mirror of
https://github.com/zebrajr/pytorch.git
synced 2025-12-07 00:21:07 +01:00
Summary: Rewritten version of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/17771 using graph C++ APIs. This PR adds the ability to do constant folding on ONNX graphs during PT->ONNX export. This is done mainly to optimize the graph and make it leaner. The two attached snapshots show a multiple-node LSTM model before and after constant folding. A couple of notes: 1. Constant folding is by default turned off for now. The goal is to turn it on by default once we have validated it through all the tests. 2. Support for folding in nested blocks is not in place, but will be added in the future, if needed. **Original Model:** 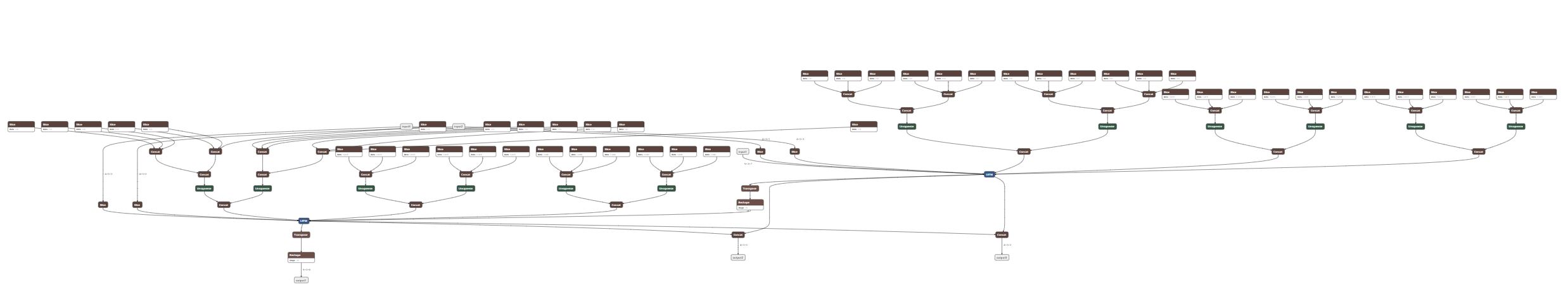 **Constant-folded model:** 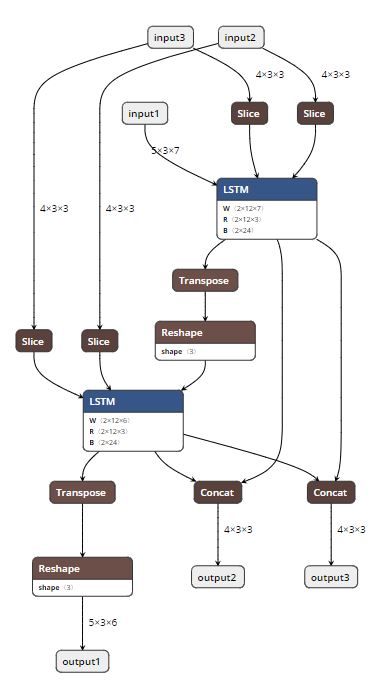 Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/18698 Differential Revision: D14889768 Pulled By: houseroad fbshipit-source-id: b6616b1011de9668f7c4317c880cb8ad4c7b631a
458 lines
19 KiB
Python
458 lines
19 KiB
Python
import torch
|
|
import torch.jit
|
|
import torch.onnx
|
|
|
|
import onnx
|
|
import onnx.helper
|
|
|
|
import numpy as np
|
|
|
|
import difflib
|
|
import contextlib
|
|
import io
|
|
|
|
|
|
def colonize(msg, sep=": "):
|
|
if not msg:
|
|
return ""
|
|
else:
|
|
return msg + sep
|
|
|
|
|
|
class Errors(object):
|
|
"""
|
|
An error-collecting object which supports error recovery.
|
|
|
|
It is intended to be used like a context manager:
|
|
|
|
>>> with Errors("Top-level error message") as errs:
|
|
>>> ...
|
|
"""
|
|
|
|
def __init__(self, msg, rtol=1e-3, atol=1e-5):
|
|
self.msg = msg
|
|
self.errors = []
|
|
self.context = []
|
|
self.rtol = rtol
|
|
self.atol = atol
|
|
|
|
# Allocated upon instance creation so that multiple Errors
|
|
# can be used
|
|
class ShortCircuit(Exception):
|
|
pass
|
|
self.exc_class = ShortCircuit
|
|
|
|
def requireAlmostEqual(self, x, y, msg=None):
|
|
"""
|
|
Test that x and y are nearly equal (equal within self.rtol
|
|
precision); aborts execution if they are not.
