Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63568
This PR adds the first solver with structure to `linalg`. This solver
has an API compatible with that of `linalg.solve` preparing these for a
possible future merge of the APIs. The new API:
- Just returns the solution, rather than the solution and a copy of `A`
- Removes the confusing `transpose` argument and replaces it by a
correct handling of conj and strides within the call
- Adds a `left=True` kwarg. This can be achieved via transposes of the
inputs and the result, but it's exposed for convenience.
This PR also implements a dataflow that minimises the number of copies
needed before calling LAPACK / MAGMA / cuBLAS and takes advantage of the
conjugate and neg bits.
This algorithm is implemented for `solve_triangular` (which, for this, is
the most complex of all the solvers due to the `upper` parameters).
Once more solvers are added, we will factor out this calling algorithm,
so that all of them can take advantage of it.
Given the complexity of this algorithm, we implement some thorough
testing. We also added tests for all the backends, which was not done
before.
We also add forward AD support for `linalg.solve_triangular` and improve the
docs of `linalg.solve_triangular`. We also fix a few issues with those of
`torch.triangular_solve`.
Resolves https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/54258
Resolves https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/56327
Resolves https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/45734
cc jianyuh nikitaved pearu mruberry walterddr IvanYashchuk xwang233 Lezcano
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: zou3519, JacobSzwejbka
Differential Revision: D32283178
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: deb672e6e52f58b76536ab4158073927a35e43a8
Summary:
### Create `linalg.cross`
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/62810
As discussed in the corresponding issue, this PR adds `cross` to the `linalg` namespace (**Note**: There is no method variant) which is slightly different in behaviour compared to `torch.cross`.
**Note**: this is NOT an alias as suggested in mruberry's [https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/62810 comment](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/62810#issuecomment-897504372) below
> linalg.cross being consistent with the Python Array API (over NumPy) makes sense because NumPy has no linalg.cross. I also think we can implement linalg.cross without immediately deprecating torch.cross, although we should definitely refer users to linalg.cross. Deprecating torch.cross will require additional review. While it's not used often it is used, and it's unclear if users are relying on its unique behavior or not.
The current default implementation of `torch.cross` is extremely weird and confusing. This has also been reported multiple times previously. (See https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/17229, https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/39310, https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/41850, https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/50273)
- [x] Add `torch.linalg.cross` with default `dim=-1`
- [x] Add OpInfo and other tests for `torch.linalg.cross`
- [x] Add broadcasting support to `torch.cross` and `torch.linalg.cross`
- [x] Remove out skip from `torch.cross` OpInfo
- [x] Add docs for `torch.linalg.cross`. Improve docs for `torch.cross` mentioning `linalg.cross` and the difference between the two. Also adds a warning to `torch.cross`, that it may change in the future (we might want to deprecate it later)
---
### Additional Fixes to `torch.cross`
- [x] Fix Doc for Tensor.cross
- [x] Fix torch.cross in `torch/overridres.py`
While working on `linalg.cross` I noticed these small issues with `torch.cross` itself.
[Tensor.cross docs](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Tensor.cross.html) still mentions `dim=-1` default which is actually wrong. It should be `dim=None` after the behaviour was updated in PR https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/17582 but the documentation for the `method` or `function` variant wasn’t updated. Later PR https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/41850 updated the documentation for the `function` variant i.e `torch.cross` and also added the following warning about the weird behaviour.
> If `dim` is not given, it defaults to the first dimension found with the size 3. Note that this might be unexpected.
But still, the `Tensor.cross` docs were missed and remained outdated. I’m finally fixing that here. Also fixing `torch/overrides.py` for `torch.cross` as well now, with `dim=None`.
To verify according to the docs the default behaviour of `dim=-1` should raise, you can try the following.
```python
a = torch.randn(3, 4)
b = torch.randn(3, 4)
b.cross(a) # this works because the implementation finds 3 in the first dimension and the default behaviour as shown in documentation is actually not true.
>>> tensor([[ 0.7171, -1.1059, 0.4162, 1.3026],
[ 0.4320, -2.1591, -1.1423, 1.2314],
[-0.6034, -1.6592, -0.8016, 1.6467]])
b.cross(a, dim=-1) # this raises as expected since the last dimension doesn't have a 3
>>> RuntimeError: dimension -1 does not have size 3
```
Please take a closer look (particularly the autograd part, this is the first time I'm dealing with `derivatives.yaml`). If there is something missing, wrong or needs more explanation, please let me know. Looking forward to the feedback.
cc mruberry Lezcano IvanYashchuk rgommers
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63285
Reviewed By: gchanan
Differential Revision: D32313346
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: e68c2687c57367274e8ddb7ef28ee92dcd4c9f2c
Summary:
Adds `torch.argwhere` as an alias to `torch.nonzero`
Currently, `torch.nonzero` is actually provides equivalent functionality to `np.argwhere`.
From NumPy docs,
> np.argwhere(a) is almost the same as np.transpose(np.nonzero(a)), but produces a result of the correct shape for a 0D array.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/64257
Reviewed By: qihqi
Differential Revision: D32049884
Pulled By: saketh-are
fbshipit-source-id: 016e49884698daa53b83e384435c3f8f6b5bf6bb
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/64430
The functionalization pass needs `{view}_scatter` versions of the slice/select/diagonal ops in order to correctly propagate mutations from a view to its base. On top of that, the implementations need to be primitive w.r.t. autograd, because they look something like `...slice().copy_()`, and the functionalization pass can't use views + mutations inside of it's own alias-removal machinery!
I added some basic tests that I tried to base off of existing tests for views (particularly around testing the derivative formulas), but I'm wondering if I should add something more comprehensive.
Also, as_strided fits into this category - the functionalization pass will need an `as_strided_scatter` op that's primitive w.r.t. autograd. I didn't add it for now, because it'll involve duplicating a bunch of logic from the current `as_strided_backward()` function, and also writing a derivative formula that I wasn't sure how to write :)
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D31942092
Pulled By: bdhirsh
fbshipit-source-id: c702a57c2748a7c771c14e4bcc3e996b48fcc4c8
Summary:
Adds mixed precision autocasting support between fp32/fp16 to torchscript/JIT. More in depth descriptoin can be found at [torch/csrc/jit/JIT-AUTOCAST.md](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63939/files#diff-1f1772aaa508841c5bb58b74ab98f49a1e577612cd9ea5c386c8714a75db830b)
This PR implemented an autocast optimization pass that inserts casting ops per AMP rule (torch/csrc/jit/passes/autocast.cpp), that mimics the behavior of eager autocast. The pass also takes into consideration the context of `torch.cuda.amp.autocast` and only inserts casting ops within the enabled context manager, giving feature parity as with eager amp autocast.
We currently provide JIT AMP autocast as a prototyping feature, so it is default off and could be turned on via `torch._C._jit_set_autocast_mode(True)`
The JIT support for autocast is subject to different constraints compared to the eager mode implementation (mostly related to the fact that TorchScript is statically typed), restriction on the user facing python code is described in doc torch/csrc/jit/JIT-AUTOCAST.md
This is a prototype, there are also implementation limitation that's necessary to keep this PR small and get something functioning quickly on upstream, so we can iterate on designs.
