Should fix#13362 and fix#83790
I think I've discovered the root cause of the intermittent nccl link
failures. If we look at the variable name in the redefinition error:
```
_02021d91_11_sendrecv_cu_0bc7b9c8_11152
```
this is the name of the file being compiled + some form of unique ID.
As part of NCCL's build process, the same file is compiled multiple
times with different macro definitions depending on which operator and
dtype are being compiled, e.g.
```
nvcc -DNCCL_OP=0 -DNCCL_TYPE=0 -dc sendrecv.cu -o sendrecv_sum_i8.o
```
Since the filename parts are the same, then if the unique IDs also
happen to collide then the entire identifier will collide and the link
fails. So the fix here is to generate a unique `.cu` file for each
object file. I've implemented this as a `.patch` file that gets
applied from our cmake code, but if we instead fork nccl that would be
cleaner.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/84245
Approved by: https://github.com/janeyx99, https://github.com/malfet
Summary: In [PR 84755](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/84755), @cccclai noticed and mentioned the presence of `message(STATUS...)` logging in caffe2/CMakeLists.txt and suggested moving it to the file cmake/Summary.cmake. This PR addresses that comment/suggestion.
Test Plan: Ran the build as `USE_NUMPY=0 USE_DISTRIBUTED=0 USE_CUDA=0 TRACING_BASED=1 python setup.py develop`
and saw the follwing being printed:
```
-- BUILD_MOBILE_AUTOGRAD : OFF
-- BUILD_LITE_INTERPRETER: OFF
-- INTERN_BUILD_MOBILE :
-- TRACING_BASED : 1
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/84814
Approved by: https://github.com/cccclai
# Summary:
- I added a new submodule Cutlass pointing to 2.10 release. The inclusion of flash_attention code should be gated by the flag: USE_FLASH_ATTENTION. This is defaulted to off resulting in flash to not be build anywhere. This is done on purpose since we don't have A100 machines to compile and test on.
- Only looked at CMake did not attempt bazel or buck yet.
- I included the mha_fwd from flash_attention that has ben refactored to use cutlass 2.10. There is currently no backwards kernel on this branch. That would be a good follow up.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/81434
Approved by: https://github.com/cpuhrsch
We're no longer building Caffe2 mobile as part of our CI, and it adds a lot of clutter to our make files. Any lingering internal dependencies will use the buck build and so wont be effected.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/84338
Approved by: https://github.com/dreiss
Since #83173 was merged I have noticed some CI being slowed down by
the nccl building step. e.g. if there are no C++ changes then sccache
compiles everything else very quickly and nccl becomes the limiting
factor.
This re-enables parallel builds with some safeguards to protect
against oversubscription. When `make` is the parent build system, we
can use `$(MAKE)` and the `make` jobserver will coordinate job
allocation with the sub-process. For other build systems, this calls
`make` with the `-l` flag which should prevent it launching jobs when
the system load average is already too high.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/83696
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
This problem updates the the PR [#73040](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/73040)
The compilation error in pyTorch with ROCm is successful with these changes when `NDEBUG` is enabled.
Solution:
For HIP we keep `__device__ __assert_fail()`
and for host side compilation we want to use the `__assert_fail()` from the glibc library.
Tested the code by compiling with below steps
```
python3 tools/amd_build/build_amd.py
python3 setup.py develop --cmake-only
cmake -DHIP_HIPCC_FLAGS_RELEASE="-DNDEBUG" build
cmake --build build
```
The UT test_fixed_cuda_assert_async is still skipped due performance overhead.
cc @jithunnair-amd
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/81790
Approved by: https://github.com/shintaro-iwasaki, https://github.com/jeffdaily, https://github.com/malfet
And use it throughout the CMakeLists and rectify `IF(APPLE)`/`IF(GNU_CXX_VERSION VERSION_GREATER A.B)` and so on
Also, add `target_compile_options_if_supported` and use it in `Dependencies.cmake` as well as in test's `CMakeListst.txt`
Delete `-Wno-unknown-warning-option` to test that conditions indeed working as expected
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/82883
Approved by: https://github.com/seemethere
- Modifies the current cmake build definitions to use `find_package` to find UCX and UCC installed in the system
- Install UCX and UCC in CUDA dockers
- Build PyTorch with `USE_UCC=1` in pipelines
- Currently, we are not running unit tests with the UCC PG. Those tests will be added in future PRs.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/81583
Approved by: https://github.com/vtlam, https://github.com/malfet
And use it throughout the CMakeLists and rectify `IF(APPLE)`/`IF(GNU_CXX_VERSION VERSION_GREATER A.B)` and so on
Also, add `target_compile_options_if_supported` and use it in `Dependencies.cmake` as well as in test's `CMakeListst.txt`
Delete `-Wno-unknown-warning-option` to test that conditions indeed working as expected
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/82883
Approved by: https://github.com/seemethere
By extending regex to match any character other than not just version
On Ubuntu version string looks as follows:
```
$ objcopy --version
GNU objcopy (GNU Binutils for Ubuntu) 2.30
```
And on some CentOSes it looks as
```
$ objcopy --version
GNU objcopy (GNU Binutils) 2.37
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/82774
Approved by: https://github.com/ngimel
### Description
These changes were made to assure, that the code that tests the vector instruction set extensions not only compiles but also runs to detect it properly for MSVC:
- INCLUDE(CheckCSourceRuns) instead of INCLUDE(CheckCSourceCompiles)
- INCLUDE(CheckCXXSourceRuns) instead of INCLUDE(CheckCXXSourceCompiles)
- CHECK_C_SOURCE_RUNS instead of CHECK_C_SOURCE_COMPILES
- CHECK_CXX_SOURCE_RUNS instead of CHECK_CXX_SOURCE_COMPILES
### Issue
#82553
### Testing
I tried the [code changes](86246b3c58) on a copy of [FindAVX.cmake](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/cmake/Modules/FindAVX.cmake) in my repository [convolution-benchmarks](https://github.com/JohT/convolution-benchmarks) and could verify that the detection works properly now.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/82554
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
To fix#78540 I committed #78983 which is reverted due to internal CI failure. Then I comitted #79215 which was only fixing the failure but didn't have the full feature of #78983. This PR is another try.
This PR adds script to dump all operators from test models and automatically write into `lightweight_dispatch_ops.yaml`. This way we don't have to manually update the yaml file.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/80791
Approved by: https://github.com/raziel
RocksDB 7 starts to use C++17 in header.
We should make this configurable, in case user needs higher std version.
List of files to changed is found by `git grep 'CMAKE_[^_]*_STANDARD'`.
Doc string is from CMake code.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/75519
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
Summary:
This diff integrates UCC process group as a native component of Pytorch Distributed core. It is based on the existing torch-ucc (https://github.com/facebookresearch/torch_ucc) as the wrapper for UCC collective communication library.
The environment and cmake variables are named in mirroring to the existing process groups such as NCCL and Gloo. Specifically,
- USE_UCC: enables UCC PG. This defaults to OFF, so there is no breakage of existing builds that do not have UCX/UCC external libraries.
- USE_SYSTEM_UCC: uses external UCX and UCC shared libraries that are set accordingly with UCX_HOME and UCC_HOME.
Currently, this diff only supports USE_SYSTEM_UCC=ON, i.e., requiring users to specify external libraries for UCX and UCC. In subsequent diffs, we will add UCX and UCC repos as third-party dependencies in pytorch/third-party.
Test Plan:
Passed Torch-UCC tests that invoke UCC process group. For example:
$ sh test/start_test.sh test/torch_allreduce_test.py --backend gloo --use-cuda
...
Test allreduce: succeeded
Differential Revision: D36973688
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/79918
Approved by: https://github.com/kwen2501, https://github.com/kingchc
The correct variable name should be USE_SYSTEM_PYBIND11, as defined in
the root CMakeLists.txt. In cmake/Dependencies.cmake, it is incorrectly
written as USE_SYSTEM_BIND11, but cmake will not complain about this.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/80272
Approved by: https://github.com/suo
When we use pytorch with unregistered blas, spack set BLAS=Generic.
pytorch is searched only libblas.
If the blas package's blas library name is not libblas, spack install py-torch is failed.
This PR set blas lirary names to GENERIC_BLAS_LIBRARIES environment variable, and py-torch is found blas library.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/74269
Approved by: https://github.com/kit1980
cpuinfo has some symbols that need to be resolved with clog.
```
Static builds fail without this fix with this error:
api.c:(.text+0xc2): undefined reference to `clog_vlog_fatal'
init.c:(.text+0x19d1): undefined reference to `clog_vlog_error'
processors.c:(.text+0x551): undefined reference to `clog_vlog_error'
smallfile.c:(.text+0x172): undefined reference to `clog_vlog_error'
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/79551
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
This PR introduces selective build to lightweight dispatch CI job. By doing so we can't run the `test_lite_intepreter_runtime` test suite anymore because it requires some other operators.
From now on, if we are adding a new unit test in `test_codegen_unboxing`, we will have to export the operators for the unit test model and add them into `lightweight_dispatch_ops.yaml`. This can be automated by introducing tracing based selective build, but that's for next PR to do.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78983
Approved by: https://github.com/kit1980
Otherwise, its possible to build TensorPipe with one version of libuv
and gloo with another.
Also, delete strange `GLOO_INSTALL` logic, as none of the install artifacts are really packaged as part of PyTorch (and it were probably used by Caffe2 builds)
This helps solve problem for compiling PyTorch for M1, where `libuv` is not available in conda
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/77312
Approved by: https://github.com/seemethere
Re-landing #68111/#74596
## Description
v0.5 PR of this [RFC](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/49444).
