constraints:
1. No support for gradient accumulation
2. CPU offload runs step() on CPU. In future PRs ideally we'd run this on GPU.
3. When CPU offload + optimizer overlap, we have to copy the flat_param grad to CPU with non_blocking=False, otherwise step() might run on invalid data.
4. Step is waited on in post backward final cb, when in theory it can wait until the next forward.
Differential Revision: [D44809582](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D44809582/)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/98667
Approved by: https://github.com/awgu, https://github.com/fegin
Purely out of preference, this PR renames the streams to `_unshard_stream` instead of `_streams_unshard` etc. since the former reads more naturally. The PR also removes some duplicated comments and adds back a unit test that streams are shared.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/104966
Approved by: https://github.com/rohan-varma
When creating DeviceMesh, _init_process_group() would validate that all calling ranks pass in the same `mesh` argument. In FSDP, we are currently creating the DeviceMesh based on the pg of the root state so the mesh will always be valid. Adding the flag to DeviceMesh, so we can skip the all_gather_tensor of the validation during construction time.
_validate_mesh is default to True, but we manually flip it to False when initializing device mesh in FSDP's _runtime_utils.py.
Will modify skipping pg creation if existed for both 1D and 2D cases and then delete _init_process_groups flag in a follow up PR.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/104807
Approved by: https://github.com/wanchaol
Not sure, how it worked before, but if arguments must be annotated is optional if they are defaulted to None
Towards enabling mypy-1.4.1 in lintrunner
<!--
copilot:poem
-->
### <samp>🤖 Generated by Copilot at 5e1b9f4</samp>
> _We annotate the arguments of doom_
> _To show the `None` values of gloom_
> _We improve the type checking and readability_
> _With `Optional` annotations of metal-ity_
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/105022
Approved by: https://github.com/izaitsevfb, https://github.com/huydhn, https://github.com/Skylion007
Originally, we didn't enable BWD for colwise embedding because we thought it was just for inference, but it turns out that we do need it for training. So, let's enable it for now and unit test is also added.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/104820
Approved by: https://github.com/fegin
Summary:
This diff does the following:
1. re-enable single_file_per_rank for FsspecWriter, as the issue of file slicing error is resolved because of [https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99167]
2. remove sync_files from FsspecWriter as there is no fsspec equivalence.
3. remove the internal implementation of FsspecWriter/Reader, as it has been upstreamed to PyTorch OSS
4. keep the internal test for manifold inside internal as we can only test it in fb environment
5. consolidate test to remove duplicates
6. remove unnecessary TARGETS
Test Plan:
```
buck test @//mode/dev-nosan //caffe2/test/distributed/checkpoint/fb:test_fsspec_filesystem -- --print-passing-details
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 1 test in 54.894s
OK
/usr/local/fbcode/platform010/lib/python3.8/tempfile.py:818: ResourceWarning: Implicitly cleaning up <TemporaryDirectory '/tmp/tmpzomokvh6'>
_warnings.warn(warn_message, ResourceWarning)
Buck UI: https://www.internalfb.com/buck2/4cb722a2-3ee7-48f2-a9ef-55ee6fb1a498
Test UI: https://www.internalfb.com/intern/testinfra/testrun/8725724447995201
Network: Up: 8.8 MiB Down: 1.5 GiB (reSessionID-04c29f56-ae94-4187-8a1a-c812f432674d)
Jobs completed: 209847. Time elapsed: 1:56.5s.
Cache hits: 100%. Commands: 85687 (cached: 85687, remote: 0, local: 0)
Tests finished: Pass 3. Fail 0. Fatal 0. Skip 0. Build failure 0
```
Differential Revision: D47266068
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/104724
Approved by: https://github.com/fegin, https://github.com/fduwjj
When using KeyedOptimizer.init_state(), some optimizers initializes the states even if the param is empty (size() == 0) while some optimizer avoid initializing the states. There is no way FSDP can tell. Instead, FSDP should look up `optim.state`. Fortunatelly, `optim.state` does not rely on FQNs which some internal users change the FQNs.
Differential Revision: [D47285562](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D47285562/)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/104765
Approved by: https://github.com/fduwjj
The "for now" is because we still have the issue that when using the parameter `ignored_states` path, we do not recover the ignored modules, so FSDP still wraps those as empty shells (no managed parameters), which is not ideal. This is not a blocking issue as far as I know.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/104418
Approved by: https://github.com/rohan-varma
This moves `fully_shard` to use `_auto_wrap()` just like `FullyShardedDataParallel`. This means that `fully_shard` goes through the `_init_param_handle_from_module()` path (i.e. 1 `fully_shard` per "wrap"), removing the need for `_init_param_handles_from_module()` (which was 1 `fully_shard` for all "wraps" of a given policy). `_auto_wrap()` simply calls `fully_shard` on target submodules.
This includes several important fixes:
- We should register the pre/post-forward hooks on the module regardless of it has managed parameters.
- We can permit `_module_handles` to return `[]` in the composable path (for when the module has no managed parameters).
- We should unify the paths for `_get_buffers_and_dtypes_for_computation()` (previously, composable path was buggy in some cases).
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/104408
Approved by: https://github.com/rohan-varma
This PR is the first in refactoring the auto wrapping, only affecting `ModuleWrapPolicy` for wrapper `FullyShardedDataParallel`. The end goal is to improve the auto wrapping infra to support:
- Checking valid frozen parameters (uniform frozenness per FSDP)
- Checking valid shared parameters (shared parameters assigned to their lowest-common-ancestor module or higher)
- Writing auto wrapping policies that may take multiple passes over the module tree
- Specifying different FSDP kwargs per FSDP instance (instead of enforcing the same for all FSDP instances constructed via an auto wrap policy)
The way I envision achieving this is that, we decouple the actual "wrapping" (which is `_post_order_apply()` in this PR) from constructing the wrapping targets and kwargs (which is `target_module_to_kwargs` in this PR). In that way, a policy reduces to just constructing that latter `target_module_to_kwargs` mapping.
I do not personally recommend the size-based policy, but if we wanted to implement that under this new organization, the tracking of wrapped/nonwrapped numel should be done in the pass over the module tree prior to the actual "wrapping". This modularization keeps the actual "wrapping" part simple.
The change to how `old_dtype` is handled is mainly to avoid keeping a reference to `_override_module_mixed_precision()` function closure in each hook and to allow the function to take in all module clases at once to return which ones actually got overridden for the downstream error message. (We can directly store the global state as a mapping.)
To-do in follow-ups (not in order):
- Add frozen parameter check before `_post_order_apply()`
- Add shared parameter check before `_post_order_apply()`
- Expose wrapping policy that allows per module / per module class kwarg customization (where any unspecified kwarg adopts the root's kwarg)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/104346
Approved by: https://github.com/rohan-varma, https://github.com/fegin
In https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/97645 and some follow up diffs, we made FSDP run in full precision in eval mode, even if mixed precision was specified.
However, this is probably not the best idea and we should provide a flag for users to have control over this a bit more. Adding an env var FSDP_FULL_PREC_IN_EVAL and defaulting it to off, users who want to run eval in fp32 can toggle this before wrapping model in FSDP:
os.environ["FSDP_FULL_PREC_IN_EVAL"] = "1"
Verified that unittests, APS workflow, TNT workloads can run eval appropriately with this change.
Differential Revision: [D47246556](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D47246556/)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/104682
Approved by: https://github.com/awgu
This allows us use use_dtensor=True for ShardedStateDictConfig() before calling model.load_state_dict(). It only works for offload_to_cpu=False now.
Next PR will make use_dtensor=True work with offload_to_cpu=True for load_state_dict().
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/104087
Approved by: https://github.com/fegin
This allows us use use_dtensor=True for ShardedStateDictConfig() before calling model.load_state_dict(). It only works for offload_to_cpu=False now.
Next PR will make use_dtensor=True work with offload_to_cpu=True for load_state_dict().
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/104087
Approved by: https://github.com/fegin
This addresses https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/104187.
After this PR, the contract with the user is that:
- If passing `param_init_fn=None`, each `nn.Module.reset_parameters()` should only initialize its own parameters/buffers (like `parameters(recurse=False)`/`buffers(recurse=False)`).
- If passing `param_init_fn` not equal to `None`, then similarly, one call to `param_init_fn(module)` should only initialize `module`'s own parameters/buffers.