|
|
"""
|
|
self.almostEqualAndThen(x, y, msg, self.failWith)
|
|
|
|
def checkAlmostEqual(self, x, y, msg=None):
|
|
"""
|
|
Test that x and y are nearly equal (equal within self.rtol
|
|
precision), but continue execution even if they are not equal.
|
|
|
|
To prevent error cascades, you should remember to call 'failIfErrs'
|
|
at some later point in time.
|
|
"""
|
|
self.almostEqualAndThen(x, y, msg, self.addErr)
|
|
|
|
def almostEqualAndThen(self, x, y, msg, k):
|
|
"""
|
|
Helper for implementing 'requireAlmostEqual' and 'checkAlmostEqual'.
|
|
Upon failure, invokes continuation 'k' with the error message.
|
|
|
|
At the moment, only tests on 'numpy.ndarray' are supported.
|
|
"""
|
|
if isinstance(x, np.ndarray) and isinstance(y, np.ndarray):
|
|
try:
|
|
np.testing.assert_allclose(x, y, rtol=self.rtol, atol=self.atol,
|
|
equal_nan=True, verbose=True)
|
|
except AssertionError as e:
|
|
raise
|
|
k("{}{}".format(colonize(msg), str(e).lstrip()))
|
|
else:
|
|
raise RuntimeError("Unsupported almost equal test")
|
|
|
|
def requireEqual(self, x, y, msg=None):
|
|
"""
|
|
Test that x and y are equal; aborts execution if they are not.
|
|
"""
|
|
self.equalAndThen(x, y, msg, self.failWith)
|
|
|
|
def checkEqual(self, x, y, msg=None):
|
|
"""
|
|
Test that x and y are equal, but continue execution even if they are not equal.
|
|
|
|
To prevent error cascades, you should remember to call 'failIfErrs'
|
|
at some later point in time.
|
|
"""
|
|
self.equalAndThen(x, y, msg, self.addErr)
|
|
|
|
# Bit-for-bit accuracy test
|
|
def equalAndThen(self, x, y, msg, k):
|
|
"""
|
|
Helper for implementing 'requireEqual' and 'checkEqual'. Upon failure,
|
|
invokes continuation 'k' with the error message.
|
|
"""
|
|
if isinstance(x, onnx.TensorProto) and isinstance(y, onnx.TensorProto):
|
|
self.equalAndThen(x.name, y.name, msg, k)
|
|
# Use numpy for the comparison
|
|
t1 = onnx.numpy_helper.to_array(x)
|
|
t2 = onnx.numpy_helper.to_array(y)
|
|
new_msg = "{}In embedded parameter '{}'".format(colonize(msg), x.name)
|
|
self.equalAndThen(t1, t2, new_msg, k)
|
|
elif isinstance(x, np.ndarray) and isinstance(y, np.ndarray):
|
|
try:
|
|
np.testing.assert_equal(x, y)
|
|
except AssertionError as e:
|
|
raise
|
|
k("{}{}".format(colonize(msg, ": "), str(e).lstrip()))
|
|
else:
|
|
if x != y:
|
|
# TODO: Better algorithm for lists
|
|
sx = str(x)
|
|
sy = str(y)
|
|
if len(sx) > 40 or len(sy) > 40 or '\n' in sx or '\n' in sy:
|
|
# long form
|
|
l = "=" * 50
|
|
k("\n{}The value\n{}\n{}\n{}\n\ndoes not equal\n\n{}\n{}\n{}"
|
|
.format(colonize(msg, ":\n"), l, sx, l, l, sy, l))
|
|
else:
|
|
k("{}{} != {}".format(colonize(msg), sx, sy))
|
|
|
|
def requireMultiLineEqual(self, x, y, msg=None):
|
|
"""
|
|
Test that long, multi-line strings x and y are equal;
|
|
aborts execution if they are not.
|
|
"""
|
|
self.multiLineEqualAndThen(x, y, msg, self.failWith)
|
|
|
|
def multiLineEqualAndThen(self, x, y, msg, k):
|
|
"""
|
|
Helper for implementing 'requireMultiLineEqual'. Upon failure,
|
|
invokes continuation 'k' with the error message.
|
|
"""
|
|
if msg is None:
|
|
msg = "Strings are not equal"
|
|
if x != y:
|
|
diff = difflib.ndiff(x.splitlines(True), y.splitlines(True))
|
|
k("{}{}".format(colonize(msg, ":\n\n"), "".join(diff)))
|
|
|
|
def addErr(self, msg):
|
|
"""
|
|
Add an error to the error context, but continue executing.
