we do not need to
rely on the buggy backend from magma for this function.
We added tests testing this function left and right. We also added tests
for the different backends. We also activated the tests for AMD, as
those should work as well.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/61657
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/77634
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
Summary: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78452 replaced
qconfig_dict with QConfigMapping as the default API for prepare_fx,
prepare_qat_fx, and convert_fx. We should update the docs to reflect
this change as well.
Test Plan:
```
cd docs
make html
cd build/html
python -m server.http
```
Reviewers: jerryzh168, vkuzo
Subscribers: jerryzh168, vkuzo
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78533
Approved by: https://github.com/vkuzo
Euler beta function:
```Python
torch.special.beta(input, other, *, out=None) → Tensor
```
`reentrant_gamma` and `reentrant_ln_gamma` implementations (using Stirling’s approximation) are provided. I started working on this before I realized we were missing a gamma implementation (despite providing incomplete gamma implementations). Uses the coefficients computed by Steve Moshier to replicate SciPy’s implementation. Likewise, it mimics SciPy’s behavior (instead of the behavior in Cephes).
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78031
Approved by: https://github.com/mruberry
(reopening due to botched merge)
The cuDNN V8 API (main support merged in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/60755) potentially exposes many more kernels with benchmark=True. While these additional kernels can improve performance, it is often unnecessary to run every kernel returned by the heuristic and doing so may degrade the user experience by causing the first model iteration to be very slow. To alleviate this issue, this PR introduces torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark_limit. benchmark_limit specifies the maximum number of working cuDNN kernels to try for a given workload, with the default being 10 (similar to what TensorFlow does). benchmark_limit = 0 yields the current behavior of trying every kernel returned by the heuristic.
CC @ptrblck @ngimel @xwang233
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/77002
Approved by: https://github.com/ngimel
Resubmit of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/77673, which was reverted due to Windows test failures: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/77673#issuecomment-1130425845.
I suspect these failures happened because I don't explicitly set a side stream for graph capture in the new test.
Not setting a side stream explicitly is alright on Linux because cuda tests implicitly use a side stream.
I think Windows cuda tests implicitly use the default stream, breaking capture and leaving the backend in a bad state.
Other graphs tests explicitly set side streams and don't error in Windows builds, so i'm 95% sure doing the same for the new test will work.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/77789
Approved by: https://github.com/ezyang
In preparation of adopting future rocblas library options, it is necessary to track when the backward pass of training is executing. The scope-based helper class `BackwardPassGuard` is provided to toggle state.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/71881
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD
Summary:
This improves the documentation page for backend_config_dict to render
the configurations in a human readable format, such as
```
{
'pattern': torch.nn.modules.pooling.AdaptiveAvgPool1d,
'dtype_configs': [
{
'input_dtype': torch.quint8,
'output_dtype': torch.quint8,
},
{
'input_dtype': torch.float16,
'weight_dtype': torch.float16,
'bias_dtype': torch.float16,
'output_dtype': torch.float16,
},
],
'observation_type': ObservationType.OUTPUT_SHARE_OBSERVER_WITH_INPUT,
},
```
The results are also now sorted alphabetically by the normalized name of
the root op in the pattern.
A couple of utility functions are created to help with this. If in the future
we convert backend_config_dict to use typed objects, we can move this logic
to the objects at that time.
Test plan:
```
cd docs
make html
cd build
python -m server.http
// renders correctly, example: https://gist.github.com/vkuzo/76adfc7c89e119c59813a733fa2cd56f
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/77535
Approved by: https://github.com/andrewor14
We don't have any coverage for meta tensor correctness for backwards
because torch function mode can only allow us to interpose on
Python torch API calls, but backwards invocations happen from C++.
To make this possible, I add torch_dispatch_meta test which runs the
tests with __torch_dispatch__
While doing this, I needed to generate fresh expected failure / skip
lists for the new test suite, and I discovered that my original
scaffolding for this purpose was woefully insufficient. So I rewrote
how the test framework worked, and at the same time rewrote the
__torch_function__ code to also use the new logic. Here's whats
new:
- Expected failure / skip is now done on a per function call basis,
rather than the entire test. This means that separate OpInfo
samples for a function don't affect each other.
- There are now only two lists: expect failure list (where the test
consistently fails on all runs) and skip list (where the test
sometimes passes and fails.
- We explicitly notate the dtype that failed. I considered detecting
when something failed on all dtypes, but this was complicated and
listing everything out seemed to be nice and simple. To keep the
dtypes short, I introduce a shorthand notation for dtypes.
- Conversion to meta tensors is factored into its own class
MetaConverter
- To regenerate the expected failure / skip lists, just run with
PYTORCH_COLLECT_EXPECT and filter on a specific test type
(test_meta or test_dispatch_meta) for whichever you want to update.
Other misc fixes:
- Fix max_pool1d to work with BFloat16 in all circumstances, by making
it dispatch and then fixing a minor compile error (constexpr doesn't
work with BFloat16)
- Add resolve_name for turning random torch API functions into string
names
- Add push classmethod to the Mode classes, so that you can more easily
push a mode onto the mode stack
- Add some more skips for missing LAPACK
- Added an API to let you query if there's already a registration for
a function, added a test to check that we register_meta for all
decompositions (except detach, that decomp is wrong lol), and then
update all the necessary sites to make the test pass.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyangfb.com>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/77477
Approved by: https://github.com/zou3519
Summary:
This PR creates a best practices guideline for debugging quantization
accuracy. The content here comes from https://fburl.com/gdoc/nzlzxeaf,
with experimental and Meta-only parts left out.
For now, a lot of the debugging is manual, with the Numeric Suite the
only tool we have to help the user find root causes of quantization
inaccuracies. As we build additional tools for equalization detection,
outlier detection, etc, we will add them to this page
Test plan:
```
cd docs
make html
cd build/html
python -m server.http
// result renders well in browser
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/77536
Approved by: https://github.com/hx89
There seems to be a typo in the main quantization docs.
