Previously, we introduced new SymInt overloads for every function we wanted. This led to a lot of boilerplate, and also a lot of confusion about how the overloads needed to be implemented.
This PR takes a simpler but more risky approach: just take the original function and changes its ints to SymInts.
This is BC-breaking in the following ways:
* The C++ API for registering implementations for aten operators will change from int64_t to SymInt whenever you make this change. Code generated registrations in PyTorch do not change as codegen handles the translation automatically, but manual registrations will need to follow the change. Typically, if you now accept a SymInt where you previously only took int64_t, you have to convert it back manually. This will definitely break XLA, see companion PR https://github.com/pytorch/xla/pull/3914 Note that not all dispatch keys get the automatic translation; all the composite keys and Meta keys are modified to take SymInt directly (because they should handle them directly), and so there are adjustments for this.
This is not BC-breaking in the following ways:
* The user facing C++ API remains compatible. Even if a function changes from int to SymInt, the default C++ binding still takes only ints. (e.g., at::empty(IntArrayRef, ...). To call with SymInts, you must call at::empty_symint instead. This involved adding two more signatures to CppSignatureGroup; in many cases I refactored code to iterate over all signatures in the group instead of hard-coding the two that previously existed.
* This is TorchScript compatible; internally we treat SymInts as ints so there is no change to what happens at runtime in TorchScript. In particular, it's OK to reference an empty schema by its old type (using int types), as long as you're not doing string equality (which you shouldn't be), these parse to the same underyling type.
Structure of the PR:
* The general strategy of this PR is that, even when you write `SymInt` inside `native_functions.yaml`, sometimes, we will treat it *as if* it were an `int`. This idea pervades the codegen changes, where we have a translation from SymInt to c10::SymInt or int64_t, and this is controlled by a symint kwarg which I added and then audited all call sites to decide which I wanted. Here are some of the major places where we pick one or the other:
* The C++ FunctionSchema representation represents `SymInt` as `int`. There are a few places we do need to know that we actually have a SymInt and we consult `real_type()` to get the real type in this case. In particular:
* When we do schema validation of C++ operator registration, we must compare against true schema (as the C++ API will provide `c10::SymInt`, and this will only be accepted if the schema is `SymInt`. This is handled with cloneWithRealTypes before we check for schema differences.
* In `toIValue` argument parsing, we parse against the true schema value. For backwards compatibility reasons, I do still accept ints in many places where Layout/SymInt/etc were expected. (Well, accepting int where SymInt is expected is not BC, it's just the right logic!)
* In particular, because SymInt never shows up as type() in FunctionSchema, this means that we no longer need a dedicated Tag::SymInt. This is good, because SymInts never show up in mobile anyway.
* Changes to functorch/aten are mostly about tracking changes to the C++ API registration convention. Additionally, since SymInt overloads no longer exist, registrations for SymInt implementations are deleted. In many cases, the old implementations did not properly support SymInts; I did not add any new functionality with this PR, but I did try to annotate with TODOs where this is work to do. Finally, because the signature of `native::` API changed from int to SymInt, I need to find alternative APIs for people who were directly calling these functions to call. Typically, I insert a new dispatch call when perf doesn't matter, or use `at::compositeexplicitautograd` namespace to handle other caes.
* The change to `make_boxed_from_unboxed_functor.h` is so that we accept a plain IntList IValue anywhere a SymIntList is expected; these are read-only arguments so covariant typing is OK.
* I change how unboxing logic works slightly. Previously, we interpret the C++ type for Layout/etc directly as IntType JIT type, which works well because the incoming IValue is tagged as an integer. Now, we interpret the C++ type for Layout as its true type, e.g., LayoutType (change to `jit_type.h`), but then we accept an int IValue for it anyway. This makes it symmetric with SymInt, where we interpret the C++ type as SymIntType, and then accept SymInt and int IValues for it.
* I renamed the `empty.names` overload to `empty_names` to make it less confusing (I kept mixing it up with the real empty overload)
* I deleted the `empty.SymInt` overload, which ended up killing a pile of functions. (This was originally a separate PR but the profiler expect test was giving me grief so I folded it in.)
* I deleted the LazyDynamicOpsTest tests. These were failing after these changes, and I couldn't figure out why they used to be passing: they make use of `narrow_copy` which didn't actually support SymInts; they were immediately converted to ints.
* I bashed LTC into working. The patches made here are not the end of the story. The big problem is that SymInt translates into Value, but what if you have a list of SymInt? This cannot be conveniently represented in the IR today, since variadic Values are not supported. To work around this, I translate SymInt[] into plain int[] (this is fine for tests because LTC dynamic shapes never actually worked); but this will need to be fixed for proper LTC SymInt support. The LTC codegen also looked somewhat questionable; I added comments based on my code reading.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/83628
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD, https://github.com/bdhirsh
Context: In order to avoid the cluttering of the `torch.nn` namespace
the quantized modules namespace is moved to `torch.ao.nn`.
The list of the `nn.quantized` files that are being migrated:
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.functional` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.functional`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.dynamic`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized._reference` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized._reference`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantizable` → `torch.ao.nn.quantizable`
- [X] [Current PR] `torch.nn.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.qat`
- [X] `torch.nn.qat.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.modules`
- [X] `torch.nn.qat.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.dynamic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.qat`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic`
Majority of the files are just moved to the new location.
However, specific files need to be double checked:
- None
Differential Revision: [D36861197](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36861197/)
**NOTE FOR REVIEWERS**: This PR has internal Facebook specific changes or comments, please review them on [Phabricator](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36861197/)!
Differential Revision: [D36861197](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36861197)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78716
Approved by: https://github.com/jerryzh168
Previously, we introduced new SymInt overloads for every function we wanted. This led to a lot of boilerplate, and also a lot of confusion about how the overloads needed to be implemented.
This PR takes a simpler but more risky approach: just take the original function and changes its ints to SymInts.
This is BC-breaking in the following ways:
* The C++ API for registering implementations for aten operators will change from int64_t to SymInt whenever you make this change. Code generated registrations in PyTorch do not change as codegen handles the translation automatically, but manual registrations will need to follow the change. Typically, if you now accept a SymInt where you previously only took int64_t, you have to convert it back manually. This will definitely break XLA, see companion PR https://github.com/pytorch/xla/pull/3914 Note that not all dispatch keys get the automatic translation; all the composite keys and Meta keys are modified to take SymInt directly (because they should handle them directly), and so there are adjustments for this.
This is not BC-breaking in the following ways:
* The user facing C++ API remains compatible. Even if a function changes from int to SymInt, the default C++ binding still takes only ints. (e.g., at::empty(IntArrayRef, ...). To call with SymInts, you must call at::empty_symint instead. This involved adding two more signatures to CppSignatureGroup; in many cases I refactored code to iterate over all signatures in the group instead of hard-coding the two that previously existed.
* This is TorchScript compatible; internally we treat SymInts as ints so there is no change to what happens at runtime in TorchScript. In particular, it's OK to reference an empty schema by its old type (using int types), as long as you're not doing string equality (which you shouldn't be), these parse to the same underyling type.
