This should be self containable to merge but other stuff that's been bugging me is
* Instructions on debugging IMA issues
* Dynamic shape instructions
* Explaining config options better
Will look at adding a config options doc
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/95802
Approved by: https://github.com/svekars
Fixed following errors in contribution guide.
"deep neural networks using a **on** tape-based autograd systems." to "deep neural networks **using a tape-based** autograd systems."
"the best entrance **point** and are great places to start." to "the best entrance **points** and are great places to start."
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/95454
Approved by: https://github.com/ezyang
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/serve/issues/1937
A fairly common query I see folks running while using pytorch is
`nvidia-smi --format=csv,noheader,nounits --query-gpu=utilization.gpu,utilization.memory,memory.total,memory.used,temperature.gpu,power.draw,clocks.current.sm,clocks.current.memory -l 10`
Existing metrics we have
* For kernel utilization`torch.cuda.utilization()`
* For memory utilization we have them under `torch.cuda.memory` the memory allocated with `torch.cuda.memory.memory_allocated()`
* For total available memory we have `torch.cuda.get_device_properties(0).total_memory`
Which means the only metrics we're missing are
* Temperature: now in `torch.cuda.temperature()`
* Power draw: now in `torch.cuda.power()`
* Clock speed: now in `torch.cuda.clock_speed()`
With some important details on each
* Clock speed settings: I picked the SM clock domain which is documented here https://docs.nvidia.com/deploy/nvml-api/group__nvmlDeviceEnumvs.html#group__nvmlDeviceEnumvs_1g805c0647be9996589fc5e3f6ff680c64
* Temperature: I use `pynvml.nvmlDeviceGetTemperature(handle, 0)` where 0 refers to the GPU die temperature
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/91717
Approved by: https://github.com/ngimel
Corrected the grammar of a sentence in "Implementing Features or Fixing Bugs" section of the contribution guide.
**Before:**
Issues that are labeled first-new-issue, low, or medium priority provide the best entrance point are great places to start.
**After:**
Issues that are labeled first-new-issue, low, or medium priority provide the best entrance point _and_ are great places to start.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/93014
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD, https://github.com/kit1980
Fixes#91824
This PR add a new dynamo backend registration mechanism through ``entry_points``. The ``entry_points`` of a package is provides a way for the package to reigster a plugin for another one.
The docs of the new mechanism:
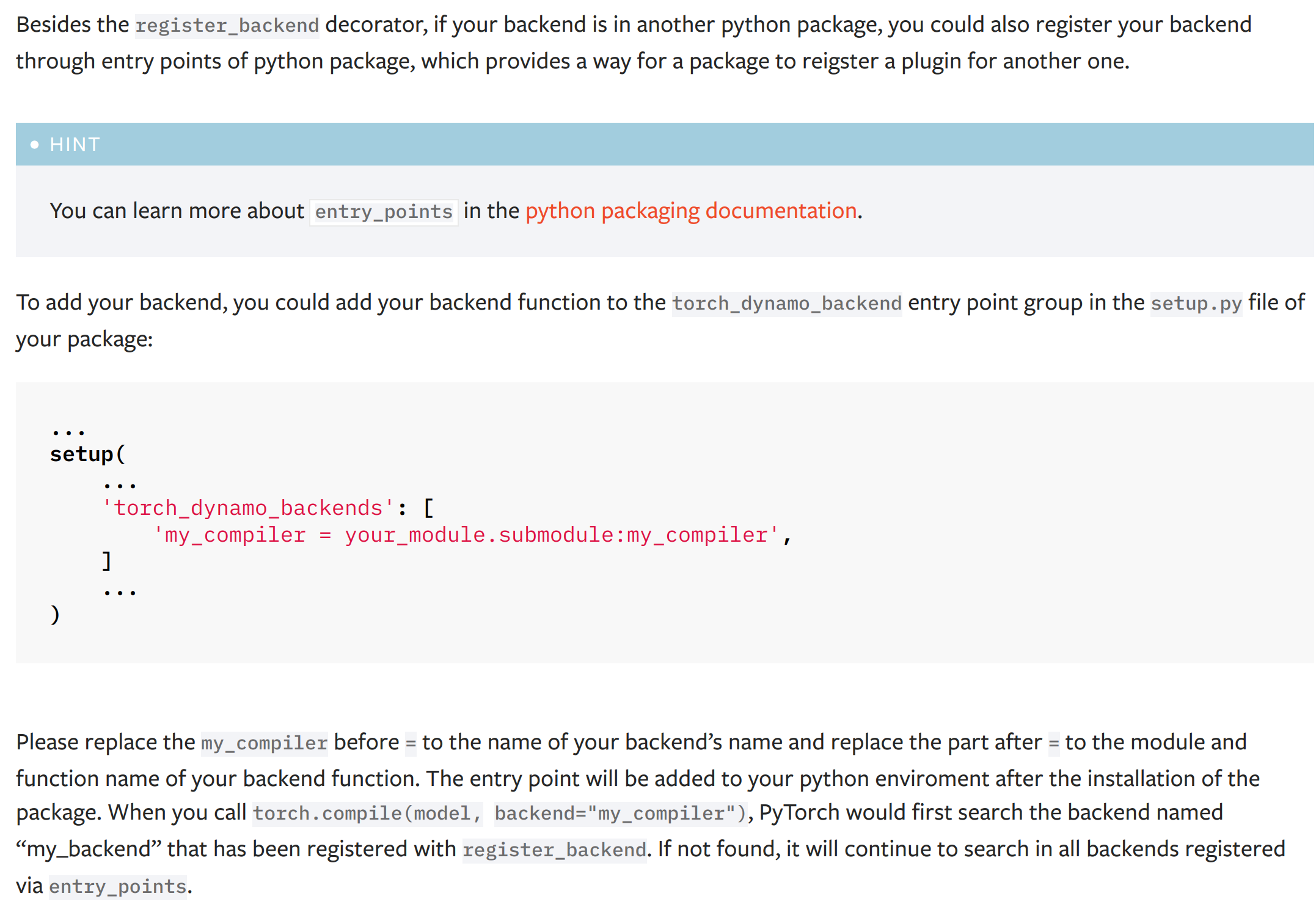
(the typo '...named "my_backend" that has been..." has been fixed to '...named "my_compiler" that has been...')
