This updates ruff to 0.285 which is faster, better, and have fixes a bunch of false negatives with regards to fstrings.
I also enabled RUF017 which looks for accidental quadratic list summation. Luckily, seems like there are no instances of it in our codebase, so enabling it so that it stays like that. :)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/107519
Approved by: https://github.com/ezyang
This updates ruff to 0.285 which is faster, better, and have fixes a bunch of false negatives with regards to fstrings.
I also enabled RUF017 which looks for accidental quadratic list summation. Luckily, seems like there are no instances of it in our codebase, so enabling it so that it stays like that. :)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/107519
Approved by: https://github.com/ezyang
Enabling more tests on ASAN, meanwhile we disable float-divide-by-zero and float-cast-overflow, both are disabled because they are also disabled by default in latest clang.
The following cited doc explains the reasons.
```
-fsanitize=float-cast-overflow: Conversion to, from, or between floating-point types
which would overflow the destination. Because the range of representable values
for all floating-point types supported by Clang is [-inf, +inf], the only cases detected are
conversions from floating point to integer types.
-fsanitize=float-divide-by-zero: Floating point division by zero.
This is undefined per the C and C++ standards,
but is defined by Clang (and by ISO/IEC/IEEE 60559 / IEEE 754) as producing
either an infinity or NaN value,
so is not included in -fsanitize=undefined.
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/103647
Approved by: https://github.com/kit1980
The `ref` property was moved down from `{Unary,Binary}UfuncInfo` into
`OpInfo` quite some time ago, but `OpInfo` uses `None` to signal no
reference is available while the others use `_NOTHING`. This makes
everything consistently use `None`.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/82348
Approved by: https://github.com/ngimel
The `ref` property was moved down from `{Unary,Binary}UfuncInfo` into
`OpInfo` quite some time ago, but `OpInfo` uses `None` to signal no
reference is available while the others use `_NOTHING`. This makes
everything consistently use `None`.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/82348
Approved by: https://github.com/ngimel
This PR makes the following improvements:
- moves the custom skip list for test_normalize_operator_exhaustive in test_fx_experimental to use the typical OpInfo skip architecture. The skips were updated to xfails, and that identified some operators which were no longer failing the test
- redundant tests with OpInfo-based testing in test_jit.py were removed
- test_dtypes was improved so its error messages are clear and it makes test_nondifferentiable redundant; the latter test has been removed
- OpInfo.supports_complex_autograd() is removed in favor of a more accurate and general test for whether the particular dtype is in the backward dtypes of the operator
- gradchecks have been improved to verify that an operator doesn't support grad if it claims not to
- gradchecks have been improved to test the gradient of all input tensors that require gradient
- the concept of "default test dtypes" has been removed
- excessive and mostly redundant out testing for elementwise unary operators has been removed
- metadata for whether an op supports nuanced "safe casting" to out behavior has been removed from OpInfos
- numerous skips have been converted to xfails
- numerous OpInfos have had their metadata fixed based on the new checks
- jit-specific utilities in common_methods_invocations.py have been moved to jit_programming_utils.py
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/75951
Approved by: https://github.com/ngimel
Summary:
Add BFloat16 support for logsigmoid, hardsigmoid, hardshrink, softshrink, hardswish and softplus on CPU, and optimize the performance of softshrink.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63134
Reviewed By: yinghai
Differential Revision: D34897992
Pulled By: frank-wei
fbshipit-source-id: 4c778f5271d6fa54dd78158258941def8d9252f5
(cherry picked from commit decda0e3debf56cc5c4d7faea41b1165a7cabe12)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/73748
This adds CPU-only slow test jobs, which previously would never run.
Includes fixes/skips for slow tests which fail (they need to be skipped now because they used to never run)
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D34628803
Pulled By: davidberard98
fbshipit-source-id: c090ab7bf7bda9e24ec5cdefa6fd35c6310dbac0
(cherry picked from commit 06f7a94a57cc7023e9c5442be8298d20cd011144)
Summary:
This PR:
- creates the "jiterator" pattern, allowing elementwise unary and binary kernels that don't accept scalars to be jit compiled when called
- ports the gcd and i1 CUDA kernels to use the jiterator
- extends elementwise binary systemic testing to be comparable to elementwise unary systemic testing
- separates one test case from test_out in test_ops.py
- updates more OpInfos to use expected failures instead of skips
The jiterator currently does not support half, bfloat16 or complex dtypes. It also (as mentioned above) doesn't support scalar inputs. In the future we expect to add support for those datatypes and scalars.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69439
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D32874968
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: d44bb9cde4f602703e75400ec5a0b209f085e9b3
Summary:
This PR absolves `_TestParametrizer`s (e.g. `ops`, `modules`, `parametrize`) of the responsibility of adding device type (e.g. `'cpu'`, `'cuda'`, etc.) / dtype (e.g. 'float32') to generated test names. This fixes repeated instances of the device string being added to generated test names (e.g. `test_batch_norm_training_True_cuda_track_running_stats_True_cuda_affine_True_cuda`).