Structure of the PR:
* The general strategy of this PR is that, even when you write `SymInt` inside `native_functions.yaml`, sometimes, we will treat it *as if* it were an `int`. This idea pervades the codegen changes, where we have a translation from SymInt to c10::SymInt or int64_t, and this is controlled by a symint kwarg which I added and then audited all call sites to decide which I wanted. Here are some of the major places where we pick one or the other:
* The C++ FunctionSchema representation represents `SymInt` as `int`. There are a few places we do need to know that we actually have a SymInt and we consult `real_type()` to get the real type in this case. In particular:
* When we do schema validation of C++ operator registration, we must compare against true schema (as the C++ API will provide `c10::SymInt`, and this will only be accepted if the schema is `SymInt`. This is handled with cloneWithRealTypes before we check for schema differences.
* In `toIValue` argument parsing, we parse against the true schema value. For backwards compatibility reasons, I do still accept ints in many places where Layout/SymInt/etc were expected. (Well, accepting int where SymInt is expected is not BC, it's just the right logic!)
* In particular, because SymInt never shows up as type() in FunctionSchema, this means that we no longer need a dedicated Tag::SymInt. This is good, because SymInts never show up in mobile anyway.
* Changes to functorch/aten are mostly about tracking changes to the C++ API registration convention. Additionally, since SymInt overloads no longer exist, registrations for SymInt implementations are deleted. In many cases, the old implementations did not properly support SymInts; I did not add any new functionality with this PR, but I did try to annotate with TODOs where this is work to do. Finally, because the signature of `native::` API changed from int to SymInt, I need to find alternative APIs for people who were directly calling these functions to call. Typically, I insert a new dispatch call when perf doesn't matter, or use `at::compositeexplicitautograd` namespace to handle other caes.
* The change to `make_boxed_from_unboxed_functor.h` is so that we accept a plain IntList IValue anywhere a SymIntList is expected; these are read-only arguments so covariant typing is OK.
* I change how unboxing logic works slightly. Previously, we interpret the C++ type for Layout/etc directly as IntType JIT type, which works well because the incoming IValue is tagged as an integer. Now, we interpret the C++ type for Layout as its true type, e.g., LayoutType (change to `jit_type.h`), but then we accept an int IValue for it anyway. This makes it symmetric with SymInt, where we interpret the C++ type as SymIntType, and then accept SymInt and int IValues for it.
* I renamed the `empty.names` overload to `empty_names` to make it less confusing (I kept mixing it up with the real empty overload)
* I deleted the `empty.SymInt` overload, which ended up killing a pile of functions. (This was originally a separate PR but the profiler expect test was giving me grief so I folded it in.)
* I deleted the LazyDynamicOpsTest tests. These were failing after these changes, and I couldn't figure out why they used to be passing: they make use of `narrow_copy` which didn't actually support SymInts; they were immediately converted to ints.
* I bashed LTC into working. The patches made here are not the end of the story. The big problem is that SymInt translates into Value, but what if you have a list of SymInt? This cannot be conveniently represented in the IR today, since variadic Values are not supported. To work around this, I translate SymInt[] into plain int[] (this is fine for tests because LTC dynamic shapes never actually worked); but this will need to be fixed for proper LTC SymInt support. The LTC codegen also looked somewhat questionable; I added comments based on my code reading.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/83628
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD, https://github.com/bdhirsh
Context: In order to avoid the cluttering of the `torch.nn` namespace
the quantized modules namespace is moved to `torch.ao.nn`.
The list of the `nn.quantized` files that are being migrated:
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.functional` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.functional`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.dynamic`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantized._reference` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized._reference`
- [X] `torch.nn.quantizable` → `torch.ao.nn.quantizable`
- [X] [Current PR] `torch.nn.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.qat`
- [X] `torch.nn.qat.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.modules`
- [X] `torch.nn.qat.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.dynamic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.qat`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules`
- [ ] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic`
Majority of the files are just moved to the new location.
However, specific files need to be double checked:
- None
Differential Revision: [D36861197](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36861197/)
**NOTE FOR REVIEWERS**: This PR has internal Facebook specific changes or comments, please review them on [Phabricator](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36861197/)!
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78716
Approved by: https://github.com/jerryzh168
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/81947
Transformer fastpath multiplexes two arguments, src_mask [seq_len x seq_len] and src_key_padding_mask [batch_size x seq_len], and later deduces the type based on mask shape.
In the event that batch_size == seq_len, any src_mask is wrongly interpreted as a src_key padding_mask. This is fixed by requiring a mask_type identifier be supplied whenever batch_size == seq_len.
Additionally, added support for src_mask in masked_softmax CPU path.
Test Plan: existing unit tests + new unit tests (batch_size == seq_len)
Differential Revision: D37932240
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/81947
Approved by: https://github.com/zrphercule
To fix https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/82060
When `input` is not explicitly converted to channels last while `conv` has, the output should also be in channels last. The root cause is that when input has IC of 1, `compute_columns2d` from `\aten\src\ATen\native\ConvolutionMM2d.cpp` would consider it as channels first:
We do have logic to make sure both input and weight have the same memory format even if they are given differently, like:
```
auto input = self.contiguous(memory_format);
auto weight = weight_.contiguous(memory_format);
```
But for a N1HW input, `.contiguous(MemoryFormat::ChannelsLast)` would not change its stride , and its `suggest_memory_format()` still returns `MemoryFormat::Contiguous`. That's how it went wrong.
Also updated the corresponding test cases, without this patch, the new test case would fail on forward path and runtime error on backward path.
attach old fail log on forward path:
```
FAIL: test_conv_thnn_nhwc_cpu_float32 (__main__.TestNNDeviceTypeCPU)
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/mingfeim/anaconda3/envs/pytorch-test-cpu/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/testing/_internal/common_device_type.py", line 377, in instantiated_test
result = test(self, **param_kwargs)
File "/home/mingfeim/anaconda3/envs/pytorch-test-cpu/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/testing/_internal/common_device_type.py", line 974, in only_fn
return fn(slf, *args, **kwargs)
File "test/test_nn.py", line 19487, in test_conv_thnn_nhwc
input_format=torch.contiguous_format, weight_format=torch.channels_last)
File "test/test_nn.py", line 19469, in helper
self.assertEqual(out, ref_out, exact_dtype=False)
File "/home/mingfeim/anaconda3/envs/pytorch-test-cpu/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/testing/_internal/common_utils.py", line 2376, in assertEqual
msg=(lambda generated_msg: f"{generated_msg} : {msg}") if isinstance(msg, str) and self.longMessage else msg,
File "/home/mingfeim/anaconda3/envs/pytorch-test-cpu/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/testing/_comparison.py", line 1093, in assert_equal
raise error_metas[0].to_error(msg)
AssertionError: Tensor-likes are not close!
Mismatched elements: 988 / 1024 (96.5%)
Greatest absolute difference: 42.0 at index (1, 2, 6, 6) (up to 1e-05 allowed)
Greatest relative difference: inf at index (0, 0, 2, 1) (up to 1.3e-06 allowed)
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/82392
Approved by: https://github.com/jbschlosser
Context: For a while slow gradcheck CI was skipping nearly all tests and this hid the fact that it should've been failing and timing out (10+h runtime for TestGradients). The CI configuration has since been fixed to correct this, revealing the test failures. This PR reenables slow gradcheck CI and makes it pass again.
