Reland of PR #94924. The purpose of this PR is to deal with the complicated interactions between MKL and OpenMP.
There are two improvements:
1. It uses a flag to avoid infinite mutual recursion in calling find_package(MKL) and find_package(OpenMP) in some cases.
2. The logic of finding iomp5 is improved and now we can test MKLDNN under ASAN.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/104224
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
**Summary**
Update onednn from v2.7.3 to v3.1.1.
It is bc-breaking as some APIs are changed on oneDNN side. Changes include:
- PyTorch code where oneDNN is directly called
- Submodule `third_party/ideep` to adapt to oneDNN's new API.
- CMAKE files to fix build issues.
**Test plan**
Building issues and correctness are covered by CI checks.
For performance, we have run TorchBench models to ensure there is no regression. Below is the comparison before and after oneDNN update.

Note:
- Base commit of PyTorch: da322ea
- CPU: Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8380 CPU @ 2.30GHz (Ice Lake)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/97957
Approved by: https://github.com/jgong5, https://github.com/jerryzh168
This one is a wrapper upon `mkl_gemm_bf16bf16f32` which is used in flash attention kernel on intel 4th gen xeon.
Fallback path has also been implemented on cpublas::gemm in case `mkl_gemm_bf16bf16f32` is not available.
The primary target of this change is to help build kernels in `scaled_dot_product_attention`, e.g. flash attention and efficient attention. In the attention kernel, `q @ k.T = attn`, q and k will be given as bfloat16 and attn is float32. This is actually both beneficial for both performance and accuracy, since attn will be used to compute lazy softmax which has to be done in float32.
This patch also adds routine from OpenBlas `sbgemm_` which also has a signature of bf16 * bf16 -> fp32; but since OpenBlas routine has different name from MKL's, we can not use `sbgemm_` in MKL.
In the fallback path, it takes two steps to do the computation: first do gemm with beta = 0; then add beta * C in full precision. Idea from @peterbell10 not to truncate C to bfloat16, so as to avoid unnecessary accuracy loss.
ref: https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/docs/onemkl/developer-reference-c/2023-0/cblas-gemm-bf16bf16f32.html
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/107196
Approved by: https://github.com/jgong5, https://github.com/peterbell10
Summary:
This stack of PR's integrates cuSPARSELt into PyTorch.
This PR adds support for cuSPARSELt into the build process.
It adds in a new flag, USE_CUSPARSELT that defaults to false.
When USE_CUSPASRELT=1 is specified, the user can also specify
CUSPASRELT_ROOT, which defines the path to the library.
Compiling pytorch with cusparselt support can be done as follows:
``
USE_CUSPARSELT=1
CUSPARSELT_ROOT=/path/to/cusparselt
python setup.py develop
```
Test Plan:
Reviewers:
Subscribers:
Tasks:
Tags:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/103700
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD
This patch is part of half float performance optimization on CPU:
* add specification for dtype `Half` in `Vectorized<>` under both avx256 and avx512.
* add specification for dtype `Half` in functional utils, e.g. `vec::map_reduce<>()`, which uses float32 as accumulate type.
Also add a helper struct `vec_hold_type<scalar_t>`, since Vectorized<Half>::value_type is pointing to its underlying storage type which is `uint16_t`, leading to error if the kernel uses `Vec::value_type`.
Half uses the same logic as BFloat16 in the Vectorized<>, each half vector is mapped to 2x float vectors for computation.
Notice that this patch modified the cmake files by adding **-mf16c** on AVX2 build, from https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/x86-Options.html, we can see that all the hardware platforms that support **avx2** already have **f16c**
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/96076
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
This is reland of PR #94402 that tries to solve the additional link issues.