With this contract and this PR's changes, meta device initialization through either `reset_parameters()` or `param_init_fn` should be correct. Those functions will run on the original parameter/buffer shapes allowing for correct shape-dependent computations like for fan-in/fan-out, and there will not be any re-initialization of any module.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/104189
Approved by: https://github.com/rohan-varma
Since we do not call `_FSDPState.__init__()` and only use it for typing, it is not possible for these attributes to be `None`. The purpose of these `assert`s is to make sure that these attributes are set by `_init_process_group_state_for_hybrid_shard()`. If we care to make that explicit, I would posit that we should be using `hasattr` checks, not `is not None` checks, because if indeed `_init_process_group_state_for_hybrid_shard()` did not set these attributes, then even checking that it is not `None` would lead to an `AttributeError`. I do not include these `hasattr` checks for now since `_init_process_group_state_for_hybrid_shard()` is short enough that we can quickly tell by inspection that it sets the desired attributes.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/104274
Approved by: https://github.com/rohan-varma
This checks that `ignored_modules` and `ignored_states` have the expected type and provides a reasonable error message if not. Otherwise, if someone passes a mix of modules and parameters to `ignored_states` for example, then our code may be silently incorrect.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/104273
Approved by: https://github.com/rohan-varma
This fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/104148 (unfreezing parameters after `n` steps).
- This fixes a bug where we did not delete the post-backward hook state properly for the `requires_grad=False` case.
- This makes the `already_resharded` correct for `SHARD_GRAD_OP`.
- This generalizes `_clear_grads_if_needed()` to `_reset_flat_param_grad_info_if_needed()` to additionally include propagating the original parameters' `requires_grad` to the flat parameter.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/104186
Approved by: https://github.com/rohan-varma, https://github.com/fegin
# Change
This PR adds two classes to DTensor:
1. `CudaRNGStateTracker`: `CudaRNGStateTracker` stores Random Number Generator (RNG) state (a `ByteTensor` object) in a `dict`, mapping from a corresponding tag to each state tensor. It also provides a set of convenient utility methods to help access/modify the state tensors. The most important interface is `_distribute_region` which will be used when DTensor executes a random op (an operator that calls RNG).
2. `OffsetBasedRNGTracker`: This subclass of `CudaRNGStateTracker` defines the default policy of how RNG states should be shared and synchronized among all ranks to respect the semantics of DTensor random operators.
# Warning
- With `Multi-threaded ProcessGroup`, the global variable `_rng_tracker` will be shared among threads(ranks) and cause issue. We need to figure out a compatible solution for that.
- The RNG state may be asynchronous outside of participating ranks. It is harmless in our current use case of submesh though.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/103235
Approved by: https://github.com/wanchaol
Summary:
Details in T133020932
First commit of collective utils library. Ported over from model store, removed scuba logging, error_trait and all dependencies on modelstore.
Test Plan: In the following diffs.
Differential Revision: D45545970
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/101037
Approved by: https://github.com/H-Huang
Map of #101157.
This PR adds support for coalesced `reduce_scatter_tensor` calls in the following syntax:
Sync communication style:
```
with dist._coalescing_manager():
for i in range(num_coll):
dist.reduce_scatter_tensor(output_tensors[i], input_tensors[i])
```
Async communication style:
```
with dist._coalescing_manager(async_ops=True) as cm:
for i in range(num_coll):
dist.reduce_scatter_tensor(output_tensors[i], input_tensors[i])
# do a bunch of other things
cm.wait()
# do things that depend on the reduce-scatters' results
```
Each `reduce_scatter_tensor` call can be independent in terms of their data and buffer locations. But could be executed in parallel by supported backends (like NCCL).
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/103561
Approved by: https://github.com/fegin
Fixes#64601 and #98906
Adds an `assign` argument to `load_state_dict` that loads params/buffers by assignment instead of doing `param.copy_(param_from_state_dict)`.
Primarily intended to remove the need for the `.to_empty()` in
```
with torch.device('meta'):
m = SomeModule()
m.to_empty()
state_dict = torch.load('...pth')
m.load_state_dict(state_dict)
```
so we can instead do
```
with torch.device('meta'):
m = SomeModule()
state_dict = torch.load('...pth')
m.load_state_dict(state_dict, assign=True)
```
**A problem with this PR for the case where the model is initialized on meta is what happens to nonpersistent buffers/params corresponding to keys missing from the state dict?**
What happens in the case where `load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=False, assign=True)` and the state_dict is missing some keys? The corresponding params missing from the `state_dict` and nonpersistent buffers would still be on `meta` and need to be manually initialized. However, I don't think we offer an API that would initialize these.
One solution would be to make these empty tensors but it might not be semantically correct...
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/102212
Approved by: https://github.com/albanD
There was an issue reported internally that with `sync_module_states=True`, if the model had buffers on CPU, even with `device_id` specified, FSDP would try to broadcast CPU buffers, leading to an error like:
```
RuntimeError: No backend type associated with device type cpu
```
After some investigation, I determined that we should _not_ fix this by moving the buffers to GPU just for the broadcast and then back to CPU. Instead, we should fix our `device_id` logic.
The issue is that we always used the _parameters_ as the proxy to tell whether we should move module states to the device specified by `device_id`. However, a module (often the root) may not have any parameters but have some buffers! In that case, the buffers are left on CPU even if `device_id` is specified. This PR fixes this by considering both parameters and buffers for movement to `device_id`.
Note that this PR preserves the logic that `ignored_modules` / `ignored_parameters` are not considered for this movement, meaning that ignored parameters are moved to `device_id`.
Note also that I had to move the unit test back from using MTPG to the normal PG since otherwise, I could not repro the original error. (It seems like MTPG does not complain if we try to use `dist._broadcast_coalesced()` with CPU tensors.)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/103504
Approved by: https://github.com/rohan-varma
**Motivation:**
For collective dispatching, we want to provide a more user friendly usage for xpu device and CCL backend (user specified backend) mapping.
**Solution:**
We add xpu to the default device list, and it can construct the mapping between xpu and the user specified backend directly.
Usage:
When using xpu device, user can specify backend name only:
`dist.init_process_group(backend='ccl')`
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/103410
Approved by: https://github.com/jgong5, https://github.com/ezyang
This PR get rids of the dim_groups attribute from DeviceMesh, the main
motivation behind this is that we should let c10d store the process
groups during its creation instead of DeviceMesh, DeviceMesh should just
handle ranks correctly.
This could enable DTensor becomes picklable! (torch.save/load could be
possible), which I will give it a try in the next PR
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/103105
Approved by: https://github.com/XilunWu, https://github.com/fduwjj
This PR makes a first attempt at improving FSDP's fine-tuning support by adding hooks to reshard frozen parameters in the backward pass.
- Without this, frozen parameters involved in gradient computation are kept as unsharded through the entire backward pass.
- The approach is to register a multi-grad ~~post~~-hook on the _input_ activations to the FSDP module, where the hook performs the resharding after all gradients for the FSDP module must have been computed (meaning that we are safe to reshard).
~~This PR relies on adding a "multi-grad post-hook" that differs from the existing "multi-grad hook" from `register_multi_grad_hook()`. I find that with `register_multi_grad_hook()`, sometimes the unit test counting the number of times `_post_backward_reshard()` is called fails (due to it not being called).~~ This was resolved in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/102859.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/101982
Approved by: https://github.com/rohan-varma
Moved SlicedBufferedReader to utils and renamed to _ReaderView.
It no longer depends on file handles and is a pure wrapper. This makes it general enought to handle non io stream objects like fsspec's.
Should help with #98386
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99167
Approved by: https://github.com/wz337
Allow DTensor support cuda-like device, fix https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/102442
Currently, DTensor supports cuda and cpu. There are other efforts to make DTensor support third-party devices, for example https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/101914 and https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/101911. However, this support only extends a portion of third-party devices and is no good support for third-party cuda-like devices. Therefore, we would like to extend DTensor to support cuda-like devices, after all, cuda is so popular!
1. Similar to what is done here, we need to initialize the communication backend for the device set by DeviceMesh. So `_default_backend_for_device` is added to `Backend`. It is worth noting that when we register a new backend for a device other than cpu and cuda, we also need to add a new default backend for this device.
2. Adding `_device_handle` to `DeviceMesh` for cuda-like devices, similar to what is set in FSDP. When `_device_handle` is not None, the device has similar behavior to `cuda`. In this way, functions like `torch.cuda.device_count()` need to be modified to `device_mesh._device_handle.device_count()`.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/102468
Approved by: https://github.com/wanchaol
Both internal and OSS users trying https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99937 report that their workloads perform normally even with the barrier removed and see a scalability win. Thus in this PR, we decide to make it default that PG do not perform a barrier after init.
In the discussion of #99937, people point out that such barrier might be needed for c10d + RPC cases. IMO, this need originates from RPC's programming model and should be RPC or RPC user's responsibility to deal with. That is, with other functions/libraries, it can happen too. So the need for c10d to do so big a favor is not justified IMO. Also good to remove it before users become reliant on this barrier.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/103033
Approved by: https://github.com/XilunWu
This PR creates a device_mesh and share it across all FSDP state. The device_mesh will later be used to test out dtensor state_dict (1d device_mesh).
