Summary:
The test loops over `upper` but does not use it effectively running the same test twice which increases test times for no gain.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/41583
Reviewed By: soumith, seemethere, izdeby
Differential Revision: D22598475
Pulled By: zou3519
fbshipit-source-id: d100f20143293a116ff3ba08b0f4eaf0cc5a8099
Summary:
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/38349
mruberry
Not entirely sure if all the changes are necessary in how functions are added to Pytorch.
Should it throw an error when called with a non-complex tensor? Numpy allows non-complex arrays in its imag() function which is used in its isreal() function but Pytorch's imag() throws an error for non-complex arrays.
Where does assertONNX() get its expected output to compare to?
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/41298
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D22610500
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 817d61f8b1c3670788b81690636bd41335788439
Summary:
lcm was missing an abs. This adds it plus extends the test for NumPy compliance. Also includes a few doc fixes.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/41552
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D22580997
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 5ce1db56f88df4355427e1b682fcf8877458ff4e
Summary:
Before, inverse for division by scalar is calculated in the precision of the non-scalar operands, which can lead to underflow:
```
>>> x = torch.tensor([3388.]).half().to(0)
>>> scale = 524288.0
>>> x.div(scale)
tensor([0.], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float16)
>>> x.mul(1. / scale)
tensor([0.0065], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float16)
```
This PR makes results of multiplication by inverse and division the same.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/41446
Reviewed By: ezyang
Differential Revision: D22542872
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: b60e3244809573299c2c3030a006487a117606e9
Summary:
Implementing the quantile operator similar to [numpy.quantile](https://numpy.org/devdocs/reference/generated/numpy.quantile.html).
For this implementation I'm reducing it to existing torch operators to get free CUDA implementation. It is more efficient to implement multiple quickselect algorithm instead of sorting but this can be addressed in a future PR.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/39417
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D22525217
Pulled By: heitorschueroff
fbshipit-source-id: 27a8bb23feee24fab7f8c228119d19edbb6cea33
Summary:
The test was always running on the CPU. This actually caused it to throw an error on non-MKL builds, since the CUDA test (which ran on the CPU) tried to execute but the test requires MKL (a requirement only checked for the CPU variant of the test).
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/41402.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/41523
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D22569344
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: e9908c0ed4b5e7b18cc7608879c6213fbf787da2
Summary:
This test function is confusing since our `assertEqual` behavior allows for tolerance to be specified, and this is a redundant mechanism.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/41514
Reviewed By: ngimel
Differential Revision: D22569348
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 2b2ff8aaa9625a51207941dfee8e07786181fe9f
Summary:
The contiguity preprocessing was mistakenly removed in
cd48fb5030 . It causes erroneous output
when the output tensor is not contiguous. Here we restore this
preprocessing.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/41286
Reviewed By: zou3519
Differential Revision: D22550822
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: ebad4e2ba83d2d808e3f958d4adc9a5513a95bec
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/36403
Copy-paste of the issue description:
* Escape hatch: Introduce unsafe_* version of the three functions above that have the current behavior (outputs not tracked as views). The documentation will explain in detail why they are unsafe and when it is safe to use them. (basically, only the outputs OR the input can be modified inplace but not both. Otherwise, you will get wrong gradients).
* Deprecation: Use the CreationMeta on views to track views created by these three ops and throw warning when any of the views is modified inplace saying that this is deprecated and will raise an error soon. For users that really need to modify these views inplace, they should look at the doc of the unsafe_* version to make sure their usecase is valid:
* If it is not, then pytorch is computing wrong gradients for their use case and they should not do inplace anymore.
* If it is, then they can use the unsafe_* version to keep the current behavior.
* Removal: Use the CreationMeta on view to prevent any inplace on these views (like we do for all other views coming from multi-output Nodes). The users will still be able to use the unsafe_ versions if they really need to do this.
Note about BC-breaking:
- This PR changes the behavior of the regular function by making them return proper views now. This is a modification that the user will be able to see.
- We skip all the view logic for these views and so the code should behave the same as before (except the change in the `._is_view()` value).
- Even though the view logic is not performed, we do raise deprecation warnings for the cases where doing these ops would throw an error.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/39299
Differential Revision: D22432885
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 324aef091b32ce69dd067fe9b13a3f17d85d0f12
Summary:
Resubmit #40927
Closes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/24679, closes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/24678
`addbmm` depends on `addmm` so needed to be ported at the same time. I also removed `THTensor_(baddbmm)` which I noticed had already been ported so was just dead code.
After having already written this code, I had to fix merge conflicts with https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/40354 which revealed there was already an established place for cpu blas routines in ATen. However, the version there doesn't make use of ATen's AVX dispatching so thought I'd wait for comment before migrating this into that style.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/40927
Reviewed By: ezyang
Differential Revision: D22468490
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: f8a22be3216f67629420939455e31a88af20201d
Summary:
Per title. `lgamma` produces a different result for `-inf` compared to scipy, so there comparison is skipped.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/41225
Differential Revision: D22473346
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: e4ebda1b10e2a061bd4cef38d1d7b5bf0f581790
Summary:
When we return to Python from C++ in PyTorch and have warnings and and error, we have the problem of what to do when the warnings throw because we can only throw one error.
Previously, if we had an error, we punted all warnings to the C++ warning handler which would write them to stderr (i.e. system fid 2) or pass them on to glog.
This has drawbacks if an error happened:
- Warnings are not handled through Python even if they don't raise,
- warnings are always printed with no way to suppress this,
- the printing bypasses sys.stderr, so Python modules wanting to
modify this don't work (with the prominent example being Jupyter).
This patch does the following instead:
- Set the warning using standard Python extension mechanisms,
- if Python decides that this warning is an error and we have a
PyTorch error, we print the warning through Python and clear
the error state (from the warning).
This resolves the three drawbacks discussed above, in particular it fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/37240 .
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/41116
Differential Revision: D22456393
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: c3376735723b092efe67319321a8a993402985c7
Summary:
Closes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/24679, closes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/24678
`addbmm` depends on `addmm` so needed to be ported at the same time. I also removed `THTensor_(baddbmm)` which I noticed had already been ported so was just dead code.
After having already written this code, I had to fix merge conflicts with https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/40354 which revealed there was already an established place for cpu blas routines in ATen. However, the version there doesn't make use of ATen's AVX dispatching so thought I'd wait for comment before migrating this into that style.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/40927
Differential Revision: D22418756
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 44e7bb5964263d73ae8cc6adc5f6d4e966476ae6
Summary:
Most time-consuming tests in test_nn (taking about half the time) were gradgradchecks on Conv3d. Reduce their sizes, and, most importantly, run gradgradcheck single-threaded, because that cuts the time of conv3d tests by an order of magnitude, and barely affects other tests.
These changes bring test_nn time down from 1200 s to ~550 s on my machine.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/40999
Differential Revision: D22396896
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 3b247caceb65d64be54499de1a55de377fdf9506
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/40513
This PR makes the following changes:
1. Complex Printing now uses print formatting for it's real and imaginary values and they are joined at the end.
2. Adding 1. naturally fixes the printing of complex tensors in sci_mode=True
```
>>> torch.tensor(float('inf')+float('inf')*1j)
tensor(nan+infj)
>>> torch.randn(2000, dtype=torch.cfloat)
tensor([ 0.3015-0.2502j, -1.1102+1.2218j, -0.6324+0.0640j, ...,
-1.0200-0.2302j, 0.6511-0.1889j, -0.1069+0.1702j])
>>> torch.tensor([1e-3, 3+4j, 1e-5j, 1e-2+3j, 5+1e-6j])
tensor([1.0000e-03+0.0000e+00j, 3.0000e+00+4.0000e+00j, 0.0000e+00+1.0000e-05j,
1.0000e-02+3.0000e+00j, 5.0000e+00+1.0000e-06j])
>>> torch.randn(3, dtype=torch.cfloat)
tensor([ 1.0992-0.4459j, 1.1073+0.1202j, -0.2177-0.6342j])
>>> x = torch.tensor([1e2, 1e-2])
>>> torch.set_printoptions(sci_mode=False)
>>> x
tensor([ 100.0000, 0.0100])
>>> x = torch.tensor([1e2, 1e-2j])
>>> x
tensor([100.+0.0000j, 0.+0.0100j])
```
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D22309294
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: 20edf9e28063725aeff39f3a246a2d7f348ff1e8
Summary:
This PR implements gh-33389.
As a result of this PR, users can now specify various reduction modes for scatter operations. Currently, `add`, `subtract`, `multiply` and `divide` have been implemented, and adding new ones is not hard.
While we now allow dynamic runtime selection of reduction modes, the performance is the same as as was the case for the `scatter_add_` method in the master branch. Proof can be seen in the graph below, which compares `scatter_add_` in the master branch (blue) and `scatter_(reduce="add")` from this PR (orange).
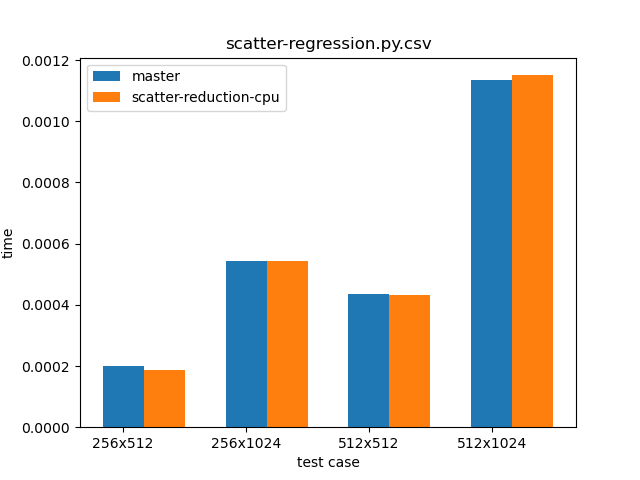
The script used for benchmarking is as follows:
``` python
import os
import sys
import torch
import time
import numpy
from IPython import get_ipython
Ms=256
Ns=512
dim = 0
top_power = 2
ipython = get_ipython()
plot_name = os.path.basename(__file__)
branch = sys.argv[1]
fname = open(plot_name + ".csv", "a+")
for pM in range(top_power):
M = Ms * (2 ** pM)
for pN in range(top_power):
N = Ns * (2 ** pN)
input_one = torch.rand(M, N)
index = torch.tensor(numpy.random.randint(0, M, (M, N)))
res = torch.randn(M, N)
test_case = f"{M}x{N}"
print(test_case)
tobj = ipython.magic("timeit -o res.scatter_(dim, index, input_one, reduce=\"add\")")
fname.write(f"{test_case},{branch},{tobj.average},{tobj.stdev}\n")
fname.close()
```
Additionally, one can see that various reduction modes take almost the same time to execute:
```
op: add
70.6 µs ± 27.3 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
26.1 µs ± 26.5 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
op: subtract
71 µs ± 20.5 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
26.4 µs ± 34.4 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
op: multiply
70.9 µs ± 31.5 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
27.4 µs ± 29.3 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
op: divide
164 µs ± 48.8 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
52.3 µs ± 132 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
```
Script:
``` python
import torch
import time
import numpy
from IPython import get_ipython
ipython = get_ipython()
nrows = 3000
ncols = 10000
dims = [nrows, ncols]
res = torch.randint(5, 10, dims)
idx1 = torch.randint(dims[0], (1, dims[1])).long()
src1 = torch.randint(5, 10, (1, dims[1]))
idx2 = torch.randint(dims[1], (dims[0], 1)).long()
src2 = torch.randint(5, 10, (dims[0], 1))
for op in ["add", "subtract", "multiply", "divide"]:
print(f"op: {op}")
ipython.magic("timeit res.scatter_(0, idx1, src1, reduce=op)")
ipython.magic("timeit res.scatter_(1, idx2, src2, reduce=op)")
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36447
Differential Revision: D22272631
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 3cdb46510f9bb0e135a5c03d6d4aa5de9402ee90
Summary:
BC-breaking NOTE:
In PyTorch 1.6 bool and integral fill values given to torch.full must set the dtype our out keyword arguments. In prior versions of PyTorch these fill values would return float tensors by default, but in PyTorch 1.7 they will return a bool or long tensor, respectively. The documentation for torch.full has been updated to reflect this.
PR NOTE:
This PR causes torch.full to throw a runtime error when it would have inferred a float dtype by being given a boolean or integer value. A versioned symbol for torch.full is added to preserve the behavior of already serialized Torchscript programs. Existing tests for this behavior being deprecated have been updated to reflect it now being unsupported, and a couple new tests have been added to validate the versioned symbol behavior. The documentation of torch.full has also been updated to reflect this change.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/40364
Differential Revision: D22176640
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: b20158ebbcb4f6bf269d05a688bcf4f6c853a965
Summary:
Updates concat kernel for contiguous input to support channels_last contig tensors.
This was tried on squeezenet model on pixel-2 device. It improves model perf by about 25%.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/39448
Test Plan: test_cat_in_channels_last
Differential Revision: D22160526
Pulled By: kimishpatel
fbshipit-source-id: 6eee6e74b8a5c66167828283d16a52022a16997f
Summary:
Many of them have already been migrated to ATen
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/39102
Differential Revision: D22162193
Pulled By: VitalyFedyunin
fbshipit-source-id: 80db9914fbd792cd610c4e8ab643ab97845fac9f
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38490
A meta tensor is a tensor that is a lot like a normal tensor,
except it doesn't actually have any data associated with it.
You can use them to carry out shape/dtype computations without
actually having to run the actual code; for example, this could
be used to do shape inference in a JIT analysis pass.
Check out the description in DispatchKey.h for more information.
Meta tensors are part of a larger project to rationalize how we
write kernels so that we don't have to duplicate shape logic
in CPU kernel, CUDA kernel and meta kernel (this PR makes the
duplication problem worse!) However, that infrastructure can
be built on top of this proof of concept, which just shows how
you can start writing meta kernels today even without this
infrastructure.
There are a lot of things that don't work:
- I special cased printing for dense tensors only; if you try to
allocate a meta sparse / quantized tensor things aren't going
to work.
- The printing formula implies that torch.tensor() can take an
ellipsis, but I didn't add this.
- I wrote an example formula for binary operators, but it isn't
even right! (It doesn't do type promotion of memory layout
correctly). The most future proof way to do it right is to
factor out the relevant computation out of TensorIterator,
as it is quite involved.
- Nothing besides torch.add works right now
- Meta functions are ALWAYS included in mobile builds (selective
build doesn't work on them). This isn't a big deal for now
but will become more pressing as more meta functions are added.
One reason I'm putting up this PR now is to check with Yinghai Lu
if we can unblock shape inference for accelerators, while we are
still working on a long term plan for how to unify all shape
computation across our kernels.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D21935609
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: f7d8636eeb8516b6bc296db99a16e56029972eee
Summary:
Enable ops used in BERT which were missed in one of my earlier PRs.
ezyang jeffdaily
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/40236
Differential Revision: D22143965
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 5464ed021687fec1485e1c061e5a7aba71687fc4
Summary:
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/39963 erroneously removed template specialization to compute offsets, causing cases relying on this specialization (topk for 4d+ tensors with topk dimension >= 1024/2048 depending on the type) to produce bogus results.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/40349
Differential Revision: D22153756
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: cac04969acb6d7733a7da2c1784df7d30fda1606
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37968
Modify memory format promotion rules to avoid promoting when one of the input is ambiguous. New rules are:
Ambiguous + Contiguous = Contiguous
Ambiguous + Channels Last = Channels Last
Contiguous + Ambiguous ( NC11 ) = Contiguous
Contiguous + Channels Last = Contiguous ( + Warning ) Before this PR: Channels Last
Channels Last + Contiguous = Channels Last ( + Warning )
Channels Last + Ambiguous = Channels Last
Bias + Channels Last = Channels Last
Channels Last + Bias = Channels Last
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D21819573
Pulled By: VitalyFedyunin
fbshipit-source-id: 7381aad11720b2419fb37a6da6ff4f54009c6532
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/40187
There were two issues:
1) The hand-written definition included an ambiguous default, which made the deprecated signature not selected. This didn't match the handwritten torch.nonzero, now they do.