In the table comparing "Eager Mode Quantization" against "FX Graph Mode Quantization", in the row named "Quantization Mode Support" both modes say they are "Quantiztion aware" instead of "Quantization aware"
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/77300
Approved by: https://github.com/H-Huang
This PR allows user to author a CUDA kernel in python.
```
from torch.cuda.jiterator import create_jit_fn
code_string = "template <typename T> T my_kernel(T x, T y, T alpha) { return -x * y + x - y + alpha; }"
jitted_fn = create_jit_fn(code_string, alpha=0)
a = torch.rand(3, device='cuda')
b = torch.rand(3, device='cuda')
result = jitted_fn(a, b, alpha=1.0)
```
Limitations:
- Only supports elementwise kernel
- 1~8 tensor inputs (empty input, e.g. factory methods, is not supported)
- inputs tensors must live in cuda device
- cpu Scalar is not supported
- kwargs must be pre-declared when calling create_jit_fn
- kwargs must be convertible to at::Scalar, one of float64, int64_t, bool. (complex not support for now)
TODOs:
- [x] consolidate union and c10::variant implementation
- [x] plug into existing op testing framework
- [ ] rename files, place files in the right folder
- [ ] place util functions in the right file
- [x] enforce assumptions in python interface e.g <8 inputs, kwargs types
- [x] Add user-facing documentation
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/76394
Approved by: https://github.com/mruberry
This PR adds `linalg.vander`, the linalg version of `torch.vander`.
We add autograd support and support for batched inputs.
We also take this chance to improve the docs (TODO: Check that they
render correctly!) and add an OpInfo.
**Discussion**: The current default for the `increasing` kwargs is extremely
odd as it is the opposite of the classical definition (see
[wiki](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vandermonde_matrix)). This is
reflected in the docs, where I explicit both the odd defaults that we
use and the classical definition. See also [this stackoverflow
post](https://stackoverflow.com/a/71758047/5280578), which shows how
people are confused by this defaults.
My take on this would be to correct the default to be `increasing=True`
and document the divergence with NumPy (as we do for other `linalg`
functions) as:
- It is what people expect
- It gives the correct determinant called "the Vandermonde determinant" rather than (-1)^{n-1} times the Vandermonde det (ugh).
- [Minor] It is more efficient (no `flip` needed)
- Since it's under `linalg.vander`, it's strictly not a drop-in replacement for `np.vander`.
We will deprecate `torch.vander` in a PR after this one in this stack
(once we settle on what's the correct default).
Thoughts? mruberry
cc kgryte rgommers as they might have some context for the defaults of
NumPy.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/60197
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/76303
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD, https://github.com/mruberry
This PR adds `linalg.lu_solve`. While doing so, I found a bug in MAGMA
when calling the batched MAGMA backend with trans=True. We work around
that by solving the system solving two triangular systems.
We also update the heuristics for this function, as they were fairly
updated. We found that cuSolver is king, so luckily we do not need to
rely on the buggy backend from magma for this function.
We added tests testing this function left and right. We also added tests
for the different backends. We also activated the tests for AMD, as
those should work as well.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/61657
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72935
Approved by: https://github.com/IvanYashchuk, https://github.com/mruberry
Re-landing #68111/#74596
## Description
v0.5 PR of this [RFC](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/49444).
On the basis of #50256, the below improvements are included:
* The [v0.5 release branch](https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneDNN/releases/tag/graph-v0.5) of the oneDNN Graph API is used
* The fuser now works with the profiling graph executor. We have inserted type check nodes to guard the profiled tensor properties.
### User API:
The optimization pass is disabled by default. Users could enable it by:
```
torch.jit.enable_onednn_fusion(True)
```
`torch.jit.freeze` should be used after tracing (recommended) or scripting a model.
### Performance:
[pytorch/benchmark](https://github.com/pytorch/benchmark) tool is used to compare the performance:
* SkyLake 8180 (1 socket of 28 cores):
* SkyLake 8180 (single thread):
* By mapping hardswish to oneDNN Graph, it’s 8% faster than PyTorch JIT (NNC + OFI)
** We expect performance gain after mapping transpose, contiguous & view to oneDNN graph ops
### Directory structure of the integration code
Fuser-related code is placed under:
```
torch/csrc/jit/codegen/onednn/
```
Optimization pass registration is done in:
```
torch/csrc/jit/passes/onednn_graph_fuser.h
```
CMake for the integration code is in:
```
caffe2/CMakeLists.txt
cmake/public/mkldnn.cmake
cmake/Modules/FindMKLDNN.cmake
```
## Limitations
* In this PR, we only support Pytorch-oneDNN-Graph integration on Linux platform. Support on Windows and MacOS will be enabled as a next step.
* We have only optimized the inference use-case.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/76622
Approved by: https://github.com/eellison
This PR modifies `lu_unpack` by:
- Using less memory when unpacking `L` and `U`
- Fuse the subtraction by `-1` with `unpack_pivots_stub`
- Define tensors of the correct types to avoid copies
- Port `lu_unpack` to be a strucutred kernel so that its `_out` version
does not incur on extra copies
Then we implement `linalg.lu` as a structured kernel, as we want to
compute its derivative manually. We do so because composing the
derivatives of `torch.lu_factor` and `torch.lu_unpack` would be less efficient.
This new function and `lu_unpack` comes with all the things it can come:
forward and backward ad, decent docs, correctness tests, OpInfo, complex support,
support for metatensors and support for vmap and vmap over the gradients.
I really hope we don't continue adding more features.
This PR also avoids saving some of the tensors that were previously
saved unnecessarily for the backward in `lu_factor_ex_backward` and
`lu_backward` and does some other general improvements here and there
to the forward and backward AD formulae of other related functions.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/67833
Approved by: https://github.com/IvanYashchuk, https://github.com/nikitaved, https://github.com/mruberry
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/76538
when running the example from the docs, I found that these steps were not working.
These are the updates necessary to get the example working.