The PR #94402 failed because caffe2::mkl had been converted to private dependency while libtorch_cuda_linalg hadn't linked to it explicitly. This is fixed in commit 4373bf0ae3dee32afc178f9d51a4154d6c5904c6
We also replace more references of MKL_LIBRARIES by caffe2::mkl in this PR.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/94924
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
We greatly simplify the handing of OpenMP in CMake by using caffe2::openmp target thoroughly. We follow the old behavior by defaulting to MKL OMP library and detecting OMP flags otherwise.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/91576
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
### Description
These changes were made to assure, that the code that tests the vector instruction set extensions not only compiles but also runs to detect it properly for MSVC:
- INCLUDE(CheckCSourceRuns) instead of INCLUDE(CheckCSourceCompiles)
- INCLUDE(CheckCXXSourceRuns) instead of INCLUDE(CheckCXXSourceCompiles)
- CHECK_C_SOURCE_RUNS instead of CHECK_C_SOURCE_COMPILES
- CHECK_CXX_SOURCE_RUNS instead of CHECK_CXX_SOURCE_COMPILES
### Issue
#82553
### Testing
I tried the [code changes](86246b3c58) on a copy of [FindAVX.cmake](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/cmake/Modules/FindAVX.cmake) in my repository [convolution-benchmarks](https://github.com/JohT/convolution-benchmarks) and could verify that the detection works properly now.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/82554
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
When we use pytorch with unregistered blas, spack set BLAS=Generic.
pytorch is searched only libblas.
If the blas package's blas library name is not libblas, spack install py-torch is failed.