Approved by: https://github.com/awgu
Add device mesh to fsdp state
skip dist.get_world_size(pg) != dist.get_world_size()
address test_fake_pg.py test failure
fix test_fake_py.py failure
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/102551
Approved by: https://github.com/fegin
Summary: Add a flag to enforce the gather data dtype. In case backward compatibility, make the default as False
Test Plan: local and mast
Reviewed By: zyan0, strisunshinewentingwang
Differential Revision: D46295190
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/102802
Approved by: https://github.com/mrshenli
fixes#101911
Currently, `DTensor` supports cuda and cpu. This PR makes some changes for easier integration with the ort backend.
* `Backend.NAME` attribute now has value `name` instead of `NAME` for backends registered through `register_backend(name)`; this matches the pattern for backends with built-in support like nccl.
* remove unused `_check_for_nccl_backend` function
* add test case that moves parameters to device in the `partition_fn` - a scenario that's useful for big models
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/101914
Approved by: https://github.com/wanchaol
Add is_backend_available for c10d backend, either the built-in backends or third-party backends through function ``Backend.register_backend``.
There is a related discussion in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/101775#discussion_r1199253553
> For example in python constructor for their backend they should explicitly add the is_X_available. Or if defining in C++ they should modify pybind like this https://github.com/H-Huang/torch_collective_extension/blob/main/custom_backend/include/dummy.hpp#L98-L101
to also add their own is_available property
It is a natural choice for users to add their own `is_available` when they create a backend. We think it might be a possible way for the user to use `is_X_available` in the same way as the native, for example by dynamically adding`torch.distributed.is_dummpy_available()` function. This is why we want to dynamically add the `is_X_available` to `torch.distributed` in `register_backend`.
> Or we could add an Is_available(backend) function, that checks for the backend.
Providing a public function is indeed another good approach. We have implemented an `is_backend_available` in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/101945 that supports both built-in backends and third-party backends.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/101945
Approved by: https://github.com/H-Huang
This attribute wasn't actually used in tests, add a test ensuring that
if replicate is used on top of FSDP, the replicated parameter names are as
expected.
TODO: there are a few ways to check if module is managed by composable API,
such as replicated param names for replicate, _get_module_state API,
_get_registry_api, etc. We should unify all composable APIs to check in a
unified way (filed an issue)
Differential Revision: [D46236377](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D46236377/)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/102401
Approved by: https://github.com/awgu
This PR switches DeviceMesh to use dispatchable process group instead,
this could enable easier backend integration as user only need to
integrate with c10d process group custom backend, without needing to
change DeviceMesh to plug in the backend
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/102336
Approved by: https://github.com/fduwjj
Enables MTPG for some FSDP tests in this file. Tests that need the
backward pass and warning logging are left as follow up work.
Backward pass issue: It seems that there is a hang with all_gather. Will sync with @kumpera on this.
Warning issue: We have a couple tests that regex check on warnings, but in the
multithreaded scenario these warnings are somehow not logged.
Differential Revision: [D43209769](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D43209769/)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/102043
Approved by: https://github.com/awgu
The main use case here is that folks would like to ignore layer norm for mixed precision. This can now be enabled with:
```
mp_config = MixedPrecision(
param_dtype=torch.float16,
reduce_dtype=torch.float16,
buffer_dtype=torch.float16,
_mixed_precision_module_classes_to_ignore=[_BatchNorm, nn.LayerNorm],
)
```
This is done by classes of types in `_mixed_precision_module_classes_to_ignore` being wrapped in their own FSDP unit with mixed preicsion disabled. This is only enabled for auto wrapping.
We also add module pre and post hooks to cast / downcast inputs to the appropriate full precision.
Differential Revision: [D46079957](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D46079957/)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/102010
Approved by: https://github.com/awgu
Add 'ignored_states' that accepts either a list of ignored_parameters or a list of nn modules for FSDP model wrapper and fully_shard composable APIs, it is recommended to use 'ignored_states' over 'ignored_modules' moving forward
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/102056
Approved by: https://github.com/awgu
This PR enables data parallel to work with non 0 batch dim, the only
thing we need to do is to expose the input_batch_dim to DataParallelMode
and the data parallel expansion automatically works as we have done
things correctly in batch dim analysis.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/100073
Approved by: https://github.com/mrshenli
This PR improves the activation handling logic of data parallel, to
support the cases where there're tensor factory ops that does not depend
on any input node, it would still produce activation, with either
sharded act (i.e. if output shape have batch size) or replcate act
It also significantly simplify the full reduction logic, now we don't
need the full reduction detection, we only need to ensure that when
compute the batch dim, we detected full reduction and mark it as sharded
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/100853
Approved by: https://github.com/mrshenli
This PR enhances batch dim analysis of data parallel to understand
more on the cases where batch dim get flattened or split, using
dtensor's view ops, we could be able to track the batch dim that got
transformed in non-trival ways.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/100852
Approved by: https://github.com/mrshenli
There are many communication operations for shardedTensor in the state dict of fsdp. They use the external passed-in pg (or the default pg), which currently supports cuda devices. Before communication, the memory will be moved to cuda, which is implicit (because it is essentially moving data to the memory type required by pg, not the computing device type). Similarly, when users use fsdp on a custom backend, they will pass in a custom pg (which does not support cuda devices), which may cause fsdp to not work properly in some cases. This PR obtains the memory type supported by the pg through _get_pg_default_device during communication, and moves the data to it when needed.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/101533
Approved by: https://github.com/awgu
1. Record time spent for init_process_group, new_group, _store_based_barrier
2. Rename c10d_error_logger to c10d_logger for generalization.
3. Refactor to move logger wrappers in distributed_c10d.py to logger to c10d_logger.py.
4. Rename the logger wrappers (bc breaking). Exception_handler is renamed to exception_logger to avoid confusion with logging handler.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/101912
Approved by: https://github.com/fduwjj
When investigating failures in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/100017 I realized that we were reentering FakeTensorMode even though there was already one on the stack. Although we have attempted assert for these cases in the past, e.g., as in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/97186 it seems that the existing protections were insufficient.
In this particular case, the reapplication of FakeTensorMode was due to an interaction with NotImplemented multiple dispatch handling. If proxy tensor mode detects an unrecognized tensor type (this includes FakeTensor, if it is not tracked with a proxy), it will return NotImplemented to give this tensor a chance to unpack itself into proxyable operation. However, this is never the right thing for FakeTensor, where no unpacking is possible. However, today, FakeTensor attempts to reapply the FakeTensorMode, resulting in FakeTensorMode being twice on the stack.
This PR does a number of things:
* It adds an assert in `FakeTensorMode.__torch_dispatch__` that you must not already have this mode on the stack, this is ALWAYS an error
* It modifies `FakeTensor.__torch_dispatch__` to return `NotImplemented` if the mode is already active. This prevents us from readding the mode on the stack
* It adds a new logging artifact `not_implemented` which you can use to get debug logs about all of the times a `__torch_dispatch__` handler returned NotImplemented and why it did so. Your subclass has to manually opt into this logging, but I inserted the necessary logs for ProxyTensorMode and FakeTensor(Mode)
* `with fake_mode` now no-ops if the fake mode is already on the stack, which is what users want anyway
* I am BREAKING pre-autograd tracing, because it is currently doing something weird with the original C++ mode stack. Brian is going to follow up with a fix next week.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@meta.com>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/102091
Approved by: https://github.com/thiagocrepaldi, https://github.com/eellison, https://github.com/wanchaol, https://github.com/bdhirsh
FSDP creates communication groups for intra-node communication through dist.new_subgroups. Previously, dist.new_subgroups only supported creation based on the number of CUDA devices. However, issue #99706 removed the avaliable-check for CUDA devices, allowing for custom backend create group based on num of custom devices per node.
This PR allows FSDP to explicitly pass device num within the node when creating communication groups for intra-node communication, instead of defaulting to the number of CUDA devices.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/100622
Approved by: https://github.com/awgu
Also not sure if this should be a public function or not. Leaving it private for now but let me know if you prefer for it to be public.
FYI @nikitaved this will logically conflict with your triton kernel PR.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/101420
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
It's easier for users to implement one Override that takes care of
all target submodules of different types, instead of specifying one
mapping pair for each FQN/type. For example, when calculating
sharding for sparse layers, the decision needs to be make globally.
In this, case it's helpful to allow user Override to get access to
all submodules and make replacement decisions accordingly.
Differential Revision: [D45879732](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D45879732)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/101427
Approved by: https://github.com/fegin
When tensor.size(self.dim) < num_chunks, we will fill empty chunk with empty tensor (https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/98722). Therefore, we no longer needs this assert.