2) A parsing bug for empty argument lists meant the signature wasn't being marked as deprecated.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D22118236
Pulled By: gchanan
fbshipit-source-id: a433ce9069fef28aea97cbd76f2adf5a285abd73
Summary:
Closes gh-35418,
PR gh-16414 added [the `CMAKE_INSTALL_RPATH_USE_LINK_PATH`directive](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/16414/files#diff-dcf5891602b4162c36c2125c806639c5R16) which is non-standard and will cause CMake to write an `RPATH` entry for libraries outside the current build. Removing it leaves an RPATH entry for `$ORIGIN` but removes the entries for things like `/usr/local/cuda-10.2/lib64/stubs:/usr/local/cuda-10.2/lib64` for `libcaffe2_nvrtc.so` on linux.
The added test fails before this PR, passes after. It is equivalent to checking `objdump -p torch/lib/libcaffe2_nvrtc.so | grep RPATH` for an external path to the directory where cuda "lives"
I am not sure if it solve the `rpath/libc++.1.dylib` problem for `_C.cpython-37m-darwin.so` on macOS in issue gh-36941
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37737
Differential Revision: D22068657
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: b04c529572a94363855f1e4dd3e93c9db3c85657
Summary:
Closes gh-39060
The `TensorIterator` splitting is based on `can_use_32bit_indexing` which assumes 32-bit signed ints, so we can get away with just 2**31 as the axis length. Also tested on an old commit that I can reproduce the test failure on just a 1d tensor, overall quartering the memory requirement for the test.
4c7d81f847/aten/src/ATen/native/TensorIterator.cpp (L879)
For reference, the test was first added in gh-33310.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/40036
Differential Revision: D22068690
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 83199fd31647d1ef106b08f471c0e9517d3516e3
Summary:
Currently compare_with_numpy requires a device and dtype, but these arguments are ignored if a tensor is provided. This PR updates the function to only take device and dtype if a tensor-like object is given. This should prevent confusion that you could, for example, pass a CPU float tensor but provided a CUDA device and integer dtype.
Several tests are updated to reflect this behavior.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/40064
Differential Revision: D22058072
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: b494bb759855977ce45b79ed3ffb0319a21c324c
Summary:
Adds `torch.experimental.deterministic` flag to enforce deterministic algorithms across all of pytorch.
Adds `torch.experimental.deterministic_error_level` to allow users to choose between error/warning/silent if determinism for an operation is not available.
Adds `torch.experimental.alert_not_deterministic()` which should be called within operations that are not deterministic.
Offers both Python and ATen interfaces
Issue https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/15359
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38683
Differential Revision: D21998093
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 23aabbddd20f6199d846f97764ff24d728163737
Summary:
Benchmark with same build settings on same system.
gcc : version 7.5.0 (Ubuntu 7.5.0-3ubuntu1~18.04)
CUDA : 10.1
GPU : 1050ti
```python
import time
import torch
import numpy as np
for n, t in [(500_000, 10),
(1_000_000, 10)]:
for dtype in (torch.half, torch.float, torch.double):
# Input Setup
p = torch.from_numpy(np.random.rand(n)).to(dtype)
want = 1000
print(f'torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == {n} for {t} times {dtype}')
start = time.time()
# Iterate
for _ in range(t):
torch.multinomial(p, want, replacement=False)
print(f'Took:', time.time() - start)
print('****' * 10)
for n, t in [(50_000, 100),
(100_000, 100)]:
for dtype in (torch.half, torch.float, torch.double):
# Input Setup
p = torch.rand(n, device='cuda', dtype=dtype)
want = 1000
print(f'torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == {n} for {t} times {dtype}')
start = time.time()
# torch.cuda.synchronize()
# Iterate
for _ in range(t):
torch.multinomial(p, want, replacement=False)
# torch.cuda.synchronize()
print(f'CUDA Took:', time.time() - start)
```
Before:
```
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 500000 for 10 times torch.float16
Took: 80.64455389976501
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 500000 for 10 times torch.float32
Took: 3.7778031826019287
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 500000 for 10 times torch.float64
Took: 5.045570611953735
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 1000000 for 10 times torch.float16
Took: 161.53191947937012
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 1000000 for 10 times torch.float32
Took: 7.640851736068726
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 1000000 for 10 times torch.float64
Took: 10.399673461914062
****************************************
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 50000 for 100 times torch.float16
CUDA Took: 4.873984098434448
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 50000 for 100 times torch.float32
CUDA Took: 4.713594436645508
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 50000 for 100 times torch.float64
CUDA Took: 11.167185068130493
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 100 times torch.float16
CUDA Took: 7.195427417755127
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 100 times torch.float32
CUDA Took: 7.669712066650391
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 100 times torch.float64
CUDA Took: 20.20938801765442
```
After:
```
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 500000 for 10 times torch.float16
Took: 81.09321522712708
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 500000 for 10 times torch.float32
Took: 0.06062650680541992
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 500000 for 10 times torch.float64
Took: 0.0862889289855957
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 1000000 for 10 times torch.float16
Took: 161.85304307937622
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 1000000 for 10 times torch.float32
Took: 0.13271093368530273
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 1000000 for 10 times torch.float64
Took: 0.17215657234191895
****************************************
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 50000 for 100 times torch.float16
CUDA Took: 0.035035133361816406
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 50000 for 100 times torch.float32
CUDA Took: 0.03631949424743652
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 50000 for 100 times torch.float64
CUDA Took: 0.05507040023803711
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 100 times torch.float16
CUDA Took: 0.05105161666870117
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 100 times torch.float32
CUDA Took: 0.05449223518371582
torch.multinomial(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 100 times torch.float64
CUDA Took: 0.09161853790283203
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/39742
Differential Revision: D21976915
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 34431f814f31b6dfd6179a89f8e4fa574da7a306
Summary:
**1.6 Deprecation Note**
In PyTorch 1.6 attempting to divide two integer tensors or an integer tensor and an integer scalar will throw a runtime error. This behavior was deprecated with a warning in PyTorch 1.5. In PyTorch 1.7 torch.div and the division operator will always perform true division like Python3 and NumPy.
To divide integer values use either torch.true_divide, for true division, or torch.floor_divide (the // operator) for floor division.
**PR Summary**
This PR updates the warning message when performing integer division to be a runtime error. Because some serialized Torchscript programs may rely on torch.div's historic behavior it also implements a "versioned symbol" for div that lets those models retain their current behavior. Extensive tests of this behavior are the majority of this PR.
Note this change bumps the produced file format version to delineate which programs should have their historic div behavior preserved.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38620
Differential Revision: D21612598
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: c9c33591abce2f7e97f67f0f859901f5b03ed47d
Summary:
**BC breaking note:**
In PyTorch 1.5 passing the out= kwarg to some functions, like torch.add, could affect the computation. That is,
```
out = torch.add(a, b)
```
could produce a different tensor than
```
torch.add(a, b, out=out)
```
This is because previously the out argument participated in the type promotion rules. For greater consistency with NumPy, Python, and C++, in PyTorch 1.6 the out argument no longer participates in type promotion, and has no effect on the computation performed.
**ORIGINAL PR NOTE**
This PR effectively rewrites Tensor Iterator's "compute_types" function to both clarify its behavior and change how our type promotion works to never consider the out argument when determining the iterator's "common dtype," AKA its "computation type." That is,
```
a = op(b, c)
```
should always produce the same result as
```
op(b, c, out=a)
```
This is consistent with NumPy and programming languages like Python and C++.
The conceptual model for this change is that a TensorIterator may have a "common computation type" that all inputs are cast to and its computation performed in. This common computation type, if it exists, is determined by applying our type promotion rules to the inputs.
A common computation type is natural for some classes of functions, like many binary elementwise functions (e.g. add, sub, mul, div...). (NumPy describes these as "universal functions.") Many functions, however, like indexing operations, don't have a natural common computation type. In the future we'll likely want to support setting the TensorIterator's common computation type explicitly to enable "floating ufuncs" like the sin function that promote integer types to the default scalar type. Logic like that is beyond the type promotion system, which can only review inputs.
Implementing this change in a readable and maintainable manner was challenging because compute_types() has had many small modifications from many authors over ~2 year period, and the existing logic was in some places outdated and in other places unnecessarily complicated. The existing "strategies" approach also painted with a broad brush, and two of them no longer made conceptual sense after this change. As a result, the new version of this function has a small set of flags to control its behavior. This has the positive effect of disentangling checks like all operands having the same device and their having the same dtype.
Additional changes in this PR:
- Unary operations now support out arguments with different dtypes. Like binary ops they check canCast(computation type, out dtype).
- The dtype checking for lerp was outdated and its error message included the wrong variable. It has been fixed.
- The check for whether all tensors are on the same device has been separated from other checks. TensorIterators used by copy disable this check.
- As a result of this change, the output dtype can be computed if only the input types are available.
- The "fast path" for checking if a common dtype computation is necessary has been updated and simplified to also handle zero-dim tensors.
- A couple helper functions for compute_types() have been inlined to improve readability.
- The confusingly named and no longer used promote_gpu_output_dtypes_ has been removed. This variable was intended to support casting fp16 reductions on GPU, but it has become a nullop. That logic is now implemented here: 856215509d/aten/src/ATen/native/ReduceOpsUtils.h (L207).
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/39655
Differential Revision: D21970878
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 5e6354c78240877ab5d6b1f7cfb351bd89049012
Summary:
It's better to have skipping logic explicitly defined in test decorators rather than in some hard-to-find blacklists
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/39693
Differential Revision: D21947893
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: 3d0855eda7e10746ead80fccf84a8db8bf5a3ef1
Summary:
This PR aims to add `arcosh`, `arcsinh` and `arctanh` support. Please see issue https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/38349 for more details.
**TODOs:**
* [x] Add test cases for `arcosh`, `arcsinh` and `arctanh`. (need help)
* [x] Overload ops if `std::op` does not work with `thrust::complex` types (like for `sinh`, `cosh`).
Note: `std::acosh, std::asinh, std::atanh` do not support `thrust::complex` types. Added support for complex types for these 3 ops (`arccosh, arcsinh, arctanh`)
cc: mruberry
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38388
Differential Revision: D21882055
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: d334590b47c5a89e491a002c3e41e6ffa89000e3
Summary:
Re-enable some test cases in `test_memory_format_operators` since their corresponding issue has been fixed.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38648
Differential Revision: D21689085
Pulled By: VitalyFedyunin
fbshipit-source-id: 0aa09e0bf31ba98c8ad0191ac3afd31dda0f1d42
Summary:
Cut from https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38994.
This is a helper function for comparing torch and NumPy behavior. It updates the existing and increasingly popular _np_compare function and moves it to be a method on TestCase.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/39179
Differential Revision: D21855082
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: edca3b78ae392d32243b02bf61960898b6ba590f
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/32866, resubmit of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/38970
The memory error in the issue is caused by int overflowing in col2vol. This version using mixed 32-bit and 64-bit indexing calculation lifts the maximum indexing possible without compromising the performance of ConvTranspose3d. vs 20-30% regression with pure 64-bit indexing.
This requires that input.numel() <= UINT_MAX, and channels * kernel.numel() <= UINT_MAX otherwise it raises an error. Previously, the code would crash or give incorrect results unless input.numel() * kernel.numel() <= INT_MAX.
Note that the test is a minimised reproducer for the issue.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/39198
Differential Revision: D21817836
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: b9adfe9f9dd00f04435be132966b33ac6b9efbef
Summary:
The test is currently only enabled for CPU, and it will be enabled for CUDA after the migration of `min` and `max` from THC to ATen is done.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38850
Differential Revision: D21819388
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 406343e96bccbf9139eb1f8f2d49ed530dd83d62
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/39033
Added `real` and `imag` views as tensor attributes. Right now, tensor.imag is disabled for real tensors. This is because if we return a new tensor of zeros, the user would be able to update the tensor returned by tensor.imag which should not be allowed as numpy returns a read-only array, and pytorch doesn't support read-only tensors yet.
TODO in follow-up PRs:
1. add a setter for `real` and `imag`
2. add special case in codegen for `real` and `imag` backward functions.
3. remove `copy_real` and `copy_imag` methods.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D21767542
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: 539febf01f01ff055e3fbc7e9ff01fd3fe729056
Summary:
Adds complex support to `cumsum`, `cumprod` and relevant test update in `test_torch::tensor_op_tests`
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/39063
Differential Revision: D21771186
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: 632916d4bdbd1c0941001898ab8146be2b7884fc
Summary:
**BC-breaking note:**
In previous versions of PyTorch zero dimensional CUDA tensors could be moved across devices implicitly. For example,
```
torch.tensor(5, device='cuda:0') + torch.tensor((1, 1), device='cuda:1')
```
would work, even though the tensors are on different CUDA devices. This is a frequent source of user confusion, however, and PyTorch generally does not move data across devices without it being explicit. This functionality is removed in PyTorch 1.6.
**PR Summary:**
Today in PyTorch we allow implicit data movement of zero dimensional CUDA tensors. For example, we allow:
```
torch.tensor(5, device='cuda:0') + torch.tensor((1, 1), device='cuda:1')
```
and
```
torch.tensor(2, device='cuda') + torch.tensor((3, 5))
```
In both of these cases TensorIterator would move the zero dim CUDA tensor to the device of the non-scalar tensor (cuda:1 in the first snippet, the CPU in the second snippet).
One of PyTorch's fundamental rules, however, is that it does not perform implicit data movement like this, and this change will causes these cases to throw an error. New tests for this behavior are added to test_torch.py, and tests of the old behavior are removed in test_torch.py and test_autograd.py. A cpp test in tensor_iterator_test.cpp is modified to account for the new behavior.
This addresses https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/36722.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38998
Differential Revision: D21757617
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 2498f07f4938d6de691fdbd5155ad2e881ff7fdb
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/32866
The memory error in the issue is caused by `int` overflowing in `col2vol`. This version using mixed 32-bit and 64-bit indexing calculation lifts the maximum indexing possible without compromising the performance of `ConvTranspose3d`. vs 20-30% regression with pure 64-bit indexing.
This requires that `input.numel() <= UINT_MAX`, and `channels * kernel.numel() <= UINT_MAX` otherwise it raises an error. Previously, the code would crash or give incorrect results unless `input.numel() * kernel.numel() <= INT_MAX`.
Note that the test is a minimised reproducer for the issue.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38970
Differential Revision: D21748644
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 95060423219dc647595e1a24b3dcac520d3aecba
Summary:
`_TestTorchMixin` is base class which is instantiated across multiple types.
It was inherited from `object` in order to hide it from unittest test discovery mechanism.
But this approach makes it almost impossible to use static code analyzer on the class.
This PR implements alternative approach by hiding base class into inner class, per https://stackoverflow.com/a/25695512
Change imported class access path in `test_cuda.py`
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/39110
Test Plan:
run `test_torch.py --discover-tests` and `test_cuda.py --discover-tests` before and after change:
```
$ python test_torch.py --discover-tests|md5sum
2ca437bb5d65700763ce04cdacf6de3e -
$ python test_cuda.py --discover-tests|md5sum
b17df916fb0eeb6f0dd7222d7dae392c -
```
Differential Revision: D21759265
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: b01b06111469e551f7b78387449975e5248f6b9e
Summary:
1.6 Deprecation Note:
In 1.6 attempting to perform integer division using addcdiv will throw a RuntimeError, and in 1.7 the behavior will change so that addcdiv always performs a true division of its tensor1 and tensor2 inputs. See the warning in torch.addcdiv's documentation for more information.
PR Summary:
This PR updates the warning that appears when addcdiv performs integer division to throw a RuntimeError. This is intended to prevent silent errors when torch.addcdiv's behavior is changed to always perform true division in 1.7. The documentation is updated (slightly) to reflect this, as our the addcdiv tests in test_torch and test_type_promotion.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38762
Differential Revision: D21657585
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: c514b44409706f2bcfeca4473424b30cc48aafbc
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37181
Now that assertEquals considers dtypes in determining tolerance, most
tests don't need explicitly set precision.