Few limitation/challenge that is not properly resolved in this PR:
1. Autocast inserts cast operation, which would have impact on scalar type of output tensor feeding downstream operations. We are not currently propagating the updated scalar types, this would give issues/wrong results on operations in promotion rules.
2. Backward for autodiff in JIT misses the casting of dgrad to input scalar type, as what autograd does in eager. This forces us to explicitly mark the casting operation for certain operations (e.g. binary ops), otherwise, we might be feeding dgrad with mismatch scalar type to input. This could potentially break gradient function consuming dgrad. (e.g. gemm backwards, which assumes grad_output to be of same scalar type as input')
3. `torch.autocast` api has an optional argument `dtype` which is not currently supported in the JIT autocast and we require a static value.
Credit goes mostly to:
tlemo
kevinstephano
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63939
Reviewed By: navahgar
Differential Revision: D31093381
Pulled By: eellison
fbshipit-source-id: da6e26c668c38b01e296f304507048d6c1794314
Summary:
Adds `torch.argwhere` as an alias to `torch.nonzero`
Currently, `torch.nonzero` is actually provides equivalent functionality to `np.argwhere`.
From NumPy docs,
> np.argwhere(a) is almost the same as np.transpose(np.nonzero(a)), but produces a result of the correct shape for a 0D array.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/64257
Reviewed By: dagitses
Differential Revision: D31474901
Pulled By: saketh-are
fbshipit-source-id: 335327a4986fa327da74e1fb8624cc1e56959c70
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/62030
Remove dtype tracking from Python Storage interface, remove all the different `<type>Storage` classes except for `ByteStorage`, and update serialization accordingly, while maintaining as much FC/BC as possible
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/47442
* **THE SERIALIZATION FORMAT IS FULLY FC/BC.** We worked very hard to make sure this is the case. We will probably want to break FC at some point to make the serialization structure of tensors make more sense, but not today.
* There is now only a single torch.ByteStorage class. Methods like `Tensor.set_` no longer check that the dtype of storage is appropriate.
* As we no longer know what dtype of a storage is, we've **removed** the size method from Storage, replacing it with nbytes. This is to help catch otherwise silent errors where you confuse number of elements with number of bytes.
* `Storage._new_shared` takes a `nbytes` kwarg and will reject previous positional only calls. `Storage._new_with_file` and `_set_from_file` require explicit element size arguments.
* It's no longer possible to convert storages to different types using the float/double/etc methods. Instead, do the conversion using a tensor.
* It's no longer possible to allocate a typed storage directly using FloatStorage/DoubleStorage/etc constructors. Instead, construct a tensor and extract its storage. The classes still exist but they are used purely for unpickling.
* The preexisting serialization format stores dtype with storage, and in fact this dtype is used to determine the dtype of the tensor overall.
To accommodate this case, we introduce a new TypedStorage concept that exists only during unpickling time which is used to temporarily store the dtype so we can construct a tensor. **If you overrode the handling of pickling/unpickling, you MUST add handling for TypedStorage** or your serialization code will degrade to standard file-based serialization.
Original pull request: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/59671
Reviewed By: soulitzer, ngimel
Differential Revision: D29466819
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 4a14e5d3c2b08e06e558683d97f7378a3180b00e
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/65621
Add a new attribute to the FusedMovingAvgObsFakeQuantize that controls if the Fake Quant operation should be applied at the output of a particular layer. The motivation is to give the users additional control to control the numerics of the fake_quant operators during training. It defaults to always fake quant the output (True).
Note: We will still observer the tensors as before (only the fake_quant operation is controlled using this flag)
For example
```
input model
x -> fc1 -> fc2 -> non_quantizable_op -> fc3
After fake_quant
x -> fake_quant(x) -> fc1 -> fake_quant(fc1) -> fc2 -> fake_quant(fc2) -> non_quantizable_op -> fake_quant() -> fc3 -> fake_quantize(fc3)
With output_fake_quant disabled at the output of fc2 and fc3 (since their outputs are non-quantizable)
x -> fake_quant(x) -> fc1 -> fake_quant(fc1) -> fc2 -> non_quantizable_op -> fake_quant() -> fc3
```
Test Plan: ./buck-out/gen/caffe2/test/quantization_fx\#binary.par -r test_disable_output_fake_quant
Reviewed By: jerryzh168
Differential Revision: D31174526
fbshipit-source-id: bffe776216d041fb09133a6fb09bfc2c0bb46b89
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/65340
I thought about a few possible ways of doing this. The main hazard is
that if I create a CPU tensor that doesn't have any real storage, the
moment I actually try to access the data on the tensor I will segfault.
So I don't want to use _make_subclass on a "cpu meta tensor" because
the CPU meta tensor (with no subclass) is radioactive: printing it
will immediately cause a segfault. So instead, I have to create
the CPU meta tensor AND subclass all in one go, and that means I need
another function for it. One downside to doing it this way is
I need another overload for explicit strides, and in general it is
difficult to get the view relationships to all work out properly;
tracked at https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/65339
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/62972
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/62730
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D31057231
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 73522769e093ae8a1bf0c7f7e594659bfb827b28
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/62671
Very crude first implementation of `torch.nanmean`. The current reduction kernels do not have good support for implementing nan* variants. Rather than implementing new kernels for each nan* operator, I will work on new reduction kernels with support for a `nan_policy` flag and then I will port `nanmean` to use that.
**TODO**
- [x] Fix autograd issue
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D30515181
Pulled By: heitorschueroff
fbshipit-source-id: 303004ebd7ac9cf963dc4f8e2553eaded5f013f0
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/64689
This brings it in line with the C++ implementation.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/64687
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D30816215
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: ed36af6c35467ae678d9548197efd97c36d38dec
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63552
In this PR, we want to exclude these 2 cases in the `Autocast` weight cache usages:
- Using `torch.jit.trace` under the `Autocast`
As report in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/50231 and several other discussions, using `torch.jit.trace` under the `Autocast`, the trace process would hit Autocast's weight cache and fails. So we should disable weight cache under the trace process.
- Using `Autocast` with `Grad mode`
- Usually we are using `Grad mode` for training. Since in the training phase, the weight will change in every step. So we doesn't need to cache the weight.
- For the recommended `Autocast` training case in the [doc](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/amp.html), `Autocast` will clear the cache every step leaving the context. We should disable it to save the clear operations.
```
model = Net().cuda()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), ...)
for input, target in data:
optimizer.zero_grad()
with autocast():
output = model(input)
loss = loss_fn(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
```
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: mrshenli
Differential Revision: D30644913
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: ad7bc87372e554e7aa1aa0795e9676871b3974e7
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/62811
Add `torch.linalg.matmul` alias to `torch.matmul`. Note that the `linalg.matmul` doesn't have a `method` variant.