This PR set blas lirary names to GENERIC_BLAS_LIBRARIES environment variable, and py-torch is found blas library.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/74269
Approved by: https://github.com/kit1980
Re-landing #68111/#74596
## Description
v0.5 PR of this [RFC](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/49444).
On the basis of #50256, the below improvements are included:
* The [v0.5 release branch](https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneDNN/releases/tag/graph-v0.5) of the oneDNN Graph API is used
* The fuser now works with the profiling graph executor. We have inserted type check nodes to guard the profiled tensor properties.
### User API:
The optimization pass is disabled by default. Users could enable it by:
```
torch.jit.enable_onednn_fusion(True)
```
`torch.jit.freeze` should be used after tracing (recommended) or scripting a model.
### Performance:
[pytorch/benchmark](https://github.com/pytorch/benchmark) tool is used to compare the performance:
* SkyLake 8180 (1 socket of 28 cores):
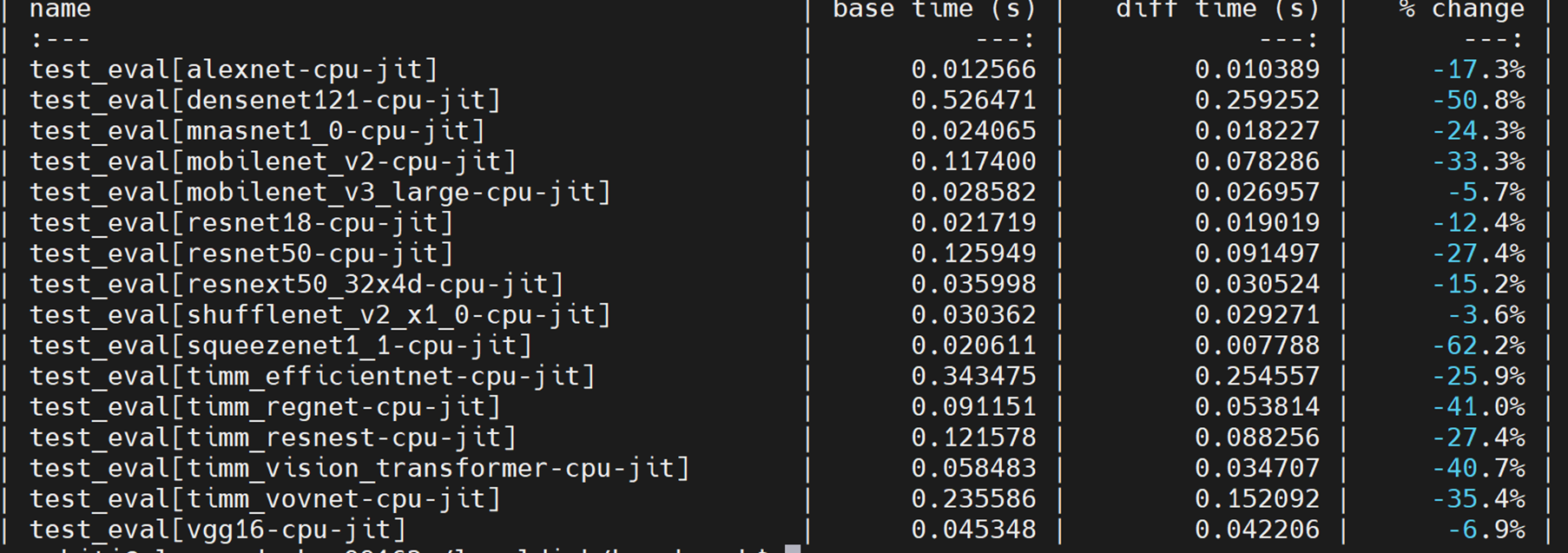
* SkyLake 8180 (single thread):
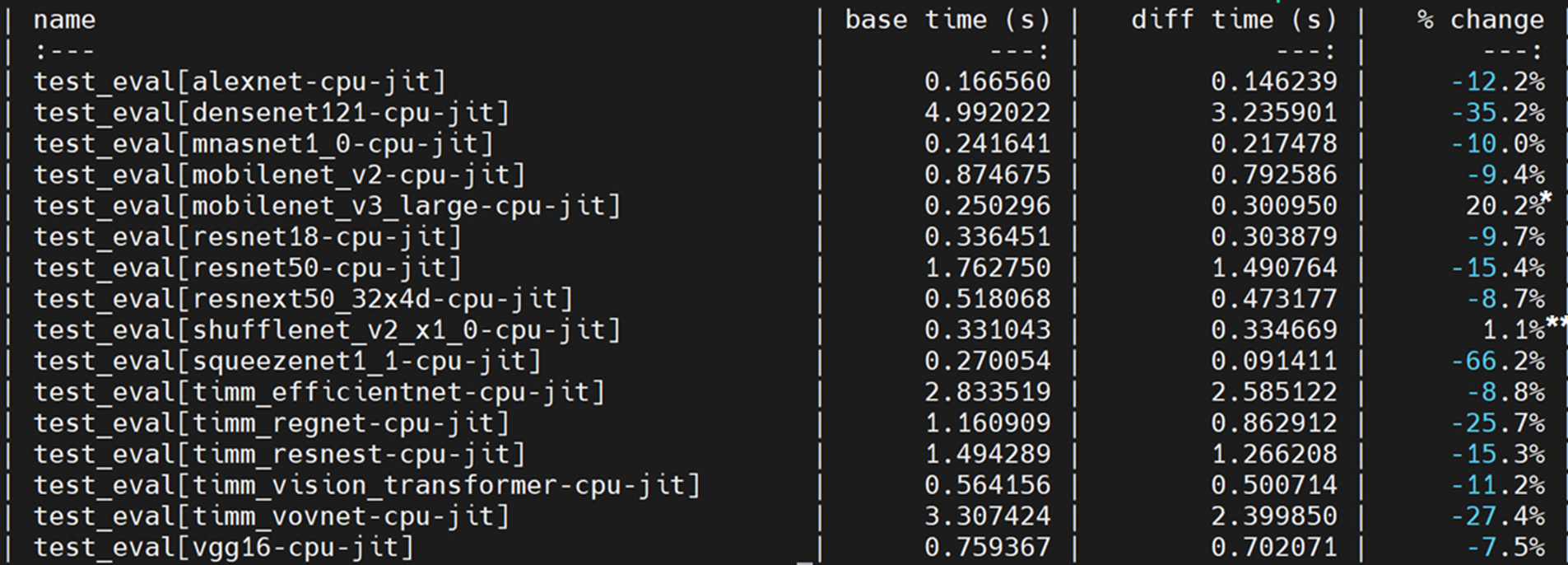
* By mapping hardswish to oneDNN Graph, it’s 8% faster than PyTorch JIT (NNC + OFI)
** We expect performance gain after mapping transpose, contiguous & view to oneDNN graph ops
### Directory structure of the integration code
Fuser-related code is placed under:
```
torch/csrc/jit/codegen/onednn/
```
Optimization pass registration is done in:
```
torch/csrc/jit/passes/onednn_graph_fuser.h
```
CMake for the integration code is in:
```
caffe2/CMakeLists.txt
cmake/public/mkldnn.cmake
cmake/Modules/FindMKLDNN.cmake
```
## Limitations
* In this PR, we only support Pytorch-oneDNN-Graph integration on Linux platform. Support on Windows and MacOS will be enabled as a next step.