For example, when sharding a tensor with 1 element on 2 ranks along dim 0, results would be as follows:
```
rank:0, dtensor:DTensor(local_tensor=tensor([0.4963], device='cuda:0'), device_mesh=DeviceMesh:([0, 1]), placements=[Shard(dim=0)])
rank:1, dtensor:DTensor(local_tensor=tensor([], device='cuda:1'), device_mesh=DeviceMesh:([0, 1]), placements=[Shard(dim=0)])
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/101218
Approved by: https://github.com/wanchaol
Enables PyLint error codes implemented in ruff. These are un-opinionated static analysis checks on Python code that finds common bugs. After running all the PLE error codes that are implemented in ruff, I fixed the bugs, added a few ignores for malformed Python code that is part of our JIT test script, and finally added a few ignores for a false positive on PLE0605 and submitted an issue upstream to fix in ruff https://github.com/charliermarsh/ruff/issues/4345 .
Common bugs found here include analysis for malformed logging format calls, bad string format calls, invalid escape sequences, and more.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/101079
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
This PR changes the context manager behavior of device mesh, now we use
a mesh env to track the current mesh and save the mesh to a stack so
that we can allow nested context manager
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/101202
Approved by: https://github.com/wz337
This PR adds support for the following use cases:
- Sync style:
```
with dist._coalescing_manager():
for i in range(num_coll):
dist.all_gather_into_tensor(output_tensors[i], input_tensors[i])
```
- Async style:
```
with dist._coalescing_manager(async_ops=True) as cm:
for i in range(num_coll):
dist.all_gather_into_tensor(output_tensors[i], input_tensors[i])
# do a bunch of other things
cm.wait()
# do things that depend on the all-gather's
```
Each `all_gather_into_tensor` would be independent in terms of data and their buffer location. But could be executed in parallel by supported backends (like NCCL).
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/101157
Approved by: https://github.com/kumpera, https://github.com/wanchaol
This is the first series of PR that adopts operator impls to use a
strategy based approach, each op utilizes OpStrategy and PlacementStrategy
to generate their own strategy. By utilizing the strategy based
approach along with the op graph, we could enable more advanced op
implementation (decomp is possible), and turn the sharding prop to be
more like a contraint satisfication problem.
This PR alone only adds some basic tensor op strategies, and it directly
works on the op graph that was used for metadata propagation. The tensor ops
added in this PR mainly follows one of the arg strategy. The next set of
PRs would add more op strategies to other ops.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/100607
Approved by: https://github.com/XilunWu
Summary:
Currently there are build configs where the torchdynamo import trips over a
strange SystemError related to some module's __dict__.items() returning NULL,
while torchdynamo tries to iterate all torch modules and process them for
its allowed functions list.
While this is hard to repro, we should be able to work around it and then fix
it properly.
Test Plan: Rely on others to test this, assuming CI passes.
Reviewed By: anijain2305
Differential Revision: D45663313
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/100901
Approved by: https://github.com/yanboliang, https://github.com/malfet
This PR puts a placeholder param handler for a new param being passed in from Inductor, enable log.
Fixes this error below, where I've been unable to run torch.compile on NanoGPT due to this error:
~~~
File "/opt/conda/envs/pytorch/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/_inductor/fx_passes/fuse_attention.py", line 219, in _sfdp_init
register_replacement(
File "/opt/conda/envs/pytorch/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/_inductor/pattern_matcher.py", line 658, in register_replacement
search_gm = trace_fn(search_fn, example_inputs)
File "/opt/conda/envs/pytorch/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/utils/_contextlib.py", line 115, in decorate_context
return func(*args, **kwargs)
File "/opt/conda/envs/pytorch/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/_inductor/pattern_matcher.py", line 828, in training_graph
aot_function(
torch._dynamo.exc.BackendCompilerFailed: backend='compile_fn' raised:
TypeError: patched_aot_function() got an unexpected keyword argument 'enable_log'
~~~
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/100814
Approved by: https://github.com/fegin
Summary: Disable buffers sync in _sync_module_states(...) when broadcast_buffers is False. This change will memory usage when a model has huge buffers and does not need broadcast buffers.
Test Plan: .
Differential Revision: D45610709
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/100729
Approved by: https://github.com/mrshenli
To make TP more generic for Attention module, we come up with this new col/rowwise parallel style.
Basically, the idea behind is that:
We only do DTensor op for Col/Rowwise sharded part. For the rest of ATen ops, we will leave it to Tensor ops.
And we set this behavior as default for Colwise and Rowwise parallel style. If people want to customize it, they can always pass in different prepare_input or prepare_output
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/100508
Approved by: https://github.com/wanchaol
We do it by making it possible to register multiple tensors for the same
worker and coordinate waiting/cleanup among them.
This ensures waiting on any number the output tensors will result in a
single stream sync. This simplifies codegen by inductor.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99763
Approved by: https://github.com/wanchaol
Summary: with the new c10d API, we don't need all ranks to call new_group. Integrate with the new API, so that every rank just call new_group 3 times, with a local barrier with the members within the group.
Reviewed By: xunnanxu, eeggl
Differential Revision: D45315615
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/100518
Approved by: https://github.com/kumpera
Summary:
This diff is reverting D45387167
D45387167: Basic dynamo support for traceable collectives (#94440) by wconstab has been identified to be causing the following test or build failures (internal)
If you believe this diff has been generated in error you may Commandeer and Abandon it.
Test Plan: NA
Reviewed By: s4ayub
Differential Revision: D45448312
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/100424
Approved by: https://github.com/rohan-varma, https://github.com/kumpera
DTensor was reusing `einop_rule` to propagate sharding for torch.cat.
However, einsum only supports up to 52 subscripts (i.e., input tensors).
We have encountered use cases where one cat operator has more than 60
input tensors. Therefore, this commit reimplements sharding prop
rule for cat without using einsum.
Differential Revision: [D45435232](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D45435232)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/100251
Approved by: https://github.com/wanchaol
This is an easy follow-up to the previous PR to (1) clarify that `view` is the original parameter's gradient and (2) that after `reshard()` the gradient is on CPU only if offloading parameters.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/100359
Approved by: https://github.com/rohan-varma
Currently, if we use NO_SHARD strategy for fully_shard and set state_dict_type to be SHARDED_STATE_DICT, a runtime error would be raised ("``sharded_state_dict`` can only be used when parameters are flatten and sharded.").
This PR updates pre_state_dict_hook, post_state_dict_hook, pre_load_state_dict_hook, and post_load_state_dict_hook to set state_dict_type and state_dict_config to full state when using NO_SHARD, even if the state_dict_type and state_dict_config of the root module is set to sharded state.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/100208
Approved by: https://github.com/rohan-varma
When use_orig_param is True and sharding is NO_SHARD, parameters and states are not flattened, so optimizer states should not be flattened as well. The unit test will fail without the fix.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/100189
Approved by: https://github.com/awgu
Fixes [#82206](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/82206)
When executing a `ShardedGradScaler` step in the context of `cpu_offload`, [the function](ecd2c71871/torch/distributed/fsdp/sharded_grad_scaler.py (L151-L152)) `_foreach_non_finite_check_and_unscale_cpu_` is grindingly slow. This issue is due to the elementwise op dispatching/redispatching/execution that is engendered by the current approach to gradient tensor validation:
ecd2c71871/torch/distributed/fsdp/sharded_grad_scaler.py (L159-L163)
The subsequent `isinf` and `isnan` checks with associated `any` checks result in unscalable elementwise op dispatches:
ecd2c71871/torch/distributed/fsdp/sharded_grad_scaler.py (L173-L181)
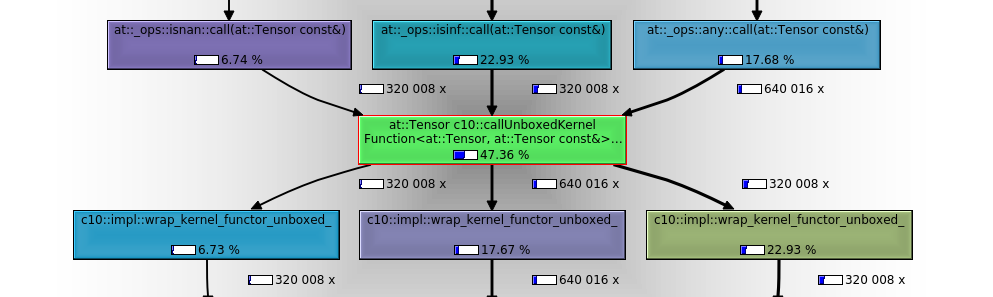
This inefficency is of course hidden in the current FSDP tests given their (appropriately) trivial parameter dimensionality. In the perf analysis below, the example test configures only the final `Linear(4, 8)` module parameters to require grad, so there are 40 elements to iterate through. However, if one increases the dimensionality to a still-modest 320008 elements (changing the final module to `Linear(40000,8)`), the execution time/cpu cost of the test is dominated by the elementwise op dispatching/redispatching/execution of the `any` validation ops in this function.