Also cleaning up `torch/_torch_docs.py` when formatting is not needed.
cc IvanYashchuk Lezcano mruberry rgommers
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63227
Reviewed By: mrshenli
Differential Revision: D30770235
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: bfba77dfcbb61fcd44f22ba41bd8d84c21132403
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/61767
## Changes
- [x] Add `torch.concat` alias to `torch.cat`
- [x] Add OpInfo for `cat`/`concat`
- [x] Fix `test_out` skips (Use `at::native::resize_output` or `at::native::resize_output_check`)
- [x] `cat`/`concat`
- [x] `stack`
- [x] `hstack`
- [x] `dstack`
- [x] `vstack`/`row_stack`
- [x] Remove redundant tests for `cat`/`stack`
~I've not added `cat`/`concat` to OpInfo `op_db` yet, since cat is a little more tricky than other OpInfos (should have a lot of tests) and currently there are no OpInfos for that. I can try to add that in a subsequent PR or maybe here itself, whatever is suggested.~
**Edit**: cat/concat OpInfo has been added.
**Note**: I've added the named tensor support for `concat` alias as well, maybe that's out of spec in `array-api` but it is still useful for consistency in PyTorch.
Thanks to krshrimali for guidance on my first PR :))
cc mruberry rgommers pmeier asmeurer leofang AnirudhDagar asi1024 emcastillo kmaehashi heitorschueroff krshrimali
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/62560
Reviewed By: saketh-are
Differential Revision: D30762069
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 6985159d1d9756238890488a0ab3ae7699d94337
Summary:
This PR implements the necessary hooks/stubs/enums/etc for complete ONNX Runtime (ORT) Eager Mode integration. The actual extension will live out of tree at https://github.com/pytorch/ort.
We have been [working on this at Microsoft](https://github.com/microsoft/onnxruntime-pytorch/tree/eager-ort/torch_onnxruntime) for the last few months, and are finally ready to contribute the PyTorch core changes upstream (nothing major or exciting, just the usual boilerplate for adding new backends).
The ORT backend will allow us to ferry [almost] all torch ops into granular ONNX kernels that ORT will eagerly execute against any devices it supports (therefore, we only need a single ORT backend from a PyTorch perspective).
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58248
Reviewed By: astaff
Differential Revision: D30344992
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 69082b32121246340d686e16653626114b7714b2
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/59077Fixes#58549
`from_buffer` constructs a tensor object from an already allocated buffer through
CPython's buffer protocol. Besides the standard `dtype`, `count`, and `offset` parameters,
this function also accepts:
- `device`: where the buffer lives
- `requires_grad`: should autograd record operations on the new tensor
A new test file _test_buffer_protocol.py_ was created. Currently, only CPU tests were
implemented. That's because neither PyTorch nor Numba implements CPython's buffer
protocol. Therefore, there's no way to create a CUDA buffer with the existing
dependencies (could use PyCUDA for that, though).
At the moment, if `device` differs from the device the buffer actually lives, two things
may happen:
- `RuntimeError`, if `device='cuda'`
- Segmentation fault (not tested -- see above), if `device='cpu'`
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: jbschlosser
Differential Revision: D29870914
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 9fa8611aeffedfe39c9af74558178157a11326bb
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/61570
Fused operator that computes moving average min/max values (in-place) of the input tensor and fake-quantizes it.
It expects the qmin/qmax values to reflect the range of the quantized tensor (instead of reduce_range)
Motivation for adding this operator is for performance reasons, since moving the computation from python to C++/CUDA can increase the performance of QAT.
Test Plan:
python test/test_quantization.py TestFusedObsFakeQuant
Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: vkuzo
Differential Revision: D29682762
fbshipit-source-id: 28e4c50e77236d6976fe4b326c9a12103ed95840
Summary:
This PR un-reverts https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/61475 + fixes compilation with MSVC, that does not recognize alternative operator spellings (i.e. using `or` instead of `||` )
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/61937
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D29805941
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 01e5963c6717c1b44b260300d87ba0bf57f26ce9
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/56058
User facing changes:
1. Adds a negative bit and corresponding new API (`is_neg()`,`resolve_neg()`)
2. `tensor.conj().imag` now returns a floating point tensor with neg bit set to 1 instead of a tensor with no notion of negative bit. Note that imag is still a view and all the view properties still hold for imag.
Non user facing changes:
1. Added a new Negative dispatch key and a backend fallback to handle it
2. Updated copy kernel to handle negative bit
3. Merged conjugate and negative bit fallback kernel
4. fixed https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/60478 (caused due to https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/54987)
Testing:
1. Added a new OpInfo based test `test_neg_view` (verifies that out-of-place and in-place operations work correctly for all operations when the input is a neg view tensor by checking the result against an actually negated tensor, verifies that autograd returns the same output for both neg view and actually negated tensors as well as it works fine when grad_out is a neg view).
2. Added a new test class containing `test_conj_view`, `test_neg_view`.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: soulitzer
Differential Revision: D29636403
fbshipit-source-id: 12214c9dc4806c51850f4a72a109db9527c0ca63
Summary:
Based from https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/50466
Adds the initial implementation of `torch.cov` similar to `numpy.cov`. For simplicity, we removed support for many parameters in `numpy.cov` that are either redundant such as `bias`, or have simple workarounds such as `y` and `rowvar`.
cc PandaBoi
closes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/19037
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58311
Reviewed By: jbschlosser
Differential Revision: D29431651
Pulled By: heitorschueroff
fbshipit-source-id: 167dea880f534934b145ba94291a9d634c25b01b
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58059
Add CUDA.used vital sign which is true only if CUDA was "used" which technically means the context was created.
Also adds the following features:
- Force vitals to be written even if vitals are disabled, to enable testing when the env variable is not set from the start of execution
- Add a read_vitals call for python to read existing vital signs.
Test Plan: buck test mode/dbg caffe2/test:torch -- --regex basic_vitals
Reviewed By: xuzhao9
Differential Revision: D28357615
fbshipit-source-id: 681bf9ef63cb1458df9f1c241d301a3ddf1e5252
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/59760
See https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/59049
There are some moving parts to this PR, I'll structure this explanation so the straightforward parts go first, and then the less straightforward parts.
**The actual dispatch to Python.** The core logic of dispatch to Python lives in `concrete_dispatch_fn` in `torch/csrc/autograd/python_variable.cpp`. It takes the input IValue stack, scans all the arguments for Tensor arguments, and defers most of the heavy lifting to `handle_torch_function_no_python_arg_parser` which actually does all of the logic for calling out to torch dispatch (in particular, this function handles multiple dispatch situations for you). Because we have a different function name than regular `__torch_function__` handling, `handle_torch_function_no_python_arg_parser` is generalized to accept a magic method name to look for when testing if Tensors have custom handling or not. Unlike `__torch_function__`, by default there is no `__torch_dispatch__` on Tensor classes.
**Maintaining the Python dispatch key.** In order to get to the dispatch to Python logic, we must tag Tensors with the `__torch_dispatch__` magic method with the newly added Python dispatch key (separated from PythonFuncTorch to allow for a transitional period while they migrate to this mechanism). We expose a new private property `_is_python_dispatch` that assists in debugging if a Tensor is participating in Python dispatch or not. We apply the Python dispatch key the first time a PyObject for a Tensor is constructed (THPVariable_NewWithVar), testing if `__torch_dispatch__` exists with then newly added `check_has_torch_dispatch`.