This PR:
- makes slow and failing tests run in fast gradcheck mode only
- reduce the input size for slow gradcheck only for unary/binary ufuncs (alternatively, skip the test entirely)
- skip entire test files on slow gradcheck runner if they don't use gradcheck (test_ops, test_meta, test_decomp, test_ops_jit)
- reduces the input size for some ops
Follow ups:
1. Investigate slow mode failures https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/80411
2. See if we can re-enable slow gradcheck tests for some of the slow tests by reducing the sizes of their inputs
The following are failing in slow mode, they are now running in fast mode only.
```
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad___rmod___cuda_float64
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_linalg_householder_product_cuda_complex128
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad__masked_prod_cuda_complex128
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad__masked_prod_cuda_float64
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_linalg_matrix_power_cuda_complex128
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_cat_cuda_complex128
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_linalg_lu_factor_ex_cuda_float64
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_copysign_cuda_float64
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_cholesky_inverse_cuda_complex128
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_float_power_cuda_complex128
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_fmod_cuda_float64
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_float_power_cuda_float64
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_linalg_lu_cuda_float64
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_remainder_cuda_float64
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_repeat_cuda_complex128
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_prod_cuda_complex128
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_slice_scatter_cuda_float64
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_tile_cuda_complex128
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_pow_cuda_float64
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_pow_cuda_complex128
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_fft_*
test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_zero__cuda_complex128
test_fn_gradgrad_linalg_lu_factor_cuda_float64
test_fn_grad_div_trunc_rounding_cuda_float64
test_fn_grad_div_floor_rounding_cuda_float64
```
Marks the OpInfos for the following ops that run slowly in slow gradcheck as `fast_gradcheck` only (the left column represents runtime in seconds):
```
0 918.722 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_nn_functional_conv_transpose3d_cuda_float64
1 795.042 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_nn_functional_unfold_cuda_complex128
2 583.63 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_nn_functional_max_pool3d_cuda_float64
3 516.946 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_svd_cuda_complex128
4 503.179 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_linalg_svd_cuda_complex128
5 460.985 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_linalg_lu_cuda_complex128
6 401.04 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_linalg_lstsq_grad_oriented_cuda_complex128
7 353.671 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_nn_functional_max_pool2d_cuda_float64
8 321.903 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_nn_functional_gaussian_nll_loss_cuda_float64
9 307.951 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_stft_cuda_complex128
10 266.104 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_svd_lowrank_cuda_float64
11 221.032 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_istft_cuda_complex128
12 183.741 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_lu_unpack_cuda_complex128
13 132.019 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_nn_functional_unfold_cuda_float64
14 125.343 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_nn_functional_pad_constant_cuda_complex128
15 124.2 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_kron_cuda_complex128
16 123.721 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_pca_lowrank_cuda_float64
17 121.074 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_nn_functional_max_unpool3d_cuda_float64
18 119.387 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_rot90_cuda_complex128
19 112.889 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad__masked_normalize_cuda_complex128
20 107.541 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_dist_cuda_complex128
21 106.727 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_diff_cuda_complex128
22 104.588 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad__masked_cumprod_cuda_complex128
23 100.135 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_nn_functional_feature_alpha_dropout_with_train_cuda_float64
24 88.359 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_mH_cuda_complex128
25 86.214 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_nn_functional_max_unpool2d_cuda_float64
26 83.037 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_nn_functional_bilinear_cuda_float64
27 79.987 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad__masked_cumsum_cuda_complex128
28 77.822 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_diag_embed_cuda_complex128
29 76.256 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_mT_cuda_complex128
30 74.039 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_linalg_lu_solve_cuda_complex128
```
```
0 334.142 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_unfold_cuda_complex128
1 312.791 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_linalg_lu_factor_cuda_complex128
2 121.963 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_nn_functional_max_unpool3d_cuda_float64
3 108.085 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_diff_cuda_complex128
4 89.418 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_nn_functional_max_unpool2d_cuda_float64
5 72.231 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad___rdiv___cuda_complex128
6 69.433 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad___getitem___cuda_complex128
7 68.582 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_ldexp_cuda_complex128
8 68.572 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_linalg_pinv_cuda_complex128
9 67.585 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_nn_functional_glu_cuda_float64
10 66.567 test_fn_fwgrad_bwgrad_lu_cuda_float64
```
```
0 630.13 test_fn_gradgrad_nn_functional_conv2d_cuda_complex128
1 81.086 test_fn_gradgrad_linalg_solve_triangular_cuda_complex128
2 71.332 test_fn_gradgrad_norm_cuda_complex128
3 64.308 test_fn_gradgrad__masked_std_cuda_complex128
4 59.519 test_fn_gradgrad_div_no_rounding_mode_cuda_complex128
5 58.836 test_fn_gradgrad_nn_functional_adaptive_avg_pool3
```
Reduces the sizes of the inputs for:
- diff
- diag_embed
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/80514
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD
`torch.nn.grad` has its own implementations of gradients for conv1d, conv2d, and conv3d. This PR simplifies them by calling into the unified `aten::convolution_backward` backend instead.
The existing implementation of conv2d_weight is incorrect for some inputs (see issue #51430). This PR fixes the issue.
This PR expands coverage in test_nn to include conv1d_weight, conv2d_weight, and conv3d_weight, which were previously untested. It also expands the cases for conv2d to cover issue #51430.
Fixes#51430
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/81839
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD
Summary: We dont have a small fast path passing test for mha before, this diff added one for better testing
Test Plan: buck build mode/dev-nosan -c fbcode.platform=platform009 -c fbcode.enable_gpu_sections=true caffe2/test:nn && buck-out/dev/gen/caffe2/test/nn\#binary.par -r test_multihead_attn_fast_path_small_test
Differential Revision: D37834319
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/81432
Approved by: https://github.com/erichan1
Fixes#69413
After applying parametrization to any `nn.Module` we lose the ability to create a deepcopy of it e.g. it makes it impossible to wrap a module by an `AveragedModel`.
Specifically, the problem is that the `deepcopy` tries to invoke `__getstate__` if object hasn't implemented its own `__deepcopy__` magic method. But we don't allow serialization of the parametrized modules: `__getstate__` raises an error.
My solution is just to create a default `__deepcopy__` method when it doesn't exist yet.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/80811
Approved by: https://github.com/pearu, https://github.com/albanD
`test_conv_transposed_large` expects bitwise perfect results in fp16 on CUDA, but this behavior isn't guaranteed by cuDNN (e.g., in the case of FFT algos).
This PR just changes the tolerance on the test to account for these cases.
CC @ptrblck @ngimel
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78147
Approved by: https://github.com/ngimel
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78298
Also back out "improve LayerNorm bfloat16 performance on CPU".
These layer norm changes seem fine, but they are causing `LayerNorm` to not use AVX2 instructions, which is causing performance on internal models to degrade. More investigation is needed to find the true root cause, but we should unland to mitigate the issue ASAP.
I left `mixed_data_type.h` around since there are some other files depending on it.
Differential Revision: [D36675352](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D36675352/)
Approved by: https://github.com/tenpercent
Fixes#68172. Generally, this corrects multiple flaky convolution unit test behavior seen on ROCm.
The MIOpen integration has been forcing benchmark=True when calling `torch._C._set_cudnn_benchmark(False)`, typically called by `torch.backends.cudnn.set_flags(enabled=True, benchmark=False)`. We now add support for MIOpen immediate mode to avoid benchmarking during MIOpen solution selection.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/77438
Approved by: https://github.com/ngimel, https://github.com/malfet
Double-header bug fix:
- As reported by jansel, dtypes are still showing up as integers
when the schema is an optional dtype. This is simple enough to
fix and I added a test for it. But while I was at it...