# Discussion
## About the test
I did not add a test for this PR as it is hard either to install a fack package during a test or manually hack the entry points function by replacing it with a fake one. I have tested this PR offline with the hidet compiler and it works fine. Please let me know if you have any good idea to test this PR.
## About the dependency of ``importlib_metadata``
This PR will add a dependency ``importlib_metadata`` for the python < 3.10 because the modern usage of ``importlib`` gets stable at this python version (see the documentation of the importlib package [here](https://docs.python.org/3/library/importlib.html)). For python < 3.10, the package ``importlib_metadata`` implements the feature of ``importlib``. The current PR will hint the user to install this ``importlib_metata`` if their python version < 3.10.
## About the name and docs
Please let me know how do you think the name ``torch_dynamo_backend`` as the entry point group name and the documentation of this registration mechanism.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/93873
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet, https://github.com/jansel
- To check for Memory Leaks in `test_mps.py`, set the env-variable `PYTORCH_TEST_MPS_MEM_LEAK_CHECK=1` when running test_mps.py (used CUDA code as reference).
- Added support for the following new python interfaces in MPS module:
`torch.mps.[empty_cache(), set_per_process_memory_fraction(), current_allocated_memory(), driver_allocated_memory()]`
- Renamed `_is_mps_on_macos_13_or_newer()` to `_mps_is_on_macos_13_or_newer()`, and `_is_mps_available()` to `_mps_is_available()` to be consistent in naming with prefix `_mps`.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/94646
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
- This PR is a prerequisite for the upcoming Memory Leak Detection PR.
- Enable global manual seeding via `torch.manual_seed()` + test case
- Add `torch.mps.synchronize()` to wait for MPS stream to finish + test case
- Enable the following python interfaces for MPS:
`torch.mps.[get_rng_state(), set_rng_state(), synchronize(), manual_seed(), seed()]`
- Added some test cases in test_mps.py
- Added `mps.rst` to document the `torch.mps` module.
- Fixed the failure with `test_public_bindings.py`
Description of new files added:
- `torch/csrc/mps/Module.cpp`: implements `torch._C` module functions for `torch.mps` and `torch.backends.mps`.
- `torch/mps/__init__.py`: implements Python bindings for `torch.mps` module.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/94417
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD
- This PR is a prerequisite for the upcoming Memory Leak Detection PR.
- Enable global manual seeding via `torch.manual_seed()` + test case
- Add `torch.mps.synchronize()` to wait for MPS stream to finish + test case
- Enable the following python interfaces for MPS:
`torch.mps.[get_rng_state(), set_rng_state(), synchronize(), manual_seed(), seed()]`
- Added some test cases in test_mps.py
- Added `mps.rst` to document the `torch.mps` module.