On the basis of #50256, the below improvements are included:
* The [v0.5 release branch](https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneDNN/releases/tag/graph-v0.5) of the oneDNN Graph API is used
* The fuser now works with the profiling graph executor. We have inserted type check nodes to guard the profiled tensor properties.
### User API:
The optimization pass is disabled by default. Users could enable it by:
```
torch.jit.enable_onednn_fusion(True)
```
`torch.jit.freeze` should be used after tracing (recommended) or scripting a model.
### Performance:
[pytorch/benchmark](https://github.com/pytorch/benchmark) tool is used to compare the performance:
* SkyLake 8180 (1 socket of 28 cores):
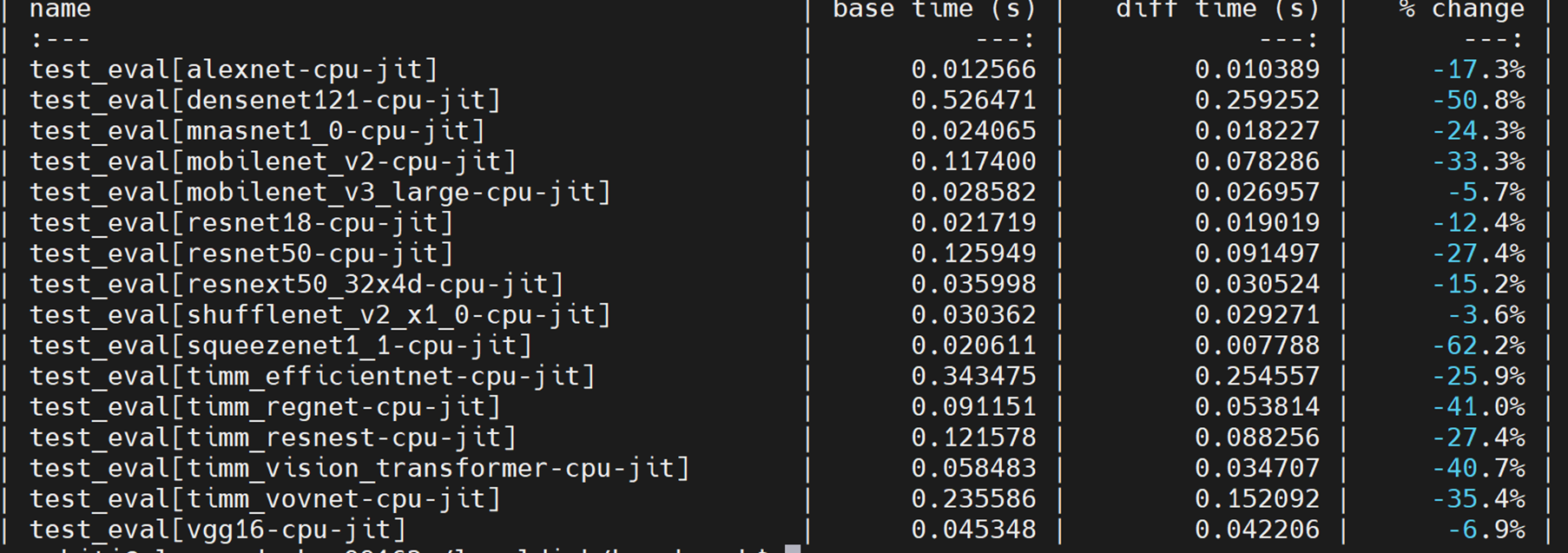
* SkyLake 8180 (single thread):
* By mapping hardswish to oneDNN Graph, it’s 8% faster than PyTorch JIT (NNC + OFI)
** We expect performance gain after mapping transpose, contiguous & view to oneDNN graph ops
### Directory structure of the integration code
Fuser-related code is placed under:
```
torch/csrc/jit/codegen/onednn/
```
Optimization pass registration is done in:
```
torch/csrc/jit/passes/onednn_graph_fuser.h
```
CMake for the integration code is in:
```
caffe2/CMakeLists.txt
cmake/public/mkldnn.cmake
cmake/Modules/FindMKLDNN.cmake
```
## Limitations
* In this PR, we only support Pytorch-oneDNN-Graph integration on Linux platform. Support on Windows and MacOS will be enabled as a next step.
* We have only optimized the inference use-case.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/76622
Approved by: https://github.com/eellison
This functionality does not seem to be used
and there are some requests to update dependency.
Add `third_party` to torch_cpu include directories if compiling with
Caffe2 support, as `caffe2/quantization/server/conv_dnnlowp_op.cc` depends on `third_party/fbgemm/src/RefImplementations.h`
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/75394
Approved by: https://github.com/janeyx99, https://github.com/seemethere
This was causing the shaders to be incorrectly templated because
both the precision argument and the format argument were being treated
as a single argument by argparse and therefore pasted into shaders
incorrectly. In turn this meant that shaders couldn't be compiled
when the precision or format options were turned on.
Fixes#76195
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/76196
Approved by: https://github.com/dagitses
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/75605
Usecase: Milan models have multiple backends and need to use static dispatch to save on static initialization time and to hit native functions directly from the unboxed APIs.
This change passes in List[BackendIndex] and adds ability to generate code for multiple static backends with 1 or 0 kernels
ghstack-source-id: 154525738
(Note: this ignores all push blocking failures!)
Test Plan:
Builds lite_predictor_flatbuffer with multiple backends
```
buck build --config pt.enable_lightweight_dispatch=1 --config pt.static_dispatch_backend=CPU,QuantizedCPU,CompositeExplicitAutograd //xplat/caffe2/fb/lite_predictor:lite_predictor_flatbuffer
```
Reviewed By: larryliu0820
Differential Revision: D35510644
fbshipit-source-id: f985718ad066f8578b006b4759c4a3bd6caac176
(cherry picked from commit a6999729c8cc26c54b8d5684f6585d6c50d8d913)
Summary:
[Comment](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/62445/files#r680132022) claims, it got added for consistency with top level CMakeLists.txt, but `-Wno-unused-variable` is not mentioned there.
Modify violations in 50+ files that were added in the interim by either removing unused variables, or decorating the code with `C10_UNUSED` if local variable is likely used to extend object lifetime until the end of the block.
Caused preventable revert in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72633#issuecomment-1092300787
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/75538
Reviewed By: anjali411
Differential Revision: D35747333
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 3fc5828e44a4c05ba0e89e92613e6ebbdb260626
(cherry picked from commit c179fba21cfa2a0093fad50ccad5a22dd7cff52c)
Summary:
RCCL is required by two components in hipified Pytorch: (1) gloo and (2) hipified ProcessGroupNCCL.
- For (1) the RCCL dependency is managed in `./third_party/gloo/cmake/Dependencies.cmake` and can be enabled/disabled via `USE_RCCL`.
- For (2) the RCCL dependency is managed via `./cmake/Dependencies.cmake` and can be on/off via `USE_NCCL`.
The additional dependency removed in this commit forced hipified Pytorch to load librccl.so even when USE_RCCL=OFF USE_NCCL=OFF is set, i.e., when using torch_ucc/ucc for AMD GPU mem type. This caused conflicts when we use a non-system default librccl.so (i.e., not in ROCM_PATH) for torch_ucc/ucc.
This commit removes the unnecessary RCCL dependency. This will ensure a cleaner way to use torch_ucc with a user-specified RCCL library.
Test Plan:
## Verify OSS pytorch on an AMD GPU machine (MI100)
```
ROCM_PATH=/opt/rocm-4.5.2
git clone https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch.git
cd pytorch
python3 tools/amd_build/build_amd.py
USE_NCCL=0 USE_RCCL=0 USE_KINETO=0 with-proxy python3 setup.py develop
USE_NCCL=0 USE_RCCL=0 USE_KINETO=0 with-proxy python3 setup.py install
```
log for develop: P492778257
log for install: P492778277
## Verify OSS pytorch + TorchUCC on an AMD GPU machine (MI100)
```
export RCCL_INSTALL_DIR=/opt/rccl-rocm-rel-4.4
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/torch_ucc.git
cd torch_ucc
UCX_HOME=$RCCL_INSTALL_DIR UCC_HOME=$RCCL_INSTALL_DIR WITH_CUDA=$ROCM_PATH python setup.py
# run param comm
export HSA_ENABLE_SDMA=0
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$RCCL_INSTALL_DIR
cd test
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/param
cd ..
/bin/bash ./test/start_test.sh ./test/param/train/comms/pt/comms.py --backend ucc --device cuda --b 4 --e 4M --c 1 --collective all_reduce
```
- log for param comm: P493033836
- Verified librccl.so in `/opt/rccl-rocm-rel-4.4` is used via checking version string in log. "[localbuild]" is added in RCCL source.
```
RCCL version 2.9.9+hip4.4 [localbuild]
```
Differential Revision: D35476911
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/75547
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet, https://github.com/jeffdaily
Summary:
This is the very first step for the UCC-NCCL integration. This PR lets `ProcessGroupNCCL` load the `torch_ucc.so` if the user specifies an environmental variable `TORCH_UCC_LIBRARY_PATH`. If this environment variable is not specified by the user, then there will be no visible change.
In the future, we may want to make PyTorch smart enough to automatically detect the `torch_ucc.so` in the user's system, but before doing that, I believe we should first make sure that `ProcessGroupUCC` is very well tested.
Note that in this PR, `ProcessGroupNCCL` just loads the library but will not use it. I am trying to make PRs small, so the usage of `torch_ucc.so` will be submitted in later PRs.