Test Plan: n/a
Reviewed By: PaliC
Differential Revision: D35998155
fbshipit-source-id: d78bb2886f94889abae5a3af5239fcd306cd5e09
(cherry picked from commit 6893812efe7443b437ccafb7b1ff6bc7bd2e6670)
This PR adds `linalg.vander`, the linalg version of `torch.vander`.
We add autograd support and support for batched inputs.
We also take this chance to improve the docs (TODO: Check that they
render correctly!) and add an OpInfo.
**Discussion**: The current default for the `increasing` kwargs is extremely
odd as it is the opposite of the classical definition (see
[wiki](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vandermonde_matrix)). This is
reflected in the docs, where I explicit both the odd defaults that we
use and the classical definition. See also [this stackoverflow
post](https://stackoverflow.com/a/71758047/5280578), which shows how
people are confused by this defaults.
My take on this would be to correct the default to be `increasing=True`
and document the divergence with NumPy (as we do for other `linalg`
functions) as:
- It is what people expect
- It gives the correct determinant called "the Vandermonde determinant" rather than (-1)^{n-1} times the Vandermonde det (ugh).
- [Minor] It is more efficient (no `flip` needed)
- Since it's under `linalg.vander`, it's strictly not a drop-in replacement for `np.vander`.
We will deprecate `torch.vander` in a PR after this one in this stack
(once we settle on what's the correct default).
Thoughts? mruberry
cc kgryte rgommers as they might have some context for the defaults of
NumPy.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/60197
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/76303
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD
This PR adds a function for computing the LDL decomposition and a function that can solve systems of linear equations using this decomposition. The result of `torch.linalg.ldl_factor_ex` is in a compact form and it's required to use it only through `torch.linalg.ldl_solve`. In the future, we could provide `ldl_unpack` function that transforms the compact representation into explicit matrices.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/54847.
cc @jianyuh @nikitaved @pearu @mruberry @walterddr @IvanYashchuk @xwang233 @Lezcano
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69828
Approved by: https://github.com/Lezcano, https://github.com/mruberry, https://github.com/albanD
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/76223
Small formatting fixes that was missed because I didn't check the generated doc last time
Test Plan:
visual inspection of the generated docs for this PR
Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: HDCharles
Differential Revision: D35853174
fbshipit-source-id: 4454a4bf5d0c998d866bbae1d6b5286827082033
(cherry picked from commit 125f60356ccc9cd6888c515889bd27ff9860ec74)
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/75464 Adds a context manager that will throw if the ops in the context are not fused.
API is :
```
with torch.jit.strict_fusion():
...
```
A few TODOs:
[+] Compose/figure out how to do with autodiff - right now it will run on autodiff as well
[+] Support all of the nvfuser operators that are added in guarding
[+] Figure out what to do with control flow that isn't taken (right now it will just error). this is probably a source of the original issue :/ - will just error
[+] (After those are figured out) add to docs
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/75777
Approved by: https://github.com/davidberard98
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/75998
Add more details to user facing docs quantization.rst, which will be displayed in the official quantization doc page: https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/quantization.html
This includes:
* docs for quantization stack (quantized tensor, quantized operator and modules, observer, fake_quantize, QConfig, quantization flow)
* Added support table for quantization mode, quantization flow mode and backend, (also moved around operator support table)
* restructured eager mode and fx mode docs as well
Test Plan:
inspect the doc that's built by github ci
Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: dzdang
Differential Revision: D35739111
fbshipit-source-id: 3762d387479bdd37472cb17d5c49da2f520effbb
(cherry picked from commit db5e6411c52c08dd9c45f841ab86713d36a75d51)
Summary:
Following https://github.com/pytorch/rfcs/blob/master/RFC-0019-Extending-PyTorch-Quantization-to-Custom-Backends.md we implemented
the backend configuration for fbgemm/qnnpack backend, currently it was under fx folder, but we'd like to use this for all different
workflows, including eager, fx graph and define by run quantization, this PR moves it to torch.ao.quantization namespace so that
it can be shared by different workflows
Also moves some utility functions specific to fx to fx/backend_config_utils.py and some files are kept in fx folder (quantize_handler.py and fuse_handler.py)
Test Plan:
python test/teset_quantization.py TestQuantizeFx
python test/teset_quantization.py TestQuantizeFxOps
python test/teset_quantization.py TestQuantizeFxModels
python test/test_quantization.py TestAOMigrationQuantization
python test/test_quantization.py TestAOMigrationQuantizationFx
Reviewers:
Subscribers:
Tasks:
Tags:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/75823
Approved by: https://github.com/vkuzo
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/75126
Quantization has a high volume of configurations of how to quantize an
op for a reference model representation which is useful for a lowering
step for a backend. An example of this is
```
{'dtype_configs': [{'input_dtype': torch.quint8,
'output_dtype': torch.quint8}],
'observation_type': <ObservationType.OUTPUT_USE_DIFFERENT_OBSERVER_AS_INPUT: 0>,
'pattern': <class 'torch.nn.modules.conv.ConvTranspose1d'>},
```
These configs are checked into master, and they are created with Python functions.
Therefore, there is no easy way for the user to see what the configs actually
are without running some Python code.
This PR is one approach to document these configs. Here is what this is doing:
1. during documentation build, write a text file of the configs
2. render that text file on a quantization page, with some additional context
In the future, this could be extended to autogenerate better looking tables
such as: op support per backend and dtype, op support per valid quantization settings per backend,
etc.
Test Plan:
```
cd docs
make html
cd html
python -m http.server 8000
// render http://[::]:8000/quantization-backend-configuration.html
// it renders correctly
```
Reviewed By: ejguan
Differential Revision: D35365461
Pulled By: vkuzo
fbshipit-source-id: d60f776ccb57da9db3d09550e4b27bd5e725635a
(cherry picked from commit 14865c0e23bc080120342c8f9278f0fae8eb8fbd)
Summary:
## Description
Preview4 PR of this [RFC](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/49444).