* We have only optimized the inference use-case.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/76622
Approved by: https://github.com/eellison
Summary:
## Description
Preview4 PR of this [RFC](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/49444).
On the basis of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/50256, the below improvements are included:
- The [preview4 release branch](https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneDNN/releases/tag/graph-v0.4.1) of the oneDNN Graph API is used
- The fuser now works with the profiling graph executor. We have inserted type check nodes to guard the profiled tensor properties.
### User API:
The optimization pass is disabled by default. Users could enable it by:
```
torch.jit.enable_onednn_fusion(True)
```
### Performance:
[pytorch/benchmark](https://github.com/pytorch/benchmark) tool is used to compare the performance:
- SkyLake 8180 (1 socket of 28 cores):

- SkyLake 8180 (single thread):

\* By mapping hardswish to oneDNN Graph, it’s 8% faster than PyTorch JIT (NNC + OFI)
\** We expect performance gain after mapping transpose, contiguous & view to oneDNN graph ops
### Directory structure of the integration code
Fuser-related code are placed under:
```
torch/csrc/jit/codegen/onednn/
```
Optimization pass registration is done in:
```
torch/csrc/jit/passes/onednn_graph_fuser.h
```
CMake for the integration code is:
```
caffe2/CMakeLists.txt
```
## Limitations
- In this PR, we have only supported the optimization on Linux platform. The support on Windows and MacOS will be enabled as the next step.
- We have only optimized the inference use case.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/68111
Reviewed By: eellison
Differential Revision: D34584878
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: ce817aa8cc9052ee9ed930c9cf66be83449e61a4
(cherry picked from commit cd17683aa7d9c0947df45a1ab53627feff795587)
Summary:
This PR upgrades oneDNN to v2.5.2, and includes some building support for oneDNN v2.5.2.
v2.4 changes:
- Improved performance for future Intel Xeon Scalable processor (code name Sapphire Rapids). The functionality is disabled by default and should be enabled via CPU dispatcher control.
- Improved binary primitive performance for cases when one of the tensors is broadcasted.
- Improved performance of reduction primitive, reorder, shuffle primitives.
- Improved performance of depthwise convolution forward propagation for processors with Intel AVX5-12 support
- Improved performance of forward inner product primitive for the shapes with minibatch equal to 1 for processors with Intel AVX-512 support
- Improved performance of int8 matmul and inner product primitives for processors with Intel AVX2 and Intel DL Boost support
v2.5 changes:
- Improved performance for future Intel Xeon Scalable processors (code name Sapphire Rapids). The functionality is now enabled by default and requires Linux kernel 5.16.
- Improved performance of matmul primitive for processors with Intel AVX-512 support.
v2.5.2 changes:
- Fixed performance regression in binary primitive with broadcast
- Fixed segmentation fault in depthwise convolution primitive for shapes with huge spatial size for processors with Intel AVX-512 support
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/71546
Reviewed By: george-qi
Differential Revision: D33827108
Pulled By: VitalyFedyunin
fbshipit-source-id: 8f5a19b331c82af5b0783f081e061e1034a93952
(cherry picked from commit 9705212fe9)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69216
Currently `torch_cpu` has command line arguments relating to cuda
libraries e.g. `-DMAGMA_V2`. This happens because
`include_directories` and `add_definitions` indescriminately change
the compile commands of all targets.
Instead creating a proper magma target allows limiting the flags to
just `torch_cuda`.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: dagitses
Differential Revision: D33794174
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 762eabf3b9576bef94e8caa3ed4764c0e2c72b08
(cherry picked from commit f7d127b654)
Summary:
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/66406
implemented z arch 14/15 vector SIMD additions.
so far besides bfloat all other types have their SIMD implementation.
it has 99% coverage and currently passing the local test.
it is concise and the main SIMD file is only one header file
it's using template metaprogramming, mostly. but still, there are a few macrosses left with the intention not to modify PyTorch much
Sleef supports z15
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/66407
Reviewed By: mrshenli
Differential Revision: D33370163
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 0e5a57f31b22a718cd2a9ac59753fb468cdda140
Summary:
This PR upgrades oneDNN to [v2.3.3](https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneDNN/releases/tag/v2.3.3) and includes [Graph API preview release](https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneDNN/releases/tag/graph-v0.2) in one package.