|
|
"""
|
|
# TODO: instead of immediately concatenating the context in the msg,
|
|
# attach it as metadata and make a decision how to format it later.
|
|
msg_w_ctx = msg
|
|
for c in reversed(self.context):
|
|
msg += "\n\n * " + "\n ".join(c.splitlines())
|
|
self.errors.append(msg)
|
|
|
|
def fail(self):
|
|
"""
|
|
Immediately fail and short-circuit to the next recovery context.
|
|
|
|
NB: It is an error to 'fail' without having added any errors to
|
|
the error context.
|
|
"""
|
|
raise self.exc_class()
|
|
|
|
def failWith(self, msg):
|
|
"""
|
|
Add an error to the error context, and then short-circuit.
|
|
"""
|
|
self.addErr(msg)
|
|
self.fail()
|
|
|
|
def failIfErrs(self):
|
|
"""
|
|
If there are any errors in the error context, short-circuit.
|
|
|
|
This is used to prevent error cascades.
|
|
"""
|
|
if self.errors:
|
|
self.fail()
|
|
|
|
def recover(self):
|
|
"""
|
|
Returns a context manager which can be used to recover in case of
|
|
an error. Example usage:
|
|
|
|
>>> with errs.recover():
|
|
>>> ...
|
|
"""
|
|
parent_self = self
|
|
|
|
class Recover(object):
|
|
def __enter__(self):
|
|
pass
|
|
|
|
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback):
|
|
if exc_type == parent_self.exc_class:
|
|
return True
|
|
return Recover()
|
|
|
|
def addErrCtxt(self, msg):
|
|
"""
|
|
Returns a context manager which encloses a fragment of code with
|
|
an extra contextual message, e.g., where an error occurred, or a hint
|
|
applicable to all errors in the area. Example usage:
|
|
|
|
>>> with errs.addErrCtx("Some text"):
|
|
>>> ...
|
|
"""
|
|
parent_self = self
|
|
|
|
class AddContext(object):
|
|
def __enter__(self):
|
|
parent_self.context.append(msg)
|
|
|
|
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback):
|
|
parent_self.context.pop()
|
|
return AddContext()
|
|
|
|
def __enter__(self):
|
|
return self
|
|
|
|
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback):
|
|
if self.errors:
|
|
errors_msg = "\n\n".join(map(lambda x: "ERROR: " + x, self.errors))
|
|
final_msg = "{}\n{}\n{}".format(self.msg, '-' * 70, errors_msg)
|
|
raise AssertionError(final_msg)
|
|
if exc_type == self.exc_class:
|
|
raise RuntimeError("ShortCircuit was raised, but no errors were recorded")
|
|
|
|
|
|
@contextlib.contextmanager
|
|
def set_training(model, mode):
|
|
"""
|
|
A context manager to temporarily set the training mode of 'model'
|
|
to 'mode', resetting it when we exit the with-block.
|
|
"""
|
|
old_mode = model.training
|
|
if old_mode != mode:
|
|
model.train(mode)
|
|
try:
|
|
yield
|
|
finally:
|
|
if old_mode != mode:
|
|
model.train(old_mode)
|
|
|
|
|
|
def verify(model, args, backend, verbose=False, training=False, rtol=1e-3, atol=1e-7,
|
|
test_args=2, do_constant_folding=False):
|
|
"""
|
|
Export a model into ONNX, import it into a specified ONNX backend, and then
|
|
on a few random inputs verify that PyTorch and the backend produced the same
|
|
results. Requires onnx to be installed.
|
|
|
|
This function may spuriously fail: some operators are implemented with
|
|
different numerical precision in an ONNX backend, in which case an unstable
|
|
network (e.g., Inception) may blow up these numerical instabilities. This
|
|
situation is less likely to happen if your model has been trained. However,
|
|
if this is not the case, you may have found a bug! Please report it to the
|
|
PyTorch developers. You can also debug the issue yourself by removing
|
|
suffixes of operators from your model until verification passes.
|
|
|
|
For reproducibility, we recommend explicitly setting PyTorch's seed before
|
|
invoking this function.
|
|
|
|
Arguments:
|
|
model (torch.nn.Module): the model to be exported and verified
|
|
args (tuple of arguments): the inputs to
|
|
the model, e.g., such that ``model(*args)`` is a valid
|
|
invocation of the model. Any non-Variable arguments will
|
|
be hard-coded into the exported model; any Variable arguments
|
|
will become inputs of the exported model, in the order they
|
|
occur in args. If args is a Variable, this is equivalent
|
|
to having called it with a 1-ary tuple of that Variable.