On the basis of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/50256, the below improvements are included:
- The [preview4 release branch](https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneDNN/releases/tag/graph-v0.4.1) of the oneDNN Graph API is used
- The fuser now works with the profiling graph executor. We have inserted type check nodes to guard the profiled tensor properties.
### User API:
The optimization pass is disabled by default. Users could enable it by:
```
torch.jit.enable_onednn_fusion(True)
```
### Performance:
[pytorch/benchmark](https://github.com/pytorch/benchmark) tool is used to compare the performance:
- SkyLake 8180 (1 socket of 28 cores):

- SkyLake 8180 (single thread):

\* By mapping hardswish to oneDNN Graph, it’s 8% faster than PyTorch JIT (NNC + OFI)
\** We expect performance gain after mapping transpose, contiguous & view to oneDNN graph ops
### Directory structure of the integration code
Fuser-related code are placed under:
```
torch/csrc/jit/codegen/onednn/
```
Optimization pass registration is done in:
```
torch/csrc/jit/passes/onednn_graph_fuser.h
```
CMake for the integration code is:
```
caffe2/CMakeLists.txt
```
## Limitations
- In this PR, we have only supported the optimization on Linux platform. The support on Windows and MacOS will be enabled as the next step.
- We have only optimized the inference use case.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/68111
Reviewed By: eellison
Differential Revision: D34584878
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: ce817aa8cc9052ee9ed930c9cf66be83449e61a4
(cherry picked from commit cd17683aa7d9c0947df45a1ab53627feff795587)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/74261
### Goal
Implement a cheap way to reclaim GPU memory (garbage collection) without incurring GPU sync.
### Why do we need this?
Currently, there are only two ways to reclaim GPU memory block already assigned to a particular stream.
- `release_available_cached_blocks(params)`: Free blocks exceeding the `CachingAllocatorConfig::max_split_size()` until we can satisfy the request.
Issue: If the `max_split_size` is unset (default), this function is a no-op. Even if this is set, the reclamation is quite conservative (e.g., never frees blocks under max_split_size).
- `release_cached_blocks()`: Waits for all the in-flight events and then reclaim blocks.
Issue: 'waiting for all event' is very expensive as it will likely stall all the GPU operations. Many GPU applications without a proper handling of potential GPU throttling would suffer/crash.
### Proposed idea
- If the garbage collection threshold is set, try to reclaim some memory blocks *without* synchronization. It should be safe to do so, as `release_available_cached_blocks` essentially does the same thing (but less aggressively).
- GC is triggered only when we fail to serve a `malloc` request from the block pool. No need to free blocks when the block pool is functioning just fine.
- Prioritize reclaiming blocks that weren't reused for long time. Reclamation stops once the used memory capacity < threshold.
- This code path is totally optional; by default it won't be invoked.
Test Plan:
- Unit tests
- Manually checked that the GPU memory usage stays as indicated by the garbage collector. If not the caching allocator at least tries to keep freeing the blocks.
Reviewed By: jianyuh
Differential Revision: D34482514
fbshipit-source-id: d5eae62ac60b94b0bca851f9d233a092d086e3c2
(cherry picked from commit 05780f1ed4b176f05e765b2411c9eaa2eaeb48b0)
Summary:
Add ONNX exporter logging facility. Supporting both C++/Python logging api. Logging can be turned on/off. Logging output stream can be either set to `stdout` or `stderr`.
A few other changes:
* When exception is raised in passes, the current IR graph being processed will be logged.
* When exception is raised from `_jit_pass_onnx` (the pass that converts nodes from namespace `ATen` to `ONNX`), both ATen IR graph and ONNX IR graph under construction will be logged.
* Exception message for ConstantFolding is truncated to avoid being too verbose.
* Update the final printed IR graph with node name in ONNX ModelProto as node attribute. Torch IR Node does not have name. Adding this to printed IR graph helps debugging.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/71342
Reviewed By: msaroufim
Differential Revision: D34433473
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 4b137dfd6a33eb681a5f2612f19aadf5dfe3d84a
(cherry picked from commit 67a8ebed5192c266f604bdcca931df6fe589699f)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/74213
In the current CUDACachingAllocator, the sizes are rounded up in multiple of blocks size of 512, so this works for smaller sizes. However for large sizes, we can have lots of different size blocks in the larger pool. This is problematic when we have variable batch sizes 1001, 1021, 1023 -> all will go to different block size and will create different size of blocks. This will create lots of unused blocks and will waste GPU memory capacity.
This diff adds a rounding approach to allocation size. It rounds up the size to nearest power-of-2 divisions and the power2-division can be changed with env variable setting.
For example, if we need to round-up size of1200 and if number of divisions is 4,
the size 1200 lies between 1024 and 2048 and if we do 4 divisions between
them, the values are 1024, 1280, 1536, and 1792. So the function will
return 1280 as the nearest ceiling of power-2 division.
env setting:
export PYTORCH_CUDA_ALLOC_CONF=roundup_power2_divisions:4
ghstack-source-id: 151446017
Reviewed By: ezyang
Differential Revision: D34868036
fbshipit-source-id: 494785add16e6b37c920dcb5a2b81d4c637b554a
(cherry picked from commit 548454ccacbd8700e7ffd2d762e40b4ba37abbae)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/74006
updated recommendations about environment variables to use during debug
and performance tuning
Test Plan: `make html`
Reviewed By: rohan-varma
Differential Revision: D34767454
fbshipit-source-id: 08cd58469bf72b58702e50e82020fa19b43b5911
(cherry picked from commit ac7e6630f8043f85d3d16be17c6a8ad1ebb2990c)
Summary:
Working towards https://docs.google.com/document/d/10yx2-4gs0gTMOimVS403MnoAWkqitS8TUHX73PN8EjE/edit?pli=1#
This PR:
- Ensure that all the submodules are listed in a rst file (that ensure they are considered by the coverage tool)
- Remove some long deprecated code that just error out on import
- Remove the allow list altogether to ensure nothing gets added back there
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/73983
Reviewed By: anjali411
Differential Revision: D34787908
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 163ce61e133b12b2f2e1cbe374f979e3d6858db7
(cherry picked from commit c9edfead7a01dc45bfc24eaf7220d2a84ab1f62e)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/73601
Some users had questions about how the RPC framework deals with
failures and whether we retry. Adding a note about this to our docs to
elaborate on our current behavior and why we chose that approach.
ghstack-source-id: 150359866
Test Plan: view docs.