- oneDNN will be located at `pytorch/third_party/ideep/mkl-dnn/third_party/oneDNN`
- The version of oneDNN will be [v2.3.3](https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneDNN/releases/tag/v2.3.3)
The main changes on CPU:
- v2.3
- Extended primitive cache to improve primitive descriptor creation performance.
- Improved primitive cache performance in multithreaded configurations.
- Introduced initial optimizations for bfloat16 compute functionality for future Intel Xeon Scalable processor (code name Sapphire Rapids).
- Improved performance of binary primitive and binary post-op for cases with broadcast and mixed source and destination formats.
- Improved performance of reduction primitive
- Improved performance of depthwise convolution primitive with NHWC activations for training cases
- v2.3.1
- Improved int8 GEMM performance for processors with Intel AVX2 and Intel DL Boost support
- Fixed integer overflow for inner product implementation on CPUs
- Fixed out of bounds access in GEMM implementation for Intel SSE 4.1
- v2.3.2
- Fixed performance regression in fp32 inner product primitive for processors with Intel AVX512 support
- v2.3.3
- Reverted check for memory descriptor stride validity for unit dimensions
- Fixed memory leak in CPU GEMM implementation
More changes can be found in https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneDNN/releases.
- The Graph API provides flexible API for aggressive fusion, and the preview2 supports fusion for FP32 inference. See the [Graph API release branch](https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneDNN/tree/dev-graph-preview2) and [spec](https://spec.oneapi.io/onednn-graph/latest/introduction.html) for more details. A separate PR will be submitted to integrate the oneDNN Graph API to Torchscript graph.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63748
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D32153889
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 536071168ffe312d452f75d54f34c336ca3778c1
Summary:
OpenBLAS recently added support for bfloat16 GEMM, so this change has PyTorch call out to OpenBLAS for that, like it does for single and double precision
Our goal is to try to enable PyTorch to make calls to "sbgemm" in OpenBLAS.
We are prepared (if it is your preference) to add fences to the code to limit this change to the Power architecture,
but our first instinct is that anyone on any architecture that enables access to sbgemm in their OpenBLAS library
should be able to use this code. (but again, we respect that as we are just starting to modify PyTorch, we respect
your guidance!)
(there is no issue number related to this)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58831
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D29951900
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 3d0a4a638ac95b2ff2e9f6d08827772e28d397c3
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/62445
PyTorch currently uses the old style of compiling CUDA in CMake which is just a
bunch of scripts in `FindCUDA.cmake`. Newer versions support CUDA natively as
a language just like C++ or C.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: ejguan
Differential Revision: D31503350
fbshipit-source-id: 2ee817edc9698531ae1b87eda3ad271ee459fd55
Summary:
This PR: (1) enables the use of a system-provided Intel TBB for building PyTorch, (2) removes `tbb:task_scheduler_init` references since it has been removed from TBB a while ago (3) marks the implementation of `_internal_set_num_threads` with a TODO as it requires a revision that fixes its thread allocation logic.
Tested with `test/run_test`; no new tests are introduced since there are no behavioral changes (removal of `tbb::task_scheduler_init` has no impact on the runtime behavior).
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/61934
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D29805416
Pulled By: cbalioglu
fbshipit-source-id: 22042b428b57b8fede9dfcc83878d679a19561dd
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/61903
### Remaining Tasks
- [ ] Collate results of benchmarks on two Intel Xeon machines (with & without CUDA, to check if CPU throttling causes issues with GPUs) - make graphs, including Roofline model plots (Intel Advisor can't make them with libgomp, though, but with Intel OpenMP).
### Summary
1. This draft PR produces binaries with with 3 types of ATen kernels - default, AVX2, AVX512 . Using the environment variable `ATEN_AVX512_256=TRUE` also results in 3 types of kernels, but the compiler can use 32 ymm registers for AVX2, instead of the default 16. ATen kernels for `CPU_CAPABILITY_AVX` have been removed.
2. `nansum` is not using AVX512 kernel right now, as it has poorer accuracy for Float16, than does AVX2 or DEFAULT, whose respective accuracies aren't very good either (#59415).
It was more convenient to disable AVX512 dispatch for all dtypes of `nansum` for now.