**Shallow copy and detach.** For the simple examples tested in this PR, most creations of Tensor route through the dispatcher. The exception to this is `shallow_copy_and_detach`, which bypasses the dispatcher and is used when saving tensors for backwards. When a Tensor is Python dispatch, we override the behavior of `shallow_copy_and_detach` to instead directly call into `__torch_dispatch__` to perform a `detach` operation (in the same way it would be invoked if you called `detach` directly). Because this Python call is triggered directly from c10::TensorImpl, it must be indirected through `PyInterpreter::detach`, which is the general mechanism for dynamic dispatching to the Python interpreter associated with a TensorImpl.
**torchdeploy compatibility.** The dispatch to Python logic cannot be directly registered to the dispatcher as it is compiled in the Python library, which will get loaded multiple times per torchdeploy interpreter. Thus, we must employ a two phase process. First, we register a fallback inside a non-Python library (aten/src/ATen/core/PythonFallbackKernel.cpp). Its job is to determine the appropriate PyInterpreter to handle the Python dispatch by going through all of the arguments and finding the first argument that has a PyObject/PyInterpreter. With this PyInterpreter, it makes another dynamic dispatch via "dispatch" which will go to the correct torchdeploy interpreter to handle dispatching to actual Python.
**Testing.** We provide a simple example of a LoggingTensor for testing, which can be used to generate TorchScript-like traces to observe what operations are being called when a Tensor is invoked. Although a LoggingTensor would be better implemented via an is-a relationship rather than a has-a relationship (as is done in the test), we've done it this way to show that arbitrarily complex compositions of tensors inside a tensor work properly.
**Known limitations.**
* We haven't adjusted any operator code, so some patterns may not work (as they lose the Python subclass in an unrecoverable way)
* `__torch_function__` must be explicitly disabled with `_disabled_torch_function_impl` otherwise things don't work quite correctly (in particular, what is being disabled is default subclass preservation behavior.)
* We don't ever populate kwargs, even when an argument is kwarg-only
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Differential Revision:
D29017912
D29017912
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: bdhirsh
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: a67714d9e541d09203a8cfc85345b8967db86238
Summary:
Reference https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/50345
`zeta` was already present in the codebase to support computation of `polygamma`.
However, `zeta` only had `double(double, double)` signature **for CPU** before the PR (which meant that computation `polygamma` were always upcasted to `double` for zeta part).
With this PR, float computations will take place in float and double in double.
Have also refactored the code and moved the duplicate code from `Math.cuh` to `Math.h`
**Note**: For scipy, q is optional, and if it is `None`, it defaults `1` which corresponds to Reimann-Zeta. However, for `torch.specia.zeta`, I made it mandatory cause for me it feels odd without `q` this is Reimann-Zeta and with `q` it is the general Hurwitz Zeta. I think sticking to just general made more sense as passing `1` for q sounds trivial.
Verify:
* [x] Docs https://14234587-65600975-gh.circle-artifacts.com/0/docs/special.html#torch.special.zeta
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/59623
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D29348269
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: a3f9ebe1f7724dbe66de2b391afb9da1cfc3e4bb
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/60464
Fixes https://github.com/szagoruyko/pytorchviz/issues/65
An alternate implementation of this PR would be to remove the
__torch_function__ interposition points for these accessors entirely.
In the end, I decided to opt for extra expressivity. See
torch.overrides for the criterion on how I decided which accessors
should get the nowrap treatment.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D29302835
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: fbe0ac4530a6cc9d6759a3fdf5514d4d7b1f7690
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/60050
It doesn't work to put torch.Tensor.prop.__get__ in the ignored
list. Now it does. (Not exercised here, see next diff in stack).
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: zou3519
Differential Revision: D29171464
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: e7354668b481f9275f2eb5bb3a6228d1815fecea
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/3025
## Background
This PR implements a function similar to numpy's [`isin()`](https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.isin.html#numpy.isin).
The op supports integral and floating point types on CPU and CUDA (+ half & bfloat16 for CUDA). Inputs can be one of:
* (Tensor, Tensor)
* (Tensor, Scalar)
* (Scalar, Tensor)
Internally, one of two algorithms is selected based on the number of elements vs. test elements. The heuristic for deciding which algorithm to use is taken from [numpy's implementation](fb215c7696/numpy/lib/arraysetops.py (L575)): if `len(test_elements) < 10 * len(elements) ** 0.145`, then a naive brute-force checking algorithm is used. Otherwise, a stablesort-based algorithm is used.
I've done some preliminary benchmarking to verify this heuristic on a devgpu, and determined for a limited set of tests that a power value of `0.407` instead of `0.145` is a better inflection point. For now, the heuristic has been left to match numpy's, but input is welcome for the best way to select it or whether it should be left the same as numpy's.
Tests are adapted from numpy's [isin and in1d tests](7dcd29aaaf/numpy/lib/tests/test_arraysetops.py).
Note: my locally generated docs look terrible for some reason, so I'm not including the screenshot for them until I figure out why.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/53125
Test Plan:
```
python test/test_ops.py # Ex: python test/test_ops.py TestOpInfoCPU.test_supported_dtypes_isin_cpu_int32
python test/test_sort_and_select.py # Ex: python test/test_sort_and_select.py TestSortAndSelectCPU.test_isin_cpu_int32
```
Reviewed By: soulitzer
Differential Revision: D29101165
Pulled By: jbschlosser
fbshipit-source-id: 2dcc38d497b1e843f73f332d837081e819454b4e
Summary:
Based from https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/50466
Adds the initial implementation of `torch.cov` similar to `numpy.cov`. For simplicity, we removed support for many parameters in `numpy.cov` that are either redundant such as `bias`, or have simple workarounds such as `y` and `rowvar`.
cc PandaBoi
TODO
- [x] Improve documentation
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58311
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D28994140
Pulled By: heitorschueroff
fbshipit-source-id: 1890166c0a9c01e0a536acd91571cd704d632f44
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/59710
This is the exact same PR as before.
The version that landed was actually outdated compared to the github PR and that's why it failed on master... Sorry for the noise.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: zou3519
Differential Revision: D28995764
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 8f7ae3356a886d45787c5e6ca53a4e7b033e306e
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/35379
- Adds `retains_grad` attribute backed by cpp as a native function. The python bindings for the function are skipped to be consistent with `is_leaf`.
- Tried writing it without native function, but the jit test `test_tensor_properties` seems to require that it be a native function (or alternatively maybe it could also work if we manually add a prim implementation?).
- Python API now uses `retain_grad` implementation from cpp
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/59362
Reviewed By: jbschlosser
Differential Revision: D28969298
Pulled By: soulitzer
fbshipit-source-id: 335f2be50b9fb870cd35dc72f7dadd6c8666cc02
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/54987
Based off of ezyang (https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/44799) and bdhirsh (https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/43702) 's prototype:
Here's a summary of the changes in this PR:
This PR adds a new dispatch key called Conjugate. This enables us to make conjugate operation a view and leverage the specialized library functions that fast path with the hermitian operation (conj + transpose).