Reviewed By: mrshenli
Differential Revision: D34560199
fbshipit-source-id: ee33ceed7fa706270d4ca5c8fcff7535583490ff
(cherry picked from commit 954a906240cc40aacf08ca13f6554a35303a678a)
Summary:
This PR adds a minimal version of a NestedTensor. It introduces the general harness future development can be built around.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72881
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D34259177
Pulled By: cpuhrsch
fbshipit-source-id: 0245c36f603424e20f3b09651043c207f526d760
(cherry picked from commit 10764e8d427f29b364567e4cbc86ed73c3933158)
Summary:
This PR introduces the `cuSolverSP` backend for `linalg.solve` with sparse CSR input matrices. The motivation comes from the issue: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/69538.
`cuSolver` provides [`cusolverSp<t>csrlsvluHost`](https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cusolver/index.html#cusolver-lt-t-gt-csrlsvlu) API, a few things to note:
1. As mentioned in the documentation: `only CPU (Host) path is provided.` From the profiling, there doesn't seem to be any GPU kernel launch for optimization, please see the profiling below.
2. Since only `host` path is provided, the CPU path uses `csrlsvluHost` (but requires PyTorch to be installed/built with CUDA support).
3. The documentation mentions reordering helps optimize stuff, but it isn't clear how it affects the performance. There are options for reordering, so we stick to `reorder = 0` as the default choice.
`cuSolver` has [`csrlsvqr`](https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cusolver/index.html#cusolver-lt-t-gt-csrlsvqr) function which provides a `device` path to solve the linear system. This function is used for the CUDA path in this PR.
**Gist:**
For CPU Path: we call [`csrlsvluHost` function of cuSolver](https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cusolver/index.html#cusolver-lt-t-gt-csrlsvlu).
For CUDA Path: we call [`csrlsvqr` function of cuSolver](https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cusolver/index.html#cusolver-lt-t-gt-csrlsvqr).
**Profiling:** (On sparse input tensor of size 1000 x 1000, with a vector of shape length 1000), for `csrlsvlu` function (to show no GPU optimization)
```cpp
==3999651== Profiling result:
Type Time(%) Time Calls Avg Min Max Name
GPU activities: 100.00% 2.1440us 1 2.1440us 2.1440us 2.1440us [CUDA memcpy HtoD]
API calls: 99.72% 1.07199s 9 119.11ms 500ns 1.07164s cudaFree
0.11% 1.2182ms 398 3.0600us 140ns 137.94us cuDeviceGetAttribute
0.06% 674.45us 4 168.61us 165.50us 173.64us cuDeviceTotalMem
0.03% 357.07us 4 89.268us 2.7800us 201.89us cudaMalloc
0.03% 309.29us 1 309.29us 309.29us 309.29us cudaGetDeviceProperties
0.01% 160.47us 332 483ns 350ns 3.3300us cudaFuncSetAttribute
0.01% 115.12us 4 28.780us 26.290us 33.410us cuDeviceGetName
0.00% 28.591us 5 5.7180us 440ns 16.921us cudaGetDevice
0.00% 22.061us 4 5.5150us 871ns 18.690us cudaDeviceSynchronize
0.00% 20.370us 18 1.1310us 410ns 6.9900us cudaEventDestroy
0.00% 16.390us 1 16.390us 16.390us 16.390us cudaMemcpy
0.00% 11.540us 2 5.7700us 1.4900us 10.050us cuDeviceGetPCIBusId
0.00% 10.510us 18 583ns 430ns 1.6200us cudaEventCreateWithFlags
0.00% 7.9100us 21 376ns 290ns 700ns cudaDeviceGetAttribute
0.00% 1.4300us 6 238ns 150ns 590ns cuDeviceGet
0.00% 1.2200us 4 305ns 190ns 500ns cuDeviceGetCount
0.00% 900ns 1 900ns 900ns 900ns cuInit
0.00% 860ns 4 215ns 180ns 260ns cuDeviceGetUuid
0.00% 240ns 1 240ns 240ns 240ns cuDriverGetVersion
0.00% 230ns 1 230ns 230ns 230ns cudaGetDeviceCount
```
Script:
```python
import torch
def solve(x, other, out):
torch.linalg.solve(x, other, out=out)
if __name__ == "__main__":
dense_inp = torch.randn((1000, 1000), dtype=torch.float64)
# Set 50% of the values to 0 randomly
dense_inp = torch.nn.functional.dropout(dense_inp, p=0.5)
sparse_inp = dense_inp.to_sparse_csr()
other = torch.randint(100, (1000,), dtype=torch.float64)
out = torch.randint(1, (1000,), dtype=torch.float64)
solve(sparse_inp, other, out)
```
The following error is raised when the function is used on a CPU device with PyTorch built/installed without CUDA support:
* When built without CUDA support:
```python
/home/krshrimali/pytorch/torch/autograd/profiler.py:151: UserWarning: CUDA is not available, disabling CUDA profiling
warn("CUDA is not available, disabling CUDA profiling")
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/krshrimali/pytorch/test_sp.py", line 17, in <module>
solve(x, other, out)
File "/home/krshrimali/pytorch/test_sp.py", line 5, in solve
torch.linalg.solve(x, other, out=out)
RuntimeError: PyTorch was not built with CUDA support. Please use PyTorch built CUDA support
```
**Performance Comparison** (vs SciPy's [`scipy.sparse.linalg.spsolve`](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.sparse.linalg.spsolve.html):
Time taken by `scipy.sparse.linalg.spsolve` : 0.595 seconds
On CPU: Time taken by `torch.linalg.solve` : 4.565 seconds
On CUDA: Time taken by `torch.linalg.solve`: 1.838 seconds
The inputs are of dimensions: (17281, 17281) and (17281, 1), and were taken from https://math.nist.gov/MatrixMarket/extreme.html.