The responsibility for placing device / dtype suffixes is now handled by `instantiate_device_type_tests()` instead so it is added a single time. It will place `<device>_<dtype>` at the end of the test name unconditionally, maintaining the current naming convention.
As part of this work, I also tightened the semantics through some additional error case handling:
* Composing multiple decorators that each try to handle the same parameter will error out with a nice message. This includes the case to trying to compose `modules` + `ops`, as they each try to handle `dtype`. Similarly, `ops` + `dtypes` is forbidden when both try to handle `dtype`. This required changes in the following test files:
* `test/test_unary_ufuncs.py`
* `test/test_foreach.py`
* The `modules` / `ops` decorators will now error out with a nice message if used with `instantiate_parametrized_tests()` instead of `instantiate_device_type_tests()`, since they're not (currently) written to work outside of a device-specific context.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/65217
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D32627303
Pulled By: jbschlosser
fbshipit-source-id: c2957228353ed46a0b7da8fa1a34c67598779312
Summary:
Adds a new class `ErrorOrWarningInput` that is a `SampleInput` with some additional metadata for validating that `SampleInput` throws the desired warning or error. The architecture to support these new tests is modeled after the existing reference tests and sample input functions.
Existing invalid input tests for neg and kthvalue are ported to the new scheme to validate it.
There may be a simpler/clearer naming scheme we can use here.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/67354
Reviewed By: jbschlosser
Differential Revision: D31989888
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 4fa816e1e8d0eef21b81c2f80813d42b2c26714e
Summary:
Partially fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/66066
This PR:
- cleans up op-specific testing from test_autograd. test_autograd should be reserved for testing generic autograd functionality
- tests related to an operator are better colocated
- see the tracker for details
What to think about when moving tests to their correct test suite:
- naming, make sure its not too generic
- how the test is parametrized, sometimes we need to add/remove a device/dtype parameter
- can this be merged with existing tests
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/67413
Reviewed By: jbschlosser, albanD
Differential Revision: D32031480
Pulled By: soulitzer
fbshipit-source-id: 8e13da1e58a38d5cecbfdfd4fe2b4fe6f816897f
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63554
Following https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/61840#issuecomment-884087809, this deprecates all the dtype getters publicly exposed in the `torch.testing` namespace. The reason for this twofold:
1. If someone is not familiar with the C++ dispatch macros PyTorch uses, the names are misleading. For example `torch.testing.floating_types()` will only give you `float32` and `float64` skipping `float16` and `bfloat16`.
2. The dtype getters provide very minimal functionality that can be easily emulated by downstream libraries.
We thought about [providing an replacement](https://gist.github.com/pmeier/3dfd2e105842ad0de4505068a1a0270a), but ultimately decided against it. The major problem is BC: by keeping it, either the namespace is getting messy again after a new dtype is added or we need to somehow version the return values of the getters.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: H-Huang
Differential Revision: D30662206
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: a2bdb10ab02ae665df1b5b76e8afa9af043bbf56
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63572
Addresses #61906. Issue will be fixed later in the stack when `torch.testing.assert_close` got the same treatment.
cc ezyang gchanan
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: ezyang
Differential Revision: D30633527
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: c2002a4998a7a75cb2ab83f87190bde43a9d4f7c
Summary:
Large complex values lead to nan/inf results when using some glibc
implementations of atanh/acos
- Skip test_reference_numerics_hard instead of "normal"
- Test the edge values only for cdouble where the stdlib/glibc implementations support those large values
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/60259
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/60450
Reviewed By: mrshenli
Differential Revision: D29304834
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: d6b97456847c5573b9d2cb447bfc62abba73cb2a
Summary:
Implements an idea by ngimel to improve the performance of `torch.flip` via a clever hack into TI to bypass the fact that TI is not designed to work with negative indices.
Something that might be added is vectorisation support on CPU, given how simple the implementation is now.
Some low-hanging fruits that I did not implement:
- Write it as a structured kernel
- Migrate the tests to opinfos
- Have a look at `cumsum_backward` and `cumprod_backward`, as I think that they could be implemented faster with `flip`, now that `flip` is fast.