- I noticed that the THPMemoryFormat_new idiom with "unused" name
doesn't actually work, the repr of the returned memory format
object is wrong and this shows up when we try to log the args/kwargs.
So I fixed memory format to do it properly along with everything
else.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/77135
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyangfb.com>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/77543
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD, https://github.com/jansel
Summary: For user to convert nested tensor more easily. Some impl detail might change on user's need.
Test Plan: buck test mode/dev caffe2/test:nn -- test_nested_tensor_from_mask
Differential Revision: D36191182
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/76942
Approved by: https://github.com/jbschlosser
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/76333
The current PyTorch multi-head attention and transformer
implementations are slow. This should speed them up for inference.
ghstack-source-id: 154737857
(Note: this ignores all push blocking failures!)
Test Plan: CI
Reviewed By: cpuhrsch
Differential Revision: D35239925
fbshipit-source-id: 5a7eb8ff79bc6afb4b7d45075ddb2a24a6e2df28
**Previous behavior**: compute inner product, then normalize.
**This patch**: first normalize, then compute inner product. This should be more numerically stable because it avoids losing precision in inner product for inputs with large norms.
By design ensures that cosine similarity is within `[-1.0, +1.0]`, so it should fix [#29442](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/29442).
P.S. I had to change tests because this implementation handles division by 0 differently.
This PR computes cosine similarity as follows: <x/max(eps, ||x||), y/max(eps, ||y||)>.
Let f(x,y) = <x,y>/(||x|| * ||y||), then
df/dx = y/(||x|| * ||y||) - (||y||/||x|| * <x,y> * x)/(||x|| * ||y||)^2.
The changed test checks division by zero in backward when x=0 and y != 0.
For this case the non-zero part of the gradient is just y / (||x|| * ||y||).
The previous test evaluates y/(||x|| * ||y||) to y / eps, and this PR to 1/eps * y/||y||.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/31378
Approved by: https://github.com/ezyang, https://github.com/albanD
Summary:
In this PR, we try to optimize PReLU op in CPU path, and enable BFloat16 support based on the optimized PReLU.
The original implementation uses parallel_for to accelerate operation speed, but vectorization is not used. It can be optimized by using TensorIterator, both including parallelization and vectorization.
The difference between PReLU and other activation function ops, is that PReLU supports a learnable parameter `weight`. When called without arguments, nn.PReLU() uses a single parameter `weight` across all input channels. If called with nn.PReLU(nChannels), a separate `weight` is used for each input channel. So we cannot simply use TensorIterator because `weight` is different for each input channel.
In order to use TensorIterator, `weight` should be broadcasted to `input` shape. And with vectorization and parallel_for, this implementation is much faster than the original one. Another advantage is, don't need to separate `share weights` and `multiple weights` in implementation.
We test the performance between the PReLU implementation of public Pytorch and the optimized PReLU in this PR, including fp32/bf16, forward/backward, share weights/multiple weights configurations. bf16 in public Pytorch directly reuses `Vectorized<scalar_t>` for `BFloat16`.
Share weights:
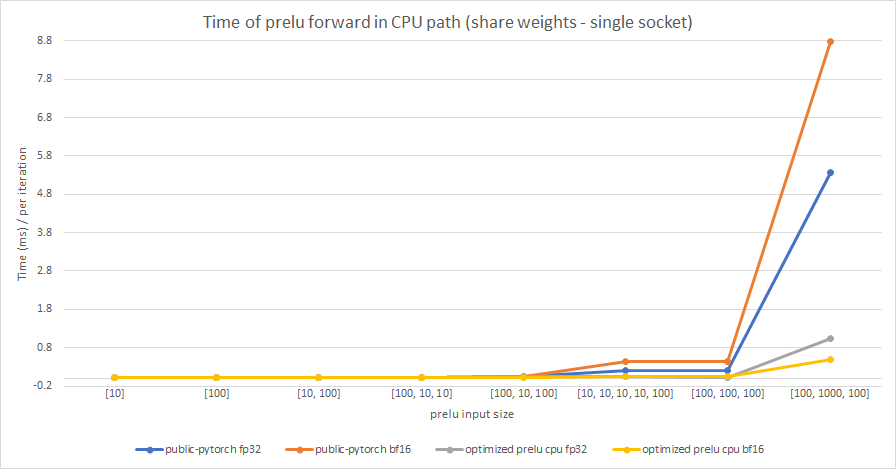
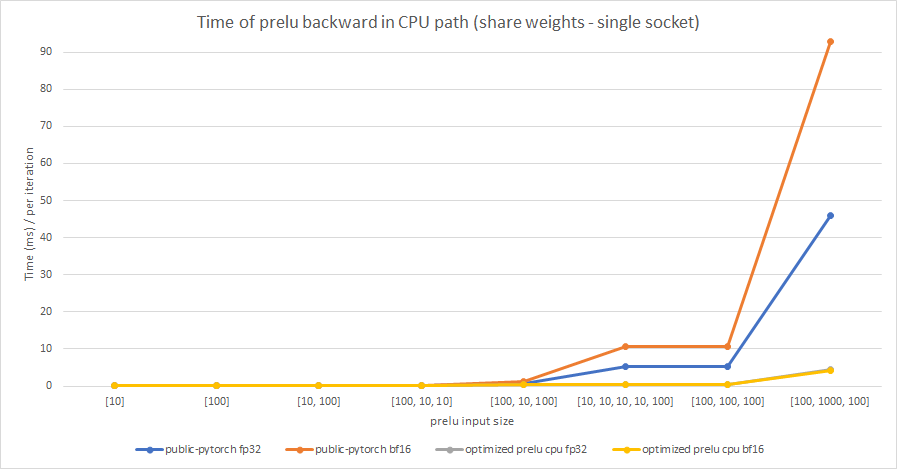
Multiple weights:
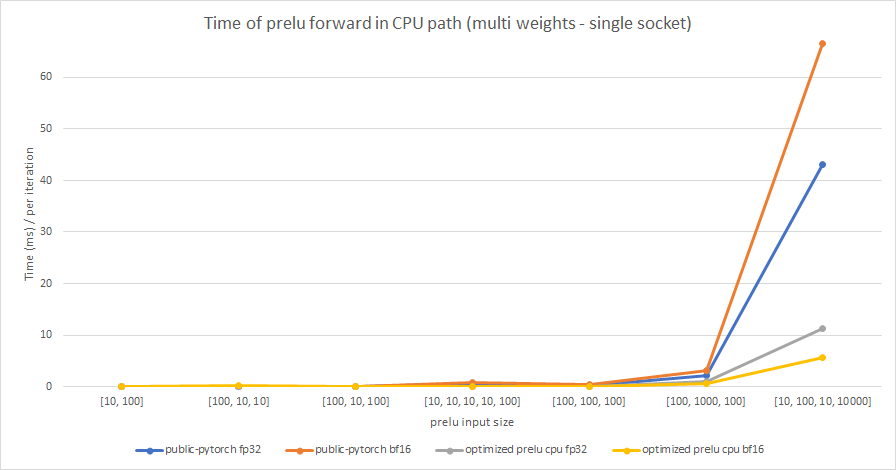
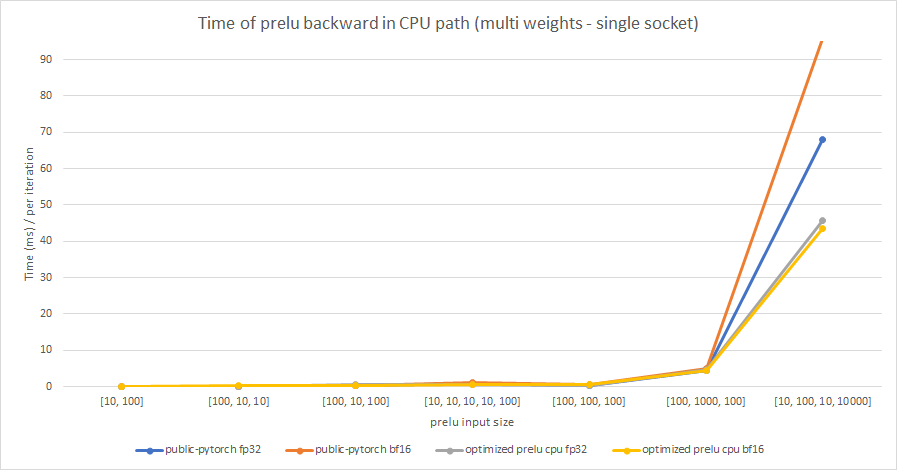
cc albanD mruberry jbschlosser walterddr
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63634
Reviewed By: yinghai
Differential Revision: D34031616
Pulled By: frank-wei
fbshipit-source-id: 04e2a0f9e92c658fba7ff56b1010eacb7e8ab44c
(cherry picked from commit ed262b15487557720bb0d498f9f2e8fcdba772d9)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/75421
As part of FSDP work, we will be relying on `_register_load_state_dict_pre_hook` to manage some specific logic related to loading state dicts.