This PR requires the change in https://github.com/facebookresearch/torch_ucc/pull/56, otherwise `torch_ucc.so` can not be successfully loaded. But his PR can be landed separately without waiting for https://github.com/facebookresearch/torch_ucc/pull/56 because, in PyTorch's unit tests, UCC is never used or tested.
cc pietern mrshenli pritamdamania87 zhaojuanmao satgera rohan-varma gqchen aazzolini osalpekar jiayisuse SciPioneer H-Huang
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69552
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D34675212
Pulled By: jiayisuse
fbshipit-source-id: a3d1fb98340dbe3a931af555423863efd381f1ae
(cherry picked from commit 3778b6fabe70c26b5a65e6ddec641d2ef9113cd1)
Summary:
Also enables bazel build to run lazy codegen. Bazel (oss) build feeds off the same filelists as cmake/buck (build_variables.bzl), so enabling it is easier than keeping it disabled.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/74111
Test Plan: Run CI and verify test_lazy_ops is running via OSS cmake builds
Reviewed By: bdhirsh
Differential Revision: D34772403
fbshipit-source-id: 8a63f58b9536e6ac1be530667932176ef2549496
(cherry picked from commit e807ffb1918853d10b924fdc24f85ee5b1a39021)
Summary:
## Description
Preview4 PR of this [RFC](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/49444).
On the basis of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/50256, the below improvements are included:
- The [preview4 release branch](https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneDNN/releases/tag/graph-v0.4.1) of the oneDNN Graph API is used
- The fuser now works with the profiling graph executor. We have inserted type check nodes to guard the profiled tensor properties.
### User API:
The optimization pass is disabled by default. Users could enable it by:
```
torch.jit.enable_onednn_fusion(True)
```
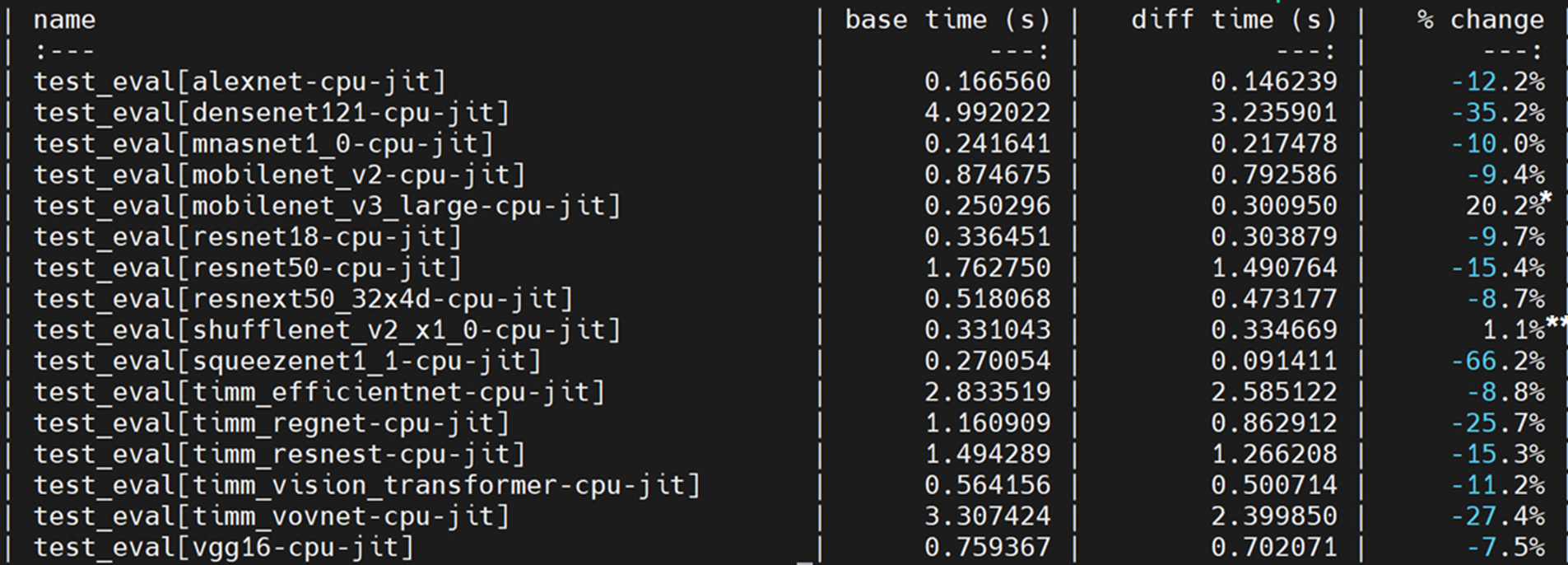
### Performance:
[pytorch/benchmark](https://github.com/pytorch/benchmark) tool is used to compare the performance:
- SkyLake 8180 (1 socket of 28 cores):

- SkyLake 8180 (single thread):

\* By mapping hardswish to oneDNN Graph, it’s 8% faster than PyTorch JIT (NNC + OFI)
\** We expect performance gain after mapping transpose, contiguous & view to oneDNN graph ops
### Directory structure of the integration code
Fuser-related code are placed under:
```
torch/csrc/jit/codegen/onednn/
```
Optimization pass registration is done in:
```
torch/csrc/jit/passes/onednn_graph_fuser.h
```
CMake for the integration code is:
```
caffe2/CMakeLists.txt
```
## Limitations
- In this PR, we have only supported the optimization on Linux platform. The support on Windows and MacOS will be enabled as the next step.
- We have only optimized the inference use case.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/68111
Reviewed By: eellison
Differential Revision: D34584878
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: ce817aa8cc9052ee9ed930c9cf66be83449e61a4
(cherry picked from commit cd17683aa7d9c0947df45a1ab53627feff795587)
Per https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/57744 statically linked CUPTI
causes exception handling to break on certain compiler configurations, likely
because CUPTI comes with incompatible libstdc++ symbols. Rather than pray that
something reasonable happens, use the safer configuration (dynamic linking) by
default and give a warning if the user inverts the setting.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyangfb.com>
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/74009
Approved by: https://github.com/malfet
Summary:
RFC: https://github.com/pytorch/rfcs/pull/40
This PR (re)introduces python codegen for unboxing wrappers. Given an entry of `native_functions.yaml` the codegen should be able to generate the corresponding C++ code to convert ivalues from the stack to their proper types. To trigger the codegen, run
```
tools/jit/gen_unboxing.py -d cg/torch/share/ATen
```
Merged changes on CI test. In https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/71782 I added an e2e test for static dispatch + codegen unboxing. The test exports a mobile model of mobilenetv2, load and run it on a new binary for lite interpreter: `test/mobile/custom_build/lite_predictor.cpp`.
## Lite predictor build specifics
1. Codegen: `gen.py` generates `RegisterCPU.cpp` and `RegisterSchema.cpp`. Now with this PR, once `static_dispatch` mode is enabled, `gen.py` will not generate `TORCH_LIBRARY` API calls in those cpp files, hence avoids interaction with the dispatcher. Once `USE_LIGHTWEIGHT_DISPATCH` is turned on, `cmake/Codegen.cmake` calls `gen_unboxing.py` which generates `UnboxingFunctions.h`, `UnboxingFunctions_[0-4].cpp` and `RegisterCodegenUnboxedKernels_[0-4].cpp`.
2. Build: `USE_LIGHTWEIGHT_DISPATCH` adds generated sources into `all_cpu_cpp` in `aten/src/ATen/CMakeLists.txt`. All other files remain unchanged. In reality all the `Operators_[0-4].cpp` are not necessary but we can rely on linker to strip them off.
## Current CI job test coverage update
Created a new CI job `linux-xenial-py3-clang5-mobile-lightweight-dispatch-build` that enables the following build options:
* `USE_LIGHTWEIGHT_DISPATCH=1`
* `BUILD_LITE_INTERPRETER=1`
* `STATIC_DISPATCH_BACKEND=CPU`
This job triggers `test/mobile/lightweight_dispatch/build.sh` and builds `libtorch`. Then the script runs C++ tests written in `test_lightweight_dispatch.cpp` and `test_codegen_unboxing.cpp`. Recent commits added tests to cover as many C++ argument type as possible: in `build.sh` we installed PyTorch Python API so that we can export test models in `tests_setup.py`. Then we run C++ test binary to run these models on lightweight dispatch enabled runtime.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69881
Reviewed By: iseeyuan
Differential Revision: D33692299
Pulled By: larryliu0820
fbshipit-source-id: 211e59f2364100703359b4a3d2ab48ca5155a023
(cherry picked from commit 58e1c9a25e3d1b5b656282cf3ac2f548d98d530b)
Summary:
Fixes : https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/73377
We've migrated to CUDA-11.3 as default toolkit in 1.9, it's time to stop builds (especially considering forward-compatibility guarantee across CUDA-11.x drivers)
Hence we are removing CUDA 11.1 support. We should also cleanup old cuda related code from our builder and pytorch repo making scripts a little more clean.
We have code that references cuda 9.2 , 10.1 , 11.0, 11.1, 11.2 and none of these are currently use
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/73514
Reviewed By: janeyx99
Differential Revision: D34551989
Pulled By: atalman
fbshipit-source-id: 9ceaaa9b25ad49689986f4b29a26d20370d9d011
(cherry picked from commit fe109c62daf429e9053c03f6e374568ba23cd041)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/73040
This patch fixes a compilation error in PyTorch with ROCm when `NDEBUG` is passed.
## Problem
Forward declaration of `__host__ __device__ __assert_fail()` is used in `c10/macros/Macros.h` for HIP compilation when `NDEBUG` is set However, HIP has `__device__ __assert_fail()` in `hip/amd_detail/amd_device_functions.h`, causing a function type error.