To characterize the current behavior, I use a slightly modified version of an existing `ShardedGradScaler` test [^1]. The following modifications to the test are made to allow the analysis:
1. Run just `CUDAInitMode.CUDA_BEFORE` for clarity instead of additional scenarios
2. Increase the final module to `Linear(40000, 8)` (along with modifying the preceding module to make the dimensions work) ,
3. For the cProfile run (but not valgrind or perf) the test runs just a single [`_train_for_several_steps`](ecd2c71871/torch/testing/_internal/common_fsdp.py (L926-L934)) step per rank (instead of 2 steps)
4. I temporarily reduce `init_scale` further to ensure we don't hit any `infs`, short-circuiting our analysis
### Current behavior
The most relevant call subgraph:
Note that:
1. Instead of dispatching to the relevant autograd op and then redispatching to the relevant CPU op implementation 8 times per test, (2 train steps x 2 any calls per parameter per step x 2 orig parameters) we (I believe unnecessarily) call the relevant dispatch flow elementwise, so 640016 times! (only 1 node in this trace so 320008 elements/2 X 2 train steps x 2 calls per element per step).
2. Nearly 50% of the relative (inclusive) instruction reads for the entire test in `callgrind` are executed by the `isnan` (320008 execs), `isinf` (320008 execs) and `any` (640016 execs) calls.
3. The `any` pre-dispatch entry point IRs (`torch::autograd::THPVariable_any`) vs actual op implementation IRs (`at::native::structured_any_all_out::impl`) are below to give one a sense of the relative dispatch and op execution cost in an elementwise context[^3].


Using cprofile stats:
```bash
python -c "import pstats; stats=pstats.Stats('/tmp/fsdp_cprofile_8wa9uw39.stats'); stats.print_stats()"
...
ncalls tottime percall cumtime percall filename:lineno(function)
1 20.159 20.159 66.805 66.805 torch/distributed/fsdp/sharded_grad_scaler.py:151(_foreach_non_finite_check_and_unscale_cpu_)
160004 18.427 0.000 18.427 0.000 {built-in method torch.isinf}
160004 6.026 0.000 6.026 0.000 {built-in method torch.isnan}
```
We see that a single step of the scaler runs for more than a minute. Though there is non-trivial cprofile overhead, we can infer from this that per-element op dispatches/executions are on the order of a 100ns.
On the order of 100 nanoseconds per dispatch is acceptable if we're using typical tensor access patterns, but if we're dispatching each element for each op, obviously everything is going to come to a grinding halt for many practical use cases.
(Given the cost of this function is currently O(n) in the number of gradient elements, feel free to set `TORCH_SHOW_DISPATCH_TRACE=1` if you want to make this function cry 🤣)
I've attached a flamegraph at the bottom of the PR[^2] that more intuitively demonstrates the manner and extent of resource consumption attributable to this function with just a modest number of gradient elements.
### After the loop refactor in this PR:
The most relevant call subgraph:
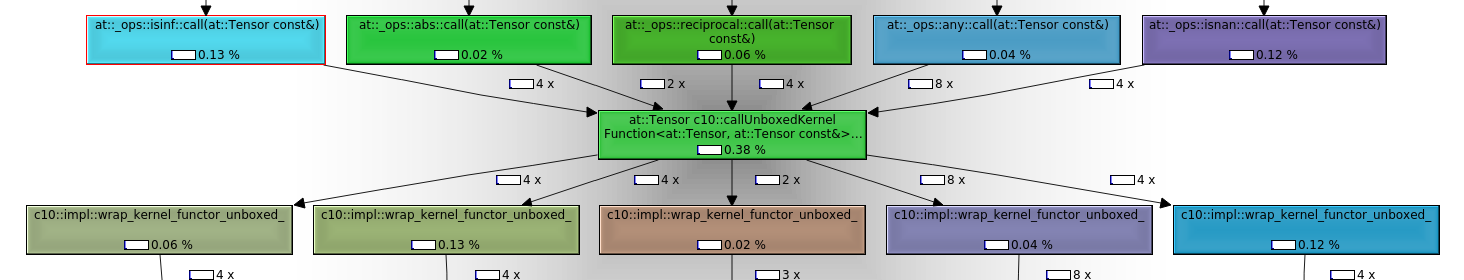
Note that:
1. Less than 0.4% of the relative (inclusive) instruction reads for the entire test in `callgrind` are executed by the `isnan` (4 execs), `isinf` (4 execs) and `any` (8 execs) calls (versus ~50% and 320008, 320008, 640016 respectively above)
2. The `any` pre-dispatch entry point IRs (`torch::autograd::THPVariable_any`) vs actual op implementation IRs (`at::native::structured_any_all_out::impl`) reflect far less overhead (of secondary importance to item number 1)


Using cprofile stats:
```bash
python -c "import pstats; stats=pstats.Stats('/tmp/fsdp_cprofile_pfap7nwk.stats'); stats.print_stats()"
...
ncalls tottime percall cumtime percall filename:lineno(function)
1 0.013 0.013 0.109 0.109 torch/distributed/fsdp/sharded_grad_scaler.py:151(_foreach_non_finite_check_and_unscale_cpu_)
2 0.022 0.011 0.022 0.011 {built-in method torch.isinf}
2 0.018 0.009 0.018 0.009 {built-in method torch.isnan}
```
We can see our function runtime has dropped from more than a minute to ~100ms.
### Assumptions associated with this loop refactor:
The key assumptions here are:
1. The grads are always on CPU in this function so any MTA-safe constraints ([`can_use_fast_route`](efc3887ea5/aten/src/ATen/native/cuda/AmpKernels.cu (L110-L111)) relating to the relevant CUDA kernel path selection, i.e. slower `TensorIterator` gpu kernel vs `multi_tensor_apply_kernel`) do not apply in this context
2. We've already filtered by dtype and device and can assume the presence of a single CPU device. Unless manually creating separate CPU devices with manually set non-default indexes (which I don't think FSDP supports and should be validated prior to this function), device equality should always be `True` for `cpu` type devices so we should just need to check that the current device is of `cpu` type. [^4].

[^1]: `TestShardedGradScalerParityWithDDP.test_fsdp_ddp_parity_with_grad_scaler_offload_true_none_mixed_precision_use_orig_params` test in `test/distributed/fsdp/test_fsdp_sharded_grad_scaler.py`
[^2]: Note the native frame stacks for `torch::autograd::THPVariable_isinf`, `torch::autograd::THPVariable_isnan`, `torch::autograd::THPVariable_any` in particular.
[^3]: There's more `TensorIterator` etc. setup overhead further up the stack beyond `structured_any_all_out`, but roughly speaking
[^4]: Device equality is based on [type and index combination](efc3887ea5/c10/core/Device.h (L47-L51)), CPU device type is -1 by default (`None` on the python side) and is intended to [always be 0](cf21240f67/c10/core/Device.h (L29)) if set explicitly. Though technically, unless in debug mode, this constraint isn't [actually validated](bb4e9e9124/c10/core/Device.h (L171-L184)), so one can actually manually create separate `cpu` devices with invalid indices. I suspect it's safe to ignore that potential incorrect/unusual configuration in this context but let me know if you'd like to add another `cpu` device equality check.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/100108
Approved by: https://github.com/awgu
Add use_local_synchronization argument to new_group.
When this argument is True, is change new_group to do a store_barrier only on the ranks that are park of the group and not the whole cluster.
This addressess both scalability and composability problems associated with new_group.
Fixes#81291.
This is relanding #84224
As part of the original PR I did a quick benchmark of creating 3 PGs per rank using both functions and perf is the following:
new_group use_local_synchronization=False:
| World Size | Time (in secs) |
| --- | ----------- |
| 4 | 0.12 |
| 8 | 0.25 |
| 16 | 0.51 |
| 32 | 0.87 |
| 64 | 1.50 |
| 128 | 2.87 |
new_group use_local_synchronization=True:
| World Size | Time (in secs) |
| --- | ----------- |
| 4 | 0.05 |
| 8 | 0.04 |
| 16 | 0.03 |
| 32 | 0.03 |
| 64 | 0.04 |
| 128 | 0.04 |
Scaling for `use_local_synchronization=False` is sub linear because the number of process groups created as a multiple of world_size decreases as we go up. It's 6 with world_size 4 and 192 with world_size 128.
Scaling for `use_local_synchronization=True` is constant as the number of store barriers executed per rank remains constant at 3.