This PR adds a test to ensure that _register_load_state_dict_pre_hook can be
used to register hooks on modules that will be used in a nested way, and then
calling load_state_dict on the overall module still calls those hooks
appropriately.
Differential Revision: [D35434726](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D35434726/)
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD
Summary: The primary issue for enabling sparsity to work with QAT
convert (unlike normal quantization convert) is that when the
parametrized module undergoes the QAT convert, the parametrizations need
to be maintained. If the parametrizations don't
get transfered during the convert, the sparsifier would lose its
connection to the model. In practice this was handled using the
transfer_parametrizations_and_params function to move the weight and
bias and any associated paramerizations to the new module. This PR also adds
tests for transfer_parametrizations_and_params and type_before_parametrizations
to test_nn.py and also added comments to the test code for
composability.
Test Plan: python test/test_ao_sparsity.py TestComposability
python test/test_nn.py TestNN
Reviewers:
Subscribers:
Tasks:
Tags:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/74848
Approved by: https://github.com/vkuzo, https://github.com/Lezcano
Summary:
Add BFloat16 support for logsigmoid, hardsigmoid, hardshrink, softshrink, hardswish and softplus on CPU, and optimize the performance of softshrink.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63134
Reviewed By: yinghai
Differential Revision: D34897992
Pulled By: frank-wei
fbshipit-source-id: 4c778f5271d6fa54dd78158258941def8d9252f5
(cherry picked from commit decda0e3debf56cc5c4d7faea41b1165a7cabe12)
For a GroupNorm module, if num_channels is not divisible by num_groups, we need to report an error when defining a module other than at the running step.
example:
```
import torch
m = torch.nn.GroupNorm(5, 6)
x = torch.randn(1, 6, 4, 4)
y = m(x)
```
before:
```
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "group_norm_test.py", line 8, in <module>
y = m(x)
File "/home/xiaobinz/miniconda3/envs/pytorch_mater/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1111, in _call_impl
return forward_call(*input, **kwargs)
File "/home/xiaobinz/miniconda3/envs/pytorch_mater/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/normalization.py", line 271, in forward
input, self.num_groups, self.weight, self.bias, self.eps)
File "/home/xiaobinz/miniconda3/envs/pytorch_mater/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/nn/functional.py", line 2500, in group_norm
return torch.group_norm(input, num_groups, weight, bias, eps, torch.backends.cudnn.enabled)
RuntimeError: Expected number of channels in input to be divisible by num_groups, but got input of shape [1, 6, 4, 4] and num_groups=5
```
after:
```
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "group_norm_test.py", line 6, in <module>
m = torch.nn.GroupNorm(5, 6)
File "/home/xiaobinz/miniconda3/envs/pytorch_test/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/normalization.py", line 251, in __init__
raise ValueError('num_channels must be divisible by num_groups')
```
This PR also update the doc of num_groups.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/74293
Approved by: https://github.com/jbschlosser
Fixes#71415
I have implemented the changes that replicate what @to-mi did in this [PR](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/65986#issue-1012959443) for the 3D case :
> Fixes#64977
>
> Avoids creating a tensor for and calculating `input` gradient if it's not needed in the backward pass of `grid_sample` (2d case, native CPU & CUDA kernels). Especially the tensor creation seemed time consuming (see #64977).
>
> Brief description of the changes:
>
> * I have tried to go with rather minimal changes. It would probably be possible to make a more elegant version with a bit larger refactoring (or possibly with better understanding of PyTorch internals and C++ functionalities).
>
> * Changed the `native_functions.yaml` and `derivatives.yaml` so that the gradient input mask is passed to the functions.
>
> * Changed the CPU kernels:
> (1) added `bool input_requires_grad` template parameter to the `backward` function,
> (2) added if branches based on it to remove `input` gradient computations if it's not requested,
> (3) feed in `TensorAccessor<scalar_t, 3>* gInp_slice_ptr` instead of `TensorAccessor<scalar_t, 3>& gInp_slice` so that I can pass a `nullptr` in case gradient for `input` is not requested. (A bit inelegant perhaps, but allows to keep one signature for `backward` function and not require breaking it to smaller pieces. Perhaps there's a more elegant way to achieve this?)
>
> * Changed CUDA kernel:
> (1) added ~`bool input_requires_grad` template parameter~ `const bool input_requires_grad` argument to the `backward` function,
> (2) added if branches based on it to remove `input` gradient computations if it's not requested,
> (3) feed in `TensorInfo<scalar_t, index_t>()` instead of `getTensorInfo<scalar_t, index_t>(grad_input)` in case gradient for `input` is not requested.
>
> * Modified tests in `test/test_nn.py` so that they run also cases with no `input` gradient needed.
>
> * Have not touched the CPU fallback kernel.
Note: the changes number (3) are N/A in this case.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/71759
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72941
Simple test for MHA, use cos similarity as metric since scaling generate mismatch. Cuda is validated, CPU fix a following (We can land this with onlyCuda flag, and remove it once CPU is also done)
Test Plan:
For cuda:
buck build mode/opt -c fbcode.enable_gpu_sections=true caffe2/test:nn && buck-out/gen/caffe2/test/nn\#binary.par -r test_native_multihead_attention_cuda_float32 2>&1 | pastry
Reviewed By: swolchok
Differential Revision: D33906921
fbshipit-source-id: ad447401eb7002f22ed533d620a6b544524b3f58
(cherry picked from commit 45b778da27)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72944
Doesn't make sense to develop it in core right now.
ghstack-source-id: 149456040
Test Plan:
CI
run MHA benchmark in benchmark_transformers.py to make sure it doesn't crash
Reviewed By: zrphercule
Differential Revision: D34283104
fbshipit-source-id: 4f0c7a6bc066f938ceac891320d4cf4c3f8a9cd6
(cherry picked from commit b9df65e97c)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72671
The existing kernel did not handle cases where D % 4 != 0 or dim_per_head % 4 != 0. Now we have a non-vectorized kernel for these cases.
ghstack-source-id: 149201477
Test Plan: Updated test_nn to cover these cases.