Those that do are a few half precision tests on cuda. In this PR, those
are broken out to be handled explicitly, though we may also want to
consider further loosening the tolerance on half-precision.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D21728402
Pulled By: nairbv
fbshipit-source-id: 85f3daf63f1bdbb5101e8dea8c125f13448ca228
Summary:
This updates assertEqual and assertEqual-like functions to either require both or neither of atol and rtol be specified. This should improve clarity around handling precision in the test suite, and it allows us to remove the legacy positional atol argument from assertEqual. In addition, the "message" kwarg is replace with a kwarg-only "msg" argument whose name is consistent with unittest's assertEqual argument.
In the future we could make "msg" an optional third positional argument to be more consistent with unittest's assertEqual, but requiring it be specified should be clear, and we can easily update the signature to make "msg" an optional positional argument in the future, too.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38872
Differential Revision: D21740237
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: acbc027aa1d7877a49664d94db9a5fff91a07042
Summary:
This updates assertEqual and assertEqual-like functions to either require both or neither of atol and rtol be specified. This should improve clarity around handling precision in the test suite, and it allows us to remove the legacy positional atol argument from assertEqual. In addition, the "message" kwarg is replace with a kwarg-only "msg" argument whose name is consistent with unittest's assertEqual argument.
In the future we could make "msg" an optional third positional argument to be more consistent with unittest's assertEqual, but requiring it be specified should be clear, and we can easily update the signature to make "msg" an optional positional argument in the future, too.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38872
Differential Revision: D21717199
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 9feb856f94eee911b44f6c7140a1d07c1b026d3a
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37098
### **Cherry-picked from another stack:**
Some code review already occurred here: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/32582
### Summary:
Fixes: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/32436
The issue caused incorrect handling of dtypes for scalar ** tensor.
e.g. before this change:
```
>>> 5.5 ** torch.ones(5, dtype=torch.int32)
tensor([5, 5, 5, 5, 5], dtype=torch.int32)
```
should return a float tensor.
Also fixes a number of incorrect cases:
* tensors to negative powers were giving incorrect results (1 instead
of 0 or error)
* Behavior wasn't consistent between cuda/cpu
* large_value ** 1 in some cases gave a result not equal
to large_value because of truncation in conversion to double and back.
BC-breaking:
Previously incorrect behavior (in 1.4):
```
>>> a
tensor([1, 1, 1, 1, 1], dtype=torch.int32)
>>> a.pow_(.5)
tensor([1, 1, 1, 1, 1], dtype=torch.int32)
```
After this change:
`RuntimeError: result type Float can't be cast to the desired output type Int`
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D21686207
Pulled By: nairbv
fbshipit-source-id: e797e7b195d224fa46404f668bb714e312ea78ac
Summary:
Related issue: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/36900
Since I feel this PR is already large enough, I didn't migrate max in this PR. Legacy code is not cleaned up either. All these remaining work will be done in later PRs after this is merged.
Benchmark on an extreme case
```python
import torch
print(torch.__version__)
t = torch.randn(100000, 2, device='cuda')
warmup = torch.arange(100000000)
torch.cuda.synchronize()
%timeit t.min(dim=0); torch.cuda.synchronize()
```
Before: 4ms; After: 24.5us.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38440
Differential Revision: D21560691
Pulled By: ngimel
Summary:
This PR fixes the tolerance values for some of the bfloat16 div tests that were enabled on ROCm with incorrect tolerance values in the PR https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38621
Also disabled(to unblock CI) `test_addcdiv*` for which the error is large when absolute values in the tensor are higher. This will have to be investigated further.
ezyang jeffdaily sunway513
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38823
Differential Revision: D21686290
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 85472680e1886bdc7c227ed2656e0b4fd5328e46
Summary:
This PR ports `masked_select` from TH to ATen and optimize the performance on CPU with TensorIterator.
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/33053
1. single socket run: up to **5.4x** speedup;
2. single core run: up to **1.16x** speedup.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/33269
Differential Revision: D20922288
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 38e183a4e3599bba29bbbebe36264026abe1c50e
Summary:
Updates our tests in preparation of integer division using torch.div and torch.addcdiv throwing a runtime error by avoiding integer division using torch.div. This creates a brief period where integer division using torch.div is untested, but that should be OK (since it will soon throw a runtime error).
These callsites were identified using https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/36897.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38621
Differential Revision: D21612823
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 749c03a69feae02590b4395335163d9bf047e162
Summary:
floordiv was missing a couple dunder registrations, which was causing __ifloordiv__ to not be called when it should. This adds the appropriate registrations and adds a test verifying that the inplace dunders are actually occuring inplace.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38695
Differential Revision: D21633980
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: a423f5ec327cdc062fd6d9d56abd36fe44ac8198
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37984
- `NumericUtils.h`
CUDA distribution kernels had two variants of transformation labdas(`uniform`/`normal` -> `lognormal`/`exponential`/`cauchy`/`geometric`...): for double-precision and optimized for CUDA single precision. It was done by using `::log`/`__logf`, `::exp`/`__expf` and `::tan/__tanf`. I moved them to `NumericUtils.h` and called them `at::exp`, `at::log` and `at::tan`. It allowed to unify CPU/CUDA transformation templates in `TransformationHelper.h`.
- `DistributionsHelper.h`
Made `normal_distribution`, `geometric_distribution`, `exponential_distribution`, `cauchy_distribution`, `lognormal_distribution` C10_HOST_DEVICE compatible to reuse them in CPU/CUDA distribution kernels.
Replaced explicit math with transformations from `TransformationHelper.h`
- `TransformationHelper.h`
Renamed `*_transformation` to `transformation::*`
Added clear unified host/device transformations templates `normal`, `cauchy`, `exponential`, `geometric`, `log_normal` which are used by both CPU and CUDA distribution kernels and custom PRNG distribution kernels.
- `cpu/DistributionTemplates.h`
Unified `normal_kernel`, `cauchy_kernel`, `log_normal_kernel`, `geometric_kernel`, `exponential_kernel`.
- `cuda/DistributionTemplates.h`
Extracted `UNIFORM_AND_TRANSFORM` and `NORMAL_AND_TRANSFORM` macros to reuse code between distribution kernel templates.
Unified transformation labdas(`uniform`/`normal` -> `lognormal`/`exponential`/`cauchy`/`geometric`...)
- `test_torch.py`
Added `scipy.stats.kstest` [Kolmogorov–Smirnov](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kolmogorov%E2%80%93Smirnov_test) tests for `uniform`/`normal`/`lognormal`/`exponential`/`cauchy` distributions and [Chi-squared](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chi-squared_test) test for `geometric` one. To make sure that our distributions are correct.
- `cpu_rng_test.cpp`, `rng_test.h`
Fixed random_()'s from and to bounds issue for floating-point types, fixed cast/overflow warnings
- `THTensorRandom.h`, `THVector.h`
Moved unnecessary includes to `THTensorRandom.cpp`
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D21477955
Pulled By: pbelevich
fbshipit-source-id: 7b793d1761a7a921c4b4a4a7d21d5d6c48f03e72
Summary:
Edit: this has been updated to reflect the PR's current status, which has changed after review.
This PR updates the behavior of the assertEqual, assertNotEqual, and assert_allclose to be consistent with each other and torch.isclose. It corrects several additional bugs in the current implementations and adds extensive testing and comments, too.
These updates follow from changes to assertEqual like https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/34258 and https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37069, and from our discussion of torch.isclose for complex tensors (see https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/36462), where we decided to implement a NumPy-compatible mathematical notion of "closeness" for complex tensors that is not a great fit for our testing framework.
The detailed changelist is:
- New test framework functions for comparing tensors and scalars
- Tensors are compared using isclose; the real and imaginary parts of complex tensors are compared independently
- Scalars are compared using the same algorithm
- assertEqual and assert_allclose now use this common comparison function, instead of each implementing their own with divergent behavior
- assertEqual-like debug messages are now available for all tensor and scalar comparisons, with additional context when comparing the components of sparse, quantized, and complex tensors
- Extensive testing of the comparison behavior and debug messages
- Small Updates
- assertEqual now takes an "exact_device" argument, analogous to "exact_dtype", which should be useful in multidevice tests
- assertEqual now takes an "equal_nan" argument for argument consistency with torch.isclose
- assertEqual no longer takes the "allow_inf" keyword, which misleadingly only applied to scalar comparisons, was only ever set (rarely) to true, and is not supported by torch.isclose
- Bug fixes:
- the exact_dtype attribute has been removed (no longer needed after https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38103)
- message arguments passed to assertEqual are now handled correctly
- bool x other dtype comparisons are now supported
- uint8 and int8 tensor comparisons now function properly
- rtol for integer comparisons is now supported (default is zero)
- rtol and atol for scalar comparisons are now supported
- complex scalar comparisons are now supported, analogous to complex tensor comparisons
- assertNotEqual is now equivalent to the logical negation of assertEqual
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37294
Differential Revision: D21596830
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: f2576669f7113a06f82581fc71883e6b772de19b
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38505
This takes the testing of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38275, but doesn't include the kernel changes which are still being worked out.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D21580574
Pulled By: gchanan
fbshipit-source-id: f12317259cb7373989f6c9ad345b19aaac524851
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38400
* #38399 Added autograd tests, disabled jit autograd tests for complex and added a separate list for tests for complex dtype only
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D21572209
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: 7036029e9f8336139f5d54e0dfff9759f3bf8376
Summary:
Together with https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/37758, this fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/37743 and fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/24861.
This follows the CUDA fix in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/37758, vectorised using a `blendv` to replace the if conditionals.
Most of the complication is from `remainder` supporting `at::Half` where `fmod` doesn't. I've now got `fmod` working on `Vec256<at::Half>` as well as enabling half dispatch for `fmod` so it matches `remainder`.
I also added `fmod` support to `Vec256<at::BFloat16>` before realising that `remainder` doesn't support `BFloat16` anyway. I could also enable `BFloat16` if that's desirable. If not, I don't think `Vec256<BFloat16>` should be missing `fmod` anyway.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38293
Differential Revision: D21539801
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: abac6a3ed2076932adc459174cd3d8d510f3e1d5
Summary:
Closes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/24561
Benchmark with same build settings on same system.
gcc : version 7.5.0 (Ubuntu 7.5.0-3ubuntu1~18.04)
CUDA : 10.1
GPU : 1050ti
```python
import timeit
for n, t in [(10_000, 20000),
(100_000, 20000)]:
for dtype in ('torch.half', 'torch.float', 'torch.double'):
print(f'torch.exp(a) a.numel() == {n} for {t} times {dtype}')
print(timeit.timeit(f'torch.exp(a); torch.cuda.synchronize()',
setup=f'import torch; a=torch.arange({n}, dtype={dtype}, device="cuda")',
number=t))
```
Before:
```
torch.exp(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.3001665159999902
torch.exp(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.28265794499998265
torch.exp(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.double
0.3432170909998149
torch.exp(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.32273333800003456
torch.exp(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.31498759600003723
torch.exp(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.double
1.079708754999956
```
After:
```
torch.exp(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.27996097300092515
torch.exp(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.2774473429999489
torch.exp(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.double
0.33066844799941464
torch.exp(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.27641824200145493
torch.exp(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.27805968599932385
torch.exp(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.double
1.0644143180015817
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36652
Differential Revision: D21164653
Pulled By: VitalyFedyunin
fbshipit-source-id: 42c7b24b0d85ff1d390231f1457968a8869b8db3
Summary:
Before, multinomial kernels did not advance random states enough, which lead to the same sequence being generated over and over with a shift of 4. This PR fixes that.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/37403
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38046
Differential Revision: D21516542
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 23248a8c3a5c44316c4c35cd71a8c3b5f76c90f2
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/38018
when calling `eq_with_nan(v, kValue)` having `v` and `kValue` both `nan` is returning `false` when it should be `true`.
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/aten/src/ATen/native/cuda/SortingKthValue.cu#L76
The implementation is using intrinsics such as `__double_as_longlong` and comparing their bit representations. But the values of the bits obtained for both nans are different.
`9221120237041090560` for `v`
`9223372036854775807` for `kValue`
two different nans have different bit representations, so we have to do additional comparisons to fix this.
I changed this comparison and it seems to be working now.
However, when compared to a CPU implementation, the returned indices for the values seems to be random but valid.
Probably this is an effect of the comparison order in the Cuda version.
I am not sure if this is ok since all the indices point to valid elements.
For the snippet in the issue I get the following:
```
# CUDA Values
tensor([nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan],
device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float64)
# CUDA indices
tensor([304, 400, 400, 528, 304, 304, 528, 336, 304, 432, 400, 280, 280, 336,
304, 336, 400, 304, 336, 560], device='cuda:0')
```
```
# CPU values
tensor([nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan],
dtype=torch.float64)
# CPU indices
tensor([515, 515, 515, 515, 515, 515, 515, 515, 515, 515, 515, 515, 515, 515,
515, 515, 515, 515, 515, 515])
```
Also, maybe its better to change the `eq_with_nan` implementations to address this instead?
I am not sure if this will cause code to break in other places though ...
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38216
Differential Revision: D21517617
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: deeb7bb0ac519a03aa0c5f365005a9150e6404e6
Summary:
Reland of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/38140. It got reverted since it broke slow tests which were only run on master branch(thanks mruberry !). Enabling all CI tests in this PR to make sure they pass.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38288
Reviewed By: mruberry
Differential Revision: D21524923
Pulled By: ailzhang
fbshipit-source-id: 3a9ecc7461781066499c677249112434b08d2783
Summary:
I'm mostly done with cleaning up test/ folder. There're a bunch of remaining callsites but they're "valid" in testing `type()` functionalities. We cannot remove them until it's fully deprecated.
Next PR would mainly focus on move some callsites to an internal API.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38140
Differential Revision: D21483808
Pulled By: ailzhang
fbshipit-source-id: 12f5de6151bae59374cfa0372e827651de7e1c0f
Summary:
`is_tensor` doesn't really have a reason to exist anymore (other than
backwards compatibility) and is worse for typechecking with mypy (see
gh-32824). Given that it may not be obvious what the fix is once mypy
gives an error, make the change in a number of places at once, and add
a note on this to the `is_tensor` docstring.
Recommending an isinstance check instead has been done for quite a
while, e.g. https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/7769#discussion_r190458971
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38062
Differential Revision: D21470963
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 98dd60d32ca0650abd2de21910b541d32b0eea41
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/38033
Pickles require class names to be actually accessible from the module
in question. _VariableFunction was not! This fixes it.
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/37703
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D21458068
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 2a5ac41f9d1972e300724981b9b4b84364ddc18c
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/37157 on my machine.
This was annoying to track down. The essence is that cublas expects column major inputs and Pytorch tensors are usually row major. Cublas lets you request that it act on transposed data, and the erroring `gemv` calls in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/37157 make that request. The problem is, [cublasSgemv and cublasDgemv](https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cublas/index.html#cublas-lt-t-gt-gemv) (called by [`gemv<float>`](091a1192d7/aten/src/ATen/cuda/CUDABlas.cpp (L318)) and `gemv<double>`) regard their `m, n` arguments values as _pre_-transpose sizes, while [cublasGemmEx](https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cublas/index.html#cublas-GemmEx) (called by `gemv<at::Half>`, see [here](091a1192d7/aten/src/ATen/cuda/CUDABlas.cpp (L342)) and [here](091a1192d7/aten/src/ATen/cuda/CUDABlas.cpp (L229))) regards its `m, k` argument values as _post_-transpose sizes. This is inconsistent. It turns out the `gemv<float>/<double>` calls are configured correctly and the `gemv<at::Half>` calls aren't.
Strikethrough text below is no longer accurate, ngimel suggested a better way to handle gemv->gemm forwarding. [Comments in code](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37569/files#diff-686aa86335f96b4ecb9b37f562feed12R323-R348) provide an up-to-date explanation.
Keeping out-of-date strikethrough text because I don't have the heart to delete it all and because it captures an intermediate state of my brain that will help orient me if i ever have to fix this again.