3. On Windows , ATen Quantized AVX512 kernels are not being used, as quantization tests are flaky. If `--continue-through-failure` is used, then `test_compare_model_outputs_functional_static` fails. But if this test is skipped, `test_compare_model_outputs_conv_static` fails. If both these tests are skipped, then a third one fails. These are hard to debug right now due to not having access to a Windows machine with AVX512 support, so it was more convenient to disable AVX512 dispatch of all ATen Quantized kernels on Windows for now.
4. One test is currently being skipped -
[test_lstm` in `quantization.bc](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/59098) - It fails only on Cascade Lake machines, irrespective of the `ATEN_CPU_CAPABILITY` used, because FBGEMM uses `AVX512_VNNI` on machines that support it. The value of `reduce_range` should be used as `False` on such machines.
The list of the changes is at https://gist.github.com/imaginary-person/4b4fda660534f0493bf9573d511a878d.
Credits to ezyang for proposing `AVX512_256` - these use AVX2 intrinsics but benefit from 32 registers, instead of the 16 ymm registers that AVX2 uses.
Credits to limo1996 for the initial proposal, and for optimizing `hsub_pd` & `hadd_pd`, which didn't have direct AVX512 equivalents, and are being used in some kernels. He also refactored `vec/functional.h` to remove duplicated code.
Credits to quickwritereader for helping fix 4 failing complex multiplication & division tests.
### Testing
1. `vec_test_all_types` was modified to test basic AVX512 support, as tests already existed for AVX2.
Only one test had to be modified, as it was hardcoded for AVX2.
2. `pytorch_linux_bionic_py3_8_gcc9_coverage_test1` & `pytorch_linux_bionic_py3_8_gcc9_coverage_test2` are now using `linux.2xlarge` instances, as they support AVX512. They were used for testing AVX512 kernels, as AVX512 kernels are being used by default in both of the CI checks. Windows CI checks had already been using machines with AVX512 support.
### Would the downclocking caused by AVX512 pose an issue?
I think it's important to note that AVX2 causes downclocking as well, and the additional downclocking caused by AVX512 may not hamper performance on some Skylake machines & beyond, because of the double vector-size. I think that [this post with verifiable references is a must-read](https://community.intel.com/t5/Software-Tuning-Performance/Unexpected-power-vs-cores-profile-for-MKL-kernels-on-modern-Xeon/m-p/1133869/highlight/true#M6450). Also, AVX512 would _probably not_ hurt performance on a high-end machine, [but measurements are recommended](https://lemire.me/blog/2018/09/07/avx-512-when-and-how-to-use-these-new-instructions/). In case it does, `ATEN_AVX512_256=TRUE` can be used for building PyTorch, as AVX2 can then use 32 ymm registers instead of the default 16. [FBGEMM uses `AVX512_256` only on Xeon D processors](https://github.com/pytorch/FBGEMM/pull/209), which are said to have poor AVX512 performance.
This [official data](https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/specification-updates/xeon-scalable-spec-update.pdf) is for the Intel Skylake family, and the first link helps understand its significance. Cascade Lake & Ice Lake SP Xeon processors are said to be even better when it comes to AVX512 performance.