**Edit**
This operation already has OpInfos and it cannot be migrated to a structured kernel because it implements quantisation
Summary of the PR:
- x1.5-3 performance boost on CPU
- x1.5-2 performance boost on CUDA
- Comparable performance across dimensions, regardless of the strides (thanks TI)
- Simpler code
<details>
<summary>
Test Script
</summary>
```python
from itertools import product
import torch
from torch.utils.benchmark import Compare, Timer
def get_timer(size, dims, num_threads, device):
x = torch.rand(*size, device=device)
timer = Timer(
"torch.flip(x, dims=dims)",
globals={"x": x, "dims": dims},
label=f"Flip {device}",
description=f"dims: {dims}",
sub_label=f"size: {size}",
num_threads=num_threads,
)
return timer.blocked_autorange(min_run_time=5)
def get_params():
sizes = ((1000,)*2, (1000,)*3, (10000,)*2)
for size, device in product(sizes, ("cpu", "cuda")):
threads = (1, 2, 4) if device == "cpu" else (1,)
list_dims = [(0,), (1,), (0, 1)]
if len(size) == 3:
list_dims.append((0, 2))
for num_threads, dims in product(threads, list_dims):
yield size, dims, num_threads, device
def compare():
compare = Compare([get_timer(*params) for params in get_params()])
compare.trim_significant_figures()
compare.colorize()
compare.print()
compare()
```
</details>
<details>
<summary>
Benchmark PR
</summary>
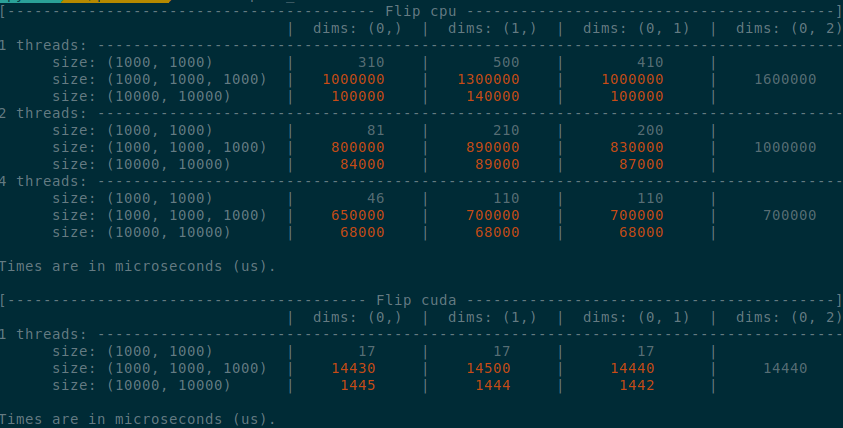
</details>
<details>
<summary>
Benchmark master
</summary>
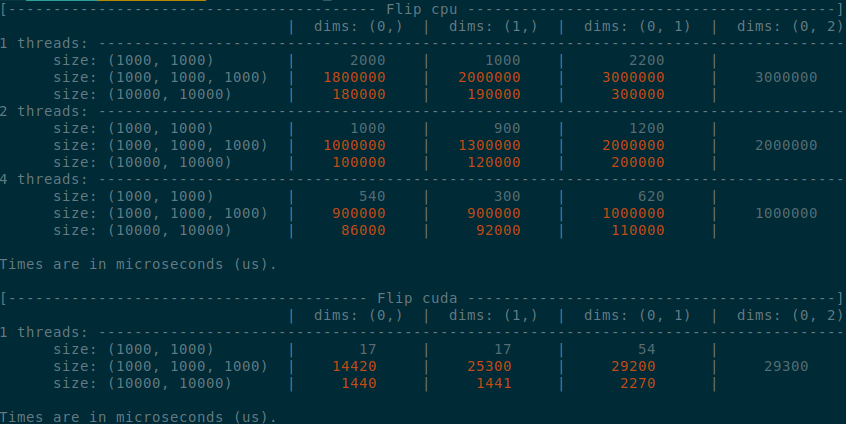
</details>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58747
Reviewed By: agolynski
Differential Revision: D28877076
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 4fa6eb519085950176cb3a9161eeb3b6289ec575
Summary:
Resubmit of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/58811, Closes gh-24745
The existing PR (gh-50655) has been stalled because `TensorIterator` doesn't guarantee iteration order in the same way that `TH_TENSOR_APPLY` does. For contiguous test cases this isn't an issue; but it breaks down for example with channels last format. I resolve this by adding a new `TensorIteratorConfig` parameter, `enforce_linear_iteration`, which disables dimension reordering. I've also added a test case for non-contiguous tensors to verify this works.
This PR also significantly improves performance by adding multithreading support to the algorithm. As part of this, I wrote a custom `count_nonzero` that gives per-thread counts which is necessary to write the outputs in the right location.
| Shape | Before | After (1 thread) | After (8 threads) |
|:----------:|--------:|-----------------:|------------------:|
| 256,128,32 | 2610 us | 2150 us | 551 us |
| 128,128,32 | 1250 us | 1020 us | 197 us |
| 64,128,32 | 581 us | 495 us | 99 us |
| 32,128,32 | 292 us | 255 us | 83 us |
| 16,128,32 | 147 us | 126 us | 75 us |
| 8,128,32 | 75 us | 65 us | 65 us |
| 4,128,32 | 39 us | 33 us | 33 us |
| 2,128,32 | 20 us | 18 us | 18 us |
| 1,128,32 | 11 us | 9 us | 9 us |
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/59149
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D28817466
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: f08f6c003c339368fd53dabd28e9ada9e59de732