~~To convince myself this PR keeps `at::cuda::blas::gemv`'s external API consistent across dtypes, I need to think through what happens when a pytorch tensor input of size `(a,b)` multiples a vector of size `(b,)` for 4 cases:~~
### ~~1. input is row-major (needs cublas internal transpose)~~
#### ~~1a. input is float or double~~
~~`gemv<float>/<double>` call `cublasS/Dgemv`, forwarding `trans`,** `m`, and `n` directly.~~
~~`cublasS/Ggemv` expects "a m × n matrix stored in column-major format" (so m is the input's fast dim). Input has size `(a, b)` in row-major format. We can reinterpret it as a column-major matrix with size `(b, a)` without any memory movement. So the gemv call should supply `m=b`, `n=a`. However, we're not trying to multiply a matrix `(b, a)` x a vector `(b,)`, we're trying to sum across `b` for matrix and vector. So we also request that cublas transpose the matrix internally by supplying `trans='t'` to `blas::gemv`, which becomes `trans=CUBLAS_OP_T` to the `cublasS/Ggemv`.~~
~~As long as the code calling `blas::gemv` thinks carefully and passes `trans='t'`, `m=b`, `n=a`, cublas carries out `(a, b) x (b,)` and all is well.~~
#### ~~1b. input is half or bfloat16~~
~~`blas::gemv<at::Half>` takes a different code path, calling `gemm<at::Half>` which calls `cublasGemmEx`. The job of this PR is to make sure the exterior `blas::gemv` caller's carefully thought-out argument choices (`trans='t'`, `m=b`, `n=a`) remain correct.~~
~~`cublasGemmEx` takes args `transa, transb, m, n, k, ....others we don't care about` and carries out~~
```
C = α op ( A ) op ( B ) + β C
where α and β are scalars, and A , B and C are matrices stored in column-major format with
dimensions op ( A ) m × k , op ( B ) k × n and C m × n Also, for matrix A
A if transa == CUBLAS_OP_N
op ( A ) = A^T if transa == CUBLAS_OP_T ...
```
~~`gemv<at::Half>` hacks a gemv by calling gemm such that the raw gemm's `m` is the output dim, `k` is the summed dim, and `n=1`, . Reasonable, as long as we get the values right, given that we also need to transpose the input.~~
~~To conform with cublas docs we interpret input as column-major with size `(b, a)`. As for the `<float>/<double>` gemv we want cublas to carry out input (interpreted as column major), internally transposed, times vector of size `(b,)`. In other words we want cublas to apply `op(A) x B`, where op is transpose and `A` is input interpreted as column major. Docs define `m` and `k` by saying `op(A)` has dims `m x k` **(`m` and `k` are _post_-`op` sizes)**. `A` was `(b, a)`, `op(A)` is `(a, b)`, so the correct thing is to supply `m=a`, `k=b` to the underlying gemm. **For the `<float>/<double>` gemv, we passed `m=b`, not `m=a`, to the raw `cublasS/Dgemv`.**~~
~~The exterior `blas::gemv` must have been called with `trans='t'`, `m=b`, `n=a` (as required by the `<float>/<double>` versions). So when gemv is about to call gemm, **we [swap](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37569/files#diff-686aa86335f96b4ecb9b37f562feed12R330) the local values of `m` and `n` so that `m=a`, `n=b`,** then put `m (=a)` in the gemm's `m` spot, 1 in the gemm's `n` spot, and `n (=b)` in the gemm's `k` spot. All is well (we made the right gemm call after ingesting the same arg values as `blas::gemv<float>/<double>`).~~
### ~~2. input is column-major (doesn't need cublas transpose)~~
#### ~~2a. input is float or double~~
~~input is `(a,b)`, already column-major with strides `(1,a)`. Code calling `blas::gemv` supplies `trans='n'` (which becomes `CUBLAS_OP_N`, no internal transpose), `m=a`, `n=b`.~~
#### ~~2b. input is half or bfloat16~~
~~`blas::gemv` should pass `transa='n'`, `m=a`, `n=1`, `k=b` to the underlying gemm. The exterior `blas::gemv` must have been called with `trans='t'`, `m=a`, `n=b` (as required by the `<float>/<double>` versions). So **in this case we _don't_ swap `blas::gemv`'s local values of `m` and `n`.** We directly put `m (=a)` in the gemm's `m` spot, 1 in the gemm's `n` spot, and `n (=b)` in the gemm's `k` spot. All is well (we made the right gemm call after ingesting the same arg values as `blas::gemv<float>/<double>`).~~
~~** `trans` is a string `t` or `n` in the `at::cuda::blas::gemv` API, which gets [converted](091a1192d7/aten/src/ATen/cuda/CUDABlas.cpp (L314)) to a corresponding cublas enum value `CUBLAS_OP_T` (do transpose internally) or `CUBLAS_OP_N` (don't transpose internally) just before the raw cublas call.~~
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37569
Differential Revision: D21405955
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: e831414bbf54860fb7a4dd8d5666ef8081acd3ee
Summary:
Closes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/24558
Benchmark with same build settings on same system.
gcc : version 7.5.0 (Ubuntu 7.5.0-3ubuntu1~18.04)
CUDA : 10.1
GPU : 1050ti
```python
import timeit
for n, t in [(10_000, 20000),
(100_000, 20000)]:
for dtype in ('torch.half', 'torch.float', 'torch.double'):
print(f'torch.erf(a) a.numel() == {n} for {t} times {dtype}')
print(timeit.timeit(f'torch.erf(a); torch.cuda.synchronize()',
setup=f'import torch; a=torch.arange({n}, dtype={dtype}, device="cuda")',
number=t))
```
Before:
```
torch.erf(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.29057903600187274
torch.erf(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.2836507789979805
torch.erf(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.double
0.44974555500084534
torch.erf(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.31807255600142526
torch.erf(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.3216503109979385
torch.erf(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.double
2.0413486910001666
```
After:
```
torch.erf(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.2867302739996376
torch.erf(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.28851128199858067
torch.erf(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.double
0.4592030350013374
torch.erf(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.28704102400115517
torch.erf(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.29036039400125446
torch.erf(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.double
2.04035638699861
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36724
Differential Revision: D21164626
Pulled By: VitalyFedyunin
fbshipit-source-id: e6f3390b2bbb6e8d21e18ffe15f5d49a170fae83
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37537
The documentation states that `random_()` samples "from the discrete uniform distribution". Floating-point types can support _discrete_ _uniform_ distribution only within range [-(2^digits), 2^digits], where `digits = std::numeric_limits<fp_type>::digits`, or
- [-(2^53), 2^53] for double
- [-(2^24), 2^24] for double
- [-(2^11), 2^11] for half
- [-(2^8), 2^8] for bfloat16
The worst scenario is when the floating-point type can not represent numbers between `from` and `to`. E.g.
```
torch.empty(10, dtype=torch.float).random_(16777217, 16777218)
tensor([16777216., 16777216., 16777216., 16777216., 16777216., 16777216.,
16777216., 16777216., 16777216., 16777216.])
```
Because 16777217 can not be represented in float
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D21380387
Pulled By: pbelevich
fbshipit-source-id: 80d77a5b592fff9ab35155a63045b71dcc8db2fd
Summary:
This pull request fixes and re-enables two of the tests disabled in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/37427
1. `test_sparse_add_out_bfloat16` in test_sparse.py fixed to use updated `atol` argument instead of `prec` for `assertEqual`
2. The conversion of `flt_min` to `int64` is divergent on HIP compared to numpy. The change removes that conversion from the `test_float_to_int_conversion_finite` test case in test_torch.py
cc: ezyang jeffdaily
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37616
Differential Revision: D21379876
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 2bfb41d67874383a01330c5d540ee516b3b07dcc
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37507
Replace `TORCH_WARN` with `TORCH_CHECK` if `Tensor.random_()`'s `from` or `to-1` is out of bounds for tensor's dtype. Previously warning said "This warning will become an error in version 1.6 release, please fix the code in advance", so the time has come.
Related to #33106
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D21349413
Pulled By: pbelevich
fbshipit-source-id: ac7c196a48fc58634611e427e65429a948119e40
Summary:
Following up on this: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/35851 cross dtype storage copy is not being used internally, so I have not included cross dtype copy for complex.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/35771
Differential Revision: D21319650
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: 07c72996ee598eba0cf401ad61534494d6f5b5b3
Summary:
Closes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/24641
Benchmark with same build settings on same system.
gcc : version 7.5.0 (Ubuntu 7.5.0-3ubuntu1~18.04)
CUDA : 10.1
GPU : 1050ti
```python
import timeit
for n, t in [(10_000, 20000),
(100_000, 20000)]:
for dtype in ('torch.half', 'torch.float', 'torch.double'):
print(f'torch.tan(a) a.numel() == {n} for {t} times {dtype}')
print(timeit.timeit(f'torch.tan(a); torch.cuda.synchronize()',
setup=f'import torch; a=torch.arange({n}, dtype={dtype}, device="cuda")',
number=t))
```
Before:
```
torch.tan(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.28325206200003095
torch.tan(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.28363607099998944
torch.tan(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.double
0.43924326799998425
torch.tan(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.3754699589999859
torch.tan(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.38143782899999223
torch.tan(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.double
1.7672172019999834
```
After:
```
torch.tan(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.28982524599996395
torch.tan(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.29121579000002384
torch.tan(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.double
0.4599610559998837
torch.tan(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.3557764019997194
torch.tan(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.34793807599999127
torch.tan(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.double
1.7564662459999454
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36906
Differential Revision: D21335320
Pulled By: VitalyFedyunin
fbshipit-source-id: efab9c175c60fb09223105380d48b93a81994fb0
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/27957
Benchmark (gcc 8.3, Debian Buster, turbo off, Release build, Intel(R) Xeon(R) E-2136):
```python
import timeit
for dtype in ('torch.double', 'torch.float', 'torch.uint8', 'torch.int8', 'torch.int16', 'torch.int32', 'torch.int64'):
for n, t in [(40_000, 50000),
(400_000, 5000)]:
print(f'torch.linspace(0, 10, {n}, dtype={dtype}) for {t} times')
print(timeit.timeit(f'torch.linspace(0, 10, {n}, dtype={dtype})', setup=f'import torch', number=t))
```
Before:
```
torch.linspace(0, 10, 40000, dtype=torch.double) for 50000 times
1.3964195849839598
torch.linspace(0, 10, 400000, dtype=torch.double) for 5000 times
1.2374563289922662
torch.linspace(0, 10, 40000, dtype=torch.float) for 50000 times
1.8631796519621275
torch.linspace(0, 10, 400000, dtype=torch.float) for 5000 times
1.6991038109990768
torch.linspace(0, 10, 40000, dtype=torch.uint8) for 50000 times
1.8358083459897898
torch.linspace(0, 10, 400000, dtype=torch.uint8) for 5000 times
1.7214750979910605
torch.linspace(0, 10, 40000, dtype=torch.int8) for 50000 times
1.8356257299892604
torch.linspace(0, 10, 400000, dtype=torch.int8) for 5000 times
1.706238206999842
torch.linspace(0, 10, 40000, dtype=torch.int16) for 50000 times
1.7463878280250356
torch.linspace(0, 10, 400000, dtype=torch.int16) for 5000 times
1.6172360889613628
torch.linspace(0, 10, 40000, dtype=torch.int32) for 50000 times
1.8656846070080064
torch.linspace(0, 10, 400000, dtype=torch.int32) for 5000 times
1.714238062966615
torch.linspace(0, 10, 40000, dtype=torch.int64) for 50000 times
1.8272205490502529
torch.linspace(0, 10, 400000, dtype=torch.int64) for 5000 times
1.6409171230043285
```
After:
```
torch.linspace(0, 10, 40000, dtype=torch.double) for 50000 times
1.0077099470072426
torch.linspace(0, 10, 400000, dtype=torch.double) for 5000 times
0.8227124120458029
torch.linspace(0, 10, 40000, dtype=torch.float) for 50000 times
1.0058343949494883
torch.linspace(0, 10, 400000, dtype=torch.float) for 5000 times
0.8376779520185664
torch.linspace(0, 10, 40000, dtype=torch.uint8) for 50000 times
1.903041019977536
torch.linspace(0, 10, 400000, dtype=torch.uint8) for 5000 times
1.7576498500420712
torch.linspace(0, 10, 40000, dtype=torch.int8) for 50000 times
1.7628699769848026
torch.linspace(0, 10, 400000, dtype=torch.int8) for 5000 times
1.6204477970022708
torch.linspace(0, 10, 40000, dtype=torch.int16) for 50000 times
2.0970272019621916
torch.linspace(0, 10, 400000, dtype=torch.int16) for 5000 times
1.9493417189805768
torch.linspace(0, 10, 40000, dtype=torch.int32) for 50000 times
2.29020385700278
torch.linspace(0, 10, 400000, dtype=torch.int32) for 5000 times
2.1212510910118
torch.linspace(0, 10, 40000, dtype=torch.int64) for 50000 times
2.3479344319785014
torch.linspace(0, 10, 400000, dtype=torch.int64) for 5000 times
2.156775983981788
```
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D20773454
Pulled By: VitalyFedyunin
fbshipit-source-id: ebeef59a90edde581669cc2afcc3d65929c8ac79
Summary:
Benchmark with same build settings on same system.
Closes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/24545
gcc : version 7.5.0 (Ubuntu 7.5.0-3ubuntu1~18.04)
CUDA : 10.1
GPU : 1050ti
```python
import timeit
for n, t in [(10_000, 20000),
(100_000, 20000)]:
for dtype in ('torch.half', 'torch.float', 'torch.double'):
print(f'torch.cos(a) a.numel() == {n} for {t} times {dtype}')
print(timeit.timeit(f'torch.cos(a); torch.cuda.synchronize()',
setup=f'import torch; a=torch.arange({n}, dtype={dtype}, device="cuda")',
number=t))
```
Before:
```
torch.cos(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.2797315450006863
torch.cos(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.283109110998339
torch.cos(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.double
0.3648525129974587
torch.cos(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.34239949499897193
torch.cos(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.33680364199972246
torch.cos(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.double
1.0512770260102116
```
After:
```
torch.cos(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.285825898999974
torch.cos(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.2781305120001889
torch.cos(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.double
0.34188826099989456
torch.cos(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.29040409300023384
torch.cos(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.28678944200009937
torch.cos(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.double
1.065477349000048
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36653
Differential Revision: D21164675
Pulled By: VitalyFedyunin
fbshipit-source-id: 5dd5d3af47c2a5527e1f4ab7669c2ed9a2293cee
Summary:
Adds support for generating Vandermonde matrices based off of the Numpy implementation found [here](https://github.com/numpy/numpy/blob/v1.17.0/numpy/lib/twodim_base.py#L475-L563).
Adds test to ensure generated matrix matches expected Numpy implementation. Note test are only limited to torch.long and torch.double due to differences in now PyTorch and Numpy deal with type promotion.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36725
Differential Revision: D21075138
Pulled By: jessebrizzi
fbshipit-source-id: 6bb1559e8247945714469b0e2b07c6f4d5fd1fd0
Summary:
Added enough operators to make sure that all unit tests from ATen/basic are passing, except for MM and IntArrayRefExpansion
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37121
Test Plan: `./bin/basic --gtest_filter=--gtest_filter=BasicTest.BasicTestHalfCPU` + `python -c "import torch; x = torch.tensor([2], dtype=torch.half); print(torch.isfinite(x+x))"`
Differential Revision: D21296863
Pulled By: malfet
fbshipit-source-id: e03d7a6939df11f611a9b317543bac52403cd009
Summary:
This pull request disables the unit tests that were observed to be failing once `test2` was enabled. These tests will be one by one looked at and fixed at the earliest, but until then disabling them to unblock `test2`
The pull request also disables fftPlanDestroy for rocFFT to avoid double-freeing FFT handles
cc: ezyang jeffdaily
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37427
Differential Revision: D21302909
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: ecadda3778e65b7f4f97e24b932b96b9ce928616
Summary:
dylanbespalko anjali411
Not sure if the test should be added to `test_torch` or `test_complex`.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36749
Differential Revision: D21290529
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: 07bc282e4c9480cd015ec5db104e79728437cd90
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/37084
There are 3 alternatives for this design.