Here is the corresponding data for [Cascade Lake](https://cdrdv2.intel.com/v1/dl/getContent/338848) -
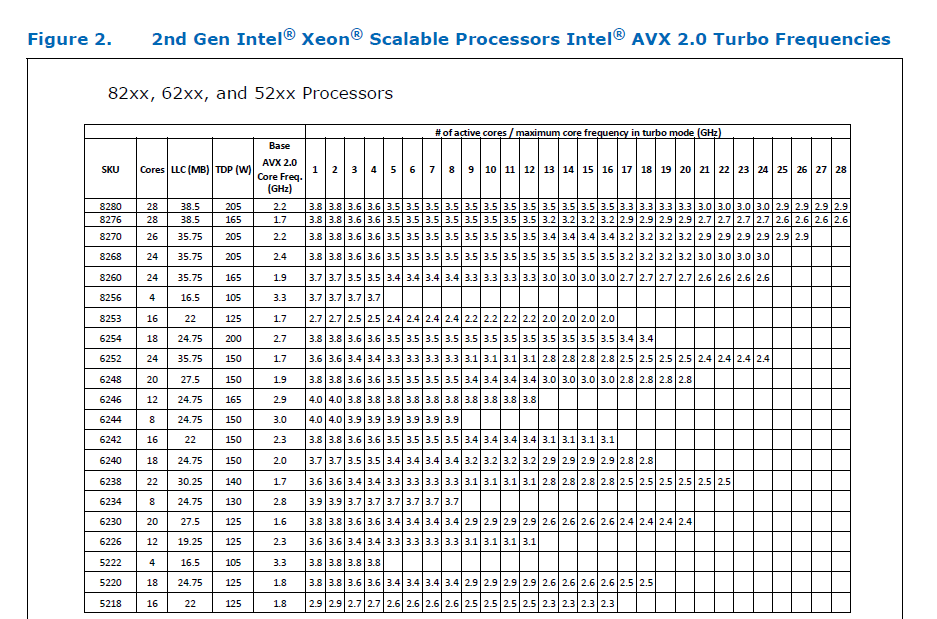
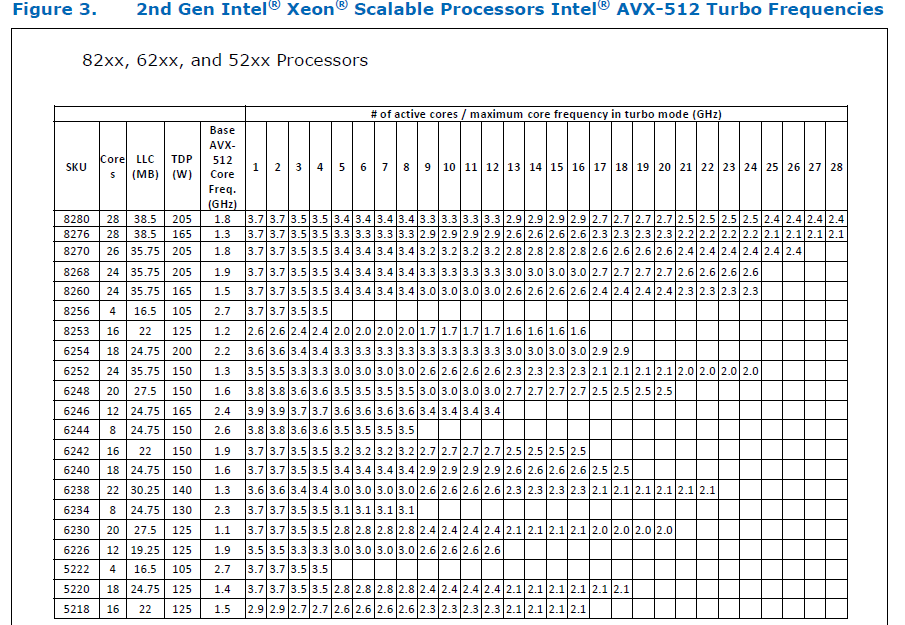
The corresponding data isn't publicly available for Intel Xeon SP 3rd gen (Ice Lake SP), but [Intel mentioned that the 3rd gen has frequency improvements pertaining to AVX512](https://newsroom.intel.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/11/2021/04/3rd-Gen-Intel-Xeon-Scalable-Platform-Press-Presentation-281884.pdf). Ice Lake SP machines also have 48 KB L1D caches, so that's another reason for AVX512 performance to be better on them.
### Is PyTorch always faster with AVX512?
No, but then PyTorch is not always faster with AVX2 either. Please refer to #60202. The benefit from vectorization is apparent with with small tensors that fit in caches or in kernels that are more compute heavy. For instance, AVX512 or AVX2 would yield no benefit for adding two 64 MB tensors, but adding two 1 MB tensors would do well with AVX2, and even more so with AVX512.
It seems that memory-bound computations, such as adding two 64 MB tensors can be slow with vectorization (depending upon the number of threads used), as the effects of downclocking can then be observed.
Original pull request: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/56992
Reviewed By: soulitzer
Differential Revision: D29266289
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 2d5e8d1c2307252f22423bbc14f136c67c3e6184
Summary:
This is a PR on build system that provides support for cross compiling on Jetson platforms.