Thanks to IvanYashchuk for helping me with the PR, and guiding me through it.
cc: IvanYashchuk pearu nikitaved cpuhrsch
cc nikitaved pearu cpuhrsch
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/71399
Reviewed By: VitalyFedyunin
Differential Revision: D33767740
Pulled By: cpuhrsch
fbshipit-source-id: a945f065210cd719096eb8d7cdbf8e8937c2fce9
(cherry picked from commit f4f35c17da414e1ca6c6d91402933521857aa1ea)
PR #72405 added four new types to the public python API:
`torch.ComplexFloatTensor`, `torch.ComplexDoubleTensor`,
`torch.cuda.ComplexFloatTensor` and `torch.cuda.ComplexDoubleTensor`.
I believe this was unintentional and a clarifying comment as to the
purpose of `all_declared_types` is needed to avoid this in future.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/73370
Summary:
This pull request introduces `SoftplusTransform` to `torch.distributions.transforms`. `SoftplusTransform` transforms via the mapping `Softplus(x) = log(1 + exp(x))`. Note that the transform is different to [`torch.nn.Softplus`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Softplus.html#torch.nn.Softplus), as that has additional `beta` and `threshold` parameters. Inverse and `log_abs_det_jacobian` for a more complex `SoftplusTransform` can be added in the future.
vitkl fritzo
Addresses the issue discussed here: [pyro issue 855](https://github.com/pyro-ppl/numpyro/issues/855)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/52300
Reviewed By: albanD, ejguan
Differential Revision: D34082655
Pulled By: neerajprad
fbshipit-source-id: 6114e74ee5d73c1527191bed612a142d691e2094
(cherry picked from commit a181a3a9e53a34214a503d38760ad7778d08a680)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/73361
This PR adds the documentation for the newly introduced `TORCH_CPP_LOG_LEVEL` and how it can be used along with `TORCH_DISTRIBUTED_DEBUG` to adjust the log level of c10d.
ghstack-source-id: 149874995
Test Plan: Locally rendered and checked the documentation.
Reviewed By: rohan-varma
Differential Revision: D34452352
fbshipit-source-id: ecb54590f3030ddef9921a7152ca9f7fc9438345
(cherry picked from commit f4c7c6f3b27dbd3006686cf26a6e9e53cd2c8f09)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/73166
This PR refactors, cleans up, and optimizes the implementation of `TORCH_DISTRIBUTED_DEBUG`. It also introduces three new user APIs: `get_debug_level()`, `set_debug_level()`, and `set_debug_level_from_env()` to retrieve and modify the debug level after a process has started.
ghstack-source-id: 149778566
Test Plan: Run the existing unit tests.
Reviewed By: rohan-varma
Differential Revision: D34371226
fbshipit-source-id: e18443b411adcbaf39b2ec999178c198052fcd5b
(cherry picked from commit 26d6bb1584b83a0490d8b766482656a5887fa21d)
Summary:
Fixespytorch/pytorch.github.io#929
The pytorch doc team would like to move to only major.minor documentation at https://pytorch.org/docs/versions.html, not major.minor.patch. This has been done in the CI scripts, but the generated documentation still has the patch version. Remove it when building RELEASE documentation. This allows simplifying the logic, using `'.'.join(torch_version.split('.')[:2])` since we no longer care about trimming off the HASH: it automatically gets removed.
holly1238, brianjo
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72706
Reviewed By: samdow
Differential Revision: D34215815
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 8437036cc6636674d9ab8b1666f37b561d0527e1
(cherry picked from commit d8caf988f9)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69550
Fix the wiki URL.
Also minor reorganization in onnx.rst.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: msaroufim
Differential Revision: D32994269
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 112acfe8b7c778d7e3c2cef684023fdaf2c6ec9c
(cherry picked from commit f0787fabde)
Summary:
It is probably the most user friendly to link to that (lesser known?) feature.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72584
Reviewed By: soulitzer
Differential Revision: D34173999
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 99fff7a55412faf54888f8317ab2388f4d7d30e4
(cherry picked from commit 2191ee7657)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/68491
* Allows implementing symbolic functions for domains other than `aten`, for example `prim`, in symbolic_opset#.py.
* Allows symbolic function to access extra context if needed, through `SymbolicFunctionState`.
* Particularly, the `prim::PythonOp` special case can access node without the need of passing node through inputs. Updates will be made downstreams, and in a follow-up PR we will remove the previous workaround in exporter.
* `prim::Loop`, `prim::If`, etc are now moved outside of `_run_symbolic_function` from utils.py, and to symbolic_opset9.py.
Motivation for this change:
- Better maintainability and reducing complexity. Easier to add symbolic for operators, both simple and complex ones (that need additional context), without the former needing to know the existence of the latter.
- The design idea was long outdated. prim ops are no longer rare special cases, and they shouldn't all be handled inside `_run_symbolic_function`. As a result this function becomes too clumsy. There were also prim ops symbolic added in symbolic_opset#.py with signature `prim_[opname]`, creating separation and confusion.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: jansel
Differential Revision: D32483782
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: f9affc31b1570af30ffa6668da9375da111fd54a
Co-authored-by: BowenBao <bowbao@microsoft.com>
(cherry picked from commit 1e04ffd2fd)
Summary:
This PR adds a transform that uses the cumulative distribution function of a given probability distribution.
For example, the following code constructs a simple Gaussian copula.
```python
# Construct a Gaussian copula from a multivariate normal.
base_dist = MultivariateNormal(
loc=torch.zeros(2),
scale_tril=LKJCholesky(2).sample(),
)
transform = CumulativeDistributionTransform(Normal(0, 1))
copula = TransformedDistribution(base_dist, [transform])
```
The following snippet creates a "wrapped" Gaussian copula for correlated positive variables with Weibull marginals.