This PR and the first one.
When a tensor is a scalar `ndim==0`, accessing view_offsets_[0] when doing reductions, yields an invalid offset for the index which is the output of `argmax` and `argmin`.
fba9b9a023/aten/src/ATen/native/cpu/Reduce.h (L217)
This also happens in cuda code:
fba9b9a023/aten/src/ATen/native/cuda/Reduce.cuh (L797)
The second alternative is to check the size of `view_offsets` before accessing it. But this introduces some burden.
The third alternative is related to the way that inputs are treated in `argmax` and `argmin`
depending on the `dim` argument value.
fba9b9a023/aten/src/ATen/native/ReduceOps.cpp (L775-L780)
If `dim` is not specified, then the scalar gets reshaped into a 1-dim tensor and everything works properly, since now `view_offsets` has an actual entry.
If dim is specified, then the input remains as a scalar causing the issue we see here.
This PR tries to solve it in a generic way for every case so I went with option 1. I am willing to discuss it and change if you think that the other alternatives are better.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37214
Differential Revision: D21258320
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 46223412187bbba4bfa7337e3f1d2518db72dea2
Summary:
Today in PyTorch, warnings triggered in C++ are printed to Python users like this:
`../aten/src/ATen/native/BinaryOps.cpp:81: UserWarning: Integer division of tensors using div or / is deprecated, and in a future release div will perform true division as in Python 3. Use true_divide or floor_divide (// in Python) instead.`
This may be unhelpful to Python users, who have complained it's difficult to relate these messages back to their programs. After this PR, warnings that go through the PyWarningHandler and allow it to add context print like this:
```
test/test_torch.py:16463: UserWarning: Integer division of tensors using div or / is deprecated, and in a future release div will perform true division as in Python 3. Use true_divide or floor_divide (// in Python) instead. (Triggered internally at ../aten/src/ATen/native/BinaryOps.cpp:81.)
cpu_result = getattr(cpu_tensor, op_str)(*cpu_args)
```
This relates the warning back to the user's program. The information about the cpp file and line number is preserved in the body of the warning message.
Some warnings, like those generated in the JIT, already account for a user's Python context, and so they specify that they should be printed verbatim and are unaffected by this change. Warnings originating in Python and warnings that go through c10's warning handler, which prints to cerr, are also unaffected.
A test is added to test_torch.py for this behavior. The test relies on uint8 indexing being deprecated and its warning originating from its current header file, which is an unfortunate dependency. We could implement a `torch.warn` function, instead.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36052
Differential Revision: D20887740
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: d3515c6658a387acb7fccaf83f23dbb452f02847
Summary:
Resolves https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/36730https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/36057
Partially resolves: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/36671
```
>>> 2j / torch.tensor([4], dtype = torch.complex64)
tensor([(0.0000+0.5000j)], dtype=torch.complex64)
>>> 1 / torch.tensor(3+4j)
tensor((0.1200-0.1600j), dtype=torch.complex64)
```
rdiv is more generally broken for all dtypes because it doesn't promote the types properly
eg.
```
>>> 1 / torch.tensor(2)
tensor(0)
>>> 2j / torch.tensor(4)
tensor(0)
```
so that issue should be fixed in a separate PR
Adding CPU acc types for complex
Added cumsum, cumprod for complex dtypes
Added complex dtypes to get_all_math_dtypes to expand testing for complex dtypes
Old PR - https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36747
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37193
Differential Revision: D21229373
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: 8a086136d8c10dabe62358d276331e3f22bb2342
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37128
In certain build modes (in fbcode, building a .par) the mechanism to get test output "expect" files doesn't work.
All other tests in test_torch.py already had assertExpectedInline instead of assertExpected, with the expected result inline in the file.
There was no equivalent for assertExpectedRaises, so I added one, and changed the tests for test_is_nonzero (the only test using this)
Test Plan: CI, specifically the test test_is_nonzero should pass
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D21197651
fbshipit-source-id: 2a07079efdcf1f0b0abe60e92cadcf55d81d4b13
Summary:
Closes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/24642
Benchmark with same build settings on same system.
gcc : version 7.5.0 (Ubuntu 7.5.0-3ubuntu1~18.04)
CUDA : 10.1
GPU : 1050ti
```python
import timeit
for n, t in [(10_000, 20000),
(100_000, 20000)]:
for dtype in ('torch.half', 'torch.float', 'torch.double'):
print(f'torch.tanh(a) a.numel() == {n} for {t} times {dtype}')
print(timeit.timeit(f'torch.tanh(a); torch.cuda.synchronize()',
setup=f'import torch; a=torch.arange({n}, dtype={dtype}, device="cuda")',
number=t))
```
Before:
```
torch.tanh(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.2816318240002147
torch.tanh(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.2728829070001666
torch.tanh(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.double
0.39797203200214426
torch.tanh(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.3228214350019698
torch.tanh(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.31780802399953245
torch.tanh(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.double
1.3745740449994628
```
After:
```
torch.tanh(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.27825374500025646
torch.tanh(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.27764024499992956
torch.tanh(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.double
0.3771585260001302
torch.tanh(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.2995866400015075
torch.tanh(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.28355561699936516
torch.tanh(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.double
1.393811182002537
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36995
Differential Revision: D21163353
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: e2216ff62cdfdd13b6a56daa63d4ef1440d991d4
Summary:
Fixes a safety issue (Nonsense values and segfaults) introduced by https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36875 when in-place gather tries to use incorrect shapes.
Consider the following block of code:
```
k0 = 8
k1 = 8
m = 100
x = torch.rand((k0, k1))
ind = torch.randint(0, k0, (m, k1))
output = torch.empty((m, k1))
print(torch.gather(x, 0, ind, out=output))
print(torch.gather(x, 1, ind, out=output))
```
The first gather is legal, the second is not. (`ind` and `output` need to be transposed) Previously this was caught when the kernel tried to restride inputs for TensorIterator, but we can no longer rely on those checks and must test explicitly. If `m` is small the second gather returns gibberish; if it is large enough to push the read out of memory block the program segfaults.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/37102
Differential Revision: D21190580
Pulled By: robieta
fbshipit-source-id: 80175620d24ad3380d78995f7ec7dbf2627d2998
Summary:
Fixes: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/24605https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/24535https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/24739https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/24680https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/30986
This does not fix https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/29984, it will be fixed in later PR.
Most of this PR is just following the same logic inside TH and THC except the handle of n-dimensional zero-sized tensor, in specific the case:
```
(m,).addmv((m, 0), (0,), beta, alpha)
```
# Legacy code bugs and how this PR deal with it
The above case is a case where BLAS often have a mismatch of semantics with PyTorch: For BLAS and cuBLAS, the above is a noop, but for PyTorch, it is a scalar-vector multiplication `output = beta * input`. The handle of this case is already very poor in legacy code and it is poorly tested:
For the CPU implementation, there are two code paths:
- Path 1: when dtype is float or double and `USE_BLAS`, then use BLAS
- Path 2: when other dtypes or not `USE_BLAS`, use a fallback kernel in PyTorch
For the CUDA implementation, there are also two code paths:
- Path 1: when float or double, then use `cublasSgemv` or `cublasDgemv` in cuBlas
- Path 2: when half, dispatch to `addmm`
`test_blas_alpha_beta_empty` is supposed to cover all cases, but unfortunately, it only tests the Path 1 of CUDA and Path 1 of CPU, and both uncovered paths (path 2 for CPU and path 2 for CUDA) are buggy in legacy code. In this PR, I expanded the coverage of `test_blas_alpha_beta_empty`, but unfortunately, I have to skip the `half` dtype on CUDA 9. See the description below for detail:
## Bug on CPU implementation
For the CPU implementation, the fallback kernel in path 2 already has the same semantics as PyTorch, not BLAS. But the code that tries to correct BLAS semantics to match PyTorch also runs on this case, leading to double correction, that is, `output = beta * input` now becomes `output = beta * beta * input`.
This leads to the issue https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/30986 I just opened, and it is fixed in this PR.
## Bug on CUDA implementation
For the CUDA implementation, path 2 dispatches to
```
(m, 1).addmm((m, 0), (0, 1), beta, alpha)
```
But unfortunately, for some old CUDA version when on old GPU on half dtype, the above is also noop, which is definitely not correct.
But from what I see, on newer CUDA version or newer GPU, this is not a problem. This is a bug of PyTorch in `addmm`, so I opened a new issue https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/31006 to track this problem. But this is highly likely a dependency bug for PyTorch originating from cuBLAS, and it is only on a rarely used edge case on old hardware and software, so this issue would be a `won't_fix` unless some real requirements strongly indicate that this should be fixed.
This issue is already with legacy code, and this PR does not make it worse. To prevent this issue from bothering us, I disable the test of `half` dtype for CUDA 9 when expanding the coverage of `test_blas_alpha_beta_empty`.
I promote a CircleCI CUDA 10.1 test to `XImportant` so that it runs on PRs, because the path 2 of CUDA implementation is only covered by this configuration. Let me know if I should revert this change.
## An additional problem
In legacy code for `addmv`, dtype `bfloat16` is enabled and dispatch to `addmm`, but `addmm` does not support `bfloat16` from what I test. I do the same thing in the new code. Let me know if I should do it differently.
# Benchmark
Code:
```python
import torch
print(torch.__version__)
for i in range(1000):
torch.arange(i, device='cuda')
print('cpu')
for i in 10, 100, 1000, 10000:
a = torch.randn((i,))
b = torch.randn((i, i))
c = torch.randn((i,))
%timeit a.addmv(b, c, alpha=1, beta=2)
print('cuda')
for i in 10, 100, 1000, 10000:
a = torch.randn((i,)).cuda()
b = torch.randn((i, i)).cuda()
c = torch.randn((i,)).cuda()
torch.cuda.synchronize()
%timeit a.addmv(b, c, alpha=1, beta=2); torch.cuda.synchronize()
```
Before:
```
1.5.0a0+2b45368
cpu
2.74 µs ± 30.8 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
8.5 µs ± 85.5 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
686 µs ± 2.95 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
74 ms ± 410 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)
cuda
The slowest run took 4.81 times longer than the fastest. This could mean that an intermediate result is being cached.
27.6 µs ± 23 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)
17.3 µs ± 151 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
20.5 µs ± 369 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
756 µs ± 6.81 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
```
After:
```
1.5.0a0+66b4034
cpu
3.29 µs ± 20 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
9.09 µs ± 7.41 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
687 µs ± 7.01 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
73.8 ms ± 453 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)
cuda
18.2 µs ± 478 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
17.7 µs ± 299 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
21.5 µs ± 2.38 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
751 µs ± 35.3 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/30898
Differential Revision: D20660338
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: db1f521f124198f63545064026f93fcb16b68f18
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36680
If torch compiled without MKL, this test fails with torch.fft requiring MKL support
Test Plan: CI
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D21051362
fbshipit-source-id: dd2e2c7d323622c1c25fc4c817b85d83d2241b3a
Summary:
Closes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/24546
Benchmark with same build settings on same system.
gcc : version 7.5.0 (Ubuntu 7.5.0-3ubuntu1~18.04)
CUDA : 10.1
GPU : 1050ti
```python
import timeit
for n, t in [(10_000, 20000),
(100_000, 20000)]:
for dtype in ('torch.half', 'torch.float', 'torch.double'):
print(f'torch.cosh(a) a.numel() == {n} for {t} times {dtype}')
print(timeit.timeit(f'torch.cosh(a); torch.cuda.synchronize()',
setup=f'import torch; a=torch.arange({n}, dtype={dtype}, device="cuda")',
number=t))
```
Before:
```
torch.cosh(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.2813017509997735
torch.cosh(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.28355878599904827
torch.cosh(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.double
0.27810572300040803
torch.cosh(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.3239932899996347
torch.cosh(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.321233343998756
torch.cosh(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.double
0.5546665399997437
```
After:
```
torch.cosh(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.2905335750001541
torch.cosh(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.27596429500044906
torch.cosh(a) a.numel() == 10000 for 20000 times torch.double
0.30358699899989006
torch.cosh(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.half
0.30139567500009434
torch.cosh(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.float
0.30246640400036995
torch.cosh(a) a.numel() == 100000 for 20000 times torch.double
0.5403946970000106
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36654
Differential Revision: D21164606
Pulled By: VitalyFedyunin
fbshipit-source-id: 55e88f94044957f81599ae3c12cda38a3e2c985c
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/35615
Python 2 has reached end-of-life and is no longer supported by PyTorch.
Now we can clean up a lot of cruft that we put in place to support it.
These changes were all done manually, and I skipped anything that seemed
like it would take more than a few seconds, so I think it makes sense to
review it manually as well (though using side-by-side view and ignoring
whitespace change might be helpful).
Test Plan: CI
Differential Revision: D20842886
Pulled By: dreiss
fbshipit-source-id: 8cad4e87c45895e7ce3938a88e61157a79504aed
Summary:
Resolves https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/36730https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/36057
Partially resolves: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/36671
```
>>> 2j / torch.tensor([4], dtype = torch.complex64)
tensor([(0.0000+0.5000j)], dtype=torch.complex64)
>>> 1 / torch.tensor(3+4j)
tensor((0.1200-0.1600j), dtype=torch.complex64)
```
rdiv is more generally broken for all dtypes because it doesn't promote the types properly
eg.
```
>>> 1 / torch.tensor(2)
tensor(0)
>>> 2j / torch.tensor(4)
tensor(0)
```
so that issue should be fixed in a separate PR
Adding CPU acc types for complex
Added cumsum, cumprod for complex dtypes
Added complex dtypes to get_all_math_dtypes to expand testing for complex dtypes
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36747
Differential Revision: D21138687
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: ad3602ccf86c70294a6e71e564cb0d46c393dfab
Summary:
Previously torch.isclose would RuntimeError when called on complex tensors. This update updates torch.isclose to run on complex tensors and be consistent with [NumPy](https://numpy.org/doc/1.18/reference/generated/numpy.isclose.html). However, NumPy's handling of NaN, -inf, and inf values is odd, so I adopted Python's [cmath.isclose](https://docs.python.org/3/library/cmath.html) behavior when dealing with them. See https://github.com/numpy/numpy/issues/15959 for more on NumPy's behavior.
While implementing complex isclose I also simplified the isclose algorithm to:
- A is close to B if A and B are equal, if equal_nan is true then NaN is equal to NaN
- If A and B are finite, then A is close to B if `abs(a - b) <= (atol + abs(rtol * b))`
This PR also documents torch.isclose, since it was undocumented, and adds multiple tests for its behavior to test_torch.py since it had no dedicated tests.
The PR leaves equal_nan=True with complex inputs an error for now, pending the outcome of https://github.com/numpy/numpy/issues/15959.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36456
Differential Revision: D21159853
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: fb18fa7048e6104cc24f5ce308fdfb0ba5e4bb30
Summary:
Addresses https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/36807. Also updates the cast testing to catch issues like this better.
In the future a more constexpr based approach to casting would be nice.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36832
Differential Revision: D21120822
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 9504ddd36cfe6d9f9f545fc277fef36855c1b221
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/34258
This PR allows both atol and rtol to be specified, uses defaults based on the prior analysis (spreadsheet attached to https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/32538), but retains the absolute tolerance behavior in cases where precision was previously specified explicitly.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D21110255
Pulled By: nairbv
fbshipit-source-id: 57b3a004c7d5ac1be80ee765f03668b1b13f4a7e
Summary:
Implements complex isfinite and isinf, consistent with NumPy.
A complex value is finite if and only if both its real and imaginary part are finite.
A complex value is infinite if and only if its real or imaginary part are infinite.
Old isfinite, isinf, and isnan tests are modernized and instead of fixtures the torch results are compared with NumPy. A new test is added for complex isfinite, isinf, and isnan. The docs for each function are updated to clarify what finite, infinite, and NaN values are.
The new tests rely on a new helper, _np_compare, that we'll likely want to generalize in the near future and use in more tests.
Addresses part of the complex support tasks. See https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/33152.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36648
Differential Revision: D21054766
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: d947707c5437385775c82f4e6c722349ca5a2174
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36351
Adds CUDA kernels for hardsigmoid, to enable its use in training.