Reviewed By: zrphercule, ngimel
Differential Revision: D34119371
fbshipit-source-id: 4e9b4d9b636224ef2c433593f6f236df040de782
(cherry picked from commit f5393878e4)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72464
We had some trouble getting this component (and this test!) right, so let's test it.
ghstack-source-id: 149201478
Test Plan: new test passes
Reviewed By: zrphercule
Differential Revision: D33992477
fbshipit-source-id: cc377eed5d4a4412b42bdabf360601c6e52947cf
(cherry picked from commit 9832867b12)
Summary:
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/71521 attempted to fix an issue where the `test_conv_large` test was producing `NaN` values after the backward pass, yielding a bogus comparison between the result and the expected result. While tweaking the initialization of the conv layer seemed to fix this behavior, it was actually just masking the real issue, which was that `grad_weight` is not guaranteed to be initialized in `raw_cudnn_convolution_backward_weight_out` when the backward operation is split.
Specifically, the `grad_weight` tensor is expected to be directly written to by a `cudnn` kernel (which does occur in most cases) so it does not need to be initialized, but splitting introduces an intermediate `grad_weight_` tensor that holds the intermediate gradients and then accumulates into `grad_weight` without initializing it first. This PR tweaks this behavior so that now accumulation is done with a zero'd tensor, and also adds the change of doing the accumulation in an accumulation dtype. The hacky workaround masking the issue is also reverted, with the safeguard against comparing `NaN` values (using the reference tensor for scale computation) kept in place.
CC ngimel ptrblck
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72157
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D34147547
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 056c19f727eeef96347db557528272e24eae4223
(cherry picked from commit 24c7f77a81)
Summary:
The only difference with plain list/dict now is that nn.Parameters are
handled specially and registered as parameters properly.
test_nn and parametrization works locally.
Will see in CI if DP is fixed as well.
Tentative fix for https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/36035
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/70499
Reviewed By: jbschlosser, alexeib
Differential Revision: D34005332
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 7e76b0873d0fec345cb537e2a6ecba0258e662b9
(cherry picked from commit dc1e6f8d86)
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/71720
This PR removes the old warnings for `recompute_scale_factor` and `align_corners`.
Looking at this, I realize that the tests I modified don't really catch whether or not a warning is created for `recompute_scale_factor`. If desired, I can add a couple lines into the tests there to pass a floating point in the `scale_factors` kwarg, along with `recompute_scale_factor=None`.
Let me know how this looks, thanks so much!
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72093
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D33917615
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: e822f0a15b813ecf312cdc6ed0b693e7f1d1ca89
(cherry picked from commit c14852b85c)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/torchrec/pull/39
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/facebookresearch/torchrec/pull/6
This makes it so that shared parameters get their own entry in `named_parameters`.
More broadly, this makes it so that
```
params_and_buffers = {**mod.named_named_parameters(remove_duplicate=False), **mod.named_buffers(remove_duplicate=False)}
_stateless.functional_call(mod, params_and_buffers, args, kwargs)
```
is identical to calling the original module's forwards pass.
cc pietern mrshenli pritamdamania87 zhaojuanmao satgera rohan-varma gqchen aazzolini osalpekar jiayisuse SciPioneer H-Huang
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/71542
Reviewed By: jbschlosser, albanD
Differential Revision: D33716716
Pulled By: Chillee
fbshipit-source-id: ff1ed9980bd1a3f7ebaf695ee5e401202b543213
(cherry picked from commit d6e3ad3cd0)
Summary:
Hi,
The PR fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/71096. It aims to scan all the test files and replace ` ALL_TENSORTYPES` and `ALL_TENSORTYPES2` with `get_all_fp_dtypes`.
I'm looking forward to your viewpoints!
Thanks!
cc: janeyx99 kshitij12345
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/71153
Reviewed By: jbschlosser, mruberry
Differential Revision: D33533346
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: 75e79ca2756c1ddaf0e7e0289257fca183a570b3
(cherry picked from commit da54b54dc5)
Summary:
This PR twiddles the parameters of the conv layer in `test_conv_large` to better avoid NaN values. Previously, this test would cause a NaN to be computed for `scale` (propagated from `.mean()` on the `.grad` tensor). This NaN would then be propagated to the scaled gradients via division, resulting in a bogus `assertEqual` check as `NaN == NaN` is by default true. (This behavior was observed on V100 and A100).
To improve visibility of failures in the event of NaNs in `grad1`, scale is now computed from `grad2`.
Interestingly enough, we discovered this issue when trying out some less common setups that broke this test; it turns out those breakages were cases where there were no NaN values (leading to an actual `assertEqual` check that would fail for `float16`).
CC ptrblck ngimel puririshi98
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/71521
Reviewed By: anjali411
Differential Revision: D33776705
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: a1ec4792cba04c6322b22ef5b80ce08579ea4cf6
(cherry picked from commit d207bd9b87)
Summary:
We found a discrepancy between cpu & CUDA when using RNN modules where input shapes containing 0s would cause an invalid configuration argument error in CUDA (kernel grid size is 0), while returning a valid tensor in CPU cases.
A reproducer:
```
import torch
x = torch.zeros((5, 0, 3)).cuda()
gru = torch.nn.GRU(input_size=3, hidden_size=4).to("cuda")
gru(x)
```
Run with `CUDA_LAUNCH_BLOCKING=1` set.
cc ngimel albanD
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/71696
Reviewed By: mikaylagawarecki
Differential Revision: D33743674
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: e9334175d10969fdf1f9c63985910d944bbd26e7
(cherry picked from commit 70838ba69b)
Summary:
Helps fix a part of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/69865
The first commit just migrates everything as is.
The second commit uses the "device" variable instead of passing "cuda" everywhere
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/70872
Reviewed By: jbschlosser
Differential Revision: D33455941
Pulled By: janeyx99
fbshipit-source-id: 9d9ec8c95f1714c40d55800e652ccd69b0c314dc
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69727
Still need to test the backward ones. We would need to update gradgradcheck to check forward over backward.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D33031728
Pulled By: soulitzer
fbshipit-source-id: 86c59df5d2196b5c8dbbb1efed9321e02ab46d30
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/68476
We implemented all of the following `dict` methods for `ParameterDict`
- `get `
- `setdefault`
- `popitem`
- `fromkeys`
- `copy`
- `__or__`
- `__ior__`
- `__reversed__`
- `__ror__`
The behavior of these new methods matches the expected behavior of python `dict` as defined by the language itself: https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#typesmapping
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69403
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D33187111
Pulled By: jbschlosser
fbshipit-source-id: ecaa493837dbc9d8566ddbb113b898997e2debcb
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69272
In transformer encoder and MHA, masked_softmax's mask is a 2D tensor (B, D), where input is a 4D tensor (B, H, D, D).