This issue does not appear in ROCm CI tests since it happens only when `NDEBUG` is passed.
## Solution
[EDIT] After the discussion on GitHub, we chose to entirely disable `CUDA_KERNEL_ASSERT()` for ROCm.
---
To solve this compilation error, this patch disables `CUDA_KERNEL_ASSERT()`, which uses `__assert_fail()` when
1. `c10/macros/Macros.h` is included for `*.hip` (precisely speaking, `__HIP__` or `__HIP_ARCH__` is defined), and
2. `NDEBUG` is passed.
Note that there's no impact on default compilation because, without a special compilation flag, those HIP files are compiled without `-NDEBUG`. And that's why this issue has not been found.
### Justification
[1] We cannot declare one host-and-device function for two separate host and device functions.
```
__device__ int func() {return 0};
__host__ int func() {return 0};
// Compile error (hipcc)
// __device__ __host__ int func();
```
[2] Forward declaration of a correct `__device__` only `__assert_fail()` for `__HIP__` causes the following error:
```
pytorch/c10/util/TypeCast.h:135:7: error: reference to __device__ function '__assert_fail' in __host__ __device__ function
ERROR_UNSUPPORTED_CAST
^
pytorch/c10/util/TypeCast.h:118:32: note: expanded from macro 'ERROR_UNSUPPORTED_CAST'
#define ERROR_UNSUPPORTED_CAST CUDA_KERNEL_ASSERT(false);
^
pytorch/c10/macros/Macros.h:392:5: note: expanded from macro 'CUDA_KERNEL_ASSERT'
__assert_fail(
```
[3] Maybe there's a way to properly define `__assert_fail()` for HIP + NDEBUG, but this might be too much. Please let me just disable it.
### Technical details
Error
```
pytorch/c10/macros/Macros.h:368:5: error: __host__ __device__ function '__assert_fail' cannot overload __device__ function '__assert_fail'
__assert_fail(
^
/opt/rocm/hip/include/hip/amd_detail/amd_device_functions.h:1173:6: note: previous declaration is here
void __assert_fail(const char *assertion,
```
CUDA definition (9.x) of `__assert_fail()`
```
#elif defined(__GNUC__)
extern __host__ __device__ __cudart_builtin__ void __assert_fail(
const char *, const char *, unsigned int, const char *)
__THROW;
```
ROCm definition (the latest version)
```
// 2b59661f3e/include/hip/amd_detail/amd_device_functions.h (L1172-L1177)
extern "C" __device__ __attribute__((noinline)) __attribute__((weak))
void __assert_fail(const char *assertion,
const char *file,
unsigned int line,
const char *function);
```
Test Plan:
CI + reproducer
```
python3 tools/amd_build/build_amd.py
python3 setup.py develop --cmake-only
cmake -DHIP_HIPCC_FLAGS_RELEASE="-DNDEBUG" build
cmake --build build
```
Reviewed By: xw285cornell
Differential Revision: D34310555
fbshipit-source-id: 7542288912590533ced3f20afd2e704b6551991b
(cherry picked from commit 9e52196e36820abe36bf6427cabc7389d3ea6cb5)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/65851
Design doc: https://docs.google.com/document/d/12rtlHnPUpaJ-I52Iob3L0WA3rKRr_OY7fXqeCvn2MVY/edit
First read the design doc to understand the user syntax. In this PR, we have converted add to use ufunc codegen; most of the cpp changes are deleting the preexisting implementations of add, and ufunc/add.h are the new implementations in the ufunc format.
The bulk of this PR is in the new codegen machinery. Here's the order to read the files:
* `tools/codegen/model.py`
* Some self-explanatory utility classes: `ScalarType`, `DTYPE_CLASSES`
* New classes for representing ufunc entries in `native_functions.yaml`: `UfuncKey` and `UfuncInnerLoop`, as well as parsing logic for these entries. UfuncKey has some unusual entries (e.g., CPUScalar) that don't show up in the documentation, more on these below).
* A predicate `is_ufunc_dispatch_key` for testing which dispatch keys should get automatically generated when an operator opts into ufuncs (CPU and CUDA, for now!)
* `tools/codegen/api/types.py`
* More self-explanatory utility stuff: ScalarTypeToCppMapping mapping ScalarType to CppTypes; Binding.rename for changing the name of a binding (used when we assign constructor variables to member variables inside CUDA functors)
* New VectorizedCType, representing `at::vec::Vectorized<T>`. This is used inside vectorized CPU codegen.
* New `scalar_t` and `opmath_t` BaseCppTypes, representing template parameters that we work with when doing codegen inside ufunc kernel loops (e.g., where you previously had Tensor, now you have `scalar_t`)
* `StructuredImplSignature` represents a `TORCH_IMPL_FUNC` definition, and straightforwardly follows from preexisting `tools.codegen.api.structured`
* `tools/codegen/translate.py` - Yes, we use translate a LOT in this PR. I improved some of the documentation, the only substantive changes are adding two new conversions: given a `scalar_t` or a `const Scalar&`, make it convertible to an `opmath_t`
* `tools/codegen/api/ufunc.py`
* OK, now we're at the meaty stuff. This file represents the calling conventions of three important concepts in ufunc codegen, which we'll describe shortly. All of these APIs are relatively simple, since there aren't any complicated types by the time you get to kernels.
* stubs are the DispatchStub trampolines that CPU kernels use to get to their vectorized versions. They drop all Tensor arguments (as they are in TensorIterator) but otherwise match the structured calling convention
* ufuncs are the inner loop template functions that you wrote in ufunc/add.h which do the actual computation in question. Here, all the Tensors and Scalars have been converted into the computation type (`opmath_t` in CUDA, `scalar_t` in CPU)
* ufunctors are a CUDA-only concept representing functors that take some of their arguments on a host-side constructor, and the rest in the device-side apply. Once again, Tensors and Scalars are converted into the computation type, `opmath_t`, but for clarity all the functions take `scalar_t` as argument (as this is the type that is most salient at the call site). Because the constructor and apply are code generated separately, `ufunctor_arguments` returns a teeny struct `UfunctorBindings`
* `tools/codegen/dest/ufunc.py` - the workhorse. This gets its own section below.
* `tools/codegen/gen.py` - just calling out to the new dest.ufunc implementation to generate UfuncCPU_add.cpp, UFuncCPUKernel_add.cpp and UfuncCUDA_add.cu files per ufunc operator. Each of these files does what you expect (small file that registers kernel and calls stub; CPU implementation; CUDA implementation). There is a new file manager for UFuncCPUKernel files as these need to get replicated by cmake for vectorization. One little trick to avoid recompilation is we directly replicate code generated forward declarations in these files, to reduce the number of headers we depend on (this is codegen, we're just doing the preprocessors job!)
* I'll talk about build system adjustments below.
OK, let's talk about tools/codegen/dest/ufunc.py. This file can be roughly understood in two halves: one for CPU code generation, and the other for CUDA code generation.
**CPU codegen.** Here's roughly what we want to generate:
```
// in UfuncCPU_add.cpp
using add_fn = void (*)(TensorIteratorBase&, const at::Scalar&);
DECLARE_DISPATCH(add_fn, add_stub);
DEFINE_DISPATCH(add_stub);
TORCH_IMPL_FUNC(ufunc_add_CPU)
(const at::Tensor& self, const at::Tensor& other, const at::Scalar& alpha, const at::Tensor& out) {
add_stub(device_type(), *this, alpha);
}
// in UfuncCPUKernel_add.cpp
void add_kernel(TensorIteratorBase& iter, const at::Scalar& alpha) {
at::ScalarType st = iter.common_dtype();
RECORD_KERNEL_FUNCTION_DTYPE("add_stub", st);
switch (st) {
AT_PRIVATE_CASE_TYPE("add_stub", at::ScalarType::Bool, bool, [&]() {
auto _s_alpha = alpha.to<scalar_t>();
cpu_kernel(iter, [=](scalar_t self, scalar_t other) {
return ufunc::add(self, other, _s_alpha);
});
})
AT_PRIVATE_CASE_TYPE(
"add_stub", at::ScalarType::ComplexFloat, c10::complex<float>, [&]() {
auto _s_alpha = alpha.to<scalar_t>();
auto _v_alpha = at::vec::Vectorized<scalar_t>(_s_alpha);
cpu_kernel_vec(
iter,
[=](scalar_t self, scalar_t other) {
return ufunc::add(self, other, _s_alpha);
},
[=](at::vec::Vectorized<scalar_t> self,
at::vec::Vectorized<scalar_t> other) {
return ufunc::add(self, other, _v_alpha);
});
})
...
```
The most interesting change about the generated code is what previously was an `AT_DISPATCH` macro invocation is now an unrolled loop. This makes it easier to vary behavior per-dtype (you can see in this example that the entry for bool and float differ) without having to add extra condtionals on top.
Otherwise, to generate this code, we have to hop through several successive API changes:
* In TORCH_IMPL_FUNC(ufunc_add_CPU), go from StructuredImplSignature to StubSignature (call the stub). This is normal argument massaging in the classic translate style.