```python
transforms = [
CumulativeDistributionTransform(Normal(0, 1)),
CumulativeDistributionTransform(Weibull(4, 2)).inv,
]
wrapped_copula = TransformedDistribution(base_dist, transforms)
```
cc fritzo
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72495
Reviewed By: ejguan
Differential Revision: D34085919
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 7917391519a96b0d9b54c52db65d1932f961d070
(cherry picked from commit 572196146e)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72499
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/benchmark/pull/740
To fx2trt out of tree to remove bloatness of PyTorch core.
It's the first and major step. Next, we will move acc_tracer out of the tree and rearrange some fx passes.
Reviewed By: suo
Differential Revision: D34065866
fbshipit-source-id: c72b7ad752d0706abd9a63caeef48430e85ec56d
(cherry picked from commit 91647adbca)
Summary:
Correcting a minor typo: "Users should pay" instead of "Users should be pay"
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72500
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D34077972
Pulled By: ejguan
fbshipit-source-id: 5d7a138d1f17eca838d2c1da76d7759d96e4375f
(cherry picked from commit d046baa89c)
Summary:
This PR ports `index_copy` implementation to structured kernels, also adds an `out` variant.
~Note to the reviewers: This is in draft mode, waiting for the tests from the CI, and I'll give a final look before requesting the review.~
Issue tracker: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/55070
cc: bdhirsh ysiraichi
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/67329
Reviewed By: ejguan
Differential Revision: D34077219
Pulled By: bdhirsh
fbshipit-source-id: 6accda33957f654b753261c5c3d765a27a64d2c0
(cherry picked from commit f3ac83217a)
Summary:
Let's make the documentation for `torch.sparse.sampled_addmm` searchable in the PyTorch documentation.
This PR shall be cherry-picked for the next 1.11 release.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72312
Reviewed By: davidberard98
Differential Revision: D34045230
Pulled By: cpuhrsch
fbshipit-source-id: c1b1dc907443284857f48c8ce1efab22c6701bbe
(cherry picked from commit 225929ecf2)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72084
make fsdp folder to be public
ghstack-source-id: 148173447
Test Plan: unit tests
Reviewed By: mrshenli
Differential Revision: D33903417
fbshipit-source-id: 7852a2adc4af09af48a5ffa52ebf210489f834d5
(cherry picked from commit bd06513cfe)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72111
For vectorize flag:
- Advertises the use of functorch
For autograd.functional.jvp:
- Advertises the use of functorch and the low-level jvp API, both of
which will be more performant than the double backprop trick.
Test Plan: - view docs
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D33918065
Pulled By: zou3519
fbshipit-source-id: 6e19699aa94f0e023ccda0dc40551ad6d932b7c7
(cherry picked from commit b4662ceb99)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72009
This simplifies the Stats interface by merging IntervalStat and FixedCountStat into a single Stat w/ a specific window size duration and an optional max samples per window. This allows for the original intention of having comparably sized windows (for statistical purposes) while also having a consistent output bandwidth.
Test Plan:
```
buck test //caffe2/test:monitor //caffe2/test/cpp/monitor:monitor
```
Reviewed By: kiukchung
Differential Revision: D33822956
fbshipit-source-id: a74782492421be613a1a8b14341b6fb2e8eeb8b4
(cherry picked from commit 293b94e0b4)
Summary:
Follow up: we would need to update the links to the tutorial later
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/71643
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D33713982
Pulled By: soulitzer
fbshipit-source-id: a314ffa4e7d5c5ebdef9c50033f338b06578d71c
(cherry picked from commit ba30daaaa5)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/66745
This PR implement NCCL gather and add gather to ProcessGroupNCCL using nccl send/recv api.
NCCL doesn’t directly provide primitives for gather, so we need to be implemented on top of NCCL’s send/recv API.
1. In ProcessGroupNCCL.cpp, the outputTensors are first flattened, then inputTensors and outputFlattened are passed by the collective class to gather() function in nccl.cpp.
1. In nccl.cpp, gather is implemented using ncclSend/ncclRecv: all the ranks send inputTensor to the root rank, and the root rank uses a for loop to receive these inputTensors.
ghstack-source-id: 147754838
Test Plan:
test_gather_ops
test_gather_checks
test_gather_stress
Reviewed By: pritamdamania87
Differential Revision: D29616361
fbshipit-source-id: b500d9b8e67113194c5cc6575fb0e5d806dc7782
(cherry picked from commit d560ee732e)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/71658
This adds the beginnings of a TensorboardEventHandler which will log stats to Tensorboard.
Test Plan: buck test //caffe2/test:monitor
Reviewed By: edward-io
Differential Revision: D33719954
fbshipit-source-id: e9847c1319255ce0d9cf2d85d8b54b7a3c681bd2
(cherry picked from commit 5c8520a6ba)
Fix the wiki URL.
Also minor reorganization in onnx.rst.
[ONNX] restore documentation of public functions (#69623)
The build-docs check requires all public functions to be documented.
These should really not be public, but we'll fix that later.'
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/71609
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69567
This exposes torch.monitor events and stats via pybind11 to the underlying C++ implementation.
* The registration interface is a tad different since it takes a lambda function in Python where as in C++ it's a full class.
* This has a small amount of changes to the counter interfaces since there's no way to create an initializer list at runtime so they now also take a vector.
* Only double based stats are provided in Python since it's intended more for high level stats where float imprecision shouldn't be an issue. This can be changed down the line if need arises.
```
events = []
def handler(event):
events.append(event)
handle = register_event_handler(handler)
log_event(Event(type="torch.monitor.TestEvent", timestamp=datetime.now(), metadata={"foo": 1.0}))
```
D32969391 is now included in this diff.
This cleans up the naming for events. type is now name, message is gone, and metadata is renamed data.