Note: the update to the cpu backward pass is to keep the cpu vs cuda
logic consistent, no change in functionality.
Test Plan:
add CI for the forward pass
run this for the backward pass:
https://gist.github.com/vkuzo/95957d365600f9ad10d25bd20f58cc1a
Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D20955589
fbshipit-source-id: dc198aa6a58e1a7996e1831f1e479c398ffcbc90
Summary:
Per title. test_abs used to be marked as slow_test and run on cpu only. Conceptually similar tests are done in TestTorchMathOps, so it's a matter of adding `abs` test there. 2 remaining checks (correct abs for large-valued long tensors, and correct abs for signed zeros) are factored into separate tests.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36465
Differential Revision: D21000248
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 8bc8b0da936b1c10fe016ff2f0dbb5ea428e7e61
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36411
This PR remove pytorch specific defined assertwarns and use the unit
test one, also format some tests
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D20998159
Pulled By: wanchaol
fbshipit-source-id: 1280ecff2dd293b95a639d13cc7417fc819c2201
Summary:
This partially addresses https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/33568 by disabling clamp for complex inputs until an appropriate solution can be implemented. test_complex_unsupported in test_torch.py is extended to validate this behavior.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36373
Differential Revision: D20984435
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 49fd2e1e3a309f6a948585023953bae7ce3734c8
Summary:
Partially addresses https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/36374 by disabling min and max for complex inputs. test_complex_unsupported in test_torch.py is extended to validate this behavior.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36377
Differential Revision: D20964661
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 79606c2e88c17c702543f4af75847d2460586c2d
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/36350
Adds CUDA kernels for hardswish in order to unblock use in training.
Test Plan:
added test coverage for forward pass
ran this script for various input sizes to test backward pass against a manual Hardswish module: https://gist.github.com/vkuzo/30e196b059427725817f2ee934ed0384
Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D20955590
fbshipit-source-id: 635706fbf18af9a4205f2309f3314f2996df904d
Summary:
Notes:
1. didn't name them as _copy_real and _copy_imag because it's desirable (but not necessary) to have these methods as tensor methods.
2. replaced old .real() and .imag() instances with _copy_real() and _copy_imag() methods
3. didn't add documentation because we plan to remove these methods when we add real and imag as tensor attributes.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/35879
Differential Revision: D20841760
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: 7267e6fbaab9a5ce426e9396f12238994666b0dd
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/35339
CPU version converts integers to their unsigned version first. The CUDA
version should also do it.
Also added tests for this.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D20826862
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 164c84cfd931d8c57177a038c1bb8b6f73134d07
Summary:
ROCm 2.10 has a hdot implementation. Use it and enable test.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/30431
Differential Revision: D20776784
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: a192a701eb418dac2015e300563ade691c24903e
Summary:
In NumPy, calling np.imag on a real-valued tensors returns a non-writable tensor (view) of zeros. In PyTorch we don't support non-writeable tensors (or views), so we can either return a writable tensor or error.
If we do the former, that may confuse people who try to write to the imaginary part of a real-valued tensor, and may cause a BC issue if we do support non-writable tensors. This PR errors to provide us flexibility implementation the solution we'd like in the future, while protecting users from unexpected behavior today.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/35728
Differential Revision: D20760687
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: f60d445746cc75ba558804c853993d9e4621dad3
Summary:
NumPy doesn't allow complex inputs to floor, ceil, or trunc, and without careful deliberation I don't think PyTorch should, either: is it intuitive that these functions apply to both the real and imaginary parts of complex tensors, or only to the real parts?
This PR disables these functions for complex inputs so we don't prematurely commit a particular behavior.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/35592
Differential Revision: D20757796
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: fdc53ac161fca7ad94c9280c3f5cf9c7c40c7f2c
Summary:
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/34891 caused a 15 minute regression in XLA test timing when it inadvertently added this test to XLA -- I think it was intended to only add this test to CUDA.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/35709
Test Plan: The XLA test job should return from ~75 to ~60 minutes.
Reviewed By: malfet
Differential Revision: D20748176
Pulled By: yns88
fbshipit-source-id: b50227a35bcbf2915b4f2013e2a4705e905d0118
Summary:
The current implementations of torch.real and torch.imag are not NumPy compatible. In particular:
- torch.real on a real tensor does not return the real tensor, like contiguous
- torch.real on a complex tensor does not return a real-valued view of the real part
- torch.imag on a complex tensor does not return a real-valued view of the imaginary part
- torch.Tensor.real and torch.Tensor.imag exist as methods, but in NumPy they are writable attributes
This PR makes the functions NumPy compatible by removing the method variants and out kwarg, restricting them to work on only real tensors, and updating the behavior of torch.real to return its input. New tests are added to test_torch.py to verify the behavior, a couple existing complex tests are skipped, and the documentation is updated to reflect the change.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/35560
Differential Revision: D20714568
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 5dd092f45757b620c8426c829dd15ee997246a26
Summary:
The Torch algorithms for linspace and logspace conceptually compute each of their values using:
`start_value + step_value * idx`
[And NumPy does the same,](cef4dc9d91/numpy/core/function_base.py (L24)) except NumPy then [sets the last value in its array directly.](cef4dc9d91/numpy/core/function_base.py (L162)) This is because the above computation is unstable when using floats, and NumPy's contract, like PyTorch's, is that the last element in the array is the stop value.
In PyTorch there can be a divergence between the computed last value and the actual value. One user reported case was:
`torch.linspace(-0.031608279794, 0.031531572342, 257, dtype=torch.float32)`
Which causes a difference of 3.7253e-09 between the last value as set by NumPy and computed by PyTorch. After this PR the difference is zero.
Instead of simply setting the last element of the tensor, this PR updates the kernels with a "symmetric" algorithm that sets the first and last array elements without requiring an additional kernel launch on CUDA. The performance impact of this change seems small. I tested with a step sizes of 2^8 and 2^22, and all timing differences were imperceptible except for 2^22 on CPU, which appears to have suffered ~5% slowdown. I think that's an acceptable performance hit for the improved precision when we consider the context of linspace.
An alternative would be to simply set the last element, as NumPy does, on CPU. But I think it's preferable to keep the CPU and CUDA algorithms aligned and keep the algorithm symmetric. In current PyTorch, for example, torch.linspace starts generating values very similar to NumPy, but as the index increases so do the errors, giving our current implementation a "left bias."
Two tests are added to test_torch.py for this behavior. The linspace test will fail on current PyTorch, but the logspace test will succeed since its more complex computation needs wider error bars.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/35461
Differential Revision: D20712539
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 2c1257c8706f4cdf080ff0331bbf2f7041ab9adf
Summary:
Issue https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/24596
This PR moves `mm` cuda to ATen. The internal `addmmImpl` that was used as the base of the old TH version of `mm` cuda is also ported.
This PR also sets up `addmm` cuda to be fairly easily ported to ATen in a future PR, since TH `mm` and `addmm` used the same `addmmImpl` function at their core.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/34891
Differential Revision: D20650713
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 692aba1bbae65a18d23855b5e101446082d64c66
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/35167
The purpose of this PR is to move `normal`/`normal_`/`normal_out` to `native/DistributionTemplates.h`, `native/cpu/DistributionTemplates.h` and `native/cuda/DistributionTemplates.h` to make it reusable for custom RNG, see cpu_rng_test.cpp as an example of custom RNG.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D20588248
Pulled By: pbelevich
fbshipit-source-id: 7ee60be97f81522cd68894ff1389007c05130a60
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/34191
`at::native::radixSelect` basically uses integer comparison which creates a defined ordering of non-finite float values. This isn't compatible with IEEE float comparison, so mixing the two leads to unwritten values in the output.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/35253
Differential Revision: D20645554
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 651bcb1742ed67086ec89cc318d862caae65b981
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/34747
Adds the hardswish FP operator from MobileNetV3 to PyTorch. This is for
common operator coverage, since this is widely used. A future PR will
add the quantized version. CUDA is saved for a future PR as well.
Test Plan:
tests pass:
```
python test/test_torch.py TestTorchDeviceTypeCPU.test_hardswish_cpu_float32
```
microbenchmark:
https://gist.github.com/vkuzo/b10d3b238f24e58c585314e8b5385aca
(batch_size == 1: 11.5GiB/s, batch_size == 4: 11.9GiB/s)
Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D20451404
fbshipit-source-id: c7e13c9ab1a83e27a1ba18182947c82c896efae2
Summary:
Per title. See related https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/34570.
In PyTorch 1.7 the plan is for torch.div and Python's division operator to perform "true" division, like Python 3, JAX, and NumPy. To facilitate this change, this PR expands true_divide to be a method so it can cover all of torch.div's use cases.
New true_divide tests are added to test_torch.py, test_type_promotion.py, and test_sparse.py.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/34794
Differential Revision: D20545507
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 55286f819716c8823d1930441a69008560ac2bd5
Summary:
In C++, casting a floating point value to an integer dtype is undefined when the value is outside the dtype's dynamic range. For example, casting 300.5 to Int8 is undefined behavior because the maximum representable Int8 value is 127, and 300.5 > 127.
PyTorch, like NumPy, deliberately allows and makes these casts, however, and when we do this we trigger undefined behavior that causes our sanitizers to (correctly) complain. I propose skipping this sanitization on our cast function.
The history of this PR demonstrates the issue, showing a single CI failure in the ASAN build when a test is added that converts a large float value to an integral value. The current PR shows a green CI after the sanitization is skipped.
There are alternatives to skipping this sanitization:
- Clamping or otherwise converting floats to the dynamic range of integral types they're cast to
- Throwing a runtime error if a float value is outside the dynamic range of the integral type it's cast to (this would not be NumPy compatible)
- Declaring programs in error if they perform these casts (this is technically true)
- Preventing this happening in PyTorch proper so the ASAN build doesn't fail
None of these alternatives seems particularly appealing, and I think it's appropriate to skip the sanitization because our behavior is deliberate.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/35086
Differential Revision: D20591163
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: fa7a90609c73c4c627bd39726a7dcbaeeffa1d1b
Summary:
Per title.
In the future we want to make div(), the division operator, and addcdiv perform true division as in Python 3, NumPy, and JAX. To do this without silently breaking users we plan to:
- Warn (once) in 1.5 when a user performs integer division using div or addcdiv
- RuntimeError in 1.6 when a user attempts to perform integer division using div or addcdiv
- Always perform true division in 1.7 using div, /, and addcdiv
Users can use true_divide or floor_divide today to explicitly specify the type of division they like.
A test for this behavior is added to test_type_promotion. Unfortunately, because we are only warning once (to avoid a deluge) the test only uses maybeWarns Regex.
The XLA failure is real but will be solved by https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/34552. I'll be sure to land that PR first to avoid temporarily breaking the XLA build.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/34570
Differential Revision: D20529211
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 65af5a9641c5825175d029e8413c9e1730c661d0
Summary:
(Updated per review feedback)
`torch.floor_divide` is currently a function that can operate on two tensors or a tensor and a scalar (scalar x scalar floor division is handled natively by Python and the JIT has a builtin function for it). This PR updates it to:
- have an out variant: `floor_divide(x, y, out=z)`
- be a method on a tensor: `x.floor_divide(y)`
- have an in-place variant: `x.floor_divide_(y)`
- work with sparse tensors
Tests are added to test_sparse.py and test_torch.py for these new behaviors.
In addition, this PR:
- cleans up the existing sparse division and true_division code and improves their error message
- adds testing of sparse true_division to test_sparse.py
- extends existing floor_divide testing in test_torch to run on CUDA, too, not just the CPU
Unfortunately, making floor_divide a method requires breaking backwards compatibility, and floor_divide has been added to the BC whitelist since this is international. The BC issue is that the first parameter name to torch.floor_divide is changing from input to self. If you previously called torch.floor_divide with keyword arguments, e.g. torch.floor_divide(input=x, other=y), you will need to update to torch.floor_divide(self=x, other=y), or the more common torch.floor_divide(x, y).
The intent of this PR is to allow floor_divide to be substituted for division (torch.div, /) wherever division was previously used. In 1.6 we expect torch.div to perform true_division, and floor_divide is how users can continue to perform integer division with tensors.
There are two potential follow-up issues suggested by this PR:
- the test framework might benefit from additional tensor construction classes, like one to create dividends and divisors for multiple dtypes
- the test framework might benefit from a universal function test class. while methods have reasonable coverage as part of test_torch.py's TestTensorOp tests, function coverage is spotty. Universal functions are similar enough it should be possible to generate tests for them.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/34552
Differential Revision: D20509850
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 2cd3c828aad67191c77f2ed8470411e246f604f8
Summary:
Per title.
Currently torch.full will always (attempt to) produce a float tensor. This is inconsistent with NumPy in (at least) two cases:
- When integral fill values (including bool) are given
- When complex fill values are given
For example:
```
np.full((1, 2), 1).dtype
: dtype('int64')
np.full((1, 2), (1 + 1j)).dtype
: dtype('complex128')
```
Whereas in PyTorch
```
torch.full((1, 2), 1).dtype
: torch.float32
torch.full((1, 2), (1 + 1j)).dtype
: RuntimeError: value cannot be converted to type float without overflow: (1,1)
```
This PR begins the process of deprecating our current behavior of returning float tensors (by default) when given integer fill values by warning the user that integer fill values will require explicitly specifying the dtype or out kwargs in 1.6, and in 1.7 the behavior will change to return a LongTensor by default (BoolTensor for bool values). The intermediate 1.6 release is to prevent changing the behavior silently and unexpectedly.
The PR also implements inference for complex types. So that with it:
```
torch.full((1, 2), (1 + 1j)).dtype
: torch.complex64
```
The complex type inference returns a ComplexFloat tensor when given a complex fill value (and no dtype or out kwarg is specified), unless the default dtype is Double, in which case a ComplexDouble tensor is returned.
A test for these behaviors is added to test_torch.py.
Implementation note:
This PR required customizing full's dispatch because currently in eager codegen the TensorOptions object passed to functions improperly sets has_dtype() to true, even if the user did not explicitly provide a dtype. torch.arange already worked around this issue with its own custom implementation. The JIT, however, does pass a properly constructed TensorOptions object.
Future Work:
This PR does not extend torch.full's complex type inference to ONNX. This seems unlikely to come up and will be a clear error if it does. When integer type inference is added to torch.full, however, then porting the behavior to ONNX may be warranted. torch.arange ported its complex type promotion logic to ONNX, for example.
Additionally, this PR mostly leaves existing call sites in PyTorch that would trigger this warning intact. This is to be more minimal (since the PR is BC breaking). I will submit a separate PR fixing PyTorch's call sites.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/34709
Differential Revision: D20509387
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 129593ba06a1662032bbbf8056975eaa59baf933
Summary:
(Updated per review feedback)
`torch.floor_divide` is currently a function that can operate on two tensors or a tensor and a scalar (scalar x scalar floor division is handled natively by Python and the JIT has a builtin function for it). This PR updates it to:
- have an out variant: `floor_divide(x, y, out=z)`
- be a method on a tensor: `x.floor_divide(y)`
- have an in-place variant: `x.floor_divide_(y)`
- work with sparse tensors
Tests are added to test_sparse.py and test_torch.py for these new behaviors.
In addition, this PR:
- cleans up the existing sparse division and true_division code and improves their error message
- adds testing of sparse true_division to test_sparse.py
- extends existing floor_divide testing in test_torch to run on CUDA, too, not just the CPU
Unfortunately, making floor_divide a method requires breaking backwards compatibility, and floor_divide has been added to the BC whitelist since this is international. The BC issue is that the first parameter name to torch.floor_divide is changing from input to self. If you previously called torch.floor_divide with keyword arguments, e.g. torch.floor_divide(input=x, other=y), you will need to update to torch.floor_divide(self=x, other=y), or the more common torch.floor_divide(x, y).
The intent of this PR is to allow floor_divide to be substituted for division (torch.div, /) wherever division was previously used. In 1.6 we expect torch.div to perform true_division, and floor_divide is how users can continue to perform integer division with tensors.