* In add_kernel, go from StubSignature to UfuncSignature. This is nontrivial, because we must do various conversions outside of the inner kernel loop. These conversions are done by hand, setting up the context appropriately, and then the final ufunc call is done using translate. (BTW, I introduce a new convention here, call on a Signature, for code generating a C++ call, and I think we should try to use this convention elsewhere)
The other piece of nontrivial logic is the reindexing by dtype. This reindexing exists because the native_functions.yaml format is indexed by UfuncKey:
```
Generic: add (AllAndComplex, BFloat16, Half)
ScalarOnly: add (Bool)
```
but when we do code generation, we case on dtype first, and then we generate a `cpu_kernel` or `cpu_kernel_vec` call. We also don't care about CUDA code generation (which Generic) hits. Do this, we lower these keys into two low level keys, CPUScalar and CPUVector, which represent the CPU scalar and CPU vectorized ufuncs, respectively (Generic maps to CPUScalar and CPUVector, while ScalarOnly maps to CPUScalar only). Reindexing then gives us:
```
AllAndComplex:
CPUScalar: add
CPUVector: add
Bool:
CPUScalar: add
...
```
which is a good format for code generation, but too wordy to force native_functions.yaml authors to write. Note that when reindexing, it is possible for there to be a conflicting definition for the same dtype; we just define a precedence order and have one override the other, so that it is easy to specialize on a particular dtype if necessary. Also note that because CPUScalar/CPUVector are part of UfuncKey, technically you can manually specify them in native_functions.yaml, although I don't expect this functionality to be used.
**CUDA codegen.** CUDA code generation has many of the same ideas as CPU codegen, but it needs to know about functors, and stubs are handled slightly differently. Here is what we want to generate:
```
template <typename scalar_t>
struct CUDAFunctorOnSelf_add {
using opmath_t = at::opmath_type<scalar_t>;
opmath_t other_;
opmath_t alpha_;
CUDAFunctorOnSelf_add(opmath_t other, opmath_t alpha)
: other_(other), alpha_(alpha) {}
__device__ scalar_t operator()(scalar_t self) {
return ufunc::add(static_cast<opmath_t>(self), other_, alpha_);
}
};
... two more functors ...
void add_kernel(TensorIteratorBase& iter, const at::Scalar & alpha) {
TensorIteratorBase& iter = *this;
at::ScalarType st = iter.common_dtype();
RECORD_KERNEL_FUNCTION_DTYPE("ufunc_add_CUDA", st);
switch (st) {
AT_PRIVATE_CASE_TYPE("ufunc_add_CUDA", at::ScalarType::Bool, bool, [&]() {
using opmath_t = at::opmath_type<scalar_t>;
if (false) {
} else if (iter.is_cpu_scalar(1)) {
CUDAFunctorOnOther_add<scalar_t> ufunctor(
iter.scalar_value<opmath_t>(1), (alpha).to<opmath_t>());
iter.remove_operand(1);
gpu_kernel(iter, ufunctor);
} else if (iter.is_cpu_scalar(2)) {
CUDAFunctorOnSelf_add<scalar_t> ufunctor(
iter.scalar_value<opmath_t>(2), (alpha).to<opmath_t>());
iter.remove_operand(2);
gpu_kernel(iter, ufunctor);
} else {
gpu_kernel(iter, CUDAFunctor_add<scalar_t>((alpha).to<opmath_t>()));
}
})
...
REGISTER_DISPATCH(add_stub, &add_kernel);
TORCH_IMPL_FUNC(ufunc_add_CUDA)
(const at::Tensor& self,
const at::Tensor& other,
const at::Scalar& alpha,
const at::Tensor& out) {
add_kernel(*this, alpha);
}
```
The functor business is the bulk of the complexity. Like CPU, we decompose CUDA implementation into three low-level keys: CUDAFunctor (normal, all CUDA kernels will have this), and CUDAFunctorOnOther/CUDAFunctorOnScalar (these are to support Tensor-Scalar specializations when the Scalar lives on CPU). Both Generic and ScalarOnly provide ufuncs for CUDAFunctor, but for us to also lift these into Tensor-Scalar specializations, the operator itself must be eligible for Tensor-Scalar specialization. At the moment, this is hardcoded to be all binary operators, but in the future we can use tags in native_functions.yaml to disambiguate (or perhaps expand codegen to handle n-ary operators).
The reindexing process not only reassociates ufuncs by dtype, but it also works out if Tensor-Scalar specializations are needed and codegens the ufunctors necessary for the level of specialization here (`compute_ufunc_cuda_functors`). Generating the actual kernel (`compute_ufunc_cuda_dtype_body`) just consists of, for each specialization, constructing the functor and then passing it off to `gpu_kernel`. Most of the hard work is in functor generation, where we take care to make sure `operator()` has the correct input and output types (which `gpu_kernel` uses to arrange for memory accesses to the actual CUDA tensor; if you get these types wrong, your kernel will still work, it will just run very slowly!)
There is one big subtlety with CUDA codegen: this won't work:
```
Generic: add (AllAndComplex, BFloat16, Half)
ScalarOnly: add_bool (Bool)
```
This is because, even though there are separate Generic/ScalarOnly entries, we only generate a single functor to cover ALL dtypes in this case, and the functor has the ufunc name hardcoded into it. You'll get an error if you try to do this; to fix it, just make sure the ufunc is named the same consistently throughout. In the code, you see this because after testing for the short circuit case (when a user provided the functor themselves), we squash all the generic entries together and assert their ufunc names are the same. Hypothetically, if we generated a separate functor per dtype, we could support differently named ufuncs but... why would you do that to yourself. (One piece of nastiness is that the native_functions.yaml syntax doesn't stop you from shooting yourself in the foot.)
A brief word about CUDA stubs: technically, they are not necessary, as there is no CPU/CPUKernel style split for CUDA kernels (so, if you look, structured impl actually calls add_kernel directly). However, there is some code that still makes use of CUDA stubs (in particular, I use the stub to conveniently reimplement sub in terms of add), so we still register it. This might be worth frying some more at a later point in time.
**Build system changes.** If you are at FB, you should review these changes in fbcode, as there are several changes in files that are not exported to ShipIt.
The build system changes in this patch are substantively complicated by the fact that I have to implement these changes five times:
* OSS cmake build
* OSS Bazel build
* FB fbcode Buck build
* FB xplat Buck build (selective build)
* FB ovrsource Buck build
Due to technical limitations in the xplat Buck build related to selective build, it is required that you list every ufunc header manually (this is done in tools/build_variables.bzl)
The OSS cmake changes are entirely in cmake/Codegen.cmake there is a new set of files cpu_vec_generated (corresponding to UfuncCPUKernel files) which is wired up in the same way as other files. These files are different because they need to get compiled multiple times under different vectorization settings. I adjust the codegen, slightly refactoring the inner loop into its own function so I can use different base path calculation depending on if the file is traditional (in the native/cpu folder) or generated (new stuff from this diff.
The Bazel/Buck changes are organized around tools/build_variables.bzl, which contain the canonical list of ufunc headers (aten_ufunc_headers), and tools/ufunc_defs.bzl (added to ShipIt export list in D34465699) which defines a number of functions that compute the generated cpu, cpu kernel and cuda files based on the headers list. For convenience, these functions take a genpattern (a string with a {} for interpolation) which can be used to easily reformat the list of formats in target form, which is commonly needed in the build systems.
The split between build_variables.bzl and ufunc_defs.bzl is required because build_variables.bzl is executed by a conventional Python interpreter as part of the OSS cmake, but we require Skylark features to implement the functions in ufunc_defs.bzl (I did some quick Googling but didn't find a lightweight way to run the Skylark interpreter in open source.)
With these new file lists, the rest of the build changes are mostly inserting references to these files wherever necessary; in particular, cpu kernel files have to be worked into the multiple vectorization build flow (intern_build_aten_ops in OSS Bazel). Most of the subtlety relates to selective build. Selective build requires operator files to be copied per overall selective build; as dhruvbird explains to me, glob expansion happens during the action graph phase, but the selective build handling of TEMPLATE_SOURCE_LIST is referencing the target graph. In other words, we can't use a glob to generate deps for another rule, because we need to copy files from wherever (included generated files) to a staging folder so the rules can pick them up.
It can be somewhat confusing to understand which bzl files are associated with which build. Here are the relevant mappings for files I edited:
* Used by everyone - tools/build_tools.bzl, tools/ufunc_defs.bzl
* OSS Bazel - aten.bzl, BUILD.bazel
* FB fbcode Buck - TARGETS
* FB xplat Buck -BUCK, pt_defs.bzl, pt_template_srcs.bzl
* FB ovrsource Buck - ovrsource_defs.bzl, pt_defs.bzl
Note that pt_defs.bzl is used by both xplat and ovrsource. This leads to the "tiresome" handling for enabled backends, as selective build is CPU only, but ovrsource is CPU and CUDA.
BTW, while I was at it, I beefed up fb/build_arvr.sh to also do a CUDA ovrsource build, which was not triggered previously.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D31306586
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 210258ce83f578f79cf91b77bfaeac34945a00c6
(cherry picked from commit d65157b0b894b6701ee062f05a5f57790a06c91c)
Summary:
- Target Sha1: ae108ef49aa5623b896fc93d4298c49d1750d9ba
- Make USE_XNNPACK a dependent option on cmake minimum version 3.12
- Print USE_XNNPACK under cmake options summary, and print the
availability from collet_env.py
- Skip XNNPACK based tests when XNNPACK is not available
- Add SkipIfNoXNNPACK wrapper to skip tests
- Update cmake version for xenial-py3.7-gcc5.4 image to 3.12.4
- This is required for the backwards compatibility test.
The PyTorch op schema is XNNPACK dependent. See,
aten/src/ATen/native/xnnpack/RegisterOpContextClass.cpp for
example. The nightly version is assumed to have USE_XNNPACK=ON,
so with this change we ensure that the test build can also
have XNNPACK.