Setup:
1 AWS host, backend gloo.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99931
Approved by: https://github.com/xw285cornell
Make traceable collectives work with torchdynamo,
bypassing problems with tracing the AsyncTensor subclass.
Accept a suboptimal solution for now, and optimize it later.
For now, wait happens immediately, which generally forces an early sync.
Later, find a way either in dynamo or AOT stack to handle
AsyncCollectiveTensor to get the wait in the optimal place.
Note on implementation:
- Dynamo traces 'user-level' fc apis that are designed to behave differently
in eager vs compiled. In eager, there will be work-obj registration and
a wrapper subclass will insert a 'wait' call at the appropriate time.
In compile/trace mode, wait will be immetiately called, and work obj
registration is required to be handled by the compile backend at runtime.
- Dynamo needs to trace into some of the helper functions in the 'user-level'
api, such as '_expand_group' which is essentially a constant transformation.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/94440
Approved by: https://github.com/kumpera
Custom backend implementation based on privateuse1 with semantics identical to CUDA (CUDA is so popular), named for example 'my_device', and registered as the same module name torch.my_device.
This PR aims to satisfy the constraints of such a backend, which can be directly integrated into the current FSDP implementation.
The main issues addressed are:
#### 1. Device decision for FSDP wrapping of Modules without Parameters
Users typically organize FSDP code as follows:
```python
m = Module().to('my_device:0')
fsdp_m = FSDP(m)
```
or like this:
```python
m = Module()
fsdp_m = FSDP(m, device_id=torch.device('my_device', 0))
```
If the model has Parameters, everything works fine because FSDP will prioritize the device where the Parameters are located. However, for Modules without Parameters, the to() call has no side effects, and FSDP will assume the current CUDA device, which prevents the use of devices other than the current CUDA device for Modules without Parameters. Therefore, when FSDP is called with a device_id argument, this configuration takes top priority.
#### 2. Abstraction of a cuda-like device
Now, in addition to compute_device, _FSDPState includes a device_handler member. In fact, this device_handler is now just a reference to either torch.cuda or torch.my_device. From now on, code that works based on _FSDPState should use state.device_handler to operate streams create, wait or sync, just like using torch.cuda previously.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99024
Approved by: https://github.com/awgu
Summary: Today, on a segfault on a single trainer , we end up keeping the gpu on all ranks blocked for 5 minutes due to elastic agents barrier timeouts
Test Plan: Rely on existing test to validate . Looking to get some feedback on adding UTs
Differential Revision: D44929488
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99051
Approved by: https://github.com/kurman, https://github.com/kiukchung
This PR enables fully_shard fused adam tests with some additional tweaks
about how to handle scalar tensor. Now we treat scalar tensors as if
it's just a scalar value, we don't distribute it as there's no need to
shard a scalar tensor
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99898
Approved by: https://github.com/mrshenli
The default option of `named_parameters` and `named_modules` is to remove the duplicated parameters and modules. However, in FSDP, we need to know what parameters are shared. As a result, setting `remove_duplicate` to False is required in FSDP. Without setting `remove_duplicate` to False, FSDP won't be able to discover shared weights in some cases (e.g., the shared weights are in the same module or there are shared modules).
The previous PR is reverted due to some modules overwriting the signature of `named_parameters()`. This new PR adds a workaround for the case.
Differential Revision: [D45065973](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D45065973/)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99448
Approved by: https://github.com/zhaojuanmao
### Description
The PR aims at reducing CPU overhead of context manager style coalescing.
By "context manager style coalescing", we mean:
Sync style:
```
with _coalescing_manager():
for i in range(num_coll):
dist.all_reduce(tensors[i])
```
Async style:
```
with _coalescing_manager(async_ops=True) as cm:
for i in range(num_coll):
dist.all_reduce(tensors[i])
cm.wait()
```
In previous implementation, each collective in the `num_coll` loop actually calls into the C++ backend, accumulating pybind overhead.
In the new implementation, we capture the collectives at Python level, and only fire towards C++ at the exit of the coalescing manager.
### Tests
In current PR, the "fast path" only applies to all-reduce.
- Flattened 512M: 16.38 ms, including CPU time 131.21 us
- Old _coalescing_manager 64 x 8M: 22.19 ms, including CPU time 2865 us
- New _coalescing_manager 64 x 8M: 16.93 ms, including CPU time 635 us
Hence a 4x reduction in CPU overhead (dependent on `num_coll`).
Cc @mrshenli @kumpera @wanchaol @fegin
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/98793
Approved by: https://github.com/kumpera
The `new_subgroups` allows for the easy creation of sub-communication groups, but it currently requires CUDA availability. For communications that do not rely on CUDA, such as the CPU-based gloo or custom communication backends, I still hope to be able to use it, such as with the CPU-based gloo (which is also the case when using a custom backend):
```python
import os
import torch
import torch.distributed as dist
import torch.multiprocessing as mp
def gloo_process(rank_id, world_size, group_size, mp_lock):
assert not torch.cuda.is_available()
def lock_print(*args, **kwargs):
with mp_lock:
print(*args, **kwargs, flush=True)
os.environ['MASTER_ADDR'] = '127.0.0.1'
os.environ['MASTER_PORT'] = '29500'
dist.init_process_group('gloo', rank=rank_id, world_size=world_size)
subgroup, _ = dist.new_subgroups(group_size)
subgroup_ranks = list(range(subgroup.rank() * group_size, (subgroup.rank() + 1) * group_size))
lock_print(f"Rank {rank_id} initialized in subgroup_{subgroup.rank()}: {subgroup_ranks}")
tensor = torch.Tensor([rank_id + 1])
subgroup.broadcast(tensor, root=0)
lock_print(f"After broadcast, rank {rank_id} in subgroup_{subgroup.rank()}:{subgroup_ranks} got {tensor}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
world_size = 4
group_size = 2
processes = []
mp.set_start_method("spawn")
mp_lock = mp.Lock()
for rank in range(world_size):
p = mp.Process(target=gloo_process, args=(rank, world_size, group_size, mp_lock))
p.start()
processes.append(p)
for p in processes:
p.join()
```
```bash
Rank 0 assigned to subgroup_0: [0, 1]
Rank 1 assigned to subgroup_1: [2, 3]
Rank 2 assigned to subgroup_0: [0, 1]
Rank 3 assigned to subgroup_1: [2, 3]
After broadcast, rank 2 in subgroup_0:[0, 1] got tensor([3.])
After broadcast, rank 3 in subgroup_1:[2, 3] got tensor([3.])
After broadcast, rank 1 in subgroup_1:[2, 3] got tensor([1.])
After broadcast, rank 0 in subgroup_0:[0, 1] got tensor([1.])
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99706
Approved by: https://github.com/kumpera
### This change
- Implements the ruff linter in pytorch lintrunner. It is adapted from https://github.com/justinchuby/lintrunner-adapters/blob/main/lintrunner_adapters/adapters/ruff_linter.py. It does **both linting and fixing**. 🔧
- Migrated all flake8 configs to the ruff config and enabled it for the repo. ✅
- **`ruff` lints the whole repo in under 2s** 🤯
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/94737 Replaces #99280
@huydhn @Skylion007
<!--
copilot:all
-->
### <samp>🤖 Generated by Copilot at 6b982dd</samp>
### Summary
🧹🛠️🎨
<!--
1. 🧹 This emoji represents cleaning or tidying up, which is what `ruff` does by formatting and linting the code. It also suggests improving the code quality and removing unnecessary or redundant code.
2. 🛠️ This emoji represents tools or fixing, which is what `ruff` is as a code formatter and linter. It also suggests enhancing the code functionality and performance, and resolving potential issues or bugs.
3. 🎨 This emoji represents art or creativity, which is what `ruff` allows by providing a consistent and configurable style for the code. It also suggests adding some flair or personality to the code, and making it more readable and enjoyable.
-->
Add `[tool.ruff]` section to `pyproject.toml` to configure `ruff` code formatter and linter. This change aims to improve code quality and consistency with a single tool.
> _`ruff` cleans the code_
> _like a spring breeze in the fields_
> _`pyproject.toml`_
### Walkthrough
* Configure `ruff` code formatter and linter for the whole project ([link](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99785/files?diff=unified&w=0#diff-50c86b7ed8ac2cf95bd48334961bf0530cdc77b5a56f852c5c61b89d735fd711R22-R79))
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99785
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet, https://github.com/Skylion007
This PR adds list handling logic to the new DataParallel expansion and
add foreach optimizer tests, currently current testing sgd optimizers
in foreach mode, for both replicate and fully shard
Next step:
Add fused optim tests
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99373
Approved by: https://github.com/mrshenli
This PR refactors the current StrategyList. It introduces a
StrategyType, which is the base class of Strategy, and it have
two sub strategies:
1. Refactor the previous StrategyList to OpStrategy
2. Add TupleStrategy, the new strategy added to deal with tuple cases where
it could return multiple different OpStrategy for an op.