There are two potential follow-up issues suggested by this PR:
- the test framework might benefit from additional tensor construction classes, like one to create dividends and divisors for multiple dtypes
- the test framework might benefit from a universal function test class. while methods have reasonable coverage as part of test_torch.py's TestTensorOp tests, function coverage is spotty. Universal functions are similar enough it should be possible to generate tests for them.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/34552
Differential Revision: D20497453
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: ac326f2007d8894f730d1278fef84d63bcb07b5d
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/34545
This is for common operator coverage, since this is widely used. A future PR
will add the quantized version.
Some initial questions for reviewers, since it's my first FP operator
diff:
* do we need a backwards.out method for this?
* do we need CUDA? If yes, should it be this PR or is it ok to split
Test Plan:
```
// test
python test/test_torch.py TestTorchDeviceTypeCPU.test_hardsigmoid_cpu_float32
// benchmark
python -m pt.hardsigmoid_test
...
Forward Execution Time (us) : 40.315
Forward Execution Time (us) : 42.603
```
Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D20371692
fbshipit-source-id: 95668400da9577fd1002ce3f76b9777c6f96c327
Summary:
This test is flaky on my computer, the error is:
```
AssertionError: tensor(1.3351e-05) not less than or equal to 1e-05
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/34764
Differential Revision: D20476006
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: dad7e702275346070552c8a98765c37e6ca2c197
Summary:
This PR enables bfloat16 type for
- Embedding, Index, Sigmoid Ops used in [DLRM](https://github.com/facebookresearch/dlrm)
- Miscellaneous ops like comparison ops, arange op used in unit tests
- Rename types list with the pattern `*_with_bfloat16` in `test_torch.py` to avoid confusion
iotamudelta ezyang
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/34630
Differential Revision: D20405093
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: aa9538acf81b3a5a9a46ce5014529707fdf25687
Summary:
This PR implements the following linear algebra algorithms for low-rank matrices:
- [x] Approximate `A` as `Q Q^H A` - using Algorithm 4.4 from [Halko et al, 2009](http://arxiv.org/abs/0909.4061).
+ exposed as `torch.lowrank.get_approximate_basis(A, q, niter=2, M=None) -> Q`
+ [x] dense matrices
+ [x] batches of dense matrices
+ [x] sparse matrices
+ [x] documentation
- [x] SVD - using Algorithm 5.1 from [Halko et al, 2009](http://arxiv.org/abs/0909.4061).
+ uses `torch.lowrank.get_approximate_basis`
+ exposed as `torch.svd_lowrank(A, q=6, niter=2, M=None) -> (U, S, V)`
+ [x] dense matrices
+ [x] batches of dense matrices
+ [x] sparse matrices
+ [x] documentation
- [x] PCA - using `torch.svd_lowrank`
+ uses `torch.svd_lowrank`
+ exposed as `torch.pca_lowrank(A, center=True, q=None, niter=2) -> (U, S, V)`
+ [x] dense matrices
+ [x] batches of dense matrices
+ [x] sparse matrices, uses non-centered sparse matrix algorithm
+ [x] documentation
- [x] generalized eigenvalue solver using the original LOBPCG algorithm [Knyazev, 2001](https://epubs.siam.org/doi/abs/10.1137/S1064827500366124)
+ exposed as `torch.lobpcg(A, B=None, k=1, method="basic", ...)`
+ [x] dense matrices
+ [x] batches of dense matrices
+ [x] sparse matrices
+ [x] documentation
- [x] generalized eigenvalue solver using robust LOBPCG with orthogonal basis selection [Stathopoulos, 2002](https://epubs.siam.org/doi/10.1137/S1064827500370883)
+ exposed as `torch.lobpcg(A, B=None, k=1, method="ortho", ...)`
+ [x] dense matrices
+ [x] batches of dense matrices
+ [x] sparse matrices
+ [x] documentation
- [x] generalized eigenvalue solver using the robust and efficient LOBPCG Algorithm 8 from [Duersch et al, 2018](https://epubs.siam.org/doi/abs/10.1137/17M1129830) that switches to orthogonal basis selection automatically
+ the "ortho" method improves iterations so rapidly that in the current test cases it does not make sense to use the basic iterations at all. If users will have matrices for which basic iterations could improve convergence then the `tracker` argument allows breaking the iteration process at user choice so that the user can switch to the orthogonal basis selection if needed. In conclusion, there is no need to implement Algorithm 8 at this point.
- [x] benchmarks
+ [x] `torch.svd` vs `torch.svd_lowrank`, see notebook [Low-rank SVD](https://github.com/Quansight/pearu-sandbox/blob/master/pytorch/Low-rank%20SVD.ipynb). In conclusion, the low-rank SVD is going to be useful only for large sparse matrices where the full-rank SVD will fail due to memory limitations.
+ [x] `torch.lobpcg` vs `scipy.sparse.linalg.lobpcg`, see notebook [LOBPCG - pytorch vs scipy](https://github.com/Quansight/pearu-sandbox/blob/master/pytorch/LOBPCG%20-%20pytorch%20vs%20scipy.ipynb). In conculsion, both implementations give the same results (up to numerical errors from different methods), scipy lobpcg implementation is generally faster.
+ [x] On very small tolerance cases, `torch.lobpcg` is more robust than `scipy.sparse.linalg.lobpcg` (see `test_lobpcg_scipy` results)
Resolves https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/8049.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/29488
Differential Revision: D20193196
Pulled By: vincentqb
fbshipit-source-id: 78a4879912424595e6ea95a95e483a37487a907e
Summary:
This PR enables bfloat16 type for loss criterion ops(and the ops they depend on) and few miscellaneous ops required to train resnet50.
iotamudelta ezyang
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/34469
Differential Revision: D20348856
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 0a8f06c2169cfa3c9cf319120e27150170095f6c
Summary:
This allows us to enable some double-based pdist tests running into accrued error from casting down to float previously.
Addresses https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/33128
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/34103
Differential Revision: D20343279
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: a2da768259fab34ef326976283b7a15bebbbb979
Summary:
Addresses https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/5442.
Per title (and see issue). A test is added to test_torch.py to verify the behavior.
Update (with new behavior):
NumPy arrays can be non-writeable (read-only). When converting a NumPy array to a Torch tensor the storage is shared, but the tensor is always writable (PyTorch doesn't have a read-only tensor). Thus, when a non-writeable NumPy array is converted to a PyTorch tensor it can be written to.
In the past, PyTorch would silently copy non-writeable NumPy arrays and then convert those copies into tensors. This behavior violates the from_numpy contract, however, which promises that the tensor and the array share memory.
This PR adds a warning message when a non-writeable NumPy array is converted into a Torch tensor. This will not break any networks, but will make end users aware of the behavior. They can work-around the warning message by marking their NumPy arrays as writeable.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/33615
Differential Revision: D20289894
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: b76df0077399eb91038b12a6bf1917ef38c2cafd
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/33825
Partially addresses #20376
I do this by overriding assertEqual in classes that opt into
this. This means I have to fix#33821. The fix is a little
unsatisfactory as idiomatic Python 2 super() calls don't work
(since the class is no longer in scope); hopefully this will just
work when we go to Python 3.
General approach taken:
- A lot of dtype mismatches are because we specified tensor constants
that infer to some dtype, but the actual dtype needed is something else.
Those are easy, just annotate the tensor() constructor (often a legacy
Tensor/FloatTensor call) with dtype
- There are a few cases where the promotion rules are nontrivial. Some of them
I just typed out the expected promotion rules manually (based on trial
and error)
- There are some more complex cases; if it gets too hairy I just
set exact_dtype=False and nope the fuck out
I don't have time to do it for all the other classes. But the setup
should work if people just incrementally add the overrides to classes,
and then eventually flip the default.
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D20125791
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 389c2d1efbd93172af02f13e38ac5e92fe730c57
Summary:
1. randn and normal_ methods will work for complex tensors after this PR
2. added an internal function for viewing complex tensors as float tensors which enables us to reuse functions defined for float tensors for complex tensors with change in arguments passed(like size, standard deviation in case of normal_). currently the resultant new float tensor doesn't share the storage with the input complex tensor which means that the version counter wouldn't be updated if any function is called on this resultant tensor, but once the dtype entry is removed from the storage class, this issue will be resolved.
Side notes:
1. didn't add a separate header for the util functions because of this issue https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/20686#issuecomment-593002293
2. we should eventually have a public API method view_complex_as_float once (2) mentioned above gets resolved
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/34037
Differential Revision: D20221793
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: a78f5e83d6104e2f55e0b250c4ec32e8d29a14eb
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/33901
After this change, the pytest profile looks like:
4.83s call test/test_torch.py::TestTorch::test_fft_ifft_rfft_irfft
4.23s call test/test_torch.py::TestTorch::test_var_dim
4.22s call test/test_torch.py::TestTorch::test_std_dim
4.19s call test/test_torch.py::TestTorch::test_max
4.06s call test/test_torch.py::TestTorch::test_min
3.60s call test/test_torch.py::TestTorchDeviceTypeCPU::test_cdist_norm_batch_cpu
2.62s call test/test_torch.py::TestTorchDeviceTypeCPU::test_pow_cpu
2.60s call test/test_torch.py::TestTorch::test_matmul_small_brute_force_1d_Nd
And the entire CPU-only test suite can be run in 88s on my Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU
E5-2650 v4 @ 2.20GHz
Signed-off-by: Edward Z. Yang <ezyang@fb.com>
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D20222288
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 4224a9117f42566e290ae202881d76f1545cebec
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/33819
These conditions are for the specific implementation, the fallback implementation works without these checks. So use that if any of these checks isn't true.
Resubmit of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/33419 (which got reverted due to a problem with XLA, but which now has been fixed)
ghstack-source-id: 99333280
Test Plan: Test included
Differential Revision: D20121460
fbshipit-source-id: c1056b8e26751e24078bbe80c7cb4b223bcca7cb
Summary:
- Modified assertEqual to handle complex tensors
- added a test in test_torch.py to test torch.zeros
- added dispatch for complex for index_kernel, index_put_kernel
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/33773
Differential Revision: D20135553
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: f716604535c0447ecffa335b0fc843431397c988
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/33696
This changes two tests:
- The batchnorm inference cannot change the memory format of the weights as they are 1D. So this is removed.
- The batchnorm test now run both in affine and not affine mode.
- I added back the test for type errors using .data. In particular, `.data` allows to change the type of a Tensor inplace (very bad, never do it!) but since it is possible, we should test it until .data is removed.
cc Enealor who did the first version of the PR.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D20069241
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: a0348f40c44df38d654fb2a2b2b526d9d42f598a
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/33419
These conditions are for the specific implementation, the fallback implementation works without these checks. So use that if any of these checks isn't true.
ghstack-source-id: 98836075
Test Plan: Previously got error for special case where k=0 which has gone. The error was in some complicated autograd, and I'm not sure how and where an simple regression test should be added.
Differential Revision: D19941103
fbshipit-source-id: e1c85d1e75744b1c51ad9b71c7b3211af3c5bcc6
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/31666
List of changes:
1) Fix a case where torch.mv was not handling NaNs correctly. In particular, with a transposed tensor and expanded vector, NaNs in the output are kept, even if beta = 0.
This is handled in the `out=` case by zero-ing out the passed-in Tensor, but this can happen just the same with the non-out variant if the allocated tensor happens to have a NaN.
Also adds tests for this case.
NOTE: we zero out the output tensor in all cases for mv and mm, even though this is probably overkill. I didn't find another case where this would be a problem, but the old code at least
attempted to do this for all mv and mm calls and I didn't add comprehensive testing to be sure that it's not a problem.
2) on CPU: move mv, mv_out, mm, mm_out to be direct wrappers on _th_addmv, _th_addmm, rather than having their own wrappers in Declarations.cwrap.
Ths is to remove the magic around cpu_zero from the codegen, which simplifies the codegen and makes testing this easier.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D19239953
Pulled By: gchanan
fbshipit-source-id: 27d0748d215ad46d17a8684696d88f4cfd8a917e
Summary:
Removes almost every usage of `.data` in test_torch to address part of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/33629.
Lines 4706-4710 had to be refactored to allow this. The changed test is fundamentally the same, as it appears to be meant to confirm that using an input of a different type than the weight causes an appropriate error.
There is one remaining usage of `.data`, and it is on line 5132. This was left as the `set_` and `resize_` methods still mention `.data` explicitly. I figure the right time to remove this is when those methods have their runtime errors updated.
Note: ~~some tests are skipped locally, and so I am still verifying that nothing has been obviously broken.~~ Appears to be passing early tests.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/33638
Differential Revision: D20062288
Pulled By: albanD
fbshipit-source-id: 672a6d7a20007baedb114a20bf1ddcf6c4c0a16a
Summary:
Changelog:
- Add a check to ensure that all inputs to `where` lie on the same device
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/33432
Test Plan:
- Added test_where_invalid_device
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/33422
Differential Revision: D19981115
Pulled By: VitalyFedyunin
fbshipit-source-id: 745896927edb53f61f3dd48ba9e1e6cd10d35434
Summary:
Although `gpu_kernel_with_index` might look like a quite general helper function at first look, it actually isn't.
The problem is not only 32bit indexing, but something more fundamental: `TensorIterator` reorder dims and shapes, so if you have non-contiguous tensor such as `torch.empty(5, 5).t()` , the index won't be correct. Since the whole point of `TensorIterator` is to manipulate shapes/strides to speedup loops, it is fundamentally impossible to get the correct linear index without tons of efforts.
Currently, the range factories are not failing on an `out=non_contiguous_tensor` is because it is so lucky that `has_internal_overlap` is stupid enough to return everything not contiguous as `TOO_HARD`.
Since `gpu_kernel_with_index` is not general, we should move it from `Loops.cuh` to `RangeFactories.cu`. And since the kernel is so simple to implement, it makes no sense to use `TensorIterator` which goes through tons of unnecessary checks like `compute_dtypes`.
`torch.range` is not tested for 64bit-indexing, and I will file a new PR to remove it (it was supposed to be removed at 0.5).
Benchmark:
The device is GTX-1650, I don't have a good GPU at home.
Code:
```python
import torch
print(torch.__version__)
for i in range(100):
torch.randn(1000, device='cuda')
torch.cuda.synchronize()
for i in range(15, 29):
%timeit torch.arange(2 ** i, device='cuda'); torch.cuda.synchronize()
```
Before:
```
1.5.0a0+c37a9b8
11.9 µs ± 412 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
12.7 µs ± 309 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
19.6 µs ± 209 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
28.9 µs ± 923 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
48.4 µs ± 1.64 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
85.7 µs ± 1.46 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
162 µs ± 1.09 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
312 µs ± 9 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
618 µs ± 15.7 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
1.22 ms ± 9.91 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
2.45 ms ± 97.1 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
4.9 ms ± 155 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
10.1 ms ± 378 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
```
After:
```
1.5.0a0+7960d19
11 µs ± 29.6 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
12.4 µs ± 550 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
18.4 µs ± 230 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
27.6 µs ± 10.9 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
46.2 µs ± 18.6 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
83.3 µs ± 5.61 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
158 µs ± 373 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
307 µs ± 1.44 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
603 µs ± 112 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
1.2 ms ± 1.05 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
2.4 ms ± 23.5 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
4.77 ms ± 25.6 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
9.51 ms ± 933 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
```
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/33370
Differential Revision: D19925990
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: f4a732fe14a5582b35a56618941120d62e82fdce
Summary:
Fixes the `TensorIterator` parts of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/32863 (THC is still broken)
`TensorIterator::split` now keeps track of the `view_offsets` into the full tensor range. With this, I can take the base offset for the reduced dimension and translate partial results from the sub-iter into the index range of the full tensor. This happens only once for each intermediate result, so we should still benefit from the performance of 32-bit indexing in loops.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/33310
Differential Revision: D19906136
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 3372ee4b8d5b115a53be79aeafc52e80ff9c490b
Summary:
- Clean up error checking code
- Avoid unecessary floating-point computation
- Use float instead of double when possible to avoid massive cast in the tensor
- Use bool instead of uint8_t for clear Boolean purpose
- Improve error message
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/32665
Differential Revision: D19601920
Pulled By: VitalyFedyunin
fbshipit-source-id: 0c6c6b5ff227b1437a6c1bae79b2c4135a13cd37
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/33050
Following what gchanan proposed in #30480
- If the (logical) shapes of mean and std are broadcastable, we broadcast them for the output
Done in tensor iterator already.