1. Conjugate operation will now return a view with conj bit (1) for complex tensors and returns self for non-complex tensors as before. This also means `torch.view_as_real` will no longer be a view on conjugated complex tensors and is hence disabled. To fill the gap, we have added `torch.view_as_real_physical` which would return the real tensor agnostic of the conjugate bit on the input complex tensor. The information about conjugation on the old tensor can be obtained by calling `.is_conj()` on the new tensor.
2. NEW API:
a) `.conj()` -- now returning a view.
b) `.conj_physical()` -- does the physical conjugate operation. If the conj bit for input was set, you'd get `self.clone()`, else you'll get a new tensor with conjugated value in its memory.
c) `.conj_physical_()`, and `out=` variant
d) `.resolve_conj()` -- materializes the conjugation. returns self if the conj bit is unset, else returns a new tensor with conjugated values and conj bit set to 0.
e) `.resolve_conj_()` in-place version of (d)
f) `view_as_real_physical` -- as described in (1), it's functionally same as `view_as_real`, just that it doesn't error out on conjugated tensors.
g) `view_as_real` -- existing function, but now errors out on conjugated tensors.
3. Conjugate Fallback
a) Vast majority of PyTorch functions would currently use this fallback when they are called on a conjugated tensor.
b) This fallback is well equipped to handle the following cases:
- functional operation e.g., `torch.sin(input)`
- Mutable inputs and in-place operations e.g., `tensor.add_(2)`
- out-of-place operation e.g., `torch.sin(input, out=out)`
- Tensorlist input args
- NOTE: Meta tensors don't work with conjugate fallback.
4. Autograd
a) `resolve_conj()` is an identity function w.r.t. autograd
b) Everything else works as expected.
5. Testing:
a) All method_tests run with conjugate view tensors.
b) OpInfo tests that run with conjugate views
- test_variant_consistency_eager/jit
- gradcheck, gradgradcheck
- test_conj_views (that only run for `torch.cfloat` dtype)
NOTE: functions like `empty_like`, `zero_like`, `randn_like`, `clone` don't propagate the conjugate bit.
Follow up work:
1. conjugate view RFC
2. Add neg bit to re-enable view operation on conjugated tensors
3. Update linalg functions to call into specialized functions that fast path with the hermitian operation.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: VitalyFedyunin
Differential Revision: D28227315
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: acab9402b9d6a970c6d512809b627a290c8def5f
Summary:
Adds `is_inference` as a native function w/ manual cpp bindings.
Also changes instances of `is_inference_tensor` to `is_inference` to be consistent with other properties such as `is_complex`.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58729
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D28874507
Pulled By: soulitzer
fbshipit-source-id: 0fa6bcdc72a4ae444705e2e0f3c416c1b28dadc7
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/56017Fixes#55686
This patch is seemingly straightforward but some of the changes are very
subtle. For the general algorithmic approach, please first read the
quoted issue. Based on the algorithm, there are some fairly
straightforward changes:
- New boolean on TensorImpl tracking if we own the pyobj or not
- PythonHooks virtual interface for requesting deallocation of pyobj
when TensorImpl is being released and we own its pyobj, and
implementation of the hooks in python_tensor.cpp
- Modification of THPVariable to MaybeOwned its C++ tensor, directly
using swolchok's nice new class
And then, there is python_variable.cpp. Some of the changes follow the
general algorithmic approach:
- THPVariable_NewWithVar is simply adjusted to handle MaybeOwned and
initializes as owend (like before)
- THPVariable_Wrap adds the logic for reverting ownership back to
PyObject when we take out an owning reference to the Python object
- THPVariable_dealloc attempts to resurrect the Python object if
the C++ tensor is live, and otherwise does the same old implementation
as before
- THPVariable_tryResurrect implements the resurrection logic. It is
modeled after CPython code so read the cited logic and see if
it is faithfully replicated
- THPVariable_clear is slightly updated for MaybeOwned and also to
preserve the invariant that if owns_pyobj, then pyobj_ is not null.
This change is slightly dodgy: the previous implementation has a
comment mentioning that the pyobj nulling is required to ensure we
don't try to reuse the dead pyobj. I don't think, in this new world,
this is possible, because the invariant says that the pyobj only
dies if the C++ object is dead too. But I still unset the field
for safety.
And then... there is THPVariableMetaType. colesbury explained in the
issue why this is necessary: when destructing an object in Python, you
start off by running the tp_dealloc of the subclass before moving up
to the parent class (much in the same way C++ destructors work). The
deallocation process for a vanilla Python-defined class does irreparable
harm to the PyObject instance (e.g., the finalizers get run) making it
no longer valid attempt to resurrect later in the tp_dealloc chain.
(BTW, the fact that objects can resurrect but in an invalid state is
one of the reasons why it's so frickin' hard to write correct __del__
implementations). So we need to make sure that we actually override
the tp_dealloc of the bottom most *subclass* of Tensor to make sure
we attempt a resurrection before we start finalizing. To do this,
we need to define a metaclass for Tensor that can override tp_dealloc
whenever we create a new subclass of Tensor. By the way, it was totally
not documented how to create metaclasses in the C++ API, and it took
a good bit of trial error to figure it out (and the answer is now
immortalized in https://stackoverflow.com/q/67077317/23845 -- the things
that I got wrong in earlier versions of the PR included setting
tp_basicsize incorrectly, incorrectly setting Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_GC on
the metaclass--you want to leave it unset so that it inherits, and
determining that tp_init is what actually gets called when you construct
a class, not tp_call as another not-to-be-named StackOverflow question
suggests).
Aside: Ordinarily, adding a metaclass to a class is a user visible
change, as it means that it is no longer valid to mixin another class
with a different metaclass. However, because _C._TensorBase is a C
extension object, it will typically conflict with most other
metaclasses, so this is not BC breaking.
The desired new behavior of a subclass tp_dealloc is to first test if
we should resurrect, and otherwise do the same old behavior. In an
initial implementation of this patch, I implemented this by saving the
original tp_dealloc (which references subtype_dealloc, the "standard"
dealloc for all Python defined classes) and invoking it. However, this
results in an infinite loop, as it attempts to call the dealloc function
of the base type, but incorrectly chooses subclass type (because it is
not a subtype_dealloc, as we have overridden it; see
b38601d496/Objects/typeobject.c (L1261) )
So, with great reluctance, I must duplicate the behavior of
subtype_dealloc in our implementation. Note that this is not entirely
unheard of in Python binding code; for example, Cython
c25c3ccc4b/Cython/Compiler/ModuleNode.py (L1560)
also does similar things. This logic makes up the bulk of
THPVariable_subclass_dealloc
To review this, you should pull up the CPython copy of subtype_dealloc
b38601d496/Objects/typeobject.c (L1230)
and verify that I have specialized the implementation for our case
appropriately. Among the simplifications I made:
- I assume PyType_IS_GC, because I assume that Tensor subclasses are
only ever done in Python and those classes are always subject to GC.