|
|
(Note: passing keyword arguments to the model is not currently
|
|
supported. Give us a shout if you need it.)
|
|
backend (onnx.backend module): ONNX backend to verify with
|
|
verbose (bool, default False): if specified, we will print out a debug
|
|
description of the trace being exported.
|
|
training (bool, default False): export the model in training mode. At
|
|
the moment, ONNX is oriented towards exporting models for inference
|
|
only, so you will generally not need to set this to True.
|
|
rtol (float, default 1e-3): relative precision required
|
|
test_args (int or iterable of args, default 2):
|
|
either an integer specifying the number
|
|
of random arguments to generate, or an iterable producing arguments
|
|
to test under.
|
|
"""
|
|
def _nested_map(condition, fn, condition_msg=None):
|
|
def _map(obj):
|
|
if condition(obj):
|
|
return fn(obj)
|
|
elif obj is None:
|
|
return None
|
|
elif isinstance(obj, (list, tuple)):
|
|
return type(obj)(_map(x) for x in obj)
|
|
else:
|
|
raise ValueError("Auto nesting doesn't know how to process "
|
|
"an input object of type " + torch.typename(obj) +
|
|
(". Accepted types: " + condition_msg +
|
|
", or lists/tuples of them"
|
|
if condition_msg else ""))
|
|
|
|
return _map
|
|
|
|
def _iter_filter(condition, allow_unknown=False, condition_msg=None):
|
|
def _iter(obj):
|
|
if condition(obj):
|
|
yield obj
|
|
elif obj is None:
|
|
return
|
|
elif isinstance(obj, (list, tuple)):
|
|
for o in obj:
|
|
for var in _iter(o):
|
|
yield var
|
|
elif allow_unknown:
|
|
yield obj
|
|
else:
|
|
raise ValueError("Auto nesting doesn't know how to process "
|
|
"an input object of type " + torch.typename(obj) +
|
|
(". Accepted types: " + condition_msg +
|
|
", or lists/tuples of them"
|
|
if condition_msg else ""))
|
|
|
|
return _iter
|
|
|
|
def is_tensor(o):
|
|
return isinstance(o, torch.Tensor)
|
|
|
|
_iter_tensors = _iter_filter(is_tensor, condition_msg="Tensors")
|
|
|
|
def randomize_arg(arg):
|
|
new_data = arg.data.clone()
|
|
# For now, don't try randomizing non-float tensors; these
|
|
# are likely to be things like indices, where just randomly
|
|
# spattering some longs is unlikely to work. One way we could
|
|
# make this work is to apply a random permutation or something.
|
|
if arg.is_floating_point():
|
|
new_data.uniform_()
|
|
return torch.autograd.Variable(new_data, requires_grad=arg.requires_grad)
|
|
|
|
randomize_args = _nested_map(is_tensor, randomize_arg)
|
|
|
|
def backend_args(args):
|
|
# TODO: onnx should accept iterables
|
|
return tuple(v.data.cpu().numpy() for v in _iter_tensors(args))
|
|
|
|
def load_bytes(b):
|
|
b.seek(0)
|
|
x = onnx.load(b)
|
|
# doc_string has stack traces - let's remove them to make comparison
|
|
# sane
|
|
onnx.helper.strip_doc_string(x)
|
|
return x
|
|
|
|
# Special case for common case of passing a single Tensor
|
|
if isinstance(args, torch.Tensor):
|
|
args = (args,)
|
|
|
|
with set_training(model, training):
|
|
proto_bytes = io.BytesIO()
|
|
torch_out = torch.onnx._export(model, args, proto_bytes, verbose=verbose,
|
|
do_constant_folding=do_constant_folding)
|
|
proto = load_bytes(proto_bytes)
|
|
prepared = backend.prepare(proto)
|
|
|
|
def run(args):
|
|
alt_proto_bytes = io.BytesIO()
|
|
torch_out = torch.onnx._export(model, args, alt_proto_bytes, verbose=verbose,
|
|
do_constant_folding=do_constant_folding)
|
|
alt_proto = load_bytes(alt_proto_bytes)
|
|
if proto.SerializeToString() != alt_proto.SerializeToString():
|
|
# OK, let's try to figure out what happened.
|
|
msg = "When I exported your model with different inputs, the result was different."