- HACK: skipping test_xnnpack_integration tests on ROCM
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72642
Reviewed By: kimishpatel
Differential Revision: D34456794
Pulled By: digantdesai
fbshipit-source-id: 85dbfe0211de7846d8a84321b14fdb061cd6c037
(cherry picked from commit 6cf48e7b64d6979962d701b5d493998262cc8bfa)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72869
The ordering here doesn't really matter, but in a future patch
I will make a change where vectorized CPU codegen does have to
be here, and moving it ahead of time (with no code changes)
will make the latter diff cleaner.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D34282229
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 3397cb0e062d63cc9853f6248f17c3558013798b
(cherry picked from commit 98c616024969f9df90c7fb09741ed9be7b7a20f1)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72761
By default, the CUPTI_INCLUDE_DIR will pick up cupti.h from /usr/include which is old (from 2017 on AWS), and missing many cupti headers. Use NO_DEFAULT_PATH to avoid that, instead search from the list of locations provided.
Test Plan:
Fixes missing headers error when building on AWS. (Avoids old cupti.h from /usr/include). Instead uses cupti.h from cuda/extras/CUPTI/include.
```
In file included from /scratch/aaronshi/pytorch/third_party/kineto/libkineto/src/CuptiRangeProfilerApi.cpp:13:0:
/scratch/aaronshi/pytorch/third_party/kineto/libkineto/src/CuptiRangeProfilerApi.h:12:10: fatal error: cupti_profiler_target.h: No such file or directory
#include <cupti_profiler_target.h>
^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
compilation terminated.
```
and
```
/scratch/aaronshi/pytorch/third_party/kineto/libkineto/src/CuptiRangeProfilerApi.cpp:7:10: fatal error: nvperf_host.h: No such file or directory
#include <nvperf_host.h>
^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
compilation terminated.
```
Reviewed By: briancoutinho
Differential Revision: D34191123
Pulled By: aaronenyeshi
fbshipit-source-id: d84f80308c9939ba8ed504e667847d136a261453
(cherry picked from commit 33368bd93b)
Summary:
In ROCm 5.0 and later the version of the ROCm platform can be obtained via
an api call vs reading from a flat file.
If the header file /opt/rocm/include/rocm_version.h exists,
LoadHIP.cmake compiles source referencing the api and prints out the
ROCM Versions.
If the file does not exist, LoadHIP.cmake will revert to the previous
approach of looking for the version-dev file.
Fixes #{issue number}
cc jeffdaily sunway513 jithunnair-amd ROCmSupport KyleCZH
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69481
Reviewed By: seemethere, janeyx99
Differential Revision: D34153435
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: f8c0650d27666d2a3cf47d812807798c47210b37
(cherry picked from commit 6cbb4f7a0c)
Summary:
`include_directories` is old-style CMake which adds the include path to every file being compiled. This instead makes `python`, `numpy` and `pybind11` into targets that only `torch_python` and `caffe2_pybind_state` are linked to. So, python libraries can't be accidentally included elsewhere.
Resubmit of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/65654, Closes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/65828
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69085
Reviewed By: anjali411
Differential Revision: D33776456
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 018b0f6cd5a4f8c9e36df961deff832bc4afd479
(cherry picked from commit 57063107d6)
Summary:
Remove forcing CUDNN_STATIC when CAFFE2_STATIC_LINK_CUDA is set
Since we are transitioning to using dynamic loading for multiple pytorch dependecies and CUDNN is the first step in this transition, hence we want to remove forcing CUDNN to statically load, and instead load it dynamically.
Tested using following workflow:
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/actions/runs/1790666862
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72290
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D34003793
Pulled By: atalman
fbshipit-source-id: 41bda7ac019a612ee53ceb18d1e372b1bb3cb68e
(cherry picked from commit 4a01940e68)
Summary:
This PR upgrades oneDNN to v2.5.2, and includes some building support for oneDNN v2.5.2.
v2.4 changes:
- Improved performance for future Intel Xeon Scalable processor (code name Sapphire Rapids). The functionality is disabled by default and should be enabled via CPU dispatcher control.
- Improved binary primitive performance for cases when one of the tensors is broadcasted.
- Improved performance of reduction primitive, reorder, shuffle primitives.
- Improved performance of depthwise convolution forward propagation for processors with Intel AVX5-12 support
- Improved performance of forward inner product primitive for the shapes with minibatch equal to 1 for processors with Intel AVX-512 support
- Improved performance of int8 matmul and inner product primitives for processors with Intel AVX2 and Intel DL Boost support
v2.5 changes:
- Improved performance for future Intel Xeon Scalable processors (code name Sapphire Rapids). The functionality is now enabled by default and requires Linux kernel 5.16.
- Improved performance of matmul primitive for processors with Intel AVX-512 support.
v2.5.2 changes:
- Fixed performance regression in binary primitive with broadcast
- Fixed segmentation fault in depthwise convolution primitive for shapes with huge spatial size for processors with Intel AVX-512 support
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/71546
Reviewed By: george-qi
Differential Revision: D33827108
Pulled By: VitalyFedyunin
fbshipit-source-id: 8f5a19b331c82af5b0783f081e061e1034a93952
(cherry picked from commit 9705212fe9)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/72081
This PR fixes the libstdc++ ABI check in CMake package configuration file (i.e. `TorchConfig.cmake`) The `_GLIBCXX_USE_CXX11_ABI` flag is a property of `libstdc++`, not GNU compiler collection. In its current form C++ libraries built with Clang on Linux fail since the `torch` CMake target propagates `_GLIBCXX_USE_CXX11_ABI` only when used with gcc.
ghstack-source-id: 148056323
Test Plan: Built a dummy C++ library that depends on libtorch with both gcc and clang on Linux
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D33899849
fbshipit-source-id: 3e933b2c7a17d1fba086caa8aaec831223760882
(cherry picked from commit 41d18c64c4)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69216
This cleans up 4 pre-processor defines not used by any code:
- HAVE_GCC_GET_CPUID
- USE_GCC_GET_CPUID
- USE_AVX
- USE_AVX2
`cpuid` isn't used in PyTorch any more, we only use `cpuinfo`.
`USE_AVX*` is also not used, instead `HAVE_*_CPU_DEFINITIONS` tells
you which `CPU_CAPABILITY` flags are being compiled.
There is also `fbgemm`'s code path adding `third_party` as an include
path, despite `fbgemm` having a dedicated include directory and a
CMake setup that properly includes it.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D33794424
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 99d504af088818d4a26c2f6ce67ec0d59a5eb703
(cherry picked from commit 2e099d41f0)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69216
Currently `torch_cpu` has command line arguments relating to cuda
libraries e.g. `-DMAGMA_V2`. This happens because
`include_directories` and `add_definitions` indescriminately change
the compile commands of all targets.
Instead creating a proper magma target allows limiting the flags to
just `torch_cuda`.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: dagitses
Differential Revision: D33794174
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 762eabf3b9576bef94e8caa3ed4764c0e2c72b08
(cherry picked from commit f7d127b654)
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/70201
Included functions:
save_mobile_module -> saves a mobile::Module to flatbuffer
load_mobile_module_from_file -> loads a flatbuffer into mobile::Module
parse_mobile_module -> parses from bytes or deserialized flatbuffer module object
Compared to previous attempts, this diff only adds flatbuffer to cmake target and leaves fbcode/xplat ones unchanged.
Test Plan: unittest
Reviewed By: malfet, gmagogsfm
Differential Revision: D33239362
fbshipit-source-id: b9ca36b83d6af2d78cc50b9eb9e2a6fa7fce0763
Summary:
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/66406
implemented z arch 14/15 vector SIMD additions.
so far besides bfloat all other types have their SIMD implementation.
it has 99% coverage and currently passing the local test.
it is concise and the main SIMD file is only one header file
it's using template metaprogramming, mostly. but still, there are a few macrosses left with the intention not to modify PyTorch much
Sleef supports z15
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/66407
Reviewed By: mrshenli
Differential Revision: D33370163
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 0e5a57f31b22a718cd2a9ac59753fb468cdda140
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/68247
This splits `Functions.h`, `Operators.h`, `NativeFunctions.h` and
`NativeMetaFunctions.h` into seperate headers per operator base name.
With `at::sum` as an example, we can include:
```cpp
<ATen/core/sum.h> // Like Functions.h
<ATen/core/sum_ops.h> // Like Operators.h
<ATen/core/sum_native.h> // Like NativeFunctions.h
<ATen/core/sum_meta.h> // Like NativeMetaFunctions.h
```
The umbrella headers are still being generated, but all they do is
include from the `ATen/ops' folder.
Further, `TensorBody.h` now only includes the operators that have
method variants. Which means files that only include `Tensor.h` don't
need to be rebuilt when you modify function-only operators. Currently
there are about 680 operators that don't have method variants, so this
is potentially a significant win for incremental builds.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: mrshenli
Differential Revision: D32596272
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 447671b2b6adc1364f66ed9717c896dae25fa272
Summary:
Remove all hardcoded AMD gfx targets
PyTorch build and Magma build will use rocm_agent_enumerator as
backup if PYTORCH_ROCM_ARCH env var is not defined
PyTorch extensions will use same gfx targets as the PyTorch build,
unless PYTORCH_ROCM_ARCH env var is defined
torch.cuda.get_arch_list() now works for ROCm builds
PyTorch CI dockers will continue to be built for gfx900 and gfx906 for now.