This mask could be simply broadcasted to a (B, H, D, D) like input, and then do a regular masked_softmax, however it will bring the problem of non-contiguous mask & consume more memory.
In this diff, we maintained mask's shape unchanged, while calc the corresponding mask for input in each cuda thread.
This new layout is not currently supported in CPU yet.
Test Plan: buck build mode/opt -c fbcode.enable_gpu_sections=true caffe2/test:nn && buck-out/gen/caffe2/test/nn\#binary.par -r test_masked_softmax
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D32605557
fbshipit-source-id: ef37f86981fdb2fb264d776f0e581841de5d68d2
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69268
This diff enabled native masked softmax on CUDA, also expanded our current warp_softmax to accept masking.
The mask in this masked softmax has to be the same shape as input, and has to be contiguous.
In a following diff I will submit later, I will have encoder mask layout included, where input is BHDD and mask is BD.
Test Plan: buck build mode/opt -c fbcode.enable_gpu_sections=true caffe2/test:nn && buck-out/gen/caffe2/test/nn\#binary.par -r test_masked_softmax
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D32338419
fbshipit-source-id: 48c3fde793ad4535725d9dae712db42e2bdb8a49
Summary:
Towards [convolution consolidation](https://fb.quip.com/tpDsAYtO15PO).
Introduces the general `convolution_backward` function that uses the factored-out backend routing logic from the forward function.
Some notes:
* `finput` is now recomputed in the backward pass for the slow 2d / 3d kernels instead of being saved from the forward pass. The logic for is based on the forward computation and is present in `compute_finput2d` / `compute_finput3d` functions in `ConvUtils.h`.
* Using structured kernels for `convolution_backward` requires extra copying since the backend-specific backward functions return tensors. Porting to structured is left as future work.
* The tests that check the routing logic have been renamed from `test_conv_backend_selection` -> `test_conv_backend` and now also include gradcheck validation using an `autograd.Function` hooking up `convolution` to `convolution_backward`. This was done to ensure that gradcheck passes for the same set of inputs / backends.
The forward pass routing is done as shown in this flowchart (probably need to download it for it to be readable since it's ridiculous):
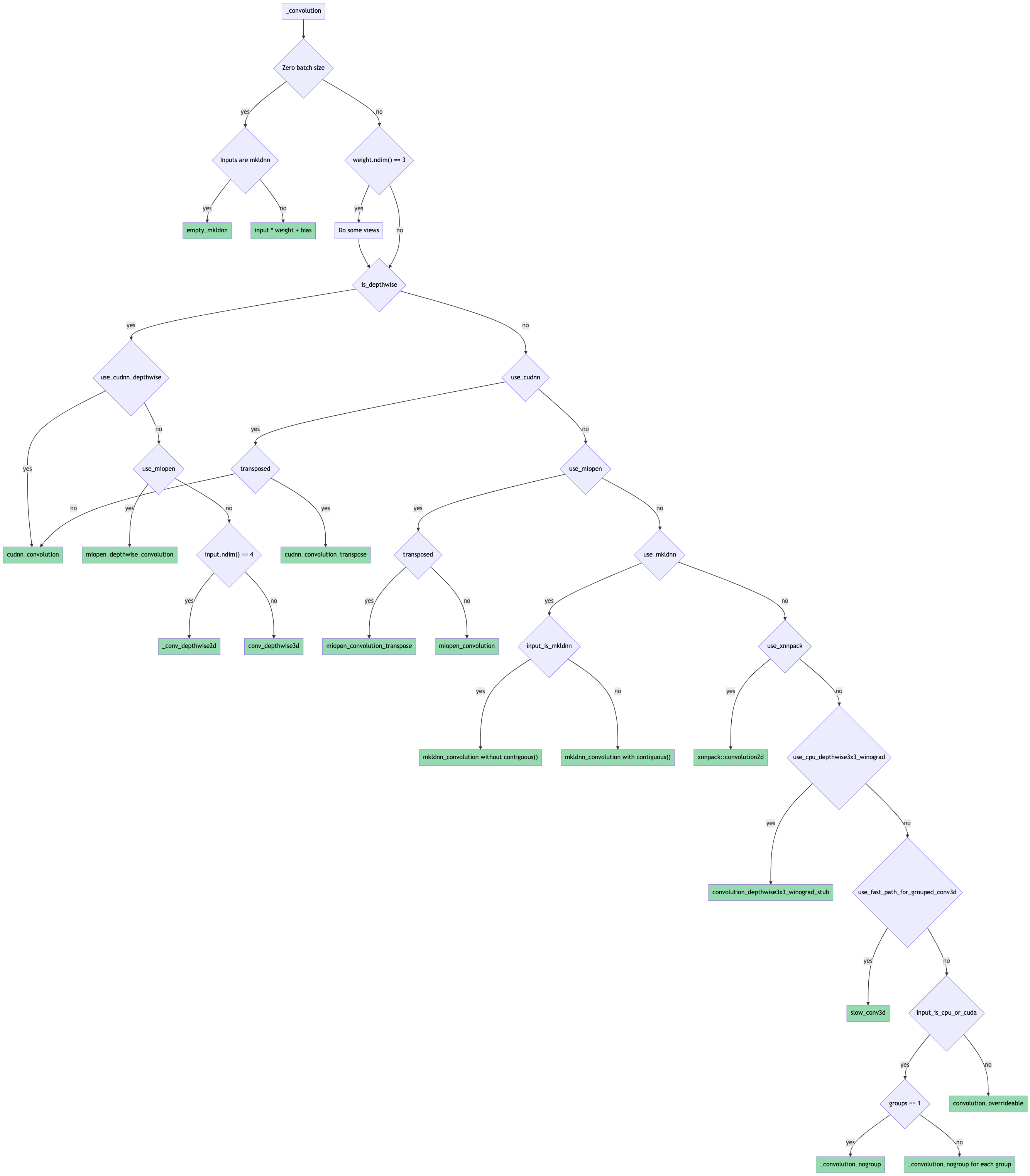
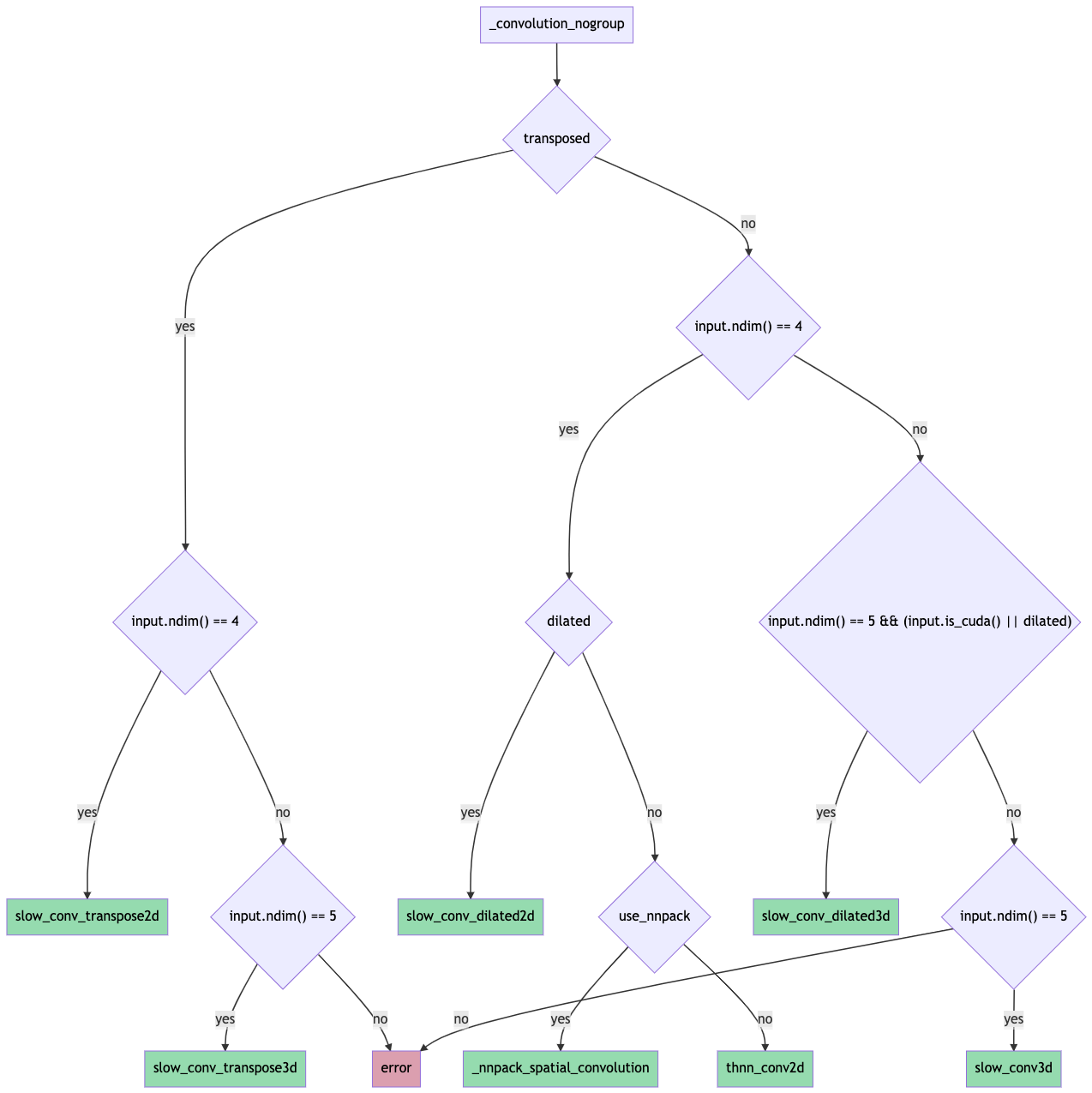
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/65219
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D32611368
Pulled By: jbschlosser
fbshipit-source-id: 26d759b7c908ab8f19ecce627acea7bd3d5f59ba
Summary:
Adds native_dropout to have a reasonable target for torchscript in auto diff. native_dropout has scale and train as arguments in its signature, this makes native_dropout more consistent with other operators and removes conditionals in the autodiff definition.
cc gmagogsfm
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63937
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D32477657
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: d37b137a37acafa50990f60c77f5cea2818454e4
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/53647
With this if a test forgets to add `dtypes` while using `dtypesIf`, following error is raised
```
AssertionError: dtypes is mandatory when using dtypesIf however 'test_exponential_no_zero' didn't specify it
```
**Tested Locally**
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/68186
Reviewed By: VitalyFedyunin
Differential Revision: D32468581
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 805e0855f988b77a5d8d4cd52b31426c04c2200b
Summary:
This PR introduces a new function `_select_conv_backend` that returns a `ConvBackend` enum representing the selected backend for a given set of convolution inputs and params.
The function and enum are exposed to python for testing purposes through `torch/csrc/Module.cpp` (please let me know if there's a better place to do this).