- If the (logical) shapes of mean and std are not broadcastable and they have the same number of elements, we fall back to the old behavior (pick the shape of mean)
Done by reshape std to the same shape of mean.
- If the (logical) shapes of mean and std are not broadcastable and don't have the same number of elements, we error out.
Done by tensor iterator already.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D19771186
Pulled By: glaringlee
fbshipit-source-id: a0b71063c7f5fdda2d4ceb84e06384414d7b4262
Summary:
Currently `torch.pdist` yields an illegal CUDA memory access for batch sizes >= 46342 as reported by SsnL in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/30583.
Thanks for the minimal code reproduction, btw! ;)
Reason for this bug:
The calculation if `i` in the [`pdist_kerne_cuda_impl`](46ad80c839/aten/src/ATen/native/cuda/DistanceKernel.cu (L112)) might overflow, if a tensor with a `batch size >= 46342` is passed to `torch.pdist`.
Detailed description:
* `result` is resizes as ` n * (n - 1) / 2 = 1073767311` ([line of code](46ad80c839/aten/src/ATen/native/Distance.cpp (L140)))
* `grid` is initialized as `result.numel()` ([line of code](46ad80c839/aten/src/ATen/native/cuda/DistanceKernel.cu (L246)))
* `k` is assigned to the `blockIdx.x` as an `int32` ([line of code](46ad80c839/aten/src/ATen/native/cuda/DistanceKernel.cu (L108)))
* `i` is calculated using `2 * k >= 2147534622` ([line of code](46ad80c839/aten/src/ATen/native/cuda/DistanceKernel.cu (L112))), which overflows, since `2147534622 > 2147483647 (int32_max)`.
Using `const int64_t k = blockIdx.x;` would solve the illegal memory access. This seems also be done for [`cdist_kernel_cuda_impl`](46ad80c839/aten/src/ATen/native/cuda/DistanceKernel.cu (L198-L201)).
However, we might expect a slowdown, so I've timed the current PyTorch master vs. this PR:
(tested with `x = torch.randn(x.size(0), 128)` on a V100)
|x.size(0) | int32 idx | int64 idx | slowdown |
|----------|-----------|-----------|----------|
| 50000 | - | 4.4460 | - |
| 25000 | 1.02522 | 1.10869 | 7.53% |
| 12500 | 0.25182 | 0.27277 | 7.68% |
| 6250 | 0.06291 | 0.06817 | 7.72% |
| 3125 | 0.01573 | 0.01704 | 7.69% |
| 1562 | 0.00393 | 0.00426 | 7.75% |
While checking the backward kernel, it seems I'm triggering another error with a size limit of
```python
x = torch.randn(1449, 1, device='cuda', requires_grad=True)
out = torch.pdist(x)
out.mean().backward()
> RuntimeError: CUDA error: invalid configuration argument
```
, while `[<=1448, 1]` works.
I'll take another look at this issue. Let me know, if the potential fix should go into this PR or if I should open a new issue.
CC ngimel, csarofeen
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/31593
Differential Revision: D19825571
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: ace9ccab49f3cf0ce894cdb6daef0795e2e8ec03
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/32243
Following what gchanan proposed in #30480
- If the (logical) shapes of mean and std are broadcastable, we broadcast them for the output
Done in tensor iterator already.
- If the (logical) shapes of mean and std are not broadcastable and they have the same number of elements, we fall back to the old behavior (pick the shape of mean)
Done by reshape std to the same shape of mean.
- If the (logical) shapes of mean and std are not broadcastable and don't have the same number of elements, we error out.
Done by tensor iterator already.
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D19417087
Pulled By: glaringlee
fbshipit-source-id: 1c4bc7df923110a803620b9e2abd11a7151fc33e
Summary:
Stacked PRs
* #32958 - Make zip serialization the default
* **#32244 - Fix some bugs with zipfile serialization**
It includes the following changes:
* Split up tests so that we can test both serialization methods
* Loading something within a buffer doesn't work anymore, so those tests are only on the old serialization method (it's possible but introduces a big slowdown since it requires a linear scan of the entire zipfile to find the magic number at the end)
* Call `readinto` on a buffer if possible instead of `read` + a copy
* Disable CRC-32 checks on read (there was some issue where miniz said the CRC was wrong but `zipinfo` and `unzip` said the zip file was fine)
](https://our.intern.facebook.com/intern/diff/19418935/)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/32244
Pulled By: driazati
Reviewed By: eellison
Differential Revision: D19418935
fbshipit-source-id: df140854f52ecd04236225417d625374fd99f573
Summary:
Understanding which ops return views and which return tensors with new storage is a common user issue, and an issue for developers connecting accelerators to PyTorch, too. This generic test suite verifies that ops which should return views do (and a few ops that shouldn't don't). The documentation has also been updated for .t(), permute(), unfold(), and select() to clarify they return views.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/32512
Differential Revision: D19659454
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: b4334be9b698253a979e1bb8746fdb3ca24aa4e3
Summary:
This PR solves Issue https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/32750.
- Changes function prod_kernel_impl to use `out_t` argument instead of `scalar_t` (which caused the garbage output for FP16 input and FP32 output tensor type).
- Adds test case for `torch.prod` (for CUDA): tests both `torch.prod` and `torch.tensor.prod`. Checks all the combinations for dtypes: `torch.float16` and `torch.float32`.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/32831
Differential Revision: D19664666
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: c275363355c832899f10325043535949cd12b2f8
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/32501
This diff will address https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/24699
We ask the input `lambda` to be >= 0 to be same as https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.15.0/reference/generated/numpy.random.exponential.html#numpy-random-exponential. This does not exist in the previous implementation.
Benchmark I am using PT operator microbenchmark
```
================================================================================
Before the change, Program Output:
================================================================================
# ----------------------------------------
# PyTorch/Caffe2 Operator Micro-benchmarks
# ----------------------------------------
# Tag : short
# Benchmarking PyTorch: exponential_
# Mode: Eager
# Name: exponential__M512_N512_cpu
# Input: M: 512, N: 512, device: cpu
Forward Execution Time (us) : 21311.746
================================================================================
After the change, Program Output:
================================================================================
# ----------------------------------------
# PyTorch/Caffe2 Operator Micro-benchmarks
# ----------------------------------------
# Tag : short
# Benchmarking PyTorch: exponential_
# Mode: Eager
# Name: exponential__M512_N512_cpu
# Input: M: 512, N: 512, device: cpu
Forward Execution Time (us) : 20919.914
================================================================================
```
Test Plan: Sandcastle and Github tests
Reviewed By: BIT-silence
Differential Revision: D19518700
fbshipit-source-id: 0e79cb6a999c1278eb08b0d94cf61b119c85a36c
Summary:
Stacked PRs
* #32244 - Make zip serialization the default
* **#32241 - Split serialization tests to their own file**
This makes them all easier to run as a batch. This PR is just a code move / fixing up imports. There are still some serialization tests in `test_torch.py` as part of `TestDeviceType`.
](https://our.intern.facebook.com/intern/diff/19415826/)
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/32241
Pulled By: driazati
Differential Revision: D19415826
fbshipit-source-id: a3f6cfe1626ff2f9b9631c409bf525bd32e4639b
Summary:
Changes the linspace functions to be more consistent as requested in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/31991. The code has also been updated to avoid an early rounding error; the line `scalar_t step = (scalar_end - scalar_start) / static_cast<static_t>(steps-1)` can result in `step = 0` for integer scalars, and this gives unintended results. I examined the new output using
```
import torch
types = [torch.uint8, torch.int8, torch.short, torch.int, torch.long, torch.half, torch.float, torch.double]
print('Testing linspace:')
for type in types:
print(type, torch.linspace(-2, 2, 10, dtype=type))
```
which returns
```
Testing linspace:
torch.uint8 tensor([254, 254, 254, 255, 255, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2], dtype=torch.uint8)
torch.int8 tensor([-2, -2, -2, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2], dtype=torch.int8)
torch.int16 tensor([-2, -2, -2, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2], dtype=torch.int16)
torch.int32 tensor([-2, -2, -2, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2], dtype=torch.int32)
torch.int64 tensor([-2, -2, -2, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2])
torch.float16 tensor([-2.0000, -1.5557, -1.1113, -0.6670, -0.2227, 0.2227, 0.6660, 1.1113,
1.5547, 2.0000], dtype=torch.float16)
torch.float32 tensor([-2.0000, -1.5556, -1.1111, -0.6667, -0.2222, 0.2222, 0.6667, 1.1111,
1.5556, 2.0000])
torch.float64 tensor([-2.0000, -1.5556, -1.1111, -0.6667, -0.2222, 0.2222, 0.6667, 1.1111,
1.5556, 2.0000], dtype=torch.float64)
```
which is the expected output: `uint8` overflows as it should, and the result of casting from a floating point to an integer is correct.
This PR does not change the logspace function.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/32218
Differential Revision: D19544224
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 2bbf2b8552900eaef2dcc41b6464fc39bec22e0b
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/30445
Create distributed and rpc directories under caffe/test for better management
of unit tests.
Differential Revision: D18702786
fbshipit-source-id: e9daeed0cfb846ef68806f6decfcb57c0e0e3606
Summary:
Continuation of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/31514, fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/28430
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/32009
Test Plan:
I verified that the deprecation warnings only occur once on a relevant workflow. Built with:
```
buck build mode/opt //vision/fair/detectron2/tools:train_net
```
Ran with:
```
DETECTRON2_ENV_MODULE=detectron2.fb.env ~/local/train_net.par --config-file configs/quick_schedules/retinanet_R_50_FPN_instant_test.yaml --num-gpus 1 SOLVER.IMS_PER_BATCH 2
```
Inspected log:
```
[01/14 07:28:13 d2.engine.train_loop]: Starting training from iteration 0
buck-out/opt/gen/caffe2/generate-code=python_variable_methods.cpp/python_variable_methods.cpp:1299: UserWarning: This overload of add is deprecated:
add(Number alpha, Tensor other)
Consider using one of the following signatures instead:
add(Tensor other, Number alpha)
buck-out/opt/gen/caffe2/generate-code=python_variable_methods.cpp/python_variable_methods.cpp:1334: UserWarning: This overload of add_ is deprecated:
add_(Number alpha, Tensor other)
Consider using one of the following signatures instead:
add_(Tensor other, Number alpha)
[01/14 07:28:25 d2.utils.events]: eta: 0:00:10 iter: 19 total_loss: 1.699 loss_cls: 1.185 loss_box_reg: 0.501 time: 0.5020 data_time: 0.0224 lr: 0.000100 max_mem: 3722M
[01/14 07:28:35 fvcore.common.checkpoint]: Saving checkpoint to ./output/model_final.pth
```
Differential Revision: D19373523
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 75756de129645501f43ecc4e3bf8cc0f78c40b90
Summary:
Currently cumprod crashes for tensors with non-empty dimensions but with zero elements, which could happen when some dimension is zero. This commit fixes the error by checking both dim() and numel() in cumprod backward
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/32070
Differential Revision: D19373200
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: d8ecde33f3330b40a7c611f6faa3b1d707ef2a9a
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/31962
I added precision tests for CUDA half, float, and double.
The precision for CUDA half seems bad, but I checked the numbers against
previous versions of pytorch. The output of CUDA Half linspace+logspace
are exactly the same when compared with 1.2.0.
Test Plan: - Run CI
Differential Revision: D19320182
Pulled By: zou3519
fbshipit-source-id: 38d3d4dea2807875ed0b0ec2b93b19c10a289988
Summary:
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/28430
The unpythonic signatures for functions such as `torch.addcdiv` are already seperated in [`deprecated.yaml`] and the signatures marked as deprecated in `PythonArgParser`. However, nothing was done with this information previously. So, this now emits a warning when the deprecated signatures are used.
One minor complication is that if all arguments are passed as keyword args then there is nothing to differentiate the deprecated overload. This can lead to false warnings being emitted. So, I've also modified `PythonArgParser` to prefer non-deprecated signatures.
[`deprecated.yaml`]: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/tools/autograd/deprecated.yaml
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/31514
Differential Revision: D19298735
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: 03cb78af17658eaab9d577cd2497c6f413f07647
Summary:
This PR adds bfloat16 support for convolutions on ROCm.
- Intergrates MIOpen bfloat16 convolution support into PyTorch
- Enables bfloat16 convolution for non-miopen paths, i.e THCUNN, native hip kernels
- Enables bfloat16 type for probability distribution functions(this is included in this PR since conv unit tests use bfloat16 random number generators)
Native cuda kernels for convolution and random functions will be compiled for CUDA as well.
iotamudelta bddppq
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/30948
Differential Revision: D19274164
Pulled By: ezyang
fbshipit-source-id: c0888a6ac72a2c5749b1ebb2195ac6f2209996be
Summary:
Currently `cumsum` crashes for tensors with non-empty dimensions but with zero elements, which could happen when some dimension is zero. This commit fixes the error by checking both `dim()` and `numel()` in cumsum backward
Fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/31515
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/31694
Reviewed By: mrshenli
Differential Revision: D19266613
Pulled By: leedtan
fbshipit-source-id: 9407e0aa55440fed911c01a3580bb6c5eab62a16
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/31517
This is going to be used by upsample (which currently uses magic values to represent optionals).
For now, we just introduce a fake function for testing (torch._test_optional_float(x)).
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D19198721
Pulled By: gchanan
fbshipit-source-id: 0a1382fde0927c5d277d02d62bfb31fb574b8c74
Summary:
Reference: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/23159
Currently we don't support reduction operations for dim>=64 and we should give a descriptive RuntimeError indicating the same
Diff: D19179039
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/31476
Differential Revision: D19179039
Pulled By: anjali411
fbshipit-source-id: 58568f64627bf3df6b3e00a1498544c030e74a0e
Summary:
Make the following changes:
- When there are more than 10k errors, cuda-memcheck only shows 10k errors, in this case we shouldn't raise an Exception
- Add UNDER_CUDA_MEMCHECK environment to allow disabling `pin_memory` tests when running cuda-memcheck.
- Add a `--ci` command option, when turned on, then this script would run output to stdout instead of writing a file, and exit with an error if cuda-memcheck fails
- Add a `--nohang` command option. When turned on, then hang would be treated as pass instead of error
- Do simple filtering on the test to run: if `'cpu'` in the test name but not `'cuda'` is not in the test name
- Add `--split` and `--rank` to allowing splitting the work (NVIDIA CI has a limitation of 3 hours, we have to split the work to satisfy this limitation)
- The error summary could be `ERROR SUMMARY: 1 error`, or `ERROR SUMMARY: 2 errors`, the tail could be `error` or `errors`, it is not of the same length. The script is fixed to handle this case.
- Ignore errors from `cufft`
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/29243
Differential Revision: D18941701
Pulled By: mruberry
fbshipit-source-id: 2048428f32b66ef50c67444c03ce4dd9491179d2
Summary:
Tests for unique_dim will be refactored in a separate PR.
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/31211
Differential Revision: D19034968
Pulled By: ngimel
fbshipit-source-id: 855d326b37638b5944f11fbbce03394cf000daf9
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/30892
Fixes all outstanding lints and actually installs a properly configured
flake8
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D18862825
Pulled By: suo
fbshipit-source-id: 08e9083338a7309272e17bb803feaa42e348aa85
Summary:
Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/30826
Previously the scalar_check for the reduction None case was:
input.dim() <= 1, but it should be target based, i.e.:
target.dim() == 0. This follows from the "correct cases", i.e.
(N, C) X (N,) -> (N,)
(C,) X () -> ()
Test Plan: Imported from OSS
Differential Revision: D18833660
Pulled By: gchanan
fbshipit-source-id: 26338b842a8311718c4b89da3e2f1b726d5409b8