PYTORCH_ROCM_ARCH env var can be a space or semicolon separated list of gfx archs eg. "gfx900 gfx906" or "gfx900;gfx906"
cc jeffdaily sunway513 jithunnair-amd ROCmSupport KyleCZH
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/61706
Reviewed By: seemethere
Differential Revision: D32735862
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 3170e445e738e3ce373203e1e4ae99c84e645d7d
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69710
Namely no range-loop-analysis (that detect when loop variable can not be const reference
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: r-barnes
Differential Revision: D32997003
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: dba0e7875e5b667e2cc394c70dd75e2403265918
Summary:
This PR upgrades oneDNN to [v2.3.3](https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneDNN/releases/tag/v2.3.3) and includes [Graph API preview release](https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneDNN/releases/tag/graph-v0.2) in one package.
- oneDNN will be located at `pytorch/third_party/ideep/mkl-dnn/third_party/oneDNN`
- The version of oneDNN will be [v2.3.3](https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneDNN/releases/tag/v2.3.3)
The main changes on CPU:
- v2.3
- Extended primitive cache to improve primitive descriptor creation performance.
- Improved primitive cache performance in multithreaded configurations.
- Introduced initial optimizations for bfloat16 compute functionality for future Intel Xeon Scalable processor (code name Sapphire Rapids).
- Improved performance of binary primitive and binary post-op for cases with broadcast and mixed source and destination formats.
- Improved performance of reduction primitive
- Improved performance of depthwise convolution primitive with NHWC activations for training cases
- v2.3.1
- Improved int8 GEMM performance for processors with Intel AVX2 and Intel DL Boost support
- Fixed integer overflow for inner product implementation on CPUs
- Fixed out of bounds access in GEMM implementation for Intel SSE 4.1
- v2.3.2
- Fixed performance regression in fp32 inner product primitive for processors with Intel AVX512 support
- v2.3.3
- Reverted check for memory descriptor stride validity for unit dimensions
- Fixed memory leak in CPU GEMM implementation
More changes can be found in https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneDNN/releases.
- The Graph API provides flexible API for aggressive fusion, and the preview2 supports fusion for FP32 inference. See the [Graph API release branch](https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneDNN/tree/dev-graph-preview2) and [spec](https://spec.oneapi.io/onednn-graph/latest/introduction.html) for more details. A separate PR will be submitted to integrate the oneDNN Graph API to Torchscript graph.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63748
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D32153889
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 536071168ffe312d452f75d54f34c336ca3778c1
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/68246
Currently the codegen produces a list of output files at CMake
configuration time and the build system has no way of knowing if the
outputs change. So if that happens, you basically need to delete the
build folder and re-run from scratch.
Instead, this generates the output list every time the code generation
is run and changes the output to be a `.cmake` file that gets included
in the main cmake configuration step. That means the build system
knows to re-run cmake automatically if a new output is added. So, for
example you could change the number of shards that `Operators.cpp` is
split into and it all just works transparently to the user.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: zou3519
Differential Revision: D32596268
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 15e0896aeaead90aed64b9c8fda70cf28fef13a2
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/69251
This adds some actual documentation for deploy, which is probably useful
since we told everyone it was experimentally available so they will
probably be looking at what the heck it is.
It also wires up various compoenents of the OSS build to actually work
when used from an external project.
Differential Revision:
D32783312
D32783312
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: wconstab
Pulled By: suo
fbshipit-source-id: c5c0a1e3f80fa273b5a70c13ba81733cb8d2c8f8
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/67656
Currently, each cpu kernel file is copied into the build folder 3 times to give them different compilation flags. This changes it to instead generate 3 files that `#include` the original file. The biggest difference is that updating a copied file requires `cmake` to re-run, whereas include dependencies are natively handled by `ninja`.
A side benefit is that included files show up directly in the build dependency graph, whereas `cmake` file copies don't.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: dagitses
Differential Revision: D32566108
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: ae75368fede37e7ca03be6ade3d4e4a63479440d
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/68180
Since we've open sourced the tracing-based selective build, we can deprecate the
op-dependency-graph-based selective build and the static analyzer tool that
produces the dependency graph.
ghstack-source-id: 143108377
Test Plan: CIs
Reviewed By: seemethere
Differential Revision: D32358467
fbshipit-source-id: c61523706b85a49361416da2230ec1b035b8b99c
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/67497
This allows more of the code-generation to happen in parallel, whereas
previously all codegen was serialized.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: dagitses, mruberry
Differential Revision: D32027250
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 6407c4c3e25ad15d542aa73da6ded6a309c8eb6a
Summary:
OpenBLAS recently added support for bfloat16 GEMM, so this change has PyTorch call out to OpenBLAS for that, like it does for single and double precision
Our goal is to try to enable PyTorch to make calls to "sbgemm" in OpenBLAS.
We are prepared (if it is your preference) to add fences to the code to limit this change to the Power architecture,
but our first instinct is that anyone on any architecture that enables access to sbgemm in their OpenBLAS library
should be able to use this code. (but again, we respect that as we are just starting to modify PyTorch, we respect
your guidance!)
(there is no issue number related to this)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/58831
Reviewed By: albanD
Differential Revision: D29951900
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 3d0a4a638ac95b2ff2e9f6d08827772e28d397c3
Summary:
This PR is to update PyTorch with the following cub changes:
- Starting cub 1.13.1, cub requires users to define `CUB_NS_QUALIFIER` if `CUB_NS_PREFIX` is also defined. Besides that, a new mechanism `CUB_WRAPPED_NAMESPACE` is added.
And I do the following change to PyTorch:
- Starting CUDA 11.5, define `CUB_WRAPPED_NAMESPACE` globally as an nvcc flag.
- Fix caffe2 failures caused by the above change.
- Add a `aten/src/ATen/cuda/cub_definitions.cuh` that defines helper macros about feature availability.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/66219
Reviewed By: bdhirsh
Differential Revision: D31626931
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 97ebf5ef671ade8bf46d0860edc317f22660f26d
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/65401
Per https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/57744 statically linked CUPTI
causes exception handling to break on certain compiler configurations, likely
because CUPTI comes with incompatible libstdc++ symbols. Rather than pray that
something reasonable happens, use the safer configuration (dynamic linking) by
default and give a warning if the user inverts the setting.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: gdankel
Differential Revision: D31082208
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 14f66af920847e158436b5801c43f3124b109b34
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/62445
PyTorch currently uses the old style of compiling CUDA in CMake which is just a
bunch of scripts in `FindCUDA.cmake`. Newer versions support CUDA natively as
a language just like C++ or C.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: ejguan
Differential Revision: D31503350
fbshipit-source-id: 2ee817edc9698531ae1b87eda3ad271ee459fd55
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/65610
- Replace HIP_PLATFORM_HCC with USE_ROCM
- Dont rely on CUDA_VERSION or HIP_VERSION and use USE_ROCM and ROCM_VERSION.
- In the next PR
- Will be removing the mapping from CUDA_VERSION to HIP_VERSION and CUDA to HIP in hipify.
- HIP_PLATFORM_HCC is deprecated, so will add HIP_PLATFORM_AMD to support HIP host code compilation on gcc.
cc jeffdaily sunway513 jithunnair-amd ROCmSupport amathews-amd
Reviewed By: jbschlosser
Differential Revision: D30909053
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 224a966ebf1aaec79beccbbd686fdf3d49267e06
Summary:
`include_directories` is old-style CMake which adds the include path to every file being compiled. This instead makes python, numpy and pybind11 into targets that only torch_python and caffe2_pybind_state are linked to. So, python libraries can't be accidentally included elsewhere.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/65654
Reviewed By: gchanan
Differential Revision: D31193205
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 5c1b554a59d0e441a701a04ebb62f0032d38b208
Summary:
Syncing nvfuser code base from devel branch, Listing a few of our development since last sync:
- Extends support to normalization and reduction kernels.
- Multiple kernel launch for single `CudaFusionGroup`. Hierarchical caching system has been updated to cache graph segmentation.
- profile_ivalue is enabled to convert dynamic scalar into compile time constants, which are required by the codegen. (e.g. reduction axes).
To keep this PR simple and relatively review-free. We stripped most external changes and submitted them as separate PRs, so this gigantic PR is easier to handle.
internal updates are files located in:
1. updates in nvfuser codegen `torch/csrc/jit/coddgen/cuda`
2. added nvfuser specific benchmarks `benchmarks/cpp/nvfuser`
3. nvfuser jit cpp tests `test/cpp/jit/test_gpu.cpp` `test/cpp/jit/test_gpu_shift.cpp` `test/cpp/jit/test_gpu_validator.h`
updates affecting integration:
1. profile_ivalue enabled for nvfuser. related changes are in `torch/csrc/jit/runtime/*`,
2. exposed a few more symbols `aten/src/ATen/core/*` used by codegen
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63745
Reviewed By: saketh-are
Differential Revision: D30752939
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: ce122e80f01bcd3865f5bd3c4dfde660665fd84c
Summary:
The library will no longer link properly on VS 2019 (14.29.30133). To
ensure that engineers building on Windows can use and debug with this
build type, incremental linking needs to be turned off for this build
flag.
Verified that this build type successfully builds, links, and provides
debuggable Python modules on Windows.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/64892
Reviewed By: jbschlosser
Differential Revision: D30902565
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: e5286a4c6f45c7cbe4cdc1b98560129bd386970b
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63714
PocketFFT was disabled for CMake < 3.9 but CMake 3.11 is the first version to support `INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES` as a target property. So updating to CMake 3.10 causes the mobile builds to fail. Instead of limiting the CMake support, this just adds the include directory to the entire target,
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: bdhirsh
Differential Revision: D30498369
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 83372e29c477c97e7015763b7c29d6d7e456bcef
Summary:
We currently build breakpad from [this fork](https://github.com/driazati/breakpad) to include extra logic to restore signal handlers that were previously present. With some [new additions](https://github.com/google/breakpad/compare/main...driazati:main) this fork now includes a CMake based build, so we can add breakpad as a proper dependency rather than rely on including it in Docker images as a system library which is error prone (we have a bunch of images) and hard to extend to MacOS / Windows. This also includes some changes to the crash handling code to support MacOS / Windows in a similar way to Linux.