The major change is:
1. Disable try runs for cross compiling in `COMPILER_WORKS`, `BLAS`, and `CUDA`. They will not be able to perform try run on a cross compile setup
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/59764
Reviewed By: soulitzer
Differential Revision: D29524363
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: f06d1ad30b704c9a17d77db686c65c0754db07b8
Summary:
Before that, only dynamically linked OpenBLAS compield with OpenMP could
be found.
Also get rid of hardcoded codepath for libgfortran.a in FindLAPACK.cmake
Only affects aarch64 linux builds
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/59428
Reviewed By: agolynski
Differential Revision: D28891314
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 5af55a14c85ac66551ad2805c5716bbefe8d55b2
Summary:
While trying to build PyTorch with BLIS as the backend library,
we found a build issue due to some missing include files.
This was caused by a missing directory in the search path.
This patch adds that path in FindBLIS.cmake.
Fixes #{issue number}
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58166
Reviewed By: zou3519
Differential Revision: D28640460
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: d0cd3a680718a0a45788c46a502871b88fbadd52
Summary:
These changes provide the user with an additional option to choose the DNNL+BLIS path for PyTorch.
This assumes BLIS is already downloaded or built from source and the necessary library file is available at the location: $BLIS_HOME/lib/libblis.so and include files are available at: $BLIS_HOME/include/blis/blis.h and $BLIS_HOME/include/blis/cblas.h
Export the below variables to build PyTorch with MKLDNN+BLIS and proceed with the regular installation procedure as below:
$export BLIS_HOME=path-to-BLIS
$export PATH=$BLIS_HOME/include/blis:$PATH LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$BLIS_HOME/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
$export BLAS=BLIS USE_MKLDNN_CBLAS=ON WITH_BLAS=blis
$python setup.py install
CPU only Dockerfile to build PyTorch with AMD BLIS is available at : docker/cpu-blis/Dockerfile
Example command line to build using the Dockerfile:
sudo DOCKER_BUILDKIT=1 docker build . -t docker-image-repo-name
Example command line to run the built docker container:
sudo docker run --name container-name -it docker-image-repo-name
Fixes #{issue number}
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/54953
Reviewed By: glaringlee
Differential Revision: D27466799
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: e03bae9561be3a67429df3b1be95a79005c63050
Summary:
*Context:* https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/53406 added a lint for trailing whitespace at the ends of lines. However, in order to pass FB-internal lints, that PR also had to normalize the trailing newlines in four of the files it touched. This PR adds an OSS lint to normalize trailing newlines.
The changes to the following files (made in 54847d0adb9be71be4979cead3d9d4c02160e4cd) are the only manually-written parts of this PR:
- `.github/workflows/lint.yml`
- `mypy-strict.ini`
- `tools/README.md`
- `tools/test/test_trailing_newlines.py`
- `tools/trailing_newlines.py`
I would have liked to make this just a shell one-liner like the other three similar lints, but nothing I could find quite fit the bill. Specifically, all the answers I tried from the following Stack Overflow questions were far too slow (at least a minute and a half to run on this entire repository):
- [How to detect file ends in newline?](https://stackoverflow.com/q/38746)
- [How do I find files that do not end with a newline/linefeed?](https://stackoverflow.com/q/4631068)
- [How to list all files in the Git index without newline at end of file](https://stackoverflow.com/q/27624800)
- [Linux - check if there is an empty line at the end of a file [duplicate]](https://stackoverflow.com/q/34943632)
- [git ensure newline at end of each file](https://stackoverflow.com/q/57770972)
To avoid giving false positives during the few days after this PR is merged, we should probably only merge it after https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/54967.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/54737
Test Plan:
Running the shell script from the "Ensure correct trailing newlines" step in the `quick-checks` job of `.github/workflows/lint.yml` should print no output and exit in a fraction of a second with a status of 0. That was not the case prior to this PR, as shown by this failing GHA workflow run on an earlier draft of this PR:
- https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/runs/2197446987?check_suite_focus=true
In contrast, this run (after correcting the trailing newlines in this PR) succeeded:
- https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/54737/checks?check_run_id=2197553241
To unit-test `tools/trailing_newlines.py` itself (this is run as part of our "Test tools" GitHub Actions workflow):
```
python tools/test/test_trailing_newlines.py
```
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D27409736
Pulled By: samestep
fbshipit-source-id: 46f565227046b39f68349bbd5633105b2d2e9b19