|
|
if not verbose:
|
|
msg += "\n(To get more information, run torch.onnx.verify(..., verbose=True))"
|
|
with Errors(msg, rtol=rtol, atol=atol) as errs:
|
|
# First, check if we have the same number of parameters, and
|
|
# that they're the same order. If they don't, something has *really* gone wrong.
|
|
initializer_order_hint = ("This is really strange! The second time I exported your model,\n"
|
|
"it had a different set of parameters. Are you assigning Parameters\n"
|
|
"in the forward() of your model definition?")
|
|
with errs.addErrCtxt(initializer_order_hint):
|
|
errs.requireEqual(list(map(lambda x: x.name, proto.graph.initializer)),
|
|
list(map(lambda x: x.name, alt_proto.graph.initializer)),
|
|
msg="Parameters list differs")
|
|
|
|
# Now check if the embedded parameters are actually the same
|
|
initializer_hint = ("A difference in embedded parameters usually means that\n"
|
|
"your model is updating parameters/buffers even in inference\n"
|
|
"mode. Look for a buggy nn.Module which isn't respecting train().\n")
|
|
with errs.recover(), errs.addErrCtxt(initializer_hint):
|
|
for x, y in zip(proto.graph.initializer, alt_proto.graph.initializer):
|
|
errs.checkEqual(x, y)
|
|
|
|
# Next, check if the model structure lines up.
|
|
structure_hint = ("A difference in model structure usually means that\n"
|
|
"your model has dynamic control flow. These models are not\n"
|
|
"currently supported by the exporter.")
|
|
with errs.recover(), errs.addErrCtxt(structure_hint):
|
|
# Delete initializers since we already tested them
|
|
stripped_proto = onnx.ModelProto()
|
|
stripped_proto.CopyFrom(proto)
|
|
del stripped_proto.graph.initializer[:]
|
|
|
|
stripped_alt_proto = onnx.ModelProto()
|
|
stripped_alt_proto.CopyFrom(alt_proto)
|
|
del stripped_alt_proto.graph.initializer[:]
|
|
|
|
# Compare the printable graph representations first
|
|
errs.requireMultiLineEqual(onnx.helper.printable_graph(stripped_proto.graph),
|
|
onnx.helper.printable_graph(stripped_alt_proto.graph))
|
|
|
|
# Compare the actual protobuf text formats now (not
|
|
# very user-friendly!)
|
|
errs.requireMultiLineEqual(str(stripped_proto), str(stripped_alt_proto))
|
|
|
|
# One last ditch effort, using built-in equality on
|
|
# protobufs
|
|
errs.requireEqual(stripped_proto, stripped_alt_proto)
|
|
|
|
errs.failIfErrs()
|
|
|
|
# At this point, we should have figured out why the binary
|
|
# protobufs differed, and short-circuited out of this code
|
|
# with a helpful error message. But what if we didn't?
|
|
# We better still try to give a good error message in this
|
|
# case. We EXPECT these requires to fail. If they don't,
|
|
# that is a bug in verify
|
|
errs.requireEqual(proto, alt_proto)
|
|
errs.requireEqual(proto_bytes.getvalue(), alt_proto_bytes.getvalue())
|
|
assert False
|
|
|
|
# TODO: test that the traced model also returns the same thing...
|
|
run_helper(torch_out, args)
|
|
|
|
# Factored out so we can avoid one run of the model
|
|
def run_helper(torch_out, args):
|
|
backend_out = prepared.run(backend_args(args))
|
|
if isinstance(torch_out, torch.Tensor):
|
|
torch_out = (torch_out,)
|
|
torch_out, _ = torch._C._jit_flatten(torch_out)
|
|
# NB: onnx backend NEVER returns bare numpy array
|
|
msg = "ONNX backend returned different results from PyTorch"
|
|
result_hint = ("If you are not using trained parameters, a difference in results\n"
|
|
"could mean that your network is numerically unstable. Otherwise\n"
|
|
"it indicates a bug in PyTorch/ONNX; please file a bug report.")
|
|
with Errors(msg, rtol=rtol, atol=atol) as errs, errs.addErrCtxt(result_hint):
|
|
for i, (x, y) in enumerate(zip(torch_out, backend_out)):
|
|
errs.checkAlmostEqual(x.data.cpu().numpy(), y, "In output {}".format(i))
|
|
|
|
run_helper(torch_out, args)
|
|
|
|
if isinstance(test_args, int):
|
|
for i in range(test_args):
|
|
run(randomize_args(args))
|
|
else:
|
|
for test_arg in test_args:
|
|
run(test_arg)
|