(BTW, yes! This means I have broken anyone who has extend PyTorch
tensor from C API directly. I'm going to guess no one has actually
done this.)
- I don't bother walking up the type bases to find the parent dealloc;
I know it is always THPVariable_dealloc. Similarly, I can get rid
of some parent type tests based on knowledge of how
THPVariable_dealloc is defined
- The CPython version calls some private APIs which I can't call, so
I use the public PyObject_GC_UnTrack APIs.
- I don't allow the finalizer of a Tensor to change its type (but
more on this shortly)
One alternative I discussed with colesbury was instead of copy pasting
the subtype_dealloc, we could transmute the type of the object that was
dying to turn it into a different object whose tp_dealloc is
subtype_dealloc, so the stock subtype_dealloc would then be applicable.
We decided this would be kind of weird and didn't do it that way.
TODO:
- More code comments
- Figure out how not to increase the size of TensorImpl with the new
bool field
- Add some torture tests for the THPVariable_subclass_dealloc, e.g.,
involving subclasses of Tensors that do strange things with finalizers
- Benchmark the impact of taking the GIL to release C++ side tensors
(e.g., from autograd)
- Benchmark the impact of adding a new metaclass to Tensor (probably
will be done by separating out the metaclass change into its own
change)
- Benchmark the impact of changing THPVariable to conditionally own
Tensor (as opposed to unconditionally owning it, as before)
- Add tests that this actually indeed preserves the Python object
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D27765125
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 857f14bdcca2900727412aff4c2e2d7f0af1415a
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/57386
Here is the PR for what's discussed in the RFC https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/55374 to enable the autocast for CPU device. Currently, this PR only enable BF16 as the lower precision datatype.
Changes:
1. Enable new API `torch.cpu.amp.autocast` for autocast on CPU device: include the python API, C++ API, new Dispatchkey etc.
2. Consolidate the implementation for each cast policy sharing between CPU and GPU devices.
3. Add the operation lists to corresponding cast policy for cpu autocast.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: soulitzer
Differential Revision: D28572219
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: db3db509973b16a5728ee510b5e1ee716b03a152
Summary:
This adds the methods `Tensor.cfloat()` and `Tensor.cdouble()`.
I was not able to find the tests for `.float()` functions. I'd be happy to add similar tests for these functions once someone points me to them.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/56014
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58137
Reviewed By: ejguan
Differential Revision: D28412288
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: ff3653cb3516bcb3d26a97b9ec3d314f1f42f83d
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58039
The new function has the following signature
`inv_ex(Tensor inpit, *, bool check_errors=False) -> (Tensor inverse, Tensor info)`.
When `check_errors=True`, an error is thrown if the matrix is not invertible; `check_errors=False` - responsibility for checking the result is on the user.
`linalg_inv` is implemented using calls to `linalg_inv_ex` now.
Resolves https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/25095
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D28405148
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: b8563a6c59048cb81e206932eb2f6cf489fd8531
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/56608
- Adds binding to the `c10::InferenceMode` RAII class in `torch._C._autograd.InferenceMode` through pybind. Also binds the `torch.is_inference_mode` function.
- Adds context manager `torch.inference_mode` to manage an instance of `c10::InferenceMode` (global). Implemented in `torch.autograd.grad_mode.py` to reuse the `_DecoratorContextManager` class.
- Adds some tests based on those linked in the issue + several more for just the context manager
Issues/todos (not necessarily for this PR):
- Improve short inference mode description
- Small example
- Improved testing since there is no direct way of checking TLS/dispatch keys
-
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58045
Reviewed By: agolynski
Differential Revision: D28390595
Pulled By: soulitzer
fbshipit-source-id: ae98fa036c6a2cf7f56e0fd4c352ff804904752c
Summary:
Backward methods for `torch.lu` and `torch.lu_solve` require the `torch.lu_unpack` method.
However, while `torch.lu` is a Python wrapper over a native function, so its gradient is implemented via `autograd.Function`,
`torch.lu_solve` is a native function, so it cannot access `torch.lu_unpack` as it is implemented in Python.
Hence this PR presents a native (ATen) `lu_unpack` version. It is also possible to update the gradients for `torch.lu` so that backward+JIT is supported (no JIT for `autograd.Function`) with this function.
~~The interface for this method is different from the original `torch.lu_unpack`, so it is decided to keep it hidden.~~
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/46913
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D28355725
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 281260f3b6e93c15b08b2ba66d5a221314b00e78
Summary:
Backward methods for `torch.lu` and `torch.lu_solve` require the `torch.lu_unpack` method.
However, while `torch.lu` is a Python wrapper over a native function, so its gradient is implemented via `autograd.Function`,
`torch.lu_solve` is a native function, so it cannot access `torch.lu_unpack` as it is implemented in Python.
Hence this PR presents a native (ATen) `lu_unpack` version. It is also possible to update the gradients for `torch.lu` so that backward+JIT is supported (no JIT for `autograd.Function`) with this function.
~~The interface for this method is different from the original `torch.lu_unpack`, so it is decided to keep it hidden.~~
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/46913
Reviewed By: astaff
Differential Revision: D28117714
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: befd33db12ecc147afacac792418b6f4948fa4a4
Summary:
This PR is focused on the API for `linalg.matrix_norm` and delegates computations to `linalg.norm` for the moment.
The main difference between the norms is when `dim=None`. In this case
- `linalg.norm` will compute a vector norm on the flattened input if `ord=None`, otherwise it requires the input to be either 1D or 2D in order to disambiguate between vector and matrix norm
- `linalg.vector_norm` will flatten the input
- `linalg.matrix_norm` will compute the norm over the last two dimensions, treating the input as batch of matrices
In future PRs, the computations will be moved to `torch.linalg.matrix_norm` and `torch.norm` and `torch.linalg.norm` will delegate computations to either `linalg.vector_norm` or `linalg.matrix_norm` based on the arguments provided.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/57127
Reviewed By: mrshenli
Differential Revision: D28186736
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 99ce2da9d1c4df3d9dd82c0a312c9570da5caf25
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/57180
We have now a separate function for computing only the singular values.
`compute_uv` argument is not needed and it was decided in the
offline discussion to remove it. This is a BC-breaking change but our
linalg module is beta, therefore we can do it without a deprecation
notice.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D28142163
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 3fac1fcae414307ad5748c9d5ff50e0aa4e1b853
Summary:
As per discussion here https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/57127#discussion_r624948215
Note that we cannot remove the optional type from the `dim` parameter because the default is to flatten the input tensor which cannot be easily captured by a value other than `None`
### BC Breaking Note
This PR changes the `ord` parameter of `torch.linalg.vector_norm` so that it no longer accepts `None` arguments. The default behavior of `2` is equivalent to the previous default of `None`.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/57662
Reviewed By: albanD, mruberry
Differential Revision: D28228870
Pulled By: heitorschueroff
fbshipit-source-id: 040fd8055bbe013f64d3c8409bbb4b2c87c99d13
Summary:
The new function has the following signature `cholesky_ex(Tensor input, *, bool check_errors=False) -> (Tensor L, Tensor infos)`. When `check_errors=True`, an error is thrown if the decomposition fails; `check_errors=False` - responsibility for checking the decomposition is on the user.