```python
import torch
# On Windows this writes crashes to C:\Users\<user>\AppData\pytorch_crashes
# On MacOS/Linux this writes crashes to /tmp/pytorch_crashes
torch.utils._crash_handler.enable_minidumps()
# Easy way to cause a segfault and trigger the handler
torch.bincount(input=torch.tensor([9223372036854775807]))
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63186
Reviewed By: malfet, seemethere
Differential Revision: D30318404
Pulled By: driazati
fbshipit-source-id: 0d7daf3701cfaba5451cc529a0730272ab1eb1dc
Summary:
When testing with clang-cl, the flag is added though it is unsupported and that generates a few warnings. Tried a few alternatives like https://cmake.org/cmake/help/latest/module/CheckLinkerFlag.html, but they just don't work.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/62949
Reviewed By: zhouzhuojie, driazati
Differential Revision: D30359206
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 1bd27ad5772fe6757fa8c3a4bddf904f88d70b7b
Summary:
Using https://github.com/mreineck/pocketfft
Also delete explicit installation of pocketfft during the build as it will be available via submodule
Limit PocketFFT support to cmake-3.10 or newer, as `set_source_files_properties` does not seem to work as expected with cmake-3.5
Partially addresses https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/62821
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/62841
Reviewed By: seemethere
Differential Revision: D30140441
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: d1a1cf1b43375321f5ec5b3d0b538f58082f7825
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/62419
This diff adds support for cpu only kineto profiler on mobile. Thus
enabling chrome trace generation on mobile. This bring cpp API for
mobile profiling on part with Torchscript.
This is done via:
1. Utilizating debug handle annotations in KinetoEvent.
2. Adding post processing capability, via callbacks, to
KinetoThreadLocalState
3. Creating new RAII stype profiler, KinetoEdgeCPUProfiler, which can be
used in surrounding scope of model execution. This will write chrome
trace to the location specified in profiler constructor.
Test Plan:
MobileProfiler.ModuleHierarchy
Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: raziel
Differential Revision: D29993660
fbshipit-source-id: 0b44f52f9e9c5f5aff81ebbd9273c254c3c03299
Summary:
- HIP_VERSION semantic versioning will change in ROCm4.3. The changes essentially remove the dependency on HIP_VERSION provided in the hip header to keep code compatible with older and newer versions of ROCm.
- TORCH_HIP_VERSION is derived from HIP_VERSION_MAJOR and HIP_VERSION_MINOR
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/62786
Reviewed By: bdhirsh
Differential Revision: D30281682
Pulled By: seemethere
fbshipit-source-id: e41e69fb9e13de5ddd1af99ba5bbdcbb7b64b673
Summary:
BLAS library is found by cmake/Dependencies.cmake and then
LAPACK library is found by FindLAPACK.cmake which in turn calls
FindBLAS.cmake. This means that we are searching for BLAS twice
and they might be different things. By setting a few variables,
this can be avoided.
cc seemethere
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/49647
Reviewed By: seemethere, ejguan
Differential Revision: D29943680
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 3cbc350ea645a1a28dd92c19e5ee7f9eecdeff59
Summary:
This PR: (1) enables the use of a system-provided Intel TBB for building PyTorch, (2) removes `tbb:task_scheduler_init` references since it has been removed from TBB a while ago (3) marks the implementation of `_internal_set_num_threads` with a TODO as it requires a revision that fixes its thread allocation logic.
Tested with `test/run_test`; no new tests are introduced since there are no behavioral changes (removal of `tbb::task_scheduler_init` has no impact on the runtime behavior).
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/61934
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D29805416
Pulled By: cbalioglu
fbshipit-source-id: 22042b428b57b8fede9dfcc83878d679a19561dd
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/61903
### Remaining Tasks
- [ ] Collate results of benchmarks on two Intel Xeon machines (with & without CUDA, to check if CPU throttling causes issues with GPUs) - make graphs, including Roofline model plots (Intel Advisor can't make them with libgomp, though, but with Intel OpenMP).
### Summary
1. This draft PR produces binaries with with 3 types of ATen kernels - default, AVX2, AVX512 . Using the environment variable `ATEN_AVX512_256=TRUE` also results in 3 types of kernels, but the compiler can use 32 ymm registers for AVX2, instead of the default 16. ATen kernels for `CPU_CAPABILITY_AVX` have been removed.
2. `nansum` is not using AVX512 kernel right now, as it has poorer accuracy for Float16, than does AVX2 or DEFAULT, whose respective accuracies aren't very good either (#59415).
It was more convenient to disable AVX512 dispatch for all dtypes of `nansum` for now.
3. On Windows , ATen Quantized AVX512 kernels are not being used, as quantization tests are flaky. If `--continue-through-failure` is used, then `test_compare_model_outputs_functional_static` fails. But if this test is skipped, `test_compare_model_outputs_conv_static` fails. If both these tests are skipped, then a third one fails. These are hard to debug right now due to not having access to a Windows machine with AVX512 support, so it was more convenient to disable AVX512 dispatch of all ATen Quantized kernels on Windows for now.
4. One test is currently being skipped -
[test_lstm` in `quantization.bc](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/59098) - It fails only on Cascade Lake machines, irrespective of the `ATEN_CPU_CAPABILITY` used, because FBGEMM uses `AVX512_VNNI` on machines that support it. The value of `reduce_range` should be used as `False` on such machines.
The list of the changes is at https://gist.github.com/imaginary-person/4b4fda660534f0493bf9573d511a878d.
Credits to ezyang for proposing `AVX512_256` - these use AVX2 intrinsics but benefit from 32 registers, instead of the 16 ymm registers that AVX2 uses.
Credits to limo1996 for the initial proposal, and for optimizing `hsub_pd` & `hadd_pd`, which didn't have direct AVX512 equivalents, and are being used in some kernels. He also refactored `vec/functional.h` to remove duplicated code.
Credits to quickwritereader for helping fix 4 failing complex multiplication & division tests.
### Testing
1. `vec_test_all_types` was modified to test basic AVX512 support, as tests already existed for AVX2.
Only one test had to be modified, as it was hardcoded for AVX2.
2. `pytorch_linux_bionic_py3_8_gcc9_coverage_test1` & `pytorch_linux_bionic_py3_8_gcc9_coverage_test2` are now using `linux.2xlarge` instances, as they support AVX512. They were used for testing AVX512 kernels, as AVX512 kernels are being used by default in both of the CI checks. Windows CI checks had already been using machines with AVX512 support.
### Would the downclocking caused by AVX512 pose an issue?
I think it's important to note that AVX2 causes downclocking as well, and the additional downclocking caused by AVX512 may not hamper performance on some Skylake machines & beyond, because of the double vector-size. I think that [this post with verifiable references is a must-read](https://community.intel.com/t5/Software-Tuning-Performance/Unexpected-power-vs-cores-profile-for-MKL-kernels-on-modern-Xeon/m-p/1133869/highlight/true#M6450). Also, AVX512 would _probably not_ hurt performance on a high-end machine, [but measurements are recommended](https://lemire.me/blog/2018/09/07/avx-512-when-and-how-to-use-these-new-instructions/). In case it does, `ATEN_AVX512_256=TRUE` can be used for building PyTorch, as AVX2 can then use 32 ymm registers instead of the default 16. [FBGEMM uses `AVX512_256` only on Xeon D processors](https://github.com/pytorch/FBGEMM/pull/209), which are said to have poor AVX512 performance.
This [official data](https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/specification-updates/xeon-scalable-spec-update.pdf) is for the Intel Skylake family, and the first link helps understand its significance. Cascade Lake & Ice Lake SP Xeon processors are said to be even better when it comes to AVX512 performance.
Here is the corresponding data for [Cascade Lake](https://cdrdv2.intel.com/v1/dl/getContent/338848) -
The corresponding data isn't publicly available for Intel Xeon SP 3rd gen (Ice Lake SP), but [Intel mentioned that the 3rd gen has frequency improvements pertaining to AVX512](https://newsroom.intel.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/11/2021/04/3rd-Gen-Intel-Xeon-Scalable-Platform-Press-Presentation-281884.pdf). Ice Lake SP machines also have 48 KB L1D caches, so that's another reason for AVX512 performance to be better on them.
### Is PyTorch always faster with AVX512?
No, but then PyTorch is not always faster with AVX2 either. Please refer to #60202. The benefit from vectorization is apparent with with small tensors that fit in caches or in kernels that are more compute heavy. For instance, AVX512 or AVX2 would yield no benefit for adding two 64 MB tensors, but adding two 1 MB tensors would do well with AVX2, and even more so with AVX512.
It seems that memory-bound computations, such as adding two 64 MB tensors can be slow with vectorization (depending upon the number of threads used), as the effects of downclocking can then be observed.
Original pull request: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/56992
Reviewed By: soulitzer
Differential Revision: D29266289
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 2d5e8d1c2307252f22423bbc14f136c67c3e6184
Summary:
This PR deletes some code in `MiscCheck.cmake` that perform the exact
same functionality as `FindAVX.cmake`.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/61748
Reviewed By: ejguan
Differential Revision: D29791282
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 6595fd1b61c8ae12b821fad8c9a34892dd52d213