This would help support a more complicated op and unblocks compile mode
FSDP
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99435
Approved by: https://github.com/mrshenli
This PR introduces compile mode Data Parallel (FSDP/DDP) using DTensor sharding.
Along with the algorithm, it also introduces a new DataParallelMode so that `compile` API can take it
and apply data parallel. This PR trys to preserve the DTensorExpand
approach first to avoid BC, we shall discuss steps to remove
DTensorExpand.
The data parallel mode uses heuristics to determine node types in the
graphs and assign the corresponding sharding. The detailed algorithm
described in the design doc.
The benefits of this approach:
- Model parameters and optimizer states are all DTensors after `spmd.compile`, which is necessary for FSDP, and also makes it super easier for checkpointing
- As model parameter/optim states are sharding in a per-parameter approach, it would be able to compose with sophisticated second order optimizer (i.e. Shampoo) in a easier way.
- We leverage the model parameter/grads information to derive data parallel pattern. In this way we don't need to worry about DTensor op coverage anymore! As data parallel is just a special case of DTensor operation.
- Use dtensor_expand might work for DDP but aren't going to work for FSDP as dtensor might choose to allgather activation, which might violate native fsdp algorithm.
- The approach is general enough to support both DDP/FSDP and a mixed mode
Follow ups:
- Add the "default" data parallel mode which supports mixing of
replicate/fully shard
- Test more e2e models with more different types of optimizers, etc
- migrate the existing stack from the DTensorExpand mode
- build optimizations on top of this prototype
Differential Revision: [D45174400](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D45174400)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99062
Approved by: https://github.com/mrshenli
## What's in this PR
DeviceMesh's __init__ function now requires all calling ranks to pass the same `mesh` argument.
## Why
We want to enforce SPMD style of programs using DTensor. Before this PR, 2-D Parallel API (e.g. _create_1d_device_mesh) defines different DeviceMesh on different ranks. After this PR, it defines each sub-meshes and simply perform communications on the one that it is associated with.
Differential Revision: [D45165511](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D45165511)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99094
Approved by: https://github.com/wanchaol
High level approach:
1. I generated a bunch of data comparing FlashAttention and Cutlass implementations (https://pastebin.com/pe0j3YeK)
2. I trained a decision tree using standard train/val split methodology and hyperparameter sweeps (https://pastebin.com/fjYX1HjR).
2a. I did a bunch of feature augmentation to capture interactions between features.
The heuristic I ended up with is:
```
use_flash = seq_len / (num_heads * batch_size) > 6
```
TL;DR: On my dataset, where FlashAttention and Cutlass differ by more than 10%, the existing heuristic achieves 69% accuracy. My new heuristic achieves 94% accuracy.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99644
Approved by: https://github.com/ngimel, https://github.com/drisspg
Fixes#99545
There is currently no topological constraint dictating FSDP instances own ``FlatParamHandle`` s directly. If all parameters are managed by descendant FSDP instances leaving an FSDP instance with no direct ``state._handles``, the ``should_cast_forward_inputs`` decisions below in both ``_root_pre_forward()`` and ``_pre_forward()`` respectively can return incorrect decisions [^1].
For [``_root_pre_forward()``](436edc5ac3/torch/distributed/fsdp/_runtime_utils.py (L514)):
436edc5ac3/torch/distributed/fsdp/_runtime_utils.py (L602-L604)
For [``_pre_forward``](436edc5ac3/torch/distributed/fsdp/_runtime_utils.py (L384)):
436edc5ac3/torch/distributed/fsdp/_runtime_utils.py (L420-L422)
See the [related issue](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/99545) for reproduction.
### Remediation
In this PR, I amend the two decision statements referenced above (in both `_root_pre_forward()` and `_pre_forward()`) to account for FSDP instances without direct handles:
```python
should_cast_forward_inputs = len(state._handles) > 0 and all(
not handle._force_full_precision for handle in state._handles
)
```
If one configures ``MixedPrecision`` in the example above with ``cast_forward_inputs=True`` and the ``should_cast_forward_inputs`` adjustment above, FSDP returns to the expected behavior and produces no error.
Though the check is the same in both ``_root_pre_forward()`` and ``_pre_forward()`` and hence could be refactored into a separate function, I figured it may make sense to retain separate statements to preserve the ability for root-specific behavior in the future. Whichever approach the team prefers I can update this PR with.
### Implementation considerations and questions:
1. Rather than write a test that would arguably have a poor utility/resource usage profile, I have not added any tests associated with this PR. The new decision logic is exercised by all existing tests (which continue to pass after this PR of course) so I think the utility of new tests is fairly modest. Let me know if you think new tests should be added and I'm happy to do so.
2. As discussed above, the decision statement shared among ``_pre_forward()`` and ``_root_pre_forward()`` could be factored out into a separate function. Given the simplicity of the statement and to retain current flexibility for root-specific decisions it might not be worth the refactor so I haven't done it yet. Let me know if you'd like me to do so.
3. The note below could be updated to indicate the utility of setting ``cast_forward_inputs=True`` for the situations addressed with this PR but I haven't done so since I'm not sure it's worth complicating the current usage guidance. I'd be happy to add verbiage describing the use case if the team wants it.
cde35b4069/torch/distributed/fsdp/api.py (L175-L181)
Thanks again to the PyTorch distributed team for your immensely valuable contributions to the open-source ML community!
[^1]: Though one could keep the existing decision logic and impose a new topological constraint requiring all FSDP instances have direct `_handles`, I think retaining the current wrapping flexibility is both convenient and useful enough (e.g. programmatic wrapping of modules that may or may not already have all parameters handled by descendant FSDP instances) to update the decision logic as discussed here instead.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99546
Approved by: https://github.com/awgu
This PR makes `use_orig_params=True` case support rank0_only loading for optim state_dict. The implementation is different from `use_orig_params=False`. The `use_orig_params=False` implementation first flatten the parameters on rank0 and then broadcast the states while this implementation broadcast the state when doing the flattening. The implementation is slower as it broadcast the original parameters instead of the flattened ones. However, the implementation introduced by this PR is simpler. As loading is usually happen once per training life, the performance difference can be ignored. In next PR, we will consolidate the implementations in favor of the simpleness.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99624
Approved by: https://github.com/wz337
This PR introduces a ParallelMode interface to define how to do
SPMD expansion and optimize the captured graph. This would be
beneifical for different parallelisms to expand differently
and apply different optimization passes
Put DTensorExpandMode as the first parallel mode that does the
existing dtensor_expand functionality.
Differential Revision: [D45174399](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D45174399)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/98452
Approved by: https://github.com/mrshenli
As functional collective being updated, using tensor_split() as the underlying sharding algorithm would require padding and unpadding on multiple ranks. Therefore, we are changing the sharding algorithm to be in line with ``torch.chunk()`` to allow padding on the last two ranks in most of the scenarios.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/98722
Approved by: https://github.com/wanchaol
### Description
The PR aims at reducing CPU overhead of context manager style coalescing.
By "context manager style coalescing", we mean:
Sync style:
```
with _coalescing_manager():
for i in range(num_coll):
dist.all_reduce(tensors[i])
```
Async style:
```
with _coalescing_manager(async_ops=True) as cm:
for i in range(num_coll):
dist.all_reduce(tensors[i])
cm.wait()
```
In previous implementation, each collective in the `num_coll` loop actually calls into the C++ backend, accumulating pybind overhead.
In the new implementation, we capture the collectives at Python level, and only fire towards C++ at the exit of the coalescing manager.
### Tests
In current PR, the "fast path" only applies to all-reduce.
- Flattened 512M: 16.38 ms, including CPU time 131.21 us
- Old _coalescing_manager 64 x 8M: 22.19 ms, including CPU time 2865 us
- New _coalescing_manager 64 x 8M: 16.93 ms, including CPU time 635 us
Hence a 4x reduction in CPU overhead (dependent on `num_coll`).
Cc @mrshenli @kumpera @wanchaol @fegin
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/98793
Approved by: https://github.com/kumpera
## What problem this PR solves?
#97170 fixed `equal` operator return type (old: Tensor, now: bool) by giving it the correct sharding propagation. This is consistent with the `aten::equal` op. However, the correctness only stays at the local result level:
* `equal` op returns True if the local copy of dtensor A equals to the the local copy of dtensor B
This is not the correct semantic of `equal` which should return True if all local copies of A are equal to the corresponding local copies of B.
## What is this PR?
1. For non-participating ranks, if the return type is scalar, `local_results` is set to `None` which means the default value is a reduced result of participating ranks only.