When `check_errors=False`, we don't have host-device memory transfers for checking the values of the `info` tensor.
Rewrote the internal code for `torch.linalg.cholesky`. Added `cholesky_stub` dispatch. `linalg_cholesky` is implemented using calls to `linalg_cholesky_ex` now.
Resolves https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/57032.
Ref. https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/34272, https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/47608, https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/47953
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/56724
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D27960176
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: f05f3d5d9b4aa444e41c4eec48ad9a9b6fd5dfa5
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/53964. cc albanD almson
## Major changes:
- Overhauled the actual loss calculation so that the shapes are now correct (in functional.py)
- added the missing doc in nn.functional.rst
## Minor changes (in functional.py):
- I removed the previous check on whether input and target were the same shape. This is to allow for broadcasting, say when you have 10 predictions that all have the same target.
- I added some comments to explain each shape check in detail. Let me know if these should be shortened/cut.
Screenshots of updated docs attached.
Let me know what you think, thanks!
## Edit: Description of change of behaviour (affecting BC):
The backwards-compatibility is only affected for the `reduction='none'` mode. This was the source of the bug. For tensors with size (N, D), the old returned loss had size (N), as incorrect summation was happening. It will now have size (N, D) as expected.
### Example
Define input tensors, all with size (2, 3).
`input = torch.tensor([[0., 1., 3.], [2., 4., 0.]], requires_grad=True)`
`target = torch.tensor([[1., 4., 2.], [-1., 2., 3.]])`
`var = 2*torch.ones(size=(2, 3), requires_grad=True)`
Initialise loss with reduction mode 'none'. We expect the returned loss to have the same size as the input tensors, (2, 3).
`loss = torch.nn.GaussianNLLLoss(reduction='none')`
Old behaviour:
`print(loss(input, target, var)) `
`# Gives tensor([3.7897, 6.5397], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>. This has size (2).`
New behaviour:
`print(loss(input, target, var)) `
`# Gives tensor([[0.5966, 2.5966, 0.5966], [2.5966, 1.3466, 2.5966]], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)`
`# This has the expected size, (2, 3).`
To recover the old behaviour, sum along all dimensions except for the 0th:
`print(loss(input, target, var).sum(dim=1))`
`# Gives tensor([3.7897, 6.5397], grad_fn=<SumBackward1>.`
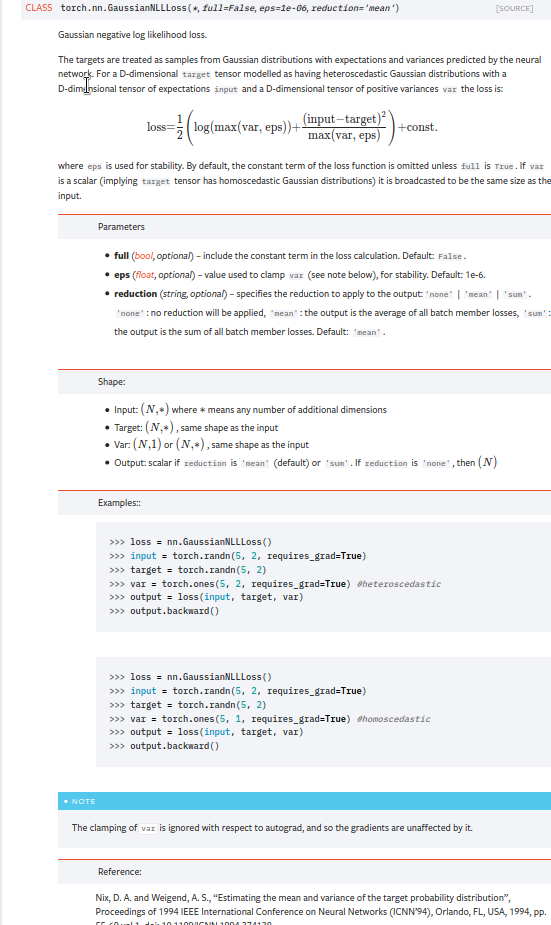
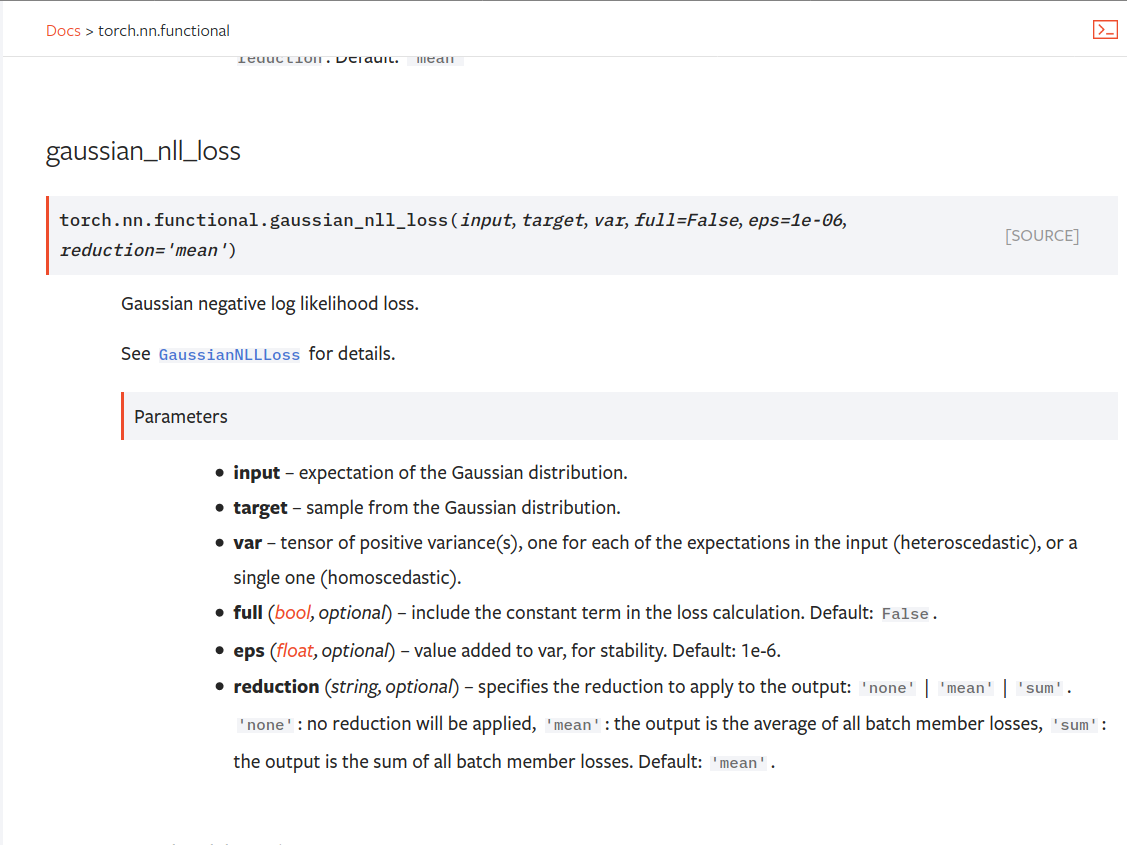
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/56469
Reviewed By: jbschlosser, agolynski
Differential Revision: D27894170
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 197890189c97c22109491c47f469336b5b03a23f
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/53238
There is a tension for the Vitals design: (1) we want a macro based logging API for C++ and (2) we want a clean python API. Furthermore, we want to this to work with "print on destruction" semantics.