Test Plan: buck test //caffe2/test:monitor //caffe2/test/cpp/monitor:monitor
Reviewed By: kiukchung
Differential Revision: D32924141
fbshipit-source-id: 563304c2e3261a4754e40cca39fc64c5a04b43e8
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/66933
This PR exposes `torch.lu` as `torch.linalg.lu_factor` and
`torch.linalg.lu_factor_ex`.
This PR also adds support for matrices with zero elements both in
the size of the matrix and the batch. Note that this function simply
returns empty tensors of the correct size in this case.
We add a test and an OpInfo for the new function.
This PR also adds documentation for this new function in line of
the documentation in the rest of `torch.linalg`.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/56590
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/64014
cc jianyuh nikitaved pearu mruberry walterddr IvanYashchuk xwang233 Lezcano
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: gchanan
Differential Revision: D32834069
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 51ef12535fa91d292f419acf83b800b86ee9c7eb
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/70185
The extraheader block in docs/source/_templates/layout.html overrides the one from the pytorch theme. The theme block adds Google Analytics, so they were missing from the `master` documentation. This came up in PR pytorch/pytorch.github.io#899.
brianjo
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/70187
Reviewed By: bdhirsh
Differential Revision: D33248466
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: b314916a3f0789b6617cf9ba6bd938bf5ca27242
Summary:
Refactor torch.profiler.profile by separate it into one low level class and one high level wrapper.
The PR include the following change:
1. separate class torch.profiler.profile into two separated class: kineto_profiler and torch.profiler.profile.
2. The former class has the low-level functionality exposed in C++ level like: prepare_profiler, start_profiler, stop_profiler.
3. The original logics in torch.profiler.profile including export_chrome_trace, export_stacks, key_averages, events, add_metadata are all moved into kineto_profiler since they are all exposed by the torch.autograd.profiler.
4. The new torch.profiler.profile is fully back-compatible with original class since it inherit from torch.profiler.kineto_profiler. Its only responsibility in new implementation is the maintenance of the finite state machine of ProfilerAction.
With the refactoring, the responsibility boundary is clear and the new logic is simple to understand.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63302
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D33006442
Pulled By: robieta
fbshipit-source-id: 30d7c9f5c101638703f1243fb2fcc6ced47fb690
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/65993
This PR attempts to port `index_add` to structured kernels, but does more than that:
* Adds an `out=` variant to `index_add`
* Revises `native_functions.yaml` registrations, to not have multiple entries and instead pass default value to `alpha`.
* Changes in `derivatives.yaml` file for autograd functioning
* Revises error messages, please see: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/65993#issuecomment-945441615
Follow-up PRs in near future will attempt to refactor the OpInfo test, and will give another look at tests in `test/test_torch.py` for this function. (hence the use of ghstack for this)
~This is WIP because there are tests failing for `Dimname` variant on mobile/android builds, and I'm working on fixing them.~
Issue tracker: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/55070
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: ejguan
Differential Revision: D32646426
fbshipit-source-id: b035ecf843a9a27d4d1e18b202b035adc2a49ab5
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69789
Add details on how to save and load quantized models without hitting errors
Test Plan:
CI autogenerated docs
Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: jerryzh168
Differential Revision: D33030991
fbshipit-source-id: 8ec4610ae6d5bcbdd3c5e3bb725f2b06af960d52
Summary:
Also fixes the documentation failing to appear and adds a test to validate that op works with multiple devices properly.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69640
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D32965391
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 4fe502809b353464da8edf62d92ca9863804f08e
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69104
Add nvidia-smi memory and utilization as native Python API
Test Plan:
testing the function returns the appropriate value.
Unit tests to come.
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D32711562
fbshipit-source-id: 01e676203299f8fde4f3ed4065f68b497e62a789
Summary:
Per title.
This PR introduces a global flag that lets pytorch prefer one of the many backend implementations while calling linear algebra functions on GPU.
Usage:
```python
torch.backends.cuda.preferred_linalg_library('cusolver')
```
Available options (str): `'default'`, `'cusolver'`, `'magma'`.
Issue https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/63992 inspired me to write this PR. No heuristic is perfect on all devices, library versions, matrix shapes, workloads, etc. We can obtain better performance if we can conveniently switch linear algebra backends at runtime.
Performance of linear algebra operators after this PR should be no worse than before. The flag is set to **`'default'`** by default, which makes everything the same as before this PR.
The implementation of this PR is basically following that of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/67790.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/67980
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D32849457
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 679fee7744a03af057995aef06316306073010a6
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69251
This adds some actual documentation for deploy, which is probably useful
since we told everyone it was experimentally available so they will
probably be looking at what the heck it is.
It also wires up various compoenents of the OSS build to actually work
when used from an external project.
Differential Revision:
D32783312
D32783312
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: wconstab
Pulled By: suo
fbshipit-source-id: c5c0a1e3f80fa273b5a70c13ba81733cb8d2c8f8
Summary:
These APIs are not yet officially released and are still under discussion. Hence, this commit removes those APIs from docs and will add them back when ready.
cc pietern mrshenli pritamdamania87 zhaojuanmao satgera rohan-varma gqchen aazzolini osalpekar jiayisuse SciPioneer H-Huang
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69011
Reviewed By: fduwjj
Differential Revision: D32703124
Pulled By: mrshenli
fbshipit-source-id: ea049fc7ab6b0015d38cc40c5b5daf47803b7ea0
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/66933
This PR exposes `torch.lu` as `torch.linalg.lu_factor` and
`torch.linalg.lu_factor_ex`.
This PR also adds support for matrices with zero elements both in
the size of the matrix and the batch. Note that this function simply
returns empty tensors of the correct size in this case.
We add a test and an OpInfo for the new function.
This PR also adds documentation for this new function in line of
the documentation in the rest of `torch.linalg`.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/56590
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/64014
cc jianyuh nikitaved pearu mruberry walterddr IvanYashchuk xwang233 Lezcano
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D32521980
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 26a49ebd87f8a41472f8cd4e9de4ddfb7f5581fb