A new set of tests validates that the correct backend is selected for several sets of inputs + params. Some backends aren't tested yet:
* nnpack (for mobile)
* xnnpack (for mobile)
* winograd 3x3 (for mobile)
Some flowcharts for reference:


Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/67790
Reviewed By: zou3519
Differential Revision: D32280878
Pulled By: jbschlosser
fbshipit-source-id: 0ce55174f470f65c9b5345b9980cf12251f3abbb
Summary:
This PR makes several changes:
- Changed function `bool cudnn_conv_use_channels_last(...)` to `at::MemoryFormat cudnn_conv_suggest_memory_format(...)`
- Removed `resize_` in cudnn convolution code. Added a new overloading method `TensorDescriptor::set` that also passes the desired memory format of the tensor.
- Disabled the usage of double + channels_last on cuDNN Conv-Relu and Conv-Bias-Relu. Call `.contiguous(memory_format)` before passing data to cuDNN functions.
- Disabled the usage of cuDNN fused Conv-Bias-Relu in cuDNN < 8.0 version due to a CUDNN_STATUS_NOT_SUPPORTED error. Instead, use the native fallback path.
- Let Conv-Bias-Relu code respect the global `allow_tf32` flag.
From cuDNN document, double + NHWC is genenrally not supported.
Close https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/66968
Fix https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/55301
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/65594
Reviewed By: jbschlosser, malfet
Differential Revision: D32175766
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 7ba079c9f7c46fc56f8bfef05bad0854acf380d7
Summary:
Partially fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/66066
This PR:
- cleans up op-specific testing from test_autograd. test_autograd should be reserved for testing generic autograd functionality
- tests related to an operator are better colocated
- see the tracker for details
What to think about when moving tests to their correct test suite:
- naming, make sure its not too generic
- how the test is parametrized, sometimes we need to add/remove a device/dtype parameter
- can this be merged with existing tests
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/67413
Reviewed By: jbschlosser, albanD
Differential Revision: D32031480
Pulled By: soulitzer
fbshipit-source-id: 8e13da1e58a38d5cecbfdfd4fe2b4fe6f816897f
Summary:
Fix https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/67239
The CUDA kernels for `adaptive_max_pool2d` (forward and backward) were written for contiguous output. If outputs are non-contiguous, first create a contiguous copy and let the kernel write output to the contiguous memory space. Then copy the output from contiguous memory space to the original non-contiguous memory space.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/67697
Reviewed By: ejguan
Differential Revision: D32112443
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 0e3bf06d042200c651a79d13b75484526fde11fe
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/66879
This adds a quantized implementation for bilinear gridsample. Bicubic interpolation cannot be supported as easily since we rely on the linearity of quantization to operate on the raw values, i.e.
f(q(a), q(b)) = q(f(a, b)) where f is the linear interpolation function.
ghstack-source-id: 141321116
Test Plan: test_quantization
Reviewed By: kimishpatel
Differential Revision: D31656893
fbshipit-source-id: d0bc31da8ce93daf031a142decebf4a155943f0f
Summary:
Removes the 3D special case logic in `_convolution_double_backward()` that never worked.
The logic was never called previously since `convolution()` expands input / weight from 3D -> 4D before passing them to backends; backend-specific backward calls thus save the 4D version to pass to `_convolution_double_backward()`.
The new general `convolution_backward()` saves the original 3D input / weight, uncovering the bug.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/67283
Reviewed By: anjali411
Differential Revision: D32021100
Pulled By: jbschlosser
fbshipit-source-id: 0916bcaa77ef49545848b344d6385b33bacf473d