The unfortunate resolution is that there are (2) ways to define vitals:
(1) Use the macros for local use only within C++ - this keeps the semantics people enjoy
(2) For vitals to be used through either C++ or Python, we use a global VitalsAPI object.
Both these go to the same place for the user: printing to stdout as the globals are destructed.
The long history on this diff shows many different ways to try to avoid having 2 different paths... we tried weak pointers & shared pointers, verbose switch cases, etc. Ultimately each ran into an ugly trade-off and this cuts the difference better the alternatives.
Test Plan:
buck test mode/dev caffe2/test:torch -- --regex vital
buck test //caffe2/aten:vitals
Reviewed By: orionr
Differential Revision: D26736443
fbshipit-source-id: ccab464224913edd07c1e8532093f673cdcb789f
Summary:
Reference: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/50345
Changes:
* Add `i0e`
* Move some kernels from `UnaryOpsKernel.cu` to `UnarySpecialOpsKernel.cu` to decrease compilation time per file.
Time taken by i0e_vs_scipy tests: around 6.33.s
<details>
<summary>Test Run Log</summary>
```
(pytorch-cuda-dev) kshiteej@qgpu1:~/Pytorch/pytorch_module_special$ pytest test/test_unary_ufuncs.py -k _i0e_vs
======================================================================= test session starts ========================================================================
platform linux -- Python 3.8.6, pytest-6.1.2, py-1.9.0, pluggy-0.13.1
rootdir: /home/kshiteej/Pytorch/pytorch_module_special, configfile: pytest.ini
plugins: hypothesis-5.38.1
collected 8843 items / 8833 deselected / 10 selected
test/test_unary_ufuncs.py ...sss.... [100%]
========================================================================= warnings summary =========================================================================
../../.conda/envs/pytorch-cuda-dev/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/backends/cudnn/__init__.py:73
test/test_unary_ufuncs.py::TestUnaryUfuncsCUDA::test_special_i0e_vs_scipy_cuda_bfloat16
/home/kshiteej/.conda/envs/pytorch-cuda-dev/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/backends/cudnn/__init__.py:73: UserWarning: PyTorch was compiled without cuDNN/MIOpen support. To use cuDNN/MIOpen, rebuild PyTorch making sure the library is visible to the build system.
warnings.warn(
-- Docs: https://docs.pytest.org/en/stable/warnings.html
===================================================================== short test summary info ======================================================================
SKIPPED [3] test/test_unary_ufuncs.py:1182: not implemented: Could not run 'aten::_copy_from' with arguments from the 'Meta' backend. This could be because the operator doesn't exist for this backend, or was omitted during the selective/custom build process (if using custom build). If you are a Facebook employee using PyTorch on mobile, please visit https://fburl.com/ptmfixes for possible resolutions. 'aten::_copy_from' is only available for these backends: [BackendSelect, Named, InplaceOrView, AutogradOther, AutogradCPU, AutogradCUDA, AutogradXLA, UNKNOWN_TENSOR_TYPE_ID, AutogradMLC, AutogradNestedTensor, AutogradPrivateUse1, AutogradPrivateUse2, AutogradPrivateUse3, Tracer, Autocast, Batched, VmapMode].
BackendSelect: fallthrough registered at ../aten/src/ATen/core/BackendSelectFallbackKernel.cpp:3 [backend fallback]
Named: registered at ../aten/src/ATen/core/NamedRegistrations.cpp:7 [backend fallback]
InplaceOrView: fallthrough registered at ../aten/src/ATen/core/VariableFallbackKernel.cpp:56 [backend fallback]
AutogradOther: registered at ../torch/csrc/autograd/generated/VariableType_4.cpp:8761 [autograd kernel]
AutogradCPU: registered at ../torch/csrc/autograd/generated/VariableType_4.cpp:8761 [autograd kernel]
AutogradCUDA: registered at ../torch/csrc/autograd/generated/VariableType_4.cpp:8761 [autograd kernel]
AutogradXLA: registered at ../torch/csrc/autograd/generated/VariableType_4.cpp:8761 [autograd kernel]
UNKNOWN_TENSOR_TYPE_ID: registered at ../torch/csrc/autograd/generated/VariableType_4.cpp:8761 [autograd kernel]
AutogradMLC: registered at ../torch/csrc/autograd/generated/VariableType_4.cpp:8761 [autograd kernel]
AutogradNestedTensor: registered at ../torch/csrc/autograd/generated/VariableType_4.cpp:8761 [autograd kernel]
AutogradPrivateUse1: registered at ../torch/csrc/autograd/generated/VariableType_4.cpp:8761 [autograd kernel]
AutogradPrivateUse2: registered at ../torch/csrc/autograd/generated/VariableType_4.cpp:8761 [autograd kernel]
AutogradPrivateUse3: registered at ../torch/csrc/autograd/generated/VariableType_4.cpp:8761 [autograd kernel]
Tracer: registered at ../torch/csrc/autograd/generated/TraceType_4.cpp:9348 [kernel]
Autocast: fallthrough registered at ../aten/src/ATen/autocast_mode.cpp:250 [backend fallback]
Batched: registered at ../aten/src/ATen/BatchingRegistrations.cpp:1016 [backend fallback]
VmapMode: fallthrough registered at ../aten/src/ATen/VmapModeRegistrations.cpp:33 [backend fallback]
==================================================== 7 passed, 3 skipped, 8833 deselected, 2 warnings in 6.33s =====================================================
```
</details>
TODO:
* [x] Check rendered docs (https://11743402-65600975-gh.circle-artifacts.com/0/docs/special.html)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/54409
Reviewed By: jbschlosser
Differential Revision: D27760472
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: bdfbcaa798b00c51dc9513c34626246c8fc10548
Summary:
This PR adds a `padding_idx` parameter to `nn.EmbeddingBag` and `nn.functional.embedding_bag`. As with `nn.Embedding`'s `padding_idx` argument, if an embedding's index is equal to `padding_idx` it is ignored, so it is not included in the reduction.
This PR does not add support for `padding_idx` for quantized or ONNX `EmbeddingBag` for opset10/11 (opset9 is supported). In these cases, an error is thrown if `padding_idx` is provided.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/3194
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/49237
Reviewed By: walterddr, VitalyFedyunin
Differential Revision: D26948258
Pulled By: jbschlosser
fbshipit-source-id: 3ca672f7e768941f3261ab405fc7597c97ce3dfc