- Fixed the failure with `test_public_bindings.py`
Description of new files added:
- `torch/csrc/mps/Module.cpp`: implements `torch._C` module functions for `torch.mps` and `torch.backends.mps`.
- `torch/mps/__init__.py`: implements Python bindings for `torch.mps` module.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/94417
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD
# Summary
- Adds type hinting support for SDPA
- Updates the documentation adding warnings and notes on the context manager
- Adds scaled_dot_product_attention to the non-linear activation function section of nn.functional docs
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/94008
Approved by: https://github.com/cpuhrsch
Preferring dash over underscore in command-line options. Add `--command-arg-name` to the argument parser. The old arguments with underscores `--command_arg_name` are kept for backward compatibility.
Both dashes and underscores are used in the PyTorch codebase. Some argument parsers only have dashes or only have underscores in arguments. For example, the `torchrun` utility for distributed training only accepts underscore arguments (e.g., `--master_port`). The dashes are more common in other command-line tools. And it looks to be the default choice in the Python standard library:
`argparse.BooleanOptionalAction`: 4a9dff0e5a/Lib/argparse.py (L893-L895)
```python
class BooleanOptionalAction(Action):
def __init__(...):
if option_string.startswith('--'):
option_string = '--no-' + option_string[2:]
_option_strings.append(option_string)
```
It adds `--no-argname`, not `--no_argname`. Also typing `_` need to press the shift or the caps-lock key than `-`.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/94505
Approved by: https://github.com/ezyang, https://github.com/seemethere
Changes:
1. `typing_extensions -> typing-extentions` in dependency. Use dash rather than underline to fit the [PEP 503: Normalized Names](https://peps.python.org/pep-0503/#normalized-names) convention.
```python
import re
def normalize(name):
return re.sub(r"[-_.]+", "-", name).lower()
```
2. Import `Literal`, `Protocal`, and `Final` from standard library as of Python 3.8+
3. Replace `Union[Literal[XXX], Literal[YYY]]` to `Literal[XXX, YYY]`.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/94490
Approved by: https://github.com/ezyang, https://github.com/albanD
The previous sentence seemed to imply that sparse may not always be helpful, ie, your execution time may increase when using sparse. But the docs mentioned otherwise.
A simple re-ordering of two words in the documentation to better align with the contextual sentiment.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/93258
Approved by: https://github.com/cpuhrsch
We want to make TorchRec sharded models TorchScriptable.
TorchRec sharded models uses generic types Awaitable[W] and LazyAwaitable[W] (https://github.com/pytorch/torchrec/blob/main/torchrec/distributed/types.py#L212).
In sharded model those types are used instead of contained type W, having the initialization function that produces object of type W.
At the moment when the first attribute of W is requested - `LazyAwaitable[W]` will call its initialization function (on the same stack), cache the result inside and work transparently as an object of W. So we can think about it as a delayed object initialization.
To support this behavior in TorchScript - we propose a new type to TorchScript - `Await`.
In eager mode it works the same as `LazyAwaitable[W]` in TorchRec, being dynamically typed - acting as a type `W` while it is `Await[W]`.
Within torchscript it is `Await[W]` and can be only explicitly converted to W, using special function `torch.jit.awaitable_wait(aw)`.
Creation of this `Await[W]` is done via another special function `torch.jit.awaitable(func, *args)`.
The semantic is close to `torch.jit.Future`, fork, wait and uses the same jit mechanics (inline fork Closures) with the difference that it does not start this function in parallel on fork. It only stores as a lambda inside IValue that will be called on the same thread when `torch.jit.awaitable_wait` is called.
For example (more examples in this PR `test/jit/test_await.py`)
```
def delayed(z: Tensor) -> Tensor:
return Tensor * 3
@torch.jit.script
def fn(x: Tensor):
aw: Await[int] = torch.jit._awaitable(delayed, 99)
a = torch.eye(2)
b = torch.jit._awaitable_wait(aw)
return a + b + x
```
Functions semantics:
`_awaitable(func -> Callable[Tuple[...], W], *args, **kwargs) -> Await[W]`
Creates Await object, owns args and kwargs. Once _awaitable_wait calls, executes function func and owns the result of the function. Following _awaitable_wait calls will return this result from the first function call.
`_awaitable_wait(Await[W]) -> W`
Returns either cached result of W if it is not the first _awaitable_wait call to this Await object or calls specified function if the first.
`_awaitable_nowait(W) -> Await[W]`
Creates trivial Await[W] wrapper on specified object To be type complaint for the corner cases.
Differential Revision: [D42502706](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D42502706)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/90863
Approved by: https://github.com/davidberard98