2. For all ranks, if the return type is scalar and the `op_call` is `aten::equal`(because `aten::equal` is the only function that returns scalar value and needs communication), all gather the `local_results` within the `default pg` and reduce on them with `operator.and_`. The result will be the new `local_result`.
## Result/Impact
For non-participating ranks and the return type is scalar:
1. op is `aten::equal`, the return value is same with all other ranks
2. op is not `aten::equal`, the return value is None. Before this PR, this will raise "NotImplementedError" but has not been tested.
For participating ranks and the return type is scalar:
1. op is `aten::equal`, the return value is the equality of two dtensor operands - True if all copies are equal, False otherwise.
2. op is not `aten::equal`, simply the local computation result.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99014
Approved by: https://github.com/wanchaol
Summary:
This diff is reverting D44897935
D44897935: [FSDP] Include duplicate parameters and modules when calling named_parameters and named_modules (#98912) by fegin has been identified to be causing the following test or build failures:
Tests affected:
- [caffe2/torch/fb/module_factory/sync_sgd/tests:test_pyper_data_parallel_wrapper - caffe2.torch.fb.module_factory.sync_sgd.tests.test_pyper_data_parallel_wrapper.PyPerDataParallelWrapperTest: test_fsdp_submodules_pyper](https://www.internalfb.com/intern/test/562950025957458/)
Here's the Multisect link:
https://www.internalfb.com/multisect/1893714
Here are the tasks that are relevant to this breakage:
We're generating a revert to back out the changes in this diff, please note the backout may land if someone accepts it.
If you believe this diff has been generated in error you may Commandeer and Abandon it.
Test Plan: NA
Reviewed By: fegin
Differential Revision: D45027286
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99353
Approved by: https://github.com/izaitsevfb, https://github.com/fegin
Fixes#99174
## Enable FSDP ``use_orig_params=True`` mixed precision training when some ranks have no (non-zero sized) parameter shards
### The issue
Now that ``use_orig_params=True`` allows non-uniform ``requires_grad`` (🎉🚀 thanks @awgu!!!) with [#98221](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/98221), there will be circumstances wherein some ranks have no (non-zero sized) local shards of the original parameters (and hence no associated gradients).
### Use Cases
For a simple Transformer case, imagine a user wraps all encoder layers in separate FSDP instances but allows the classifier head to be wrapped in the same FSDP instance as the relatively large embeddings layers. While this is a sub-optimal wrapping strategy for most use-cases, I believe it is expected to be supported (full precision training works in that context).
I originally encountered this issue while extending a package I maintain, leveraging the relaxed ``requires_grad`` contstraint to simplify multi-phase scheduled fine-tuning FSDP configuration, so a [concrete example is there](https://finetuning-scheduler.readthedocs.io/en/latest/advanced/fsdp_scheduled_fine_tuning.html#basic-scheduled-fine-tuning-with-fsdp).
### Reproduction and Remediation
Currently, ``ShardedGradScaler`` does not accommodate these situations, failing to initialize ``optimizer_state["found_inf_per_device"]`` when ``unscale_`` is called.
In this PR, I extend the existing ``ShardedGradScaler`` tests with an ``use_orig_params=True`` dimension added to the parameterization and test scenarios wherein one rank possesses no (non-zero sized) parameter shards.
The relevant issue can be reproduced with the tests I'm adding in this PR. The current (pre-PR) execution of these tests fail in ``use_orig_params=True`` mode with this error:
```python
./test_fsdp_sharded_grad_scaler.py::TestShardedGradScalerParityWithDDP::test_fsdp_ddp_parity_with_grad_scaler_offload_false_none_mixed_precision_use_orig_params Failed with Error: Process 0 exited with error code 10 and exception:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/speediedan/repos/pytorch/torch/testing/_internal/common_distributed.py", line 657, in run_test
getattr(self, test_name)()
File "/home/speediedan/repos/pytorch/torch/testing/_internal/common_distributed.py", line 543, in wrapper
fn()
File "/home/speediedan/repos/pytorch/torch/testing/_internal/common_utils.py", line 259, in instantiated_test
test(self, **param_kwargs)
File "/home/speediedan/repos/pytorch/torch/testing/_internal/common_distributed.py", line 174, in wrapper
return func(*args, **kwargs)
File "/home/speediedan/repos/pytorch/test/distributed/fsdp/test_fsdp_sharded_grad_scaler.py", line 187, in test_fsdp_ddp_parity_with_grad_scaler
self._test_fsdp_parity(
File "/home/speediedan/repos/pytorch/torch/testing/_internal/common_fsdp.py", line 1152, in _test_fsdp_parity
fsdp_loss = self._train_for_several_steps(
File "/home/speediedan/repos/pytorch/torch/testing/_internal/common_fsdp.py", line 1016, in _train_for_several_steps
sharded_grad_scaler.step(optim)
File "/home/speediedan/repos/pytorch/torch/distributed/fsdp/sharded_grad_scaler.py", line 291, in step
return super().step(optimizer, *args, **kwargs)
File "/home/speediedan/repos/pytorch/torch/cuda/amp/grad_scaler.py", line 368, in step
assert len(optimizer_state["found_inf_per_device"]) > 0, "No inf checks were recorded for this optimizer."
AssertionError: No inf checks were recorded for this optimizer.
```
A few implementation notes/considerations and questions:
1. Rather than just initialize ``per_device_found_inf``, one could disable the grad scalar altogether for relevant ranks, altering ``unscale_`` to reduce with a subgroup or some rank mask construct to avoid the ``all_reduce`` s in ``distributed/fsdp/sharded_grad_scaler.py:unscale_()`` from hanging. Given that users may subsequently add parameter groups to an optimizer that would require re-enabling the scaler and the complexity associated with maintaining a separate mask construct or process subgroup, I thought this implementation was cleaner.
2. I extended ``_train_for_several_steps`` and ``_test_fsdp_parity`` in ``/torch/testing/_internal/common_fsdp.py`` with the ability to configure ``sharded_grad_scaler_kwargs`` for future testing flexibility.
3. Should the user be warned that no parameter shards were associated with a given rank? My initial thought is that this should be considered an implementation detail, part of supporting ``use_orig_params`` with heterogeneous ``requires_grad``, and therefore should be transparently handled by PyTorch. Should a DEBUG level message be added? If so, likely further upstream rather than at the scaler step level.
4. Rather than extend the existing ``ShardedGradScaler`` tests with an ``use_orig_params=True`` dimension added to the parameterization, let me know if you prefer that I instead narrow the scope of the new testing to a single additional test, e.g.:
```python
# from typing import Optional
from typing import Optional, List
# ...
# use_orig_params = ["enable_use_orig_params", None]
use_orig_params: List[Optional[str]] = [None]
# ...
configs = list(itertools.product(cpu_offload_config, sharding_strategy_config, mixed_precision, use_orig_params))
configs.append((CPUOffload(offload_params=False), None, "enable_mixed_precision", "enable_use_orig_params"))
```
Thanks as always to the PyTorch distributed team for your astonishingly impressive and valuable contributions to the open-source ML engineering community!
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99175
Approved by: https://github.com/awgu
replicate + trec_shard works if we shard / replicate individually, such as follows:
```
m = TestSparseNN()
shard(m.sparse)
replicate(m.dense)
```
but does not work if users do the following:
```
m = TestSparseNN()
shard(m, sharders=[...])
replicate(m)
```
Many upstream trainers use the latter use case, as sharding is not done on individual module level but rather overall module by specifying planners that contain logic for how to shard different embedding table types.
This diff enables the latter approach (while keeping the former intact), but users need to specify `ignored_modules` to ignore embedding tables in replicate(). This is similar to FSDP (class based and composable) and DDP today.
Differential Revision: [D44899155](https://our.internmc.facebook.com/intern/diff/D44899155/)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/98890
Approved by: https://github.com/mrshenli, https://github.com/yhcharles
Summary:
Original commit changeset: ba36f8751adc
Original Phabricator Diff: D44788697
Test Plan: model loading is fine after reverting the diff
Reviewed By: zyan0, sayitmemory
Differential Revision: D44921259
---
Fixes #ISSUE_NUMBER
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99168
Approved by: https://github.com/izaitsevfb
At present, DDP forward uses `_get_stream` to get a stream,which is cudaStream.
If the custom module already registered to torch, I can use `getattr` to get it and it's stream. Then, the custom stream is used to copy the tensor.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/98723
Approved by: https://github.com/ezyang
Currently, aten.expand always expands to the global dimension. Then, it
introduces additional slice and clone ops before running compute on
the expanded tensor with a local tensor.
In this commit, if we detect the op consumes a SymInt size, it respects
both local size and the dimension placements from where the SymInt was
extracted.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99058
Approved by: https://